
Does Author Schema Help with AI Citations? Complete Guide for 2025
Learn how author schema markup improves AI citations in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Discover implementation strategies to increase your brand ...
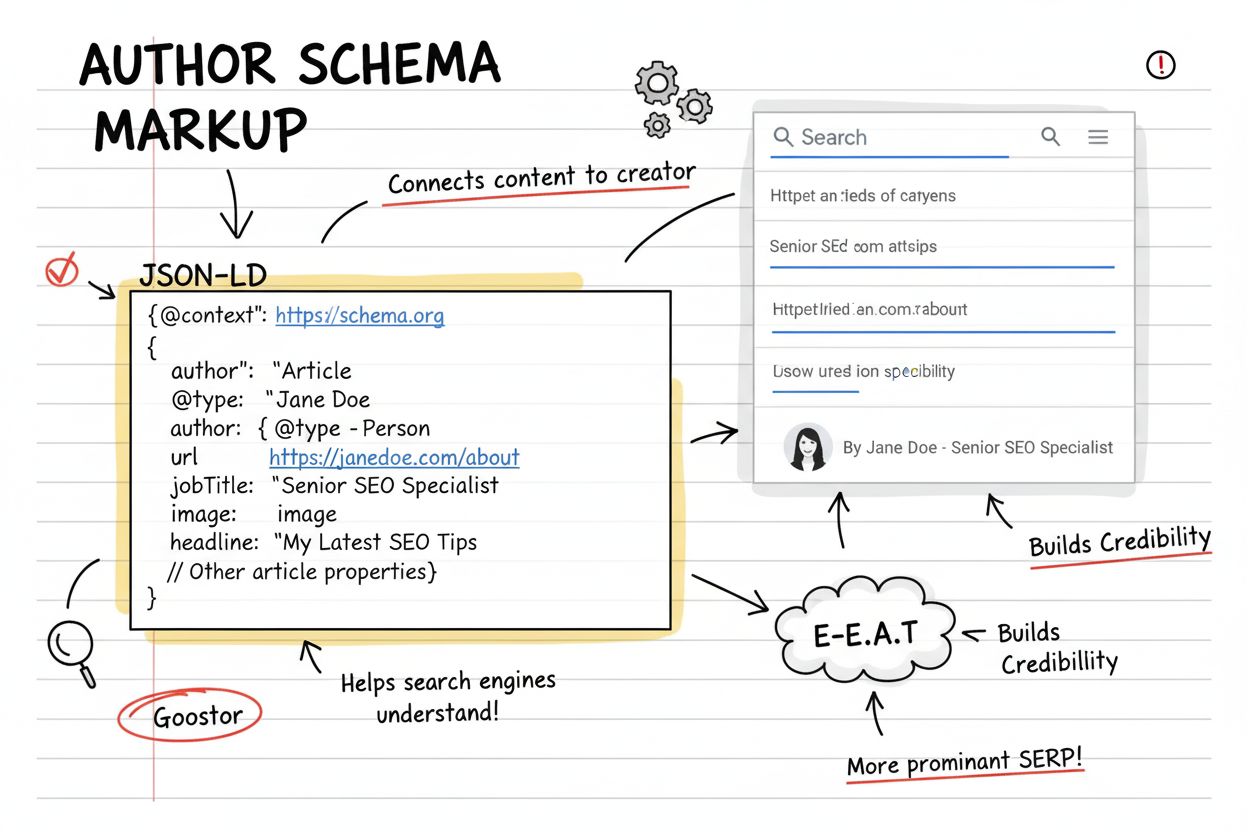
Author Schema is a standardized structured data markup that explicitly identifies the creator of web content to search engines and AI systems. Implemented using JSON-LD, Microdata, or RDFa formats, it includes author information such as name, URL, credentials, and professional details to establish content authority and support E-E-A-T signals.
Author Schema is a standardized structured data markup that explicitly identifies the creator of web content to search engines and AI systems. Implemented using JSON-LD, Microdata, or RDFa formats, it includes author information such as name, URL, credentials, and professional details to establish content authority and support E-E-A-T signals.
Author Schema is a standardized structured data markup format that explicitly communicates to search engines and AI systems who created a piece of web content. Implemented through JSON-LD, Microdata, or RDFa formats, Author Schema provides machine-readable information about content creators, including their name, professional URL, credentials, job title, and organizational affiliation. This markup is typically nested within broader content schema types like Article, BlogPosting, or NewsArticle, serving as a critical component of modern SEO and content attribution strategies. By embedding author information directly into a webpage’s code, publishers eliminate ambiguity about content authorship and help search engines connect content to real, verifiable individuals or organizations with demonstrated expertise in specific domains.
The concept of author identification in search has evolved significantly since Google’s early attempts to surface author information through its now-defunct Google Authorship program (2011-2014). While that program was discontinued, the underlying principle—that author credibility matters for search quality—has only strengthened. As of 2024, over 45 million web domains have implemented schema.org structured data, with JSON-LD reaching 41% adoption across the web, representing a 7% year-over-year increase. This widespread adoption reflects the growing recognition that structured data is essential not just for traditional search visibility, but for emerging AI-powered search systems. Google’s emphasis on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) in its Quality Rater Guidelines has made author identification increasingly important for content evaluation. The rise of AI-generated search results from platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude has further elevated the importance of Author Schema, as these systems require clear attribution data to properly credit original content sources.
Author Schema markup typically includes several key properties that work together to create a comprehensive author profile. The @type property specifies whether the author is a Person or Organization, allowing flexibility for different content scenarios. The name property contains the author’s full name exactly as it appears across all platforms, ensuring consistency that helps search engines recognize the author across multiple pieces of content. The url property links to a dedicated author page, biography page, or professional profile that uniquely identifies the author—this is arguably the most powerful property as it helps Google definitively confirm the author’s identity and expertise. Additional properties like jobTitle specify the author’s professional role, affiliation identifies their organizational connection, image provides a professional headshot URL, and sameAs can list multiple URLs pointing to the author’s social media profiles or other web presences. The description property allows for a brief biographical summary, while honorificPrefix and honorificSuffix can denote titles like “Dr.” or “Ph.D.” when appropriate.
The relationship between Author Schema and E-E-A-T is fundamental to modern SEO strategy. Experience is demonstrated through an author’s biography page that details their professional history and hands-on work in their field. Expertise is established by linking to content that showcases the author’s knowledge and credentials in specific domains. Authoritativeness is reinforced when Author Schema connects to external validation sources like professional certifications, published works, or recognized industry affiliations. Trustworthiness is built through transparent author information, consistent attribution across platforms, and clear disclosure of the author’s background and qualifications. For YMYL (Your Money Your Life) content—particularly in health, finance, legal, and scientific domains—Author Schema becomes even more critical. Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines explicitly instruct evaluators to assess the authoritativeness of content creators when determining page quality. A well-implemented Author Schema that links to a comprehensive author profile page provides concrete, verifiable evidence supporting all four E-E-A-T pillars, significantly improving a page’s chances of ranking well for competitive, authority-sensitive queries.
Author Schema can be implemented using three primary formats, each with distinct advantages. JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is the most widely recommended format by Google, accounting for 41% of structured data implementations. It’s placed in a <script> tag within the page’s <head> section and doesn’t interfere with HTML structure, making it ideal for modern web development. Microdata uses HTML attributes like itemscope, itemtype, and itemprop directly within the page’s HTML body, making author information visible to both search engines and users. RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes) provides another semantic markup option, though it’s less commonly used than JSON-LD. For most publishers, JSON-LD is the preferred choice due to its flexibility, ease of implementation, and direct compatibility with modern web technologies and CMS platforms. WordPress users can leverage plugins like Yoast SEO, Rank Math, or Schema Pro to automatically generate Author Schema without manual coding. For custom-built websites, developers can implement JSON-LD directly or use schema generator tools that create the necessary code snippets for copy-and-paste implementation.
| Aspect | JSON-LD | Microdata | RDFa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adoption Rate | 41% (highest) | Lower adoption | Lowest adoption |
| Implementation Location | <head> section in <script> tag | Inline HTML attributes | Inline HTML attributes |
| HTML Structure Impact | No interference | Integrated into HTML | Integrated into HTML |
| Ease of Use | Very easy, developer-friendly | Moderate complexity | Higher complexity |
| Search Engine Support | Excellent (Google recommended) | Good | Good |
| CMS Plugin Support | Extensive | Moderate | Limited |
| Visibility to Users | Hidden from page display | Can be visible | Can be visible |
| Best For | Modern websites, WordPress | Semantic HTML integration | Advanced semantic markup |
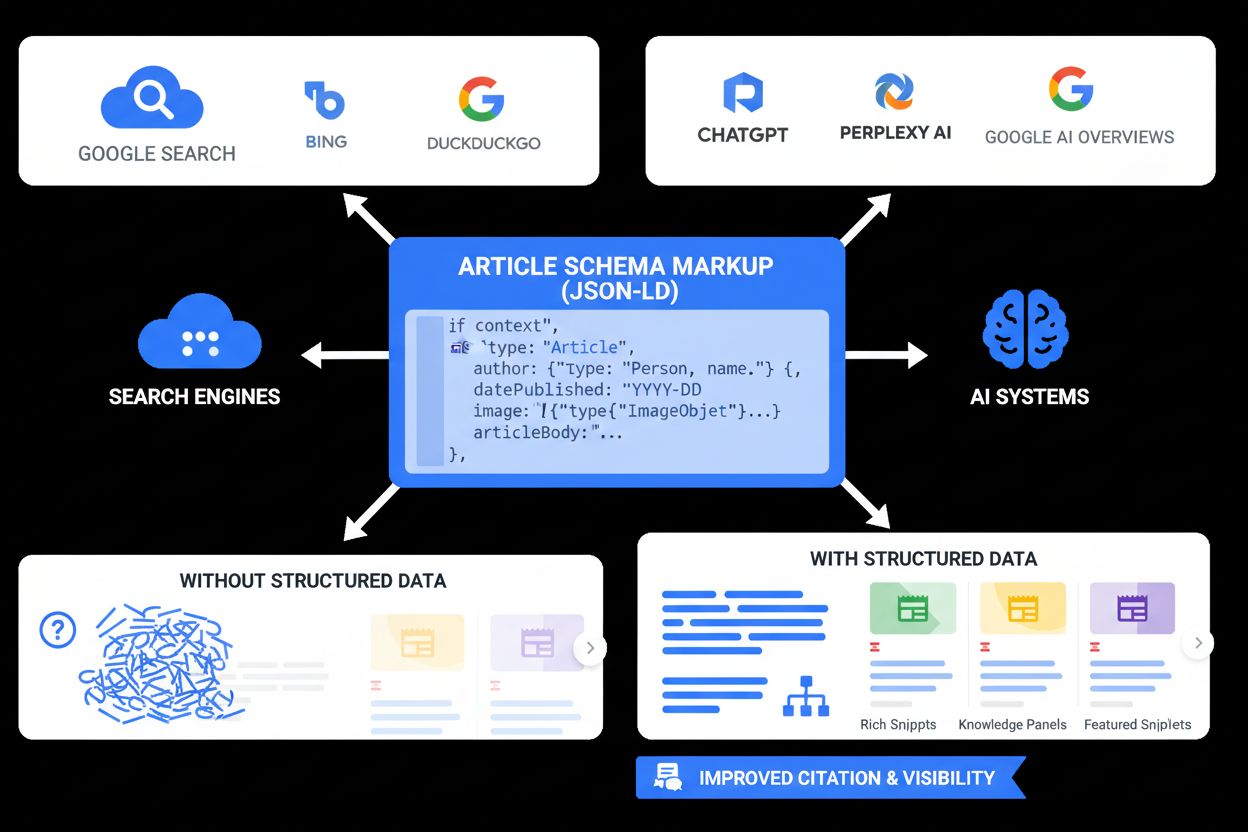
As AI-powered search systems become increasingly prevalent, Author Schema has emerged as a critical mechanism for content attribution and creator recognition. Platforms like Perplexity, ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, and Claude rely on structured data to understand content sources and provide proper attribution in their responses. When an AI system encounters well-implemented Author Schema, it can extract author information, verify credentials, and include proper attribution in its generated responses. This is particularly important for content monitoring platforms like AmICited, which track brand and domain mentions across AI search systems. By analyzing Author Schema markup, these platforms can determine not just whether content was cited, but who created it and how prominently it was featured in AI-generated responses. For content creators and publishers, this means that implementing Author Schema is no longer just an SEO best practice—it’s a fundamental requirement for ensuring proper attribution in the emerging AI-powered search landscape. Studies show that websites implementing schema markup experience an average 30% increase in click-through rates compared to those without it, and this advantage extends to AI visibility as well.
Implementing Author Schema effectively requires attention to several critical best practices. Consistency is paramount: the author’s name in the schema should match exactly how it appears on the author’s biography page, social media profiles, and other published works. This consistency helps search engines recognize the author across multiple pieces of content and build a stronger author profile. Completeness matters significantly—while only the author’s name is technically necessary, including additional properties like url, jobTitle, affiliation, and image creates a richer author entity that search engines can better understand and evaluate. Accuracy is essential; all information in Author Schema should be verifiable and truthful, as misleading author information could violate Google’s guidelines and result in manual actions against the site. Visibility should be considered: the author information in the schema should match what’s visible on the page itself, as discrepancies between markup and visible content can raise quality concerns. Maintenance is ongoing; author information should be kept current, with job titles, affiliations, and biographical details updated as the author’s career evolves. Validation should be performed using Google’s Rich Results Test to ensure the markup is correctly formatted and free of errors. Finally, linking strategy is crucial—the author.url property should ideally point to a dedicated author page on your own website rather than external profiles, as this provides the strongest signal of author authority and helps build your site’s topical authority.
Author Schema plays a significant role in how search engines build and maintain Knowledge Graphs—comprehensive databases of entities and their relationships. When search engines encounter well-structured Author Schema across multiple pieces of content, they can aggregate this information to create detailed author profiles within their Knowledge Graphs. This aggregation helps search engines understand an author’s expertise areas, professional history, and credibility across different topics. For example, if a medical doctor publishes multiple articles with proper Author Schema markup, Google can recognize that this person is an authority on medical topics and weight their content accordingly in health-related searches. The Knowledge Graph integration also enables search engines to display author panels in search results—those information boxes that appear to the right of search listings showing author details, social profiles, and related content. As AI systems increasingly rely on Knowledge Graphs to ground their responses in factual, verifiable information, Author Schema becomes even more critical. AI systems trained on data that includes Author Schema can better understand author expertise and provide more accurate, properly-attributed responses. This creates a virtuous cycle where well-implemented Author Schema improves both traditional search visibility and AI-powered search attribution.
The importance of Author Schema is expected to grow significantly as the digital landscape continues to evolve. With AI-generated content becoming increasingly prevalent, search engines and AI systems will place even greater emphasis on author credibility and content attribution. The rise of zero-click searches and AI Overviews means that content visibility increasingly depends on proper attribution and structured data that allows AI systems to understand and cite sources accurately. Future developments may include more sophisticated author verification mechanisms, integration with blockchain-based identity systems, and enhanced author reputation scoring based on structured data signals. As voice search and conversational AI become more dominant, Author Schema will play a crucial role in helping these systems understand who created content and whether that creator is a trustworthy source for the query being asked. Publishers that invest in comprehensive Author Schema implementation now will be better positioned to maintain visibility and attribution as search continues to evolve. Additionally, as regulatory requirements around AI transparency and content attribution become more stringent, Author Schema may become not just a best practice but a compliance requirement for certain industries and content types. The intersection of semantic SEO, AI discovery, and content attribution means that Author Schema is transitioning from a tactical SEO tool to a strategic component of digital presence and brand protection.
+++
Article Schema is a broader structured data type that describes the entire article and can include multiple properties like headline, datePublished, and image. Author Schema is a nested component within Article Schema that specifically identifies and provides details about the content creator. While Article Schema describes what the content is, Author Schema clarifies who created it and establishes their credibility.
Author Schema directly supports E-E-A-T by providing verifiable information about the creator's expertise, experience, and trustworthiness. By linking to an author's biography page with credentials and professional history, search engines can better assess content quality. This is especially critical for YMYL (Your Money Your Life) topics like health, finance, and legal content where author authority is paramount.
Yes, Author Schema supports both Person and Organization types. For organizational content, you can specify the company as the author using the Organization schema type. This is useful for corporate announcements, press releases, or company-wide content where the organization itself is the authoritative source rather than an individual author.
Author Schema provides machine-readable attribution data that AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google's AI Overviews can parse to properly credit content sources. As AI-generated search results become more prevalent, Author Schema ensures that original creators receive proper attribution when their content is cited or referenced by AI systems, supporting content monitoring platforms like AmICited.
Author Schema is not a direct ranking factor, but it supports ranking indirectly by strengthening E-E-A-T signals and enabling rich snippets. Pages with properly implemented Author Schema are more likely to qualify for enhanced search features, which can increase click-through rates. The improved visibility and user engagement from rich results can positively influence overall SEO performance.
While there are no strictly required properties, Google recommends including at minimum the author's name and a URL linking to their profile or biography page. Best practices suggest also including jobTitle, affiliation, and image properties to provide comprehensive author information that helps search engines and users understand the creator's expertise and credibility.
Author Schema enables platforms like AmICited to track when and where content creators' work appears in AI-generated responses across systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. By providing structured author information, it allows AI monitoring tools to properly attribute content and help creators understand their brand's visibility in AI search results.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn how author schema markup improves AI citations in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Discover implementation strategies to increase your brand ...

Learn how article schema with author markup builds trust signals for AI systems. Implement authorship markup to improve visibility in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and G...
Article Schema is structured data markup that defines news and blog article properties for search engines and AI systems. Learn how to implement Article, NewsAr...