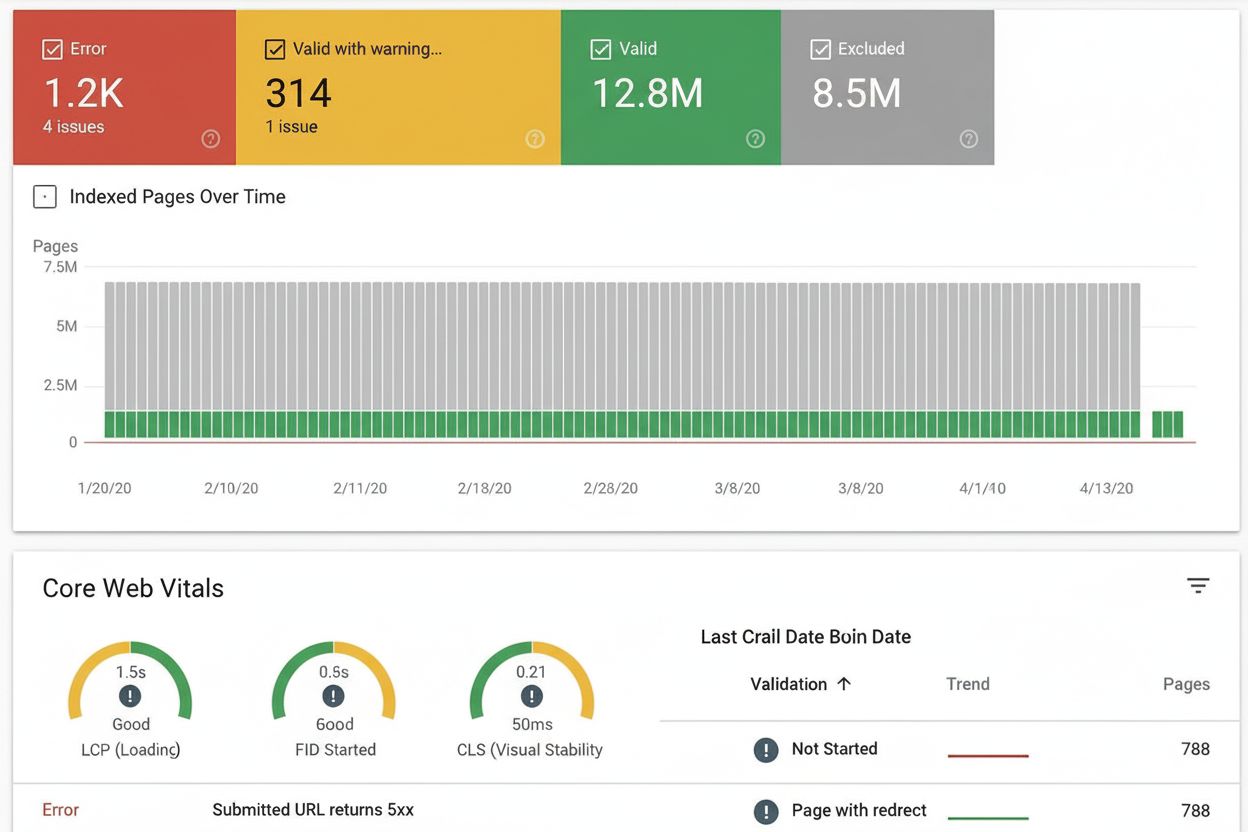
Index Coverage
Index coverage measures which website pages are indexed by search engines. Learn what it means, why it matters for SEO, and how to monitor and fix indexing issu...
The percentage of site content successfully indexed and accessible to AI systems such as ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, and Perplexity. Strong AI index coverage ensures your content is discoverable in AI-generated responses and can be cited as a source. Unlike traditional search indexing, AI index coverage determines visibility across multiple AI platforms and LLM-powered systems.
The percentage of site content successfully indexed and accessible to AI systems such as ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, and Perplexity. Strong AI index coverage ensures your content is discoverable in AI-generated responses and can be cited as a source. Unlike traditional search indexing, AI index coverage determines visibility across multiple AI platforms and LLM-powered systems.
AI Index Coverage refers to the percentage of your website’s content that is successfully discovered, crawled, and indexed by artificial intelligence systems such as ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and other large language models (LLMs). Unlike traditional search engine indexing, which focuses on making content visible in search results, AI index coverage determines whether your content is accessible to AI systems for training, citation, and inclusion in AI-generated responses. When your content has strong AI index coverage, it becomes discoverable across multiple AI platforms, increasing the likelihood that your brand, products, or information will be mentioned when users query these systems. Poor AI index coverage means your valuable content remains invisible to AI systems, missing critical opportunities for brand visibility in the rapidly growing AI-powered search landscape.
AI index coverage directly impacts your brand’s visibility in an increasingly AI-driven digital ecosystem. With AI-powered results now appearing in over 91% of product-related searches and AI platforms like ChatGPT handling over 1 billion searches weekly, ensuring your content is indexed by these systems is essential for modern digital strategy. The business implications are significant: content with strong AI index coverage can be cited in AI responses, driving qualified traffic and brand awareness, while content that’s blocked or poorly indexed remains completely invisible to these powerful discovery channels. Additionally, AI systems often cite sources that don’t rank in traditional search results—in fact, only about 20% of pages cited in AI responses appear in Google’s top 10 organic results, meaning AI indexing creates entirely new visibility opportunities.
| Scenario | Impact on AI Visibility | Business Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Properly indexed, high-quality content | Frequently cited in AI responses | Increased brand mentions, qualified traffic, authority building |
| Indexed but rarely cited | Minimal mentions in AI results | Limited visibility despite technical accessibility |
| Blocked or not indexed | Zero visibility in AI systems | Missed opportunities, competitors gain share of voice |
AI systems index content through specialized crawlers designed to understand and process information for large language models. ChatGPT uses crawlers like GPTBot to continuously scan the web and gather training data, though it also relies on real-time web search capabilities for current information. Google AI Overviews leverages Google’s existing crawl infrastructure but applies additional processing to understand content structure, relevance, and authority for AI-generated summaries. Perplexity AI takes a different approach, emphasizing real-time web search and pulling from over 20 sources per query, with a notable preference for platforms like Reddit and community-driven content. Each AI platform has distinct indexing preferences: some prioritize structured data and schema markup, others favor comprehensive, well-written content, and some weight third-party citations and reviews more heavily. Understanding these differences is crucial because optimizing for one AI system doesn’t automatically optimize for all of them—your content strategy must account for the specific indexing behaviors of the platforms most relevant to your audience.
Several technical factors directly influence whether AI systems can successfully index your content. The most critical are:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex"> are explicitly excluded from AI indexing. These tags are sometimes accidentally left on production pages during development.Addressing these technical factors is foundational to improving AI index coverage. Tools like AmICited.com can help monitor how effectively your content is being indexed across different AI platforms, providing visibility into which technical issues might be limiting your coverage.
Tracking your AI index coverage requires a combination of traditional SEO tools and AI-specific monitoring solutions. Google Search Console provides index coverage reports showing which pages are indexed by Google, though this reflects traditional search indexing rather than AI system indexing. Bing Webmaster Tools offers similar functionality for Bing’s index. For AI-specific monitoring, AmICited.com specializes in tracking how your brand appears across ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and other AI systems, showing citation frequency, sentiment, and share of voice. Third-party SEO platforms like Semrush, Ahrefs, and Moz increasingly include AI visibility metrics alongside traditional SEO data. Key metrics to monitor include: the percentage of your site’s pages that appear in AI responses, how frequently your brand is cited compared to competitors, the sentiment of AI mentions, and which content types generate the most AI citations. Regular monitoring helps identify technical issues, content gaps, and opportunities to improve your AI index coverage over time.
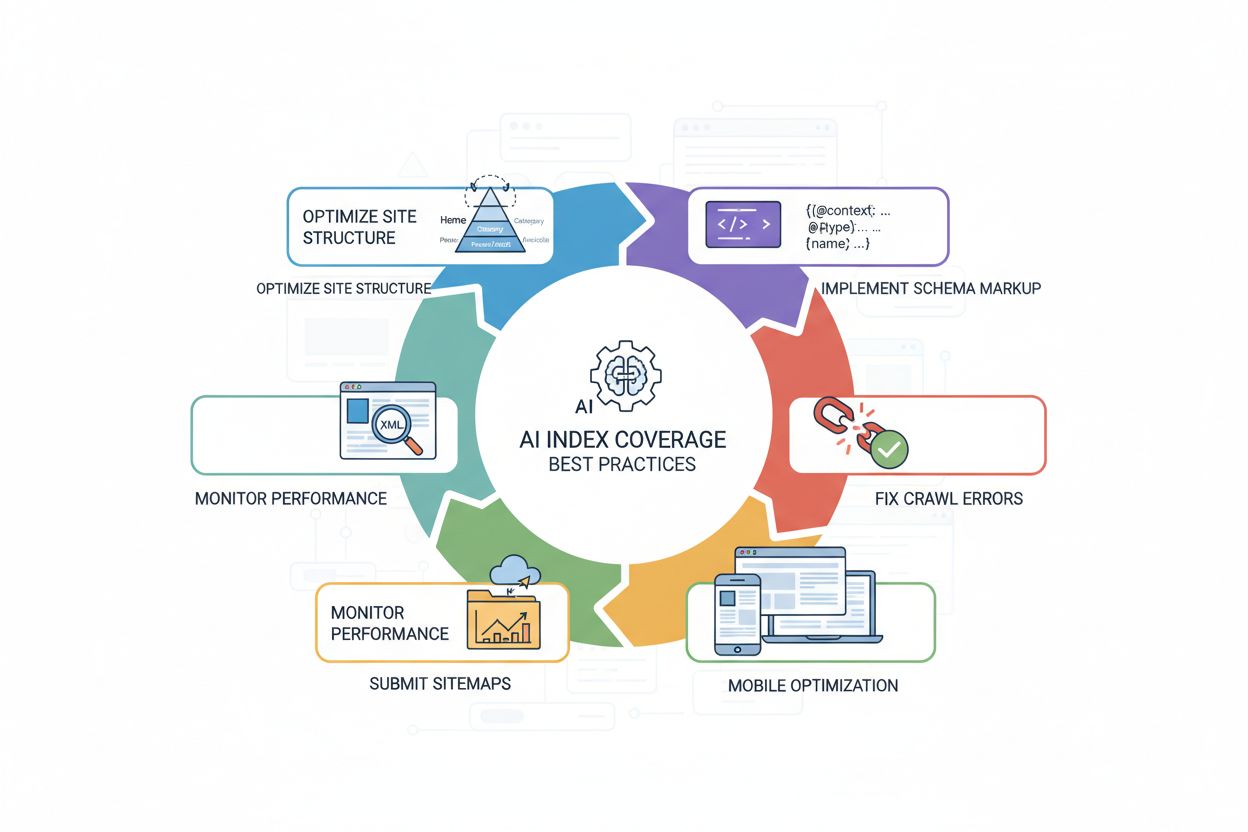
Improving your AI index coverage requires a strategic approach combining technical optimization with content excellence. The most effective practices include:
<article>, <section>, <header>, <nav>) to clearly communicate content structure and meaning to AI systems.These practices work together to create an AI-friendly website that’s easy for crawlers to access, understand, and cite. The result is stronger AI index coverage and increased visibility across AI-powered platforms.
While AI index coverage and traditional search index coverage are related, they’re not identical. Traditional search indexing focuses on making content visible in search engine results pages (SERPs), with ranking determined by factors like backlinks, keyword relevance, and user engagement signals. AI index coverage, by contrast, determines whether content is accessible to AI systems for training and real-time citation, with different ranking factors entirely. AI systems often cite sources that don’t rank well in traditional search—the 20% overlap between AI-cited pages and top 10 organic results demonstrates this fundamental difference. Additionally, AI systems may prioritize different content types: while traditional search favors authoritative domain-level signals, AI systems often weight specific content formats (FAQs, listicles, comparison guides, reviews) more heavily. A page can rank well in Google but be rarely cited by AI systems, or vice versa. This means your optimization strategy must address both channels: traditional SEO practices improve search visibility, while AI-specific optimizations (schema markup, content structure, accessibility) improve AI index coverage and citation likelihood.
Several common issues prevent websites from achieving strong AI index coverage. Overly restrictive robots.txt files are among the most frequent culprits—many sites accidentally block AI crawlers while intending only to block traditional search bots, completely preventing AI indexing. Misplaced noindex tags left on production pages during development or migration can render entire sections invisible to AI systems. Poor content structure makes it difficult for AI crawlers to understand and extract information; pages without clear headings, semantic HTML, or logical organization are less likely to be indexed and cited. Missing or incomplete schema markup deprives AI systems of explicit context about your content, reducing indexing effectiveness and citation likelihood. JavaScript-heavy sites without server-side rendering present a significant challenge because many AI crawlers can’t execute JavaScript, meaning critical content remains hidden. Duplicate content without proper canonicalization confuses AI systems about which version is authoritative, potentially reducing coverage. Finally, slow page load times and poor mobile optimization reduce crawl efficiency, limiting how much of your site gets indexed. Addressing these issues systematically—starting with robots.txt verification, adding schema markup, improving site structure, and ensuring fast, mobile-friendly pages—can dramatically improve your AI index coverage and visibility across AI platforms.
Currently, there's no standardized metric for AI index coverage across all websites, but research shows that AI-powered results appear in over 91% of product-related searches. However, many websites have poor AI index coverage due to technical issues like robots.txt blocks, missing schema markup, or JavaScript rendering problems. Websites with strong technical SEO and structured data typically achieve better AI index coverage.
Traditional Google index coverage focuses on making content visible in search results, while AI index coverage determines whether content is accessible to AI systems for training and citation. AI systems often cite sources that don't rank in Google's top 10 results—only about 20% of AI-cited pages appear in traditional top 10 organic results. Different AI platforms also have different indexing preferences and source weighting.
Yes, you can block specific AI crawlers using your robots.txt file. For example, you can disallow GPTBot (OpenAI), CCBot (Common Crawl), or Claude-Web (Anthropic). However, blocking AI crawlers means your content won't be indexed by these systems and won't appear in AI-generated responses. Most businesses benefit from allowing AI crawlers to improve visibility across AI platforms.
Indexing timelines vary by AI platform. ChatGPT's GPTBot crawls continuously but may take days or weeks to discover new content. Google AI Overviews uses Google's existing crawl infrastructure, so indexing can happen within hours to days. Perplexity emphasizes real-time web search, so recent content can appear in responses quickly. Using XML sitemaps and requesting indexing through webmaster tools can speed up the process.
AI index coverage and traditional search rankings are related but distinct. Optimizing for AI index coverage (through schema markup, site structure, and accessibility) also improves traditional SEO. However, a page can rank well in Google but be rarely cited by AI systems, or vice versa. The best strategy is to optimize for both: traditional SEO practices improve search visibility, while AI-specific optimizations improve AI index coverage.
The most common reasons are: 1) Overly restrictive robots.txt files that accidentally block AI crawlers, 2) Missing or incomplete schema markup that prevents AI systems from understanding content context, 3) JavaScript-heavy sites without server-side rendering that AI crawlers can't process, and 4) Poor site structure that makes content difficult for crawlers to navigate. Addressing these technical issues typically improves AI index coverage significantly.
You can monitor AI index coverage using tools like AmICited.com, which tracks how your brand appears across ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and other AI systems. Look for metrics like citation frequency, share of voice compared to competitors, and sentiment of mentions. You can also manually test by searching for your brand and key topics in AI systems and noting whether your content appears in responses.
While not strictly required, schema markup significantly improves AI index coverage. Structured data (JSON-LD) helps AI systems understand content context, extract information accurately, and determine relevance. Pages with proper schema markup for products, articles, FAQs, and organizations are more likely to be indexed and cited by AI systems. It's considered a best practice for optimizing AI index coverage.
Track how AI systems discover and cite your brand across ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and more. Get real-time insights into your AI visibility, citation frequency, and share of voice in AI-generated responses.

Index coverage measures which website pages are indexed by search engines. Learn what it means, why it matters for SEO, and how to monitor and fix indexing issu...

Learn how to identify and close AI visibility content gaps across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Discover analysis methods and tools to improve y...

Learn how to identify and capitalize on AI content opportunities by monitoring brand mentions in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI platforms. Discover strategie...