Setting Up GA4 for AI Referral Traffic Tracking
Learn how to track AI referral traffic in Google Analytics 4. Discover 4 methods to monitor ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI platforms, plus optimization strat...

AI Traffic refers to website visitors arriving from artificial intelligence platforms such as ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Gemini, and Copilot. This represents a new discovery channel where users receive AI-generated recommendations or citations that direct them to your website, distinct from traditional search engine or social media referrals.
AI Traffic refers to website visitors arriving from artificial intelligence platforms such as ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Gemini, and Copilot. This represents a new discovery channel where users receive AI-generated recommendations or citations that direct them to your website, distinct from traditional search engine or social media referrals.
AI Traffic encompasses website visitors who arrive at your site because an artificial intelligence platform recommended, cited, or linked to your content in response to a user query. Unlike traditional traffic sources such as search engines or social media, AI traffic originates from large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Google Gemini, and Microsoft Copilot. When a user asks an AI assistant a question and the model includes your website as a source or recommendation in its response, any resulting visitor is classified as AI traffic. This represents a fundamentally new discovery mechanism where users are directed to your content through conversational AI interfaces rather than through keyword rankings or social shares. The significance of AI traffic lies not only in its explosive growth rate but also in the exceptional quality and conversion propensity of these visitors compared to traditional channels.
The emergence of AI traffic marks a paradigm shift in how users discover and access web content. For decades, search engine optimization (SEO) and organic search traffic dominated digital strategy, with Google’s algorithm determining visibility and click-through rates. However, the rapid adoption of generative AI platforms has introduced an entirely new discovery layer that operates independently of traditional search rankings. According to research from Previsible, AI-referred sessions grew 527% year-over-year between January and May 2025, jumping from 17,076 to 107,100 sessions across analyzed properties. This growth trajectory far exceeds traditional channels: search traffic grew only 24%, social traffic increased 21.5%, and direct traffic rose 14.9% during the same period. The acceleration is particularly pronounced in high-consultative industries where users seek expert guidance. Legal, Finance, Health, SMB, and Insurance sectors account for 55% of all LLM-sourced sessions, indicating that AI traffic is not evenly distributed but concentrated in domains requiring trust, accuracy, and contextual expertise.
The infrastructure enabling AI traffic differs fundamentally from search engines. While Google’s crawlers index pages based on relevance and authority signals, LLM crawlers like GPTBot and ClaudeBot collect content to train or update language models. Additionally, on-demand RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) scrapers fetch real-time data to supplement AI responses with current information. This multi-layered approach means that AI traffic can originate from several distinct mechanisms: direct user queries to AI assistants, AI-powered shopping agents, enterprise chatbots, and autonomous browsing systems. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for organizations seeking to optimize their presence in the AI-driven discovery ecosystem.
AI traffic exhibits distinct behavioral and performance characteristics that differentiate it from organic search, social, and direct traffic. First, AI traffic is more qualified and conversion-focused. Research from Microsoft Clarity analyzing over 1,200 publisher sites found that AI traffic converts at 3x the rate of other channels. Specifically, sign-up conversion rates from AI traffic reached 1.66% compared to 0.15% from search, while subscription conversion rates hit 1.34% versus 0.55% from search. Even more striking, Copilot referrals converted at 17x the rate of direct traffic and 15x the rate of search traffic for subscriptions. This exceptional conversion performance reflects the nature of AI traffic visitors: they arrive with high intent, having already received contextual information from the AI model, and are typically deeper in the purchase funnel than users arriving from traditional search.
Second, AI traffic is currently small in volume but growing exponentially. While AI referrals account for less than 1% of overall website traffic across most industries, the growth rate is unprecedented. Adobe Analytics reported that traffic from generative AI sources increased by 1,300% during the 2024 holiday season compared to the prior year, and Q2 2025 data showed AI start rates 7% higher than non-AI traffic. This creates a strategic paradox: AI traffic is too small to ignore but too valuable to overlook. Third, AI traffic visitors expect high content relevance and clarity. Because users receive hyper-personalized answers from AI tools, they expect your page to seamlessly continue that conversation with accurate, well-structured information. Finally, AI traffic attribution is complex because many AI platforms do not always pass referrer information, meaning some AI traffic may be categorized as direct or unassigned traffic in analytics platforms.
| Characteristic | AI Traffic | Organic Search | Social Media | Direct Traffic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current Volume | <1% of total traffic | 40-50% of total traffic | 5-15% of total traffic | 10-20% of total traffic |
| Growth Rate (2024-2025) | +527% YoY | +24% YoY | +21.5% YoY | +14.9% YoY |
| Sign-Up Conversion Rate | 1.66% | 0.15% | 0.46% | 0.13% |
| Subscription Conversion Rate | 1.34% | 0.55% | 0.37% | 0.41% |
| Visitor Intent | High (contextual, consultative) | Medium (keyword-driven) | Low to Medium (discovery-based) | High (direct intent) |
| User Journey Depth | Mid to Bottom Funnel | Top to Mid Funnel | Top Funnel | Mid to Bottom Funnel |
| Primary Platforms | ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Gemini, Copilot | Google, Bing | Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram, TikTok | Bookmarks, Direct URLs |
| Attribution Tracking | Complex (referrer often missing) | Clear (UTM parameters) | Clear (platform-specific) | Simple (direct source) |
| Content Preference | Structured, scannable, FAQ-optimized | Keyword-optimized, long-form | Visual, shareable, trending | Brand-specific, navigational |
| Relative Value per Visitor | Highest (3x other channels) | Medium | Low to Medium | Medium to High |
AI traffic originates through several distinct technical pathways, each with different implications for visibility and measurement. The primary mechanism involves user-initiated queries to AI assistants. When a user asks ChatGPT, Perplexity, or another LLM a question, the model searches its training data and, increasingly, performs real-time web searches to provide current information. If your content is deemed relevant and authoritative, the AI model cites or links to your website in its response. The user then clicks that link, generating a session that analytics platforms attribute to the AI platform referrer. This process differs fundamentally from Google search because the AI model controls the presentation and framing of your content within its response interface, rather than your page appearing as a standalone result.
A second pathway involves RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) scrapers, which fetch real-time data from websites to supplement AI responses. These scrapers are triggered by specific user queries and pull targeted information—such as pricing, product specifications, or current news—to enrich the AI’s answer. While RAG scraper traffic may inflate pageview counts, it represents a different value proposition than direct user visits. Third, agentic browsers like those used by Perplexity and emerging autonomous shopping agents navigate websites dynamically, executing JavaScript and interacting with page elements much like human users. These systems can generate meaningful traffic and even conversions, though they operate at machine speed and with machine-like precision. Finally, LLM training crawlers like GPTBot and ClaudeBot systematically collect web content to train or update language models. While this traffic doesn’t directly generate conversions, it influences how your brand and content are represented in future AI responses.
AI traffic distribution is highly concentrated in specific industries, reflecting where users most commonly turn to AI for answers. According to Previsible’s 2025 AI Traffic Report, Legal leads with 0.28% of total traffic from LLMs, followed by Finance at 0.24%, and Health at 0.15%. These high-consultative industries dominate because users ask AI assistants contextual, trust-heavy questions that require expert guidance. For example, a user might ask: “What should I ask a lawyer before signing this contract?” or “Is this medication safe with my specific conditions?” These are precisely the types of queries where AI models surface authoritative, trustworthy sources, making AI traffic particularly valuable in regulated and expertise-driven sectors.
SaaS companies show breakout performance in AI traffic, with selected domains receiving over 1% of total sessions from LLMs. This reflects the nature of SaaS discovery: users often ask AI assistants for product recommendations, comparisons, and implementation guidance before making purchasing decisions. Insurance, SMB services, and Healthcare also show strong AI traffic penetration, driven by the consultative nature of these industries. Conversely, e-commerce and retail currently show lower AI traffic penetration, though this is rapidly changing as AI shopping agents and autonomous purchasing systems mature. The implication is clear: organizations in high-trust, high-expertise industries should prioritize AI traffic optimization immediately, while those in other sectors should prepare for rapid growth in the coming 12-24 months.
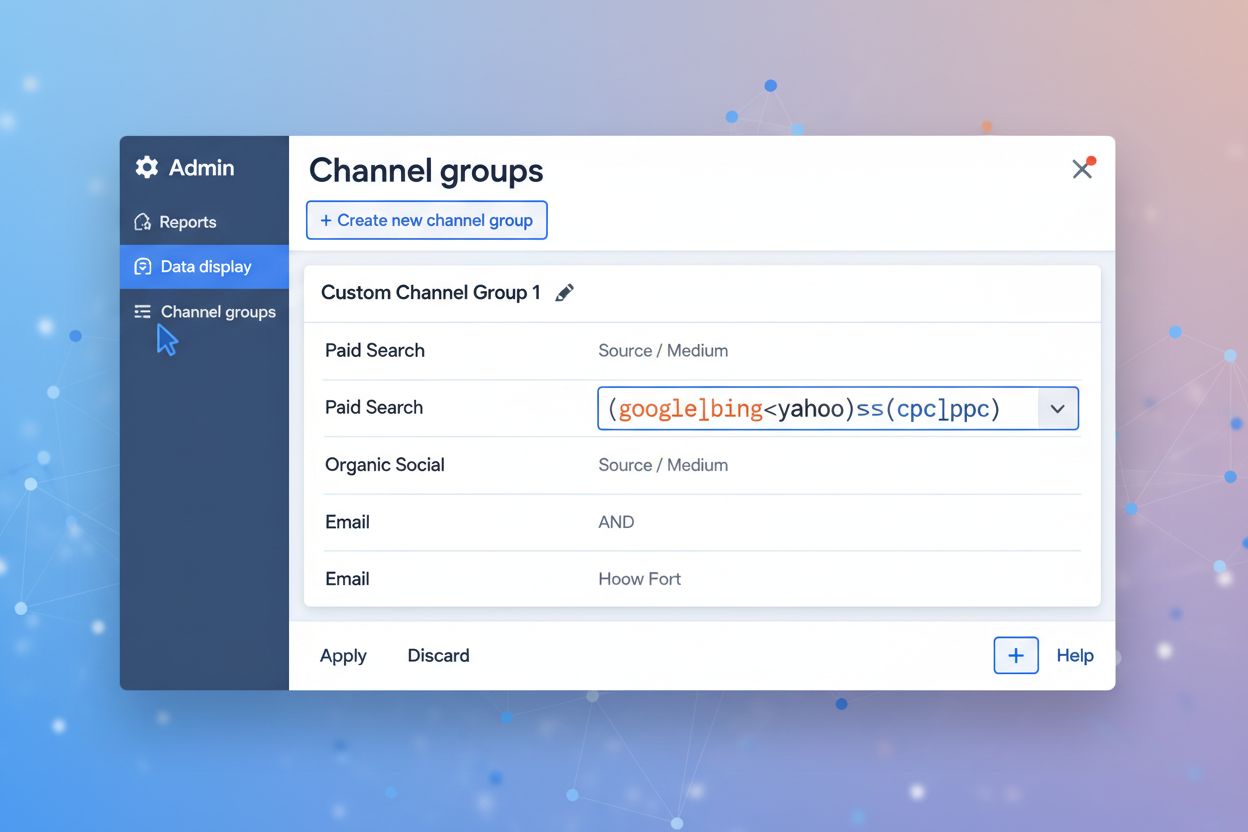
Tracking AI traffic requires a multi-layered approach because AI platforms do not always pass referrer information consistently. The most straightforward method involves configuring analytics filters in Google Analytics 4 (GA4). Users can create regex (regular expression) filters that match AI platform referrer domains, allowing them to segment AI traffic separately from other sources. The standard regex pattern includes major LLMs: (chatgpt\.com|openai\.com|perplexity\.ai|claude\.ai|gemini\.google\.com|bard\.google\.com|you\.com|search\.brave\.com|copilot\.microsoft\.com).*. This filter can be applied to the Session source/medium dimension in GA4’s Traffic Acquisition report, providing visibility into AI-driven sessions.
However, GA4 tracking has limitations. Some AI traffic is categorized as direct or unassigned traffic because AI platforms don’t always pass referrer information, meaning actual AI traffic volumes are likely higher than reported. Additionally, Google AI Overviews traffic cannot currently be tracked through standard analytics, though Google Search Console may show increased impressions without corresponding clicks as an indicator of AI Overview inclusion. For more comprehensive AI traffic tracking, organizations can implement dedicated platforms like Contentsquare, Microsoft Clarity, or SE Ranking’s AI Traffic Analytics. These tools offer out-of-the-box AI traffic segmentation without requiring custom regex setup, and they often provide retroactive data and cross-platform comparison capabilities.
Distinguishing between human AI traffic and bot traffic requires examining server logs and behavioral patterns. LLM crawlers and RAG scrapers typically exhibit anomalous behavior: sessions that complete in milliseconds, journeys that skip the homepage, high bounce rates, and zero time on page. Agentic browsers, by contrast, may appear similar to human sessions but operate at unnaturally fast speeds. By analyzing interaction patterns, scroll depth, and engagement metrics, organizations can segment genuine AI traffic (human users arriving from AI platforms) from bot traffic (automated crawlers and scrapers). This distinction is critical for accurate KPI measurement and conversion attribution.
Optimizing content for AI traffic requires a fundamentally different approach than traditional SEO. While search engine optimization prioritizes keyword matching, backlinks, and ranking position, AI traffic optimization (sometimes called AEO or Artificial Engine Optimization) prioritizes clarity, structure, and trustworthiness. AI models favor content that is scannable and well-organized, including FAQ sections, bullet points, tight introductions, and strong summaries. This format allows LLMs to extract relevant information quickly and present it coherently in their responses. Additionally, structured data and schema markup improve how AI systems understand and represent your content, increasing the likelihood of citation and linking.
Content freshness and accuracy are paramount for AI traffic optimization. Because AI models increasingly perform real-time web searches to supplement their responses, outdated or inaccurate information may be deprioritized or excluded entirely. Organizations should maintain current pricing information, up-to-date product specifications, and accurate contact details across their entire website. Product pages, help documentation, case studies, and knowledge bases are all eligible to be surfaced in AI conversations, so cross-functional alignment between SEO, content, UX, and product teams is essential. Finally, building authority and trust signals remains critical. AI models are trained to cite authoritative sources, so earning backlinks, maintaining consistent branding, and demonstrating expertise continue to influence AI traffic just as they do traditional search visibility.
AI traffic is poised to become a dominant discovery channel within the next 2-3 years, fundamentally reshaping digital strategy. Current projections suggest that AI traffic could overtake organic search traffic by 2029, though this timeline may accelerate as AI adoption increases and model capabilities improve. The multi-model landscape is solidifying, with ChatGPT maintaining dominance but Perplexity, Copilot, and Gemini gaining meaningful share. This diversification means that organizations cannot optimize for a single AI platform but must ensure visibility across multiple LLMs simultaneously.
The evolution of AI agents—autonomous systems that browse, compare, decide, and even purchase on behalf of users—represents the next frontier of AI traffic. Unlike current AI assistants that provide information to human users, AI agents will execute transactions directly, potentially generating conversions without human intervention. This shift will require digital teams to balance design for two audiences: the human who feels and the agent that calculates. Content clarity, data accuracy, and structured information will become even more critical. Additionally, AI traffic monitoring and attribution will become increasingly sophisticated, with platforms like AmICited enabling organizations to track brand mentions, domain citations, and URL appearances across the entire AI ecosystem. This visibility will shift from a competitive advantage to a competitive necessity.
The strategic implication is clear: organizations that begin optimizing for AI traffic now will establish authority and visibility before the channel becomes saturated. Just as early adopters of mobile optimization and social media marketing gained disproportionate advantage, early movers in AI traffic optimization will shape how AI systems learn, recommend, and decide in their favor. The organizations that treat AI traffic as a core discovery channel—not a peripheral experiment—will maintain visibility and conversion advantage as the web becomes increasingly automated and AI-driven.
According to Microsoft Clarity's analysis of over 1,200 publisher sites, AI traffic currently accounts for less than 1% of overall website traffic. However, growth is explosive—AI referral traffic grew 155.6% over eight months, significantly outpacing search (+24%), social (+21.5%), and direct traffic (+14.9%). Some SaaS and specialized sites are already seeing over 1% of total sessions from AI platforms, with certain verticals like Legal, Finance, and Health experiencing even higher penetration rates.
ChatGPT dominates AI traffic, consistently driving 40-60% of all LLM-sourced sessions across industries. However, the landscape is diversifying rapidly. Perplexity, Microsoft Copilot, and Google Gemini are gaining significant traction, with Perplexity contributing over 0.073% of Finance traffic and Copilot making up meaningful portions of Legal and Finance referrals. Claude is still marginal but present across all verticals, indicating a multi-model future for AI discovery.
Yes, significantly. According to Microsoft Clarity research, AI traffic converts at 3x the rate of traditional channels. Specifically, AI traffic achieved a 1.66% sign-up conversion rate compared to 0.15% from search, and a 1.34% subscription conversion rate versus 0.55% from search. Copilot referrals converted at 17x the rate of direct traffic and 15x the rate of search for subscriptions, making AI visitors exceptionally high-quality prospects.
AI traffic refers to human visitors who arrive at your site because an AI platform recommended or cited your content in response to a user query. Bot traffic, by contrast, consists of automated crawlers and scrapers that visit your site without human intent—including LLM training crawlers (like GPTBot), RAG scrapers for real-time data enrichment, and agentic browsers. While both are non-traditional traffic sources, AI traffic represents genuine user interest, whereas bot traffic is machine-driven data collection.
You can track AI traffic in Google Analytics 4 by creating regex filters that match AI platform referrer domains. Set up a filter in Reports > Acquisition > Traffic Acquisition, change the dimension to 'Session source/medium,' and use a regex pattern like (chatgpt\.com|perplexity\.ai|claude\.ai|gemini\.google\.com|copilot\.microsoft\.com). Alternatively, use dedicated analytics platforms like Contentsquare or Microsoft Clarity that offer out-of-the-box AI traffic segmentation without requiring custom setup.
AI traffic is growing because large language models are becoming primary discovery tools for users seeking contextual, trust-heavy answers. Between January and May 2025, AI-referred sessions jumped 527% year-over-year, from 17,076 to 107,100 sessions across analyzed properties. This growth is driven by increased LLM adoption, improved model capabilities, and user preference for conversational interfaces over traditional search. High-consultative industries like Legal, Finance, Health, and Insurance account for 55% of all LLM-sourced sessions.
AI platforms favor clear, structured, and scannable content including FAQ sections, bullet points, tight introductions, and strong summaries. Product pages, help documentation, case studies, and knowledge bases all perform well. Unlike traditional SEO which prioritizes ranking position, AI discovery rewards content that directly answers user questions with accuracy and clarity. Structured data, schema markup, and up-to-date metadata also improve how AI systems represent and cite your content in responses.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn how to track AI referral traffic in Google Analytics 4. Discover 4 methods to monitor ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI platforms, plus optimization strat...
Learn how AI traffic attribution software tracks and measures website traffic from ChatGPT, Gemini, and other LLMs. Discover tools, best practices, and how to o...

Learn how to track AI search traffic in GA4, monitor ChatGPT and Perplexity referrals, and measure AI visibility across platforms. Complete guide to AI traffic ...