
What is AI-native content creation and how does it work?
Learn what AI-native content creation means, how it differs from traditional approaches, and how to leverage AI technologies to create better content faster whi...
Companies built from the ground up with artificial intelligence as foundational infrastructure rather than as an add-on to existing operations. AI-native brands treat AI as the core enabler of their entire business model, strategy, and operations, designing products and workflows from AI capabilities upward. Unlike traditional companies that adopt AI to augment current processes, these organizations embed AI integration into every layer from inception. This foundational approach fundamentally differentiates AI-native brands from companies simply implementing AI tools into legacy systems.
Companies built from the ground up with artificial intelligence as foundational infrastructure rather than as an add-on to existing operations. AI-native brands treat AI as the core enabler of their entire business model, strategy, and operations, designing products and workflows from AI capabilities upward. Unlike traditional companies that adopt AI to augment current processes, these organizations embed AI integration into every layer from inception. This foundational approach fundamentally differentiates AI-native brands from companies simply implementing AI tools into legacy systems.
AI-native brands are companies built from the ground up with artificial intelligence as foundational infrastructure rather than as an add-on to existing operations. Unlike traditional companies that adopt AI to augment their current processes, AI-native brands treat AI as the core enabler of their entire business model, strategy, and operations. The distinction is critical: these organizations design products, workflows, and decision-making systems from AI capabilities upward, not retrofitting AI into human-centric processes. This foundational approach fundamentally differentiates AI-native brands from companies simply implementing AI tools into legacy systems.
AI-native brands share several defining characteristics that set them apart from traditional organizations. First, they embed AI integration into every layer of operations from inception, treating AI as a strategic utility similar to electricity or the internet rather than a specialized technology. Second, their decision-making architecture assumes AI-generated insights will drive value, with managers and teams required to justify why tasks cannot be accomplished through AI before allocating human resources. Third, these organizations operate with continuous learning and autonomous execution, where AI systems run 24/7 without human intervention. Fourth, their workforce structure evolves to include AI agents as team members, with employees transitioning from task executors to AI orchestrators and supervisors. Finally, AI-native brands prioritize execution velocity as a competitive weapon, operating leaner and faster than traditional vendors through autonomous AI execution layers that eliminate bottlenecks inherent in human-dependent workflows.
| Aspect | AI-Native Brands | Traditional Companies |
|---|---|---|
| AI Integration | Foundational from inception | Added to existing processes |
| Decision Making | AI-driven insights as default | Human-centric with AI tools |
| Operations | Autonomous agents 24/7 | Human-led with AI support |
| Workforce Structure | Human-AI collaboration | Humans with AI assistance |
| Execution Speed | Rapid, continuous cycles | Slower, traditional cycles |
| Cost Model | Dramatically reduced unit costs | Traditional cost structures |
Several major companies have made explicit public declarations of their AI-native transformation. Google initiated this movement in 2016 when CEO Sundar Pichai announced the company would shift from “mobile-first to an AI-first world,” integrating AI across Search, Cloud, Assistant, Ads, Photos, and Pixel devices with products designed from AI capabilities inception. NVIDIA made one of the boldest early commitments in 2014 when CEO Jensen Huang emailed staff: “We are no longer a graphics card company—we are an AI-first company. From now on, we are betting the company on AI,” pivoting entirely toward AI chip design and infrastructure. Duolingo announced in 2023 it would “go AI-first,” with AI now generating and evaluating language lessons across all content while employees initiate every task using AI. Shopify established that reflexive AI usage is a “baseline expectation” for all staff, requiring teams to prove why they cannot achieve outcomes using AI before requesting human headcount. Moderna positioned AI as a universal utility, operating over 1,800 internal GPTs in production and merging HR and IT into a single “People and Digital Technology” function to emphasize that AI success depends on culture and workforce engagement. Klarna implemented AI-first transformation in fintech, using AI systems to automate customer service and restructure operations around AI capabilities.

AI-native brands operate fundamentally differently from traditional companies through their outcome-driven organizational structure. Rather than organizing around departments and hierarchies, these companies structure themselves around autonomous AI execution, where intelligent systems handle continuous operations without waiting for human approval cycles. Their real-time operations model means decisions are made and implemented by AI systems analyzing live data, enabling response speeds impossible in human-dependent organizations. Continuous learning is embedded into their infrastructure—AI systems improve performance through ongoing data analysis and feedback loops, creating compounding advantages over time. The economic model of AI-native brands centers on achieving dramatically lower unit costs and reduced headcount requirements compared to traditional operations, with the same output delivered by fewer humans working alongside AI agents. This structural transformation represents a complete reimagining of how organizations execute strategy, not merely an incremental technology upgrade.
The human workforce in AI-native brands undergoes profound transformation in role, skill requirements, and daily operations. Employees evolve from task executors to AI orchestrators, spending less time on routine work and more time directing, refining, and supervising AI agent performance. Human-AI collaboration becomes the operating model, with AI agents handling execution while humans focus on strategy, creativity, and judgment calls requiring contextual understanding. Skill evolution accelerates dramatically—employees must develop AI fluency to work effectively with intelligent systems, understanding how to prompt, train, and optimize AI agents for specific outcomes. Performance evaluation shifts to measure how effectively employees leverage AI capabilities, with AI utilization factored directly into compensation and advancement decisions. Organizational culture transforms to embrace continuous learning and adaptation, as the pace of AI capability improvement requires constant upskilling. Importantly, this transformation creates new categories of roles—AI trainers, prompt engineers, AI quality auditors—while eliminating routine positions, fundamentally reshaping career paths and organizational hierarchies.
For AI-native brands, ensuring visibility within AI systems has become as critical as traditional search engine optimization. As customers increasingly use ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude to research solutions and make purchasing decisions, brands must ensure they appear in AI-generated responses through both citations (linked sources) and brand mentions (unlinked references). AI-native brands recognize that fewer than 30% of brands most mentioned by AI are also among the most cited, requiring distinct strategies for each visibility type. Citation strategy focuses on creating original research, transparent documentation, and structured content that AI systems can easily parse and reference as authoritative sources. Brand mention strategy emphasizes community engagement, positive user reviews, and earned media coverage in publications that AI systems favor as trusted sources. Monitoring tools like Semrush Enterprise AIO and Exploding Topics’ AI Visibility Index enable real-time tracking of brand mentions across AI platforms, allowing companies to measure their competitive share of voice and adjust strategies accordingly.
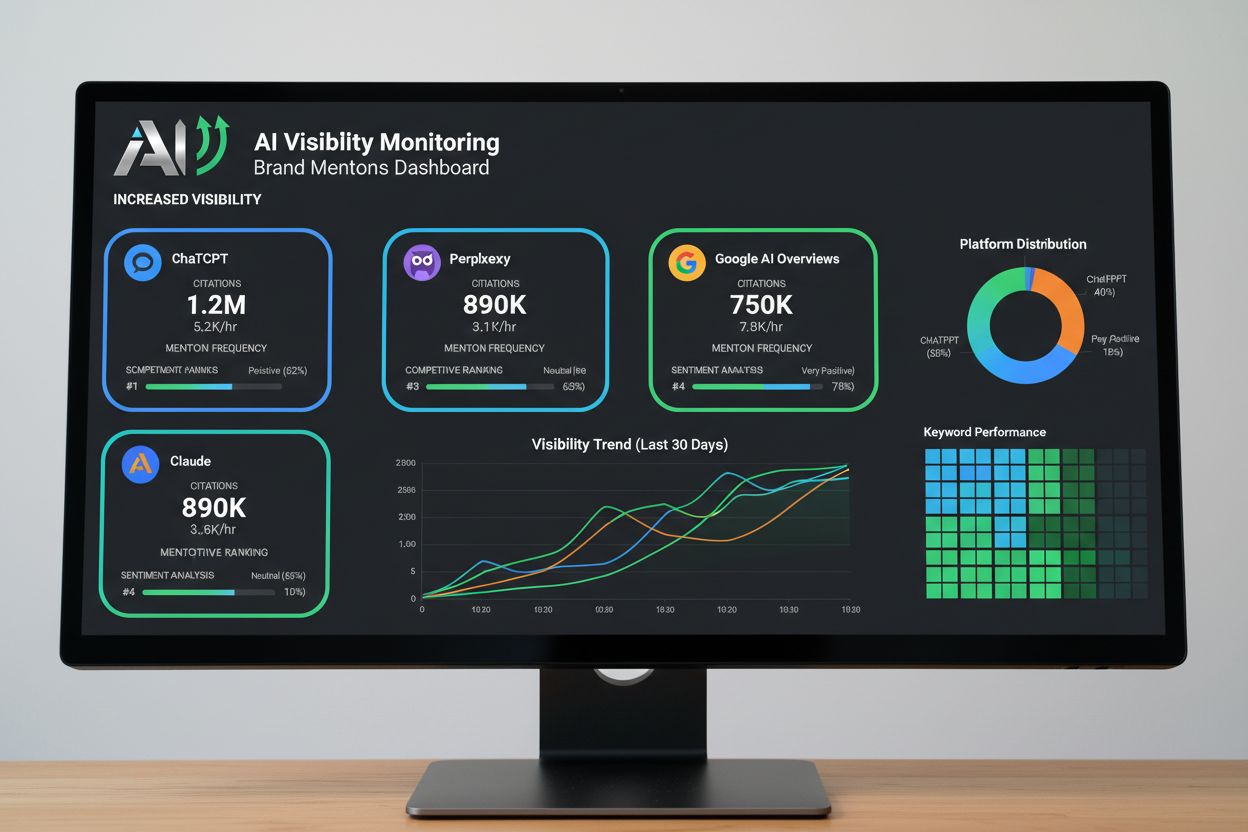
AI-native brands achieve substantial competitive advantages through their foundational approach to artificial intelligence. Economic superiority emerges through dramatically reduced operational costs—companies achieve the same output with significantly fewer employees, improving unit economics and profit margins. Speed advantages are transformative; AI-native organizations execute decisions and implement changes at velocities traditional companies cannot match, enabling faster market response and product iteration. Innovation acceleration occurs because AI systems can explore vastly more possibilities than human teams, identifying opportunities and optimizing solutions at scale impossible through manual processes. Customer experience improvements result from AI systems providing personalized, real-time interactions at scale, with 24/7 availability and consistent quality that human teams cannot deliver. Data-driven decision making becomes the default, with AI systems analyzing patterns humans would miss, leading to better strategic choices across product development, marketing, and operations. Research indicates that AI search visitors convert 4.4 times better than traditional organic search visitors, demonstrating the commercial value of AI visibility and the advantages accruing to brands that dominate AI-generated responses.
Despite significant advantages, AI-native transformation presents substantial challenges that organizations must navigate carefully. Workforce disruption remains the most visible challenge—transitioning to AI-native operations requires eliminating routine positions, creating legitimate concerns about employment and requiring thoughtful change management. Organizational resistance emerges from employees and managers accustomed to traditional hierarchies and decision-making processes, with cultural transformation proving more difficult than technical implementation. Implementation complexity is significant; companies must simultaneously modernize infrastructure, redesign workflows, retrain workforces, and manage business continuity during transformation, requiring sustained investment and executive commitment. Ethical considerations arise around AI decision-making, bias in automated systems, and the societal implications of large-scale automation, requiring robust governance frameworks and transparency. Execution risk is real—companies that fail to manage the transition effectively may experience operational disruption, talent loss, and competitive disadvantage rather than the promised benefits.
Companies transitioning to AI-native models should follow a structured implementation path that balances ambition with practical execution. Pilot projects provide the foundation, allowing organizations to test AI-native principles on specific workflows or business units before enterprise-wide rollout, generating learnings and building internal confidence. Workflow redesign must precede technology implementation—companies should map existing processes and fundamentally reimagine them around AI capabilities rather than simply automating current workflows. Infrastructure investment requires upfront capital allocation for AI platforms, data infrastructure, and integration systems that enable autonomous execution at scale; this investment must be made before market demand fully materializes. Cultural shift demands executive leadership and clear communication about why transformation is necessary, how it will unfold, and what success looks like for different stakeholder groups. Talent strategy should combine retraining existing employees for AI-native roles with selective hiring of AI-fluent talent who understand how to build and operate in AI-first environments. Measurement frameworks must track both technical metrics (AI system performance, automation rates) and business outcomes (cost reduction, speed improvements, revenue impact) to validate that transformation is delivering promised benefits and justify continued investment.
AI-native brands are companies built from inception with AI as foundational infrastructure, while AI-first is a strategic declaration by existing companies to reorganize around AI. AI-native companies design their entire business model around AI capabilities from the start, whereas AI-first companies retrofit AI into existing operations. True AI-native brands have AI embedded in their DNA, while AI-first companies are transforming their legacy systems to prioritize AI.
Traditional companies can adopt AI-first strategies and transform significantly, but they cannot fully become AI-native in the purest sense. AI-native status requires foundational design from inception, which legacy companies lack. However, companies like Shopify and Moderna have successfully implemented AI-native operating models by fundamentally redesigning their workflows, organizational structures, and decision-making processes around AI capabilities.
AI-native brands must ensure they're cited and mentioned by AI systems because customers increasingly use ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude to research solutions. If your brand doesn't appear in AI-generated responses, you're invisible to this growing segment of decision-makers. AI search visitors convert 4.4 times better than traditional organic search visitors, making AI visibility essential for business growth.
AI-native brands address workforce concerns through comprehensive reskilling programs, focusing on transitioning employees from task execution to AI orchestration and strategic roles. They emphasize that AI handles routine work while humans focus on creativity, judgment, and strategic decisions. Companies like Moderna merged HR and IT functions to emphasize that AI success depends on culture and workforce engagement, not just technology.
AI-native brands achieve dramatic competitive advantages including lower operational costs, faster execution velocity, 24/7 autonomous operations, accelerated innovation cycles, and superior customer experiences. These companies operate leaner and faster than traditional vendors, with AI systems continuously improving through data analysis. The economic model delivers significantly reduced unit costs and headcount requirements while maintaining or improving output quality.
AI-native models work across industries but are particularly suited to technology, fintech, education, healthcare, manufacturing, and any sector with data-driven operations. Industries with high volumes of routine decisions, customer interactions, or data analysis benefit most from AI-native transformation. However, the principles apply universally—any company can redesign operations around AI capabilities.
AI-native brands use specialized monitoring tools like AmICited, Profound, and Semrush Enterprise AIO to track brand mentions and citations across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, Claude, and other AI platforms. These tools provide real-time visibility into how often your brand appears in AI responses, which sources cite you, sentiment analysis, and competitive positioning. This data drives strategy refinement and content optimization.
The first step is auditing current processes to identify automation opportunities and understand which workflows could be redesigned around AI capabilities. Companies should then invest in AI infrastructure, pilot AI-native principles on specific business units, and build internal AI fluency. Starting with high-impact, lower-risk workflows allows organizations to generate learnings and build confidence before enterprise-wide transformation.
Discover how AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews are mentioning your brand. Track citations, brand mentions, and competitive positioning across all major AI platforms with AmICited.

Learn what AI-native content creation means, how it differs from traditional approaches, and how to leverage AI technologies to create better content faster whi...

Learn how to identify and fix negative brand sentiment in AI-generated answers. Discover techniques for improving how ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overvie...
Learn what AI brand equity is, why it matters for modern marketing, and how to build consistent positive visibility across ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, and other AI...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.