
What is Brand SERP Optimization for AI? Complete Strategy Guide
Learn how brand SERP optimization for AI works, why it matters for your visibility in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews, and how to get your brand ci...
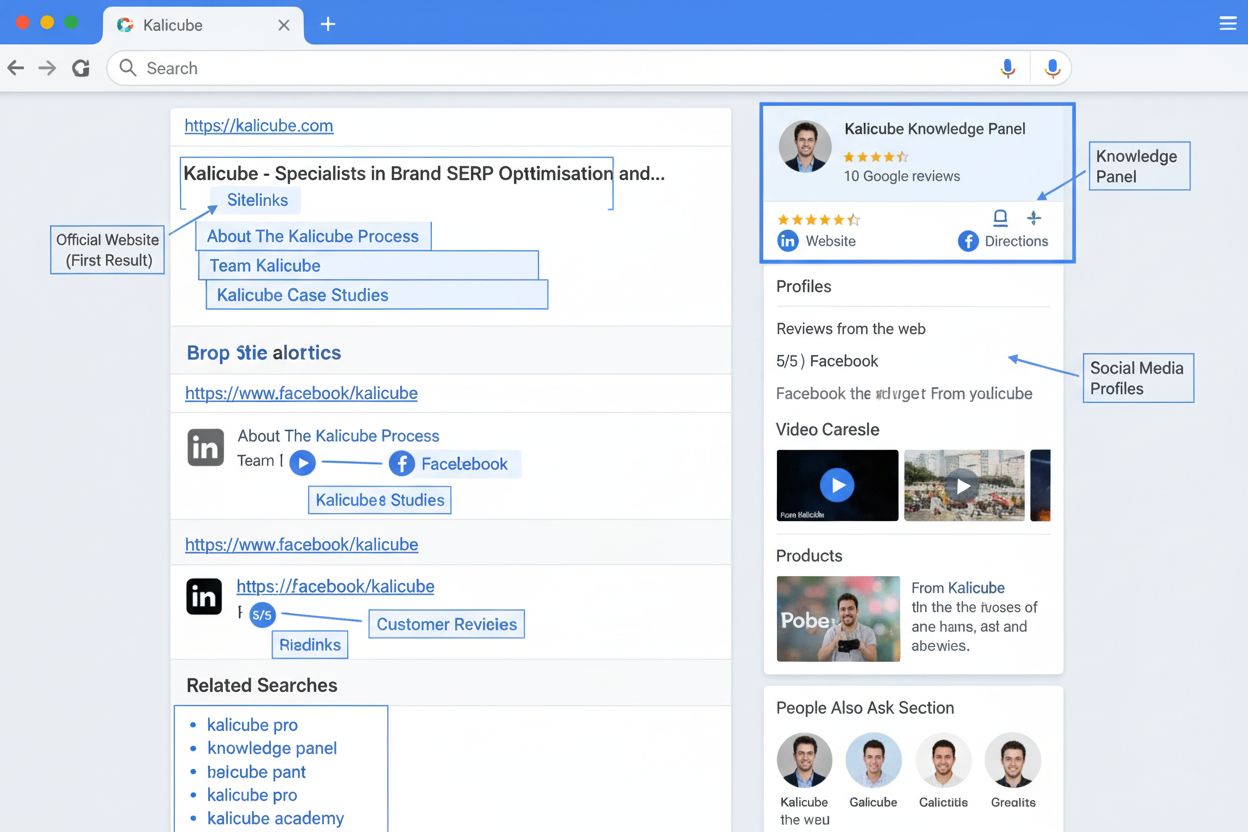
A Brand SERP is the search engine results page displayed when a user searches for an exact brand name on Google or other search engines. It represents Google’s evaluation of the most relevant and helpful information about that brand, including the official website, social profiles, knowledge panels, reviews, and other rich elements that collectively form the brand’s digital business card.
A Brand SERP is the search engine results page displayed when a user searches for an exact brand name on Google or other search engines. It represents Google's evaluation of the most relevant and helpful information about that brand, including the official website, social profiles, knowledge panels, reviews, and other rich elements that collectively form the brand's digital business card.
A Brand SERP is the search engine results page that appears when a user searches for an exact brand name on Google or other search engines. This is distinct from generic or non-branded searches, as it specifically targets queries using a company’s, product’s, or individual’s exact name. When someone types “Apple,” “Nike,” or “Coca-Cola” into Google’s search bar, the results they see constitute that brand’s Brand SERP. The Brand SERP represents Google’s algorithmic evaluation of what information is most relevant, helpful, and valuable for users seeking information about that specific brand. It functions as a digital business card that communicates the brand’s credibility, authority, and trustworthiness at a critical moment in the customer journey. Most prospects, investors, partners, journalists, and job candidates will search for a brand name at some point before or during their relationship with that organization, making the Brand SERP one of the most important touchpoints in modern digital marketing.
The concept of Brand SERPs has evolved significantly since the early days of search engine optimization. In the early 2000s, Brand SERPs were relatively simple, displaying primarily text-based organic results with minimal visual elements. However, as Google has continuously refined its algorithms and introduced new SERP features, Brand SERPs have become increasingly sophisticated and information-rich. The introduction of Knowledge Panels around 2012 marked a major shift, allowing Google to display structured information about brands directly in search results. Over the past decade, Google has progressively added more visual and interactive elements to Brand SERPs, including video carousels, image packs, social media profiles, review aggregations, and People Also Ask (PAA) boxes. According to industry research, approximately 70% of Brand SERPs now include PAA sections, indicating Google’s increased focus on answering user questions comprehensively. The emergence of AI Overviews and other generative features represents the latest evolution, as search engines now synthesize information from multiple sources to provide direct answers. This evolution reflects Google’s broader shift from being a link aggregator to being an answer engine, fundamentally changing how brands must approach their search visibility strategy.
A comprehensive Brand SERP typically includes multiple distinct elements that work together to present a complete picture of the brand. The official website almost always appears as the first organic result, ideally with rich sitelinks that direct users to important pages like About, Contact, Products, or Services sections. The Knowledge Panel, which appears on the right side of desktop SERPs, displays key facts about the brand pulled from Google’s Knowledge Graph and corroborated sources. Social media profiles frequently rank on Brand SERPs, with LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram profiles often appearing prominently, particularly when they have strong engagement metrics. Video results from YouTube or other platforms may appear in carousel format, especially if the brand has invested in video content. Customer reviews and ratings from platforms like Trustpilot, Google Reviews, or industry-specific review sites provide social proof and influence purchasing decisions. People Also Ask boxes display related questions that users frequently ask about the brand, providing opportunities for brands to control the narrative around common inquiries. Featured snippets may appear for specific brand-related queries, and news results can surface for brands in news-heavy industries. The specific combination and prominence of these elements varies based on the brand’s industry, size, and digital strategy maturity.
| Aspect | Brand SERP | Non-Branded SERP | AI Overview | Knowledge Panel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Search Query Type | Exact brand name | Generic keywords or topics | AI-generated summary | Entity-specific information |
| Primary Purpose | Display brand-specific results | Answer general questions | Synthesize multiple sources | Show structured brand facts |
| Typical Results | Official website, social profiles, reviews | Competitor content, guides, resources | Direct answer with citations | Key facts and attributes |
| User Intent | Research specific brand | Find general information | Get quick answer | Learn about entity |
| Ranking Factors | Brand authority, consistency, E-E-A-T | Relevance, content quality, backlinks | Source credibility, comprehensiveness | Corroboration, Wikipedia, structured data |
| Optimization Focus | Knowledge panel, sitelinks, rich elements | Keyword optimization, content depth | Source authority, citation potential | Structured data, Wikipedia presence |
| Frequency of Appearance | Varies by brand recognition | Highly variable | 8.19% of SERPs (2024) | 23.83% of SERPs (2024) |
| Business Impact | Critical for reputation and conversion | Important for discovery | Growing importance for AI visibility | Essential for brand credibility |
Google’s algorithm evaluates Brand SERPs through a complex process that differs from how it ranks results for non-branded queries. When a user searches for an exact brand name, Google’s systems first identify that the query is brand-specific rather than informational or transactional. The search engine then applies specialized ranking signals that prioritize brand authority, consistency, and corroboration across multiple sources. The official brand website almost always ranks first because Google recognizes it as the authoritative source for that brand. However, the presence and ranking of other elements depend on various factors: social media profiles rank based on engagement metrics and follower counts; review sites rank based on review volume and recency; video results appear based on view counts and relevance; and knowledge panels are populated from Google’s Knowledge Graph, which aggregates information from Wikipedia, structured data markup, and other authoritative sources. E-E-A-T signals (Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) play a particularly important role in Brand SERP rankings. Google evaluates whether the brand demonstrates genuine expertise in its field, has real-world experience, maintains authority through citations and mentions, and demonstrates trustworthiness through consistent, accurate information. The algorithm also considers entity consistency—whether the brand’s name, logo, description, and contact information remain consistent across all platforms and sources. This consistency signals to Google that the information is reliable and that the brand is actively managing its online presence.
The Brand SERP directly influences critical business outcomes including customer acquisition, conversion rates, brand perception, and competitive positioning. Research indicates that most decision-makers will search for a brand name before engaging with it, making the Brand SERP a crucial touchpoint in the customer journey. A strong, optimized Brand SERP with rich elements and positive information can significantly increase conversion rates by building trust and credibility at the moment of decision. Conversely, a weak Brand SERP with missing elements or negative content can damage brand perception and drive prospects toward competitors. The Brand SERP also serves as a diagnostic tool for overall digital strategy health. By analyzing what appears on the Brand SERP, marketing teams can quickly identify strengths and weaknesses in their digital presence. For example, if a brand is investing heavily in YouTube but no video results appear on the Brand SERP, it indicates that the video strategy isn’t resonating with the target audience or isn’t optimized for search visibility. Similarly, if a brand’s social media profiles don’t rank on the Brand SERP despite significant investment, it suggests that engagement metrics are insufficient or that the platform isn’t relevant to the brand’s audience. The Brand SERP also provides early warning signals for reputation issues. Negative content typically appears on pages 5-10 of search results before rising to page 1, allowing brands to identify and address problems proactively. By building a strong foundation of positive, evergreen content on the Brand SERP, brands create a “reputation cushion” that prevents temporary negative news from easily reaching the first page.
While Google dominates with over 90% search market share, Brand SERPs appear differently across various search engines and increasingly across AI platforms. On Google, Brand SERPs are typically the most comprehensive, featuring knowledge panels, rich sitelinks, social profiles, videos, reviews, and PAA boxes. Bing displays Brand SERPs with a different layout, often featuring Copilot Search cards and related searches positioned on the side rather than at the bottom. DuckDuckGo shows more minimal Brand SERPs with fewer rich elements, reflecting its privacy-focused approach. The emergence of AI-powered search platforms like Perplexity, ChatGPT, and Google AI Overviews has created a new dimension to Brand SERP strategy. These platforms don’t display traditional SERPs but instead generate synthesized answers that cite sources. When users ask AI systems questions about brands, the AI pulls information from web sources—often the same sources that rank on traditional Brand SERPs. This means that optimizing your Brand SERP for traditional search directly impacts your visibility in AI responses. Brands that appear prominently on Google’s Brand SERP are more likely to be cited by AI systems when answering questions about that brand. Additionally, Google AI Overviews now appear on approximately 8.19% of SERPs, and these AI-generated summaries pull from top-ranking results. A strong Brand SERP increases the likelihood that your brand will be included in these AI-generated summaries, extending your visibility beyond traditional click-through traffic.
Optimizing your Brand SERP requires a systematic, multi-faceted approach that addresses both on-site and off-site factors. The first step is ensuring your official website is properly optimized with clear information architecture, fast loading speeds, mobile responsiveness, and comprehensive Schema.org markup. Your homepage should clearly communicate what your brand does, who it serves, and why it’s trustworthy. Implement structured data for your organization, including name, logo, contact information, social profiles, and business type. This helps Google understand and display your brand information accurately. Second, claim and optimize your Knowledge Panel by verifying your brand on Google Search Console and ensuring all information is accurate and up-to-date. Provide high-quality images, accurate descriptions, and links to authoritative sources that corroborate your brand information. Third, build consistent brand presence across platforms by maintaining identical business information (name, address, phone number) across Google Business Profile, social media, review sites, and industry directories. This consistency signals to Google that your information is reliable. Fourth, invest in content that answers common questions about your brand by creating an FAQ section on your website and answering the questions that appear in your Brand SERP’s People Also Ask box. Fifth, encourage and manage customer reviews on relevant platforms, as review volume and ratings significantly influence Brand SERP rankings and user trust. Sixth, develop a social media strategy focused on engagement rather than just follower count, as engagement metrics influence whether social profiles rank on your Brand SERP. Finally, monitor your Brand SERP regularly using tools like AmICited to track changes, identify emerging issues, and measure the impact of your optimization efforts.
The future of Brand SERPs is inextricably linked to the rise of AI-powered search and answer engines. As platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude become increasingly central to how people search for information, the definition and importance of Brand SERPs will continue to evolve. Traditional Brand SERP optimization will remain important, but brands must now think beyond Google’s search results to consider how they appear in AI-generated answers. This represents a fundamental shift from link-based visibility to citation-based visibility. In the near future, we can expect to see more integration between traditional SERPs and AI-generated content, with Google increasingly using AI Overviews to synthesize information from top-ranking results. Brands that optimize their Brand SERP for both human readers and AI systems will have a significant competitive advantage. Additionally, as voice search and conversational AI become more prevalent, the nature of Brand SERPs may shift to accommodate more natural language queries and multi-turn conversations. The importance of structured data and entity optimization will only increase, as AI systems rely heavily on well-organized, semantically meaningful information to understand and cite brands accurately. Furthermore, the rise of vertical search (industry-specific search engines and platforms) means that brands may need to optimize their presence across multiple specialized SERPs beyond Google. The concept of Brand SERP will likely expand to encompass a brand’s visibility across the entire AI Brand Results Ecosystem, including traditional search, AI answer engines, social platforms, and specialized industry platforms. Organizations that take a holistic approach to managing their brand visibility across all these channels will be best positioned to maintain relevance and authority in an increasingly AI-driven search landscape.
A Brand SERP is the actual search results page that appears when someone searches for your brand name, while a branded search refers to the search query itself. The Brand SERP is Google's response to that branded search query, showing what the search engine considers most relevant and helpful for users searching for your brand. Understanding this distinction is crucial because the Brand SERP represents your brand's digital presence and credibility as evaluated by Google's algorithm.
As AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews increasingly pull information from search results to generate answers, your Brand SERP becomes critical for AI visibility. These AI tools often reference and cite sources that appear prominently in traditional SERPs. By optimizing your Brand SERP with rich elements and authoritative content, you increase the likelihood that AI systems will cite your brand when answering user queries, extending your visibility beyond traditional search.
A strong Brand SERP typically includes: your official website as the first result with sitelinks, a knowledge panel with accurate brand information, social media profiles (LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook), video results from YouTube or other platforms, customer reviews and ratings, People Also Ask (PAA) boxes with relevant questions, and rich snippets with structured data. The presence of these elements indicates that Google has strong understanding of your brand and considers it authoritative and trustworthy.
You should monitor your Brand SERP regularly—ideally weekly or at minimum monthly—to track changes in rankings, new SERP features, and emerging reputation issues. Consistent monitoring helps you identify problems early, such as negative content rising in rankings or loss of rich elements. Tools like AmICited can automate this process by tracking how your brand appears across search engines and AI platforms, providing real-time alerts when significant changes occur.
Yes, negative content can appear on your Brand SERP, particularly on pages 2-10 of search results. This is why proactive reputation management is essential. By building a strong foundation of positive, authoritative content on your official website and earning mentions from reputable sources, you create a 'reputation cushion' that prevents negative content from easily reaching the first page. If negative content does appear, you can work to push it down by creating and promoting positive content.
Brand SERP optimization focuses specifically on controlling how your brand appears when someone searches your exact brand name, while traditional SEO targets broader keyword rankings. Brand SERP optimization emphasizes accuracy, consistency, and rich elements that build trust and credibility. It involves managing your knowledge panel, ensuring consistent business information across platforms, optimizing your official website structure, and building a cohesive digital presence that Google recognizes as authoritative.
Structured data (Schema.org markup) is crucial for Brand SERP optimization because it helps Google understand your brand's information more accurately. Implementing proper schema markup for your organization, contact information, social profiles, and content types signals to Google that your website is well-organized and trustworthy. This structured data directly influences whether rich elements like knowledge panels, sitelinks, and featured snippets appear on your Brand SERP, making it a foundational element of any optimization strategy.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn how brand SERP optimization for AI works, why it matters for your visibility in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews, and how to get your brand ci...
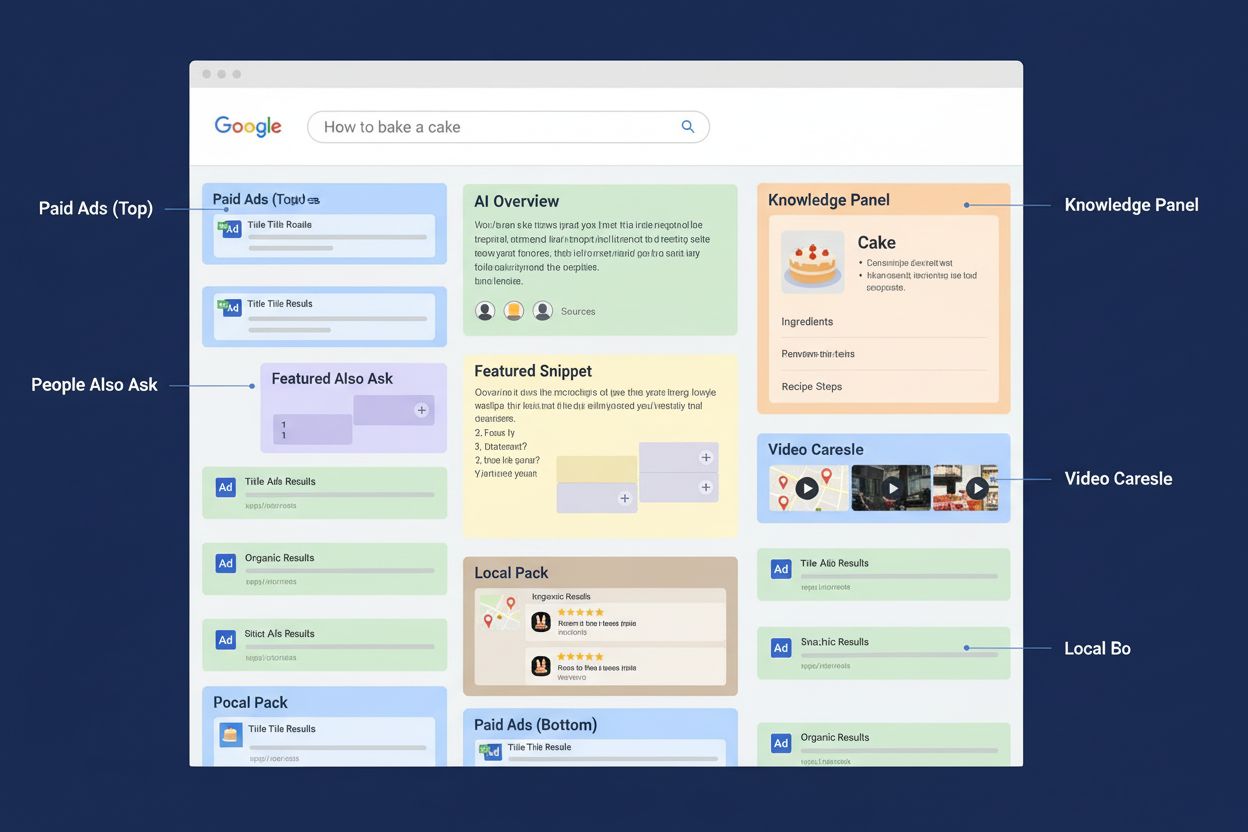
Learn what a SERP is, how it works, and why it matters for SEO, AI monitoring, and brand visibility. Understand SERP features and their impact on search ranking...

Brand signals are ranking indicators search engines use to measure brand authority and credibility. Learn how branded searches, citations, and trust signals imp...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.