
ChatGPT Memory
Learn about ChatGPT Memory, OpenAI's feature for retaining user preferences and context across conversations. Understand how it works, its benefits, limitations...
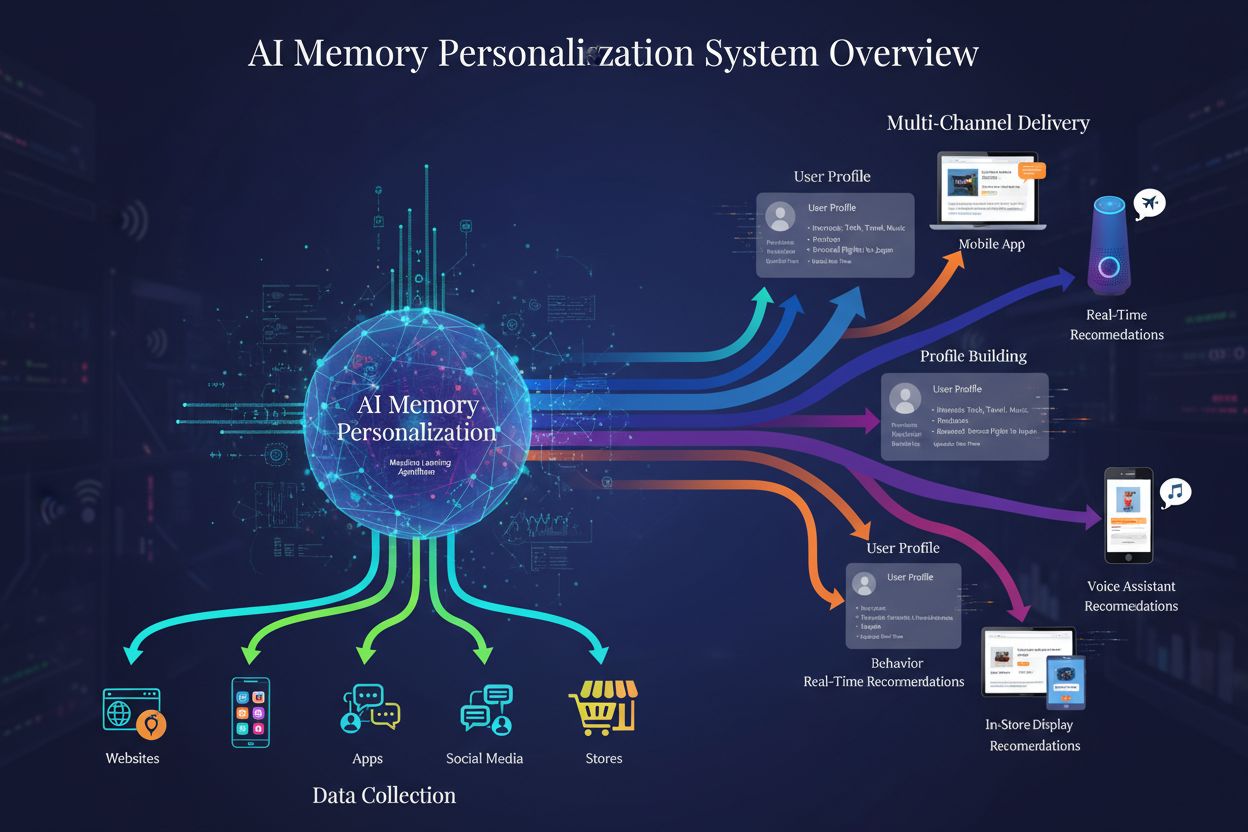
AI Memory Personalization is the technology that enables AI systems to build and maintain detailed individual user profiles by analyzing behavioral data, preferences, and interactions. These profiles allow AI to deliver highly tailored brand recommendations, content, and experiences that adapt in real-time to each user’s unique needs and evolving preferences.
AI Memory Personalization is the technology that enables AI systems to build and maintain detailed individual user profiles by analyzing behavioral data, preferences, and interactions. These profiles allow AI to deliver highly tailored brand recommendations, content, and experiences that adapt in real-time to each user's unique needs and evolving preferences.
AI Memory Personalization is the technology that enables artificial intelligence systems to build and maintain detailed individual user profiles by continuously analyzing behavioral data, preferences, and interactions. Unlike traditional personalization methods that rely on static segmentation and batch processing, AI memory personalization operates in real-time, dynamically updating user profiles as new data arrives. This fundamental difference means that AI systems can recognize and respond to changes in customer behavior within minutes rather than days or weeks.
The core mechanics of AI memory personalization involve three essential components: data collection from multiple touchpoints, pattern recognition through machine learning algorithms, and profile enrichment through continuous learning. Traditional personalization approaches typically segment customers into broad categories based on demographics or purchase history, then apply the same rules to everyone in that segment. In contrast, AI memory systems treat each customer as a unique individual, recognizing that preferences evolve, contexts change, and behaviors shift over time. This individual-level approach is particularly important for brand visibility in AI-generated answers and recommendations—when AI systems have rich memory of user preferences, they can recommend brands that genuinely align with each user’s needs, rather than generic suggestions that may not resonate.
The shift from batch processing to real-time processing represents a critical advancement. Traditional systems might update customer profiles weekly or monthly, creating a lag between customer actions and marketing responses. An abandoned shopping cart might trigger an email days later, long after the customer has moved on. AI memory systems, by contrast, can detect this abandonment within minutes and trigger an immediate, personalized response. This real-time capability extends to all customer interactions—website visits, app usage, social media engagement, support interactions, and purchase behavior—creating a continuously updated, comprehensive view of each individual customer.
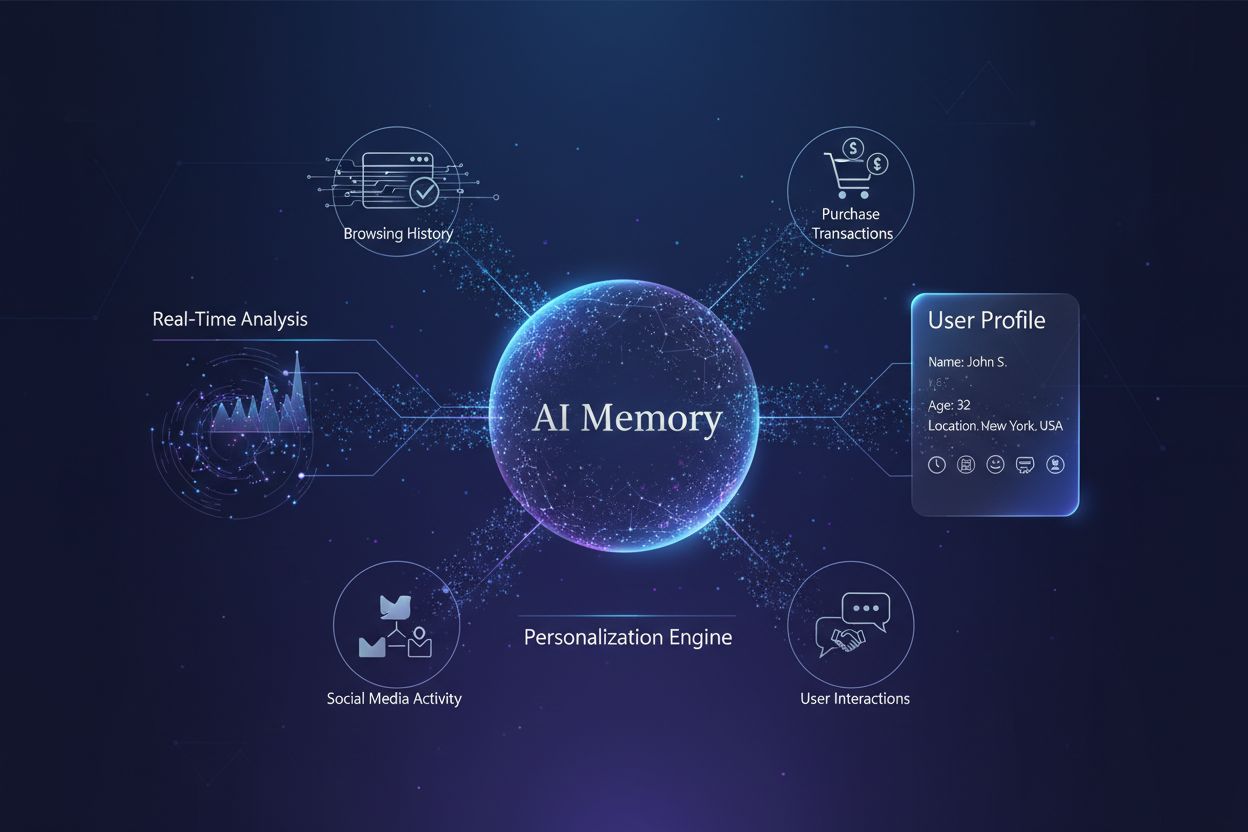
AI memory systems construct detailed user profiles by integrating data from multiple sources and applying sophisticated machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and predict future behavior. The data collection process begins with behavioral data—how users interact with websites, apps, and digital properties. This includes click patterns, pages visited, time spent on specific content, search queries, and product views. Simultaneously, systems capture transactional data from purchases, including what was bought, when, at what price, and through which channel.
Beyond these primary data sources, AI systems incorporate contextual information such as the time of day, geographic location, device type, weather conditions, and seasonal factors. They also analyze social data from social media platforms, including likes, shares, comments, and follows, which reveal interests and engagement patterns. Finally, demographic and stated preference data from user profiles, surveys, and explicit preference settings provide additional context for personalization.
| Data Type | Source | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Behavioral | Website/App interactions | Understand user preferences and interests | Click patterns, pages visited, time spent |
| Transactional | Purchase history and order data | Predict future needs and buying patterns | Previous purchases, order value, frequency |
| Contextual | Time, location, device, weather | Deliver situationally relevant recommendations | Time of day, geographic location, device type |
| Social | Social media activity | Identify interests and engagement patterns | Likes, shares, follows, comments |
| Demographic | User profile information | Segment and target appropriately | Age, location, stated interests, preferences |
Once collected, this data flows through machine learning algorithms that identify patterns humans would never detect manually. These algorithms recognize that customers who browse certain product categories at specific times, from particular devices, in certain locations, are more likely to convert when engaged through specific channels. The system learns that a customer who previously purchased premium products but recently browsed budget options might be price-sensitive due to changing circumstances. It recognizes seasonal patterns—customers who buy winter clothing in September are likely to purchase again in November.
The power of AI memory systems lies in their continuous learning capability. Unlike static rule-based systems that require manual updates, AI systems automatically refine their understanding with each new interaction. They adapt to changing preferences, recognize when customers move through different lifecycle stages, and adjust recommendations accordingly. This continuous learning also extends to sentiment analysis, where natural language processing analyzes customer communications—support tickets, reviews, social media posts, and chat interactions—to detect emotional context and urgency, adding another dimension to the user profile.
The concept of “memory” in AI personalization fundamentally distinguishes modern systems from earlier approaches. Long-term memory allows AI systems to retain and reference historical interactions across months or years, while short-term memory focuses on recent interactions and current session context. This dual-memory approach enables AI to recognize both enduring preferences and temporary shifts in behavior. A customer who has consistently purchased professional clothing for five years but recently started browsing casual wear might be changing jobs or lifestyle—the system recognizes this shift and adjusts recommendations accordingly.
Key Memory Functions in AI Personalization:
This memory capability is particularly valuable for understanding how customers interact with brands across multiple touchpoints. A customer might research products on mobile, read reviews on desktop, and make purchases in-store—memory systems link all these interactions to create a complete picture. The system recognizes that this customer prefers mobile research but in-store purchases, and can optimize the experience accordingly. Memory also enables predictive personalization, where the system anticipates needs before customers explicitly express them. If the system recognizes that customers who purchased a specific product typically need complementary items within 30 days, it can proactively offer those items at the optimal moment.
AI memory personalization directly influences how brands are recommended to individual users, with profound implications for brand visibility and customer engagement. When AI systems have rich, detailed memory of user preferences, they can recommend brands that genuinely align with each customer’s needs, values, and past experiences. This goes far beyond simple product recommendations—it’s about understanding which brands resonate with specific customer segments and individuals.
Real-world examples demonstrate the power of this approach:
Netflix uses AI memory to recommend shows and movies, analyzing not just what users watch but how they watch it—which genres they pause on, which they skip, which they complete. The platform’s recommendation engine considers viewing history, time of day, device type, and even seasonal patterns. Netflix reports that personalized recommendations account for approximately 80% of hours watched on the platform, demonstrating the massive impact of memory-driven personalization on user engagement and brand loyalty.
Amazon leverages AI memory to drive product recommendations, analyzing browsing history, purchase patterns, wish lists, and even items customers view but don’t purchase. The company reports that personalized recommendations contribute to approximately 35% of total revenue, showing how memory-based personalization directly impacts business outcomes. Amazon’s system recognizes that customers who purchased a specific product category are likely to need complementary items, and it times these recommendations for maximum relevance.
Spotify uses AI memory to create personalized playlists and recommendations, analyzing listening history, skip patterns, repeat plays, and even the time of day users listen to specific genres. The platform’s recommendation engine considers not just what users listen to, but how they listen—whether they’re discovering new music or returning to favorites, whether they’re in an active or passive listening mode.
The impact on conversion and revenue is substantial:
Timing and channel optimization represent another critical dimension of AI memory personalization. The system learns not just what to recommend, but when and how to deliver that recommendation. If the system recognizes that a customer typically makes purchase decisions on Sunday evenings via mobile app, it can time recommendations accordingly. If a customer prefers email communication over push notifications, the system respects that preference. This attention to individual communication preferences and optimal timing windows significantly improves engagement rates and customer satisfaction.
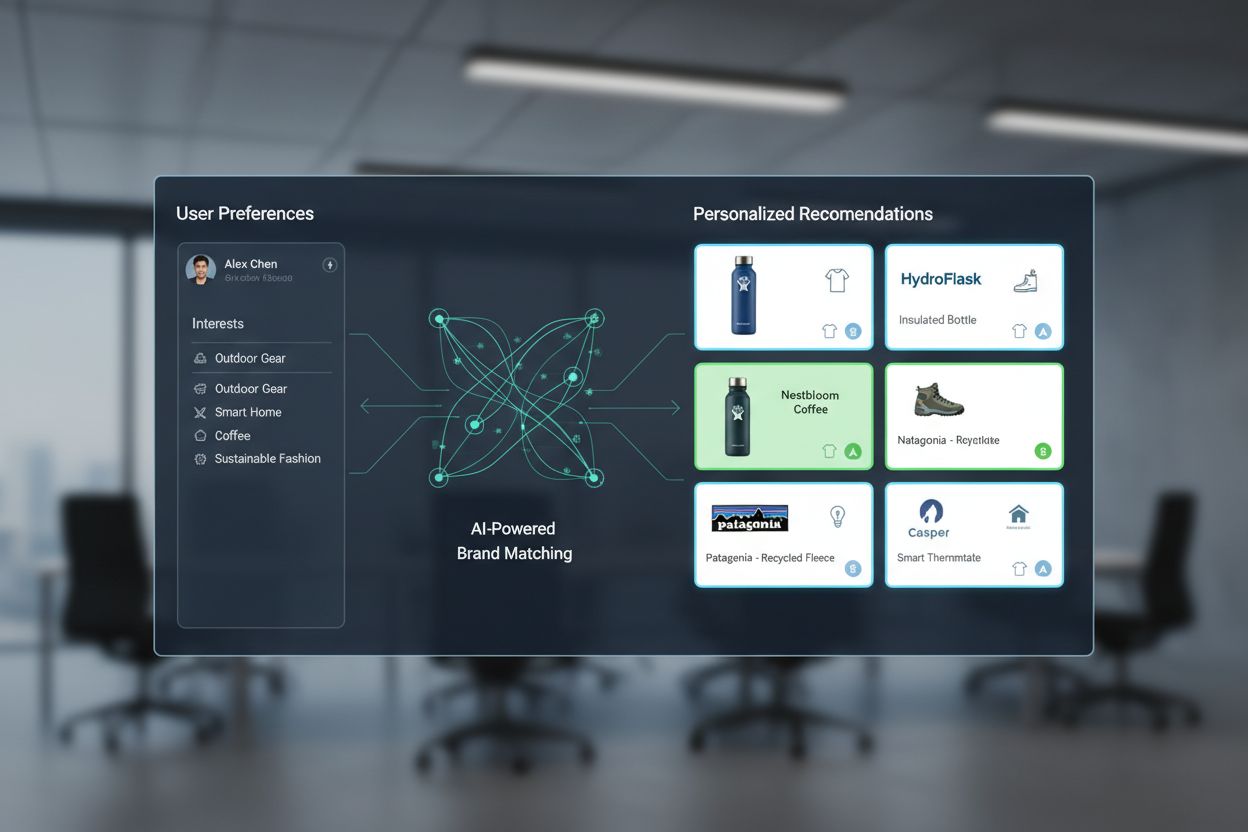
While AI memory personalization delivers tremendous value, it raises significant privacy and ethical concerns that must be addressed thoughtfully. Building detailed user profiles requires collecting and analyzing substantial amounts of personal data, including information about browsing habits, purchase history, location, and even emotional responses. Without proper safeguards, this data collection can violate privacy regulations, breach consumer trust, and enable misuse of sensitive information.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements:
The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) establish strict requirements for data collection, use, and protection. These regulations require organizations to obtain explicit consent before collecting personal data, provide transparency about how data is used, and give individuals the right to access, correct, and delete their data. Organizations must also implement data protection by design, meaning privacy considerations must be built into systems from the start, not added as an afterthought.
Best Practices for Privacy-Conscious AI Personalization:
Beyond regulatory compliance, organizations must address ethical considerations around AI personalization. Algorithmic bias can lead to discriminatory outcomes—for example, if historical data reflects past discrimination, AI systems might perpetuate those biases. Emotional manipulation is another concern; while personalization should enhance user experience, it shouldn’t manipulate users into decisions against their interests. The balance between personalization and privacy requires ongoing attention, transparency, and a genuine commitment to user welfare.
The advantages of AI memory personalization become clear when compared directly with traditional personalization approaches. Rule-based personalization, the predecessor to AI-driven systems, relies on manually created rules that specify which customers receive which recommendations. For example, a rule might state: “If customer purchased Product A, recommend Product B.” While this approach works for simple scenarios, it quickly becomes unmanageable as complexity increases.
Traditional rule-based systems face several critical limitations:
AI memory personalization overcomes these limitations through continuous learning and adaptation. Rather than requiring humans to anticipate every possible scenario and create rules for it, AI systems learn from actual customer behavior. They recognize patterns across millions of data points that would be impossible for humans to process manually. They adapt in real-time, adjusting recommendations as customer behavior changes.
The business impact is substantial:
The cost-effectiveness of AI systems becomes apparent at scale. While implementing AI personalization requires upfront investment in technology and expertise, the per-customer cost decreases dramatically as the system scales. A rule-based system might cost $10 per customer to personalize; an AI system might cost $0.10 per customer at scale, while delivering superior results.
The field of AI memory personalization is evolving rapidly, with several emerging trends reshaping how organizations approach customer engagement. Hyper-personalization represents the next evolution, going beyond traditional personalization to deliver experiences that feel uniquely crafted for each individual in real-time. Rather than showing the same product recommendations to all customers in a segment, hyper-personalization delivers different recommendations to each individual based on their specific context, preferences, and behavior at that exact moment.
Agentic AI represents another significant trend, where AI systems move beyond providing recommendations to actually taking actions on behalf of users. Rather than simply suggesting a product, an agentic AI system might autonomously purchase items, book appointments, or manage communications—all based on learned preferences and explicit user authorization. This requires even richer memory systems that understand not just preferences but also decision-making patterns and risk tolerance.
Emotional AI is emerging as systems become more sophisticated at detecting and responding to emotional context. Natural language processing can now identify not just what customers say, but how they feel—frustration, enthusiasm, confusion, or satisfaction. AI systems can adjust their responses accordingly, becoming more empathetic and contextually appropriate. A customer expressing frustration receives different treatment than one expressing enthusiasm, with the system adapting tone, urgency, and approach.
Omnichannel personalization ensures consistent, personalized experiences across all customer touchpoints—website, mobile app, email, social media, in-store, and customer service. Rather than treating each channel separately, integrated AI systems maintain unified customer profiles that inform personalization across all channels. A customer who researches on mobile receives consistent recommendations when they visit the website or receive email communications.
Privacy-preserving technologies are advancing to address growing privacy concerns. Federated learning allows AI models to be trained on data stored locally on user devices rather than centralized servers, reducing the amount of sensitive data that must be transmitted and stored centrally. Differential privacy adds mathematical noise to data to protect individual privacy while still enabling aggregate analysis. These technologies enable personalization without requiring the massive centralized data collection that has raised privacy concerns.
Despite the clear benefits of AI memory personalization, organizations face significant challenges in implementation. Data quality represents the first major hurdle. AI systems are only as good as the data they’re trained on; if data is incomplete, inaccurate, or biased, the resulting personalization will be flawed. Many organizations struggle with data scattered across multiple systems, inconsistent data formats, and missing information. Solving this requires investment in data governance—establishing clear standards for data collection, storage, and quality assurance.
Integration with legacy systems presents another challenge. Many organizations have invested heavily in existing marketing technology stacks, CRM systems, and data warehouses that weren’t designed to work together. Integrating AI personalization systems with these legacy platforms requires significant technical work and often involves custom development. Cloud-based solutions can help by providing flexible integration points, but the transition still requires careful planning and execution.
Skill gaps and resource constraints affect many organizations. Building and maintaining AI personalization systems requires expertise in data science, machine learning, software engineering, and marketing strategy. Many organizations lack these skills internally and must either hire new talent or work with external partners. This represents a significant cost and can slow implementation timelines.
Cost considerations extend beyond initial implementation. Ongoing costs include data storage, computing resources for model training and inference, and personnel to manage and optimize systems. However, these costs must be weighed against the substantial revenue benefits—organizations that successfully implement AI personalization typically see ROI within 6-12 months.
Practical solutions to these challenges include:
Success requires viewing AI memory personalization not as a one-time project but as an ongoing capability that evolves with customer needs and technological advances.
Traditional personalization relies on static segmentation and batch processing, grouping customers into broad categories and updating profiles weekly or monthly. AI memory personalization operates in real-time, treating each customer as an individual, continuously updating profiles as new data arrives, and adapting recommendations dynamically based on evolving preferences and behaviors.
Privacy-conscious AI systems implement encryption, secure storage, explicit user consent, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. They provide users with data access and deletion options, conduct regular privacy audits, and minimize data collection to only what's necessary. Emerging technologies like federated learning and differential privacy further protect individual privacy while enabling personalization.
AI memory systems collect behavioral data (clicks, browsing patterns), transactional data (purchases, order history), contextual information (time, location, device), social data (likes, shares, follows), and demographic information. They also analyze sentiment from customer communications to understand emotional context and preferences.
AI memory personalization increases conversion rates by 10-30%, generates 6x higher transaction rates, and increases average order value by 20-30%. Organizations implementing AI personalization see 15-25% revenue increases and achieve up to 800% ROI on marketing spend by delivering timely, relevant recommendations that resonate with individual customers.
Yes, privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA require organizations to provide users with the ability to access their profiles, correct inaccuracies, and request deletion. Responsible AI personalization systems give users control over their data, allow them to opt out of personalization, and provide transparency about how their data is used.
Key challenges include data quality issues (incomplete or biased data), integration with legacy systems, skill gaps in data science and AI expertise, and cost considerations. Solutions include starting with pilot programs, investing in data infrastructure, partnering with technology providers, and building internal expertise gradually.
When customers feel understood through personalized experiences, they develop stronger emotional connections with brands, leading to increased loyalty and repeat purchases. AI memory personalization enables consistent, relevant interactions across all touchpoints, which builds trust and increases customer lifetime value significantly.
Key regulations include the European Union's GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). These regulations require explicit consent for data collection, transparency about data use, and user rights to access and delete data. Organizations must also comply with industry-specific regulations in healthcare, finance, and other sectors.
AI memory personalization influences how your brand is recommended in AI answers and responses. AmICited helps you track brand mentions, visibility, and recommendations across GPTs, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI systems.

Learn about ChatGPT Memory, OpenAI's feature for retaining user preferences and context across conversations. Understand how it works, its benefits, limitations...

Discover how AI memory systems create lasting brand relationships through recurring, personalized recommendations that evolve over time. Learn about persistent ...
Learn how AI-powered recommendations work, from collaborative filtering to hybrid systems. Discover how machine learning personalizes product and content sugges...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.