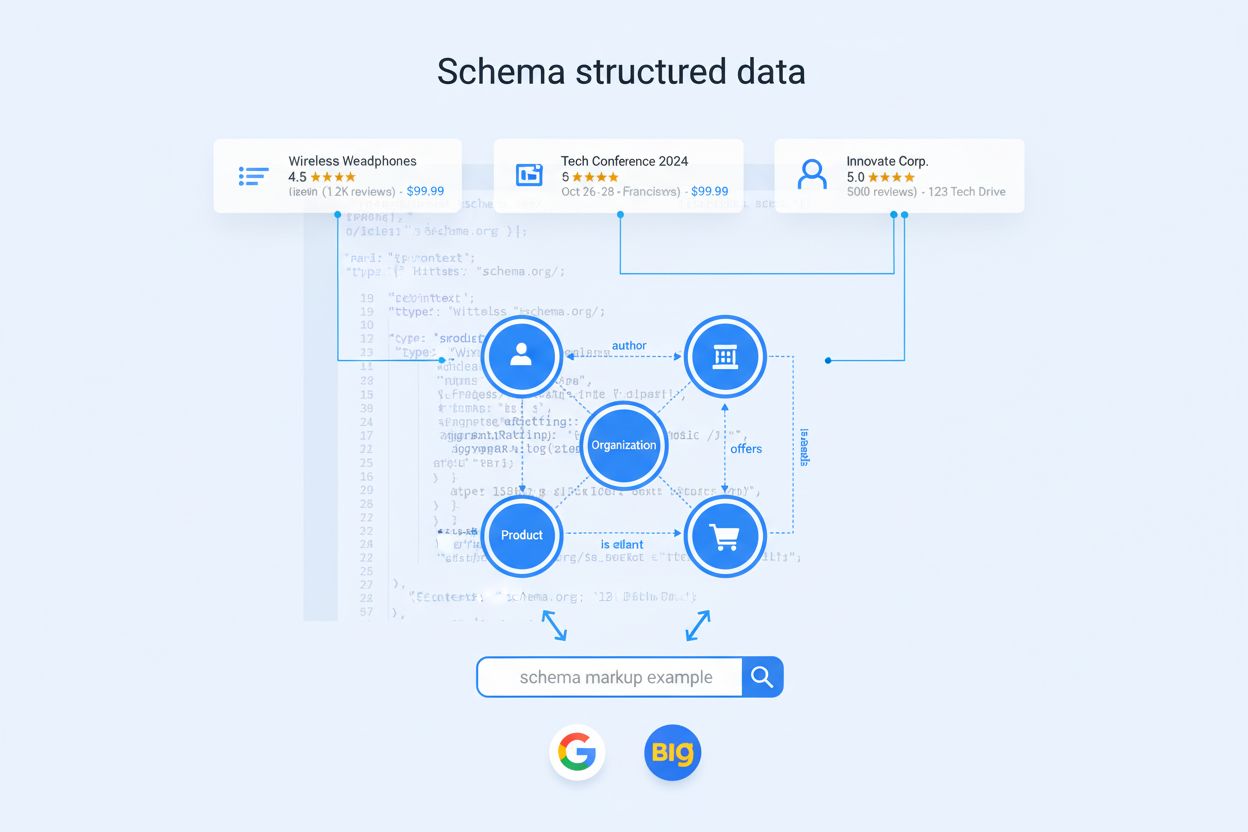
Schema Markup
Schema markup is standardized code that helps search engines understand content. Learn how structured data improves SEO, enables rich results, and supports AI s...
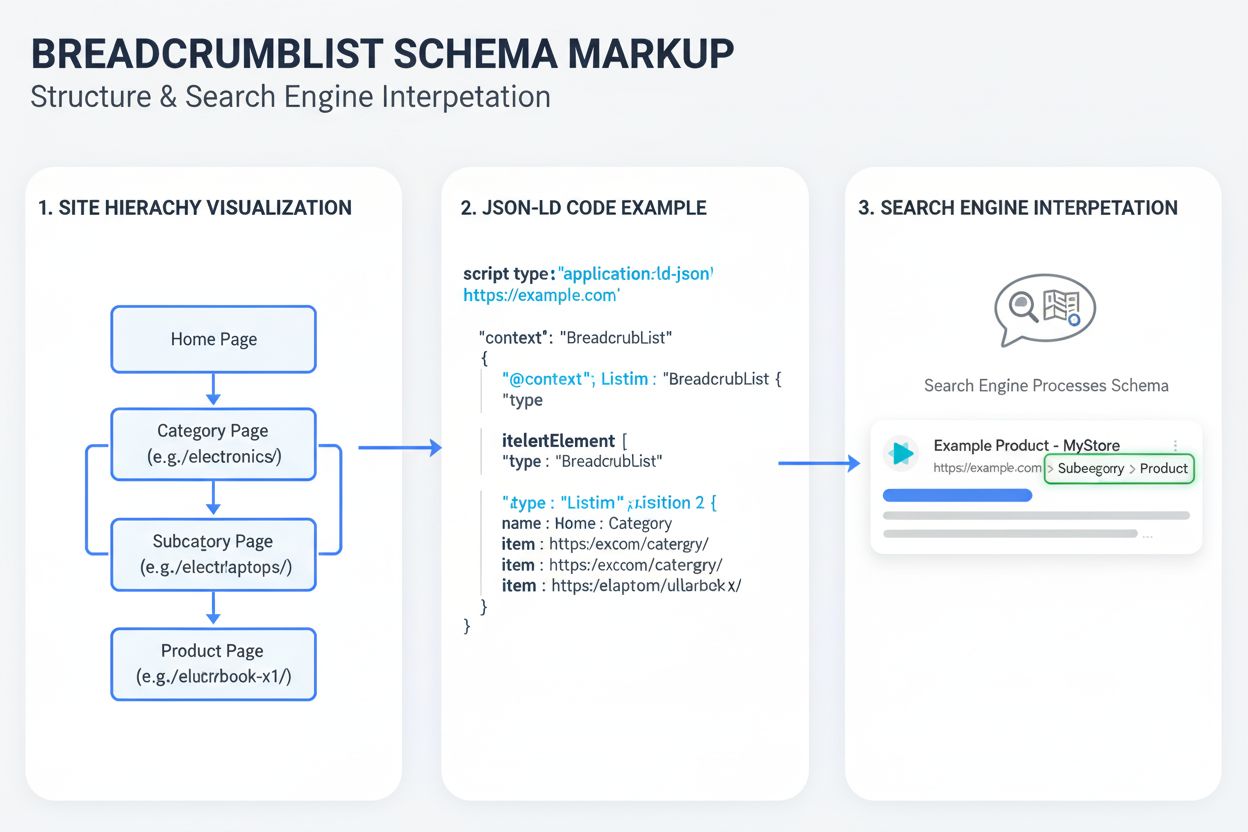
BreadcrumbList Schema is a structured data markup from schema.org that defines a hierarchical navigation trail on a website, helping search engines and AI systems understand site structure and display breadcrumb paths in search results. It uses JSON-LD, RDFa, or Microdata formats to explicitly label each step in a user’s navigation path from the homepage to the current page.
BreadcrumbList Schema is a structured data markup from schema.org that defines a hierarchical navigation trail on a website, helping search engines and AI systems understand site structure and display breadcrumb paths in search results. It uses JSON-LD, RDFa, or Microdata formats to explicitly label each step in a user's navigation path from the homepage to the current page.
BreadcrumbList Schema is a standardized structured data markup from schema.org that explicitly defines a hierarchical navigation trail on a website. It helps search engines and AI systems understand the relationship between pages and the site’s organizational structure. Implemented using JSON-LD, RDFa, or Microdata formats, BreadcrumbList Schema transforms visual breadcrumb navigation into machine-readable data that search engines can interpret and display directly in search results. The schema consists of a container element (BreadcrumbList) that holds multiple ListItem elements, each representing a step in the navigation hierarchy from the homepage to the current page. By adding this structured data, website owners enable search engines to display breadcrumb trails in search engine results pages (SERPs), which can significantly improve click-through rates and user experience. BreadcrumbList Schema is particularly valuable in the era of AI search and large language models, where structured data helps AI systems better understand content context and relationships.
Breadcrumb navigation derives its name from the Hansel and Gretel fairytale, where characters left breadcrumbs to retrace their steps through the forest. This metaphor perfectly captures the purpose of digital breadcrumbs: helping users navigate back through a website’s hierarchy. The concept of breadcrumb navigation emerged in the early 2000s as websites became increasingly complex with deeper hierarchical structures. Initially, breadcrumbs were purely visual elements created with HTML and CSS, serving only user experience purposes. However, as search engines evolved and began prioritizing structured data, the need for machine-readable breadcrumb information became apparent. In 2011, schema.org was launched as a collaborative initiative by Google, Bing, Yahoo!, and Yandex to create a standardized vocabulary for structured data. This led to the formalization of BreadcrumbList as a schema type, enabling webmasters to explicitly communicate site structure to search engines. The adoption of BreadcrumbList Schema has grown significantly, with research showing that approximately 66% of websites use some form of structured data, and breadcrumbs represent one of the most commonly implemented schema types. Today, BreadcrumbList Schema is essential not only for traditional search engines but also for AI search platforms like Perplexity, ChatGPT, and Google AI Overviews, which rely on structured data to understand content relationships and provide accurate, contextual responses.
The BreadcrumbList Schema follows a specific technical structure defined by schema.org. At its core, it consists of a BreadcrumbList container that holds an array of ListItem elements. Each ListItem must include three key properties: position (an integer indicating the item’s order in the trail), name (the text label displayed to users), and item (the URL of the page). The position property is critical for maintaining the correct sequence, typically starting from 1 for the homepage or top-level category. The most common implementation format is JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data), which Google explicitly recommends. JSON-LD allows developers to insert structured data within a <script> tag in the page’s <head> section without affecting the page’s visual layout or design. A typical JSON-LD BreadcrumbList implementation includes the @context property set to “https://schema.org
” and the @type property set to “BreadcrumbList”. The itemListElement property contains an array of ListItem objects, each with its own @type, position, name, and item properties. Alternative formats include RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes), which embeds structured data directly into HTML attributes, and Microdata, which uses HTML5 attributes like itemscope and itemprop. While all three formats are valid, JSON-LD has achieved the highest adoption rate at 41% across the web, making it the industry standard. The flexibility of BreadcrumbList Schema allows for both single and multiple breadcrumb trails on the same page, accommodating complex site structures where products or content can be accessed through different category hierarchies.
| Aspect | BreadcrumbList Schema | HTML Breadcrumbs | Sitemaps | Navigation Meta Tags |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Machine-readable site hierarchy for search engines and AI | Visual navigation aid for users | XML file listing all site URLs | Meta tags indicating page relationships |
| Format | JSON-LD, RDFa, or Microdata structured data | HTML <ol>, <ul>, or <nav> elements | XML file (sitemap.xml) | HTML <link> tags in page head |
| Search Engine Visibility | Displayed in SERPs as breadcrumb trails | Not directly visible in search results | Used for crawling and indexing | Minimal direct visibility |
| User Experience Impact | Indirect (improves CTR when displayed) | Direct (helps users navigate) | No direct user impact | No direct user impact |
| AI System Interpretation | Excellent (structured data aids LLM understanding) | Limited (requires parsing) | Good (helps understand site structure) | Limited (minimal context) |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate (requires code addition) | Simple (basic HTML) | Simple (XML file creation) | Simple (HTML meta tags) |
| SEO Impact | Indirect (improves CTR and crawlability) | Indirect (improves UX and internal linking) | Indirect (aids crawling efficiency) | Minimal direct impact |
| Adoption Rate | ~35-40% of websites | ~60% of websites | ~70% of websites | ~45% of websites |
| Best For | Complex hierarchical sites, ecommerce, AI visibility | All websites with multiple levels | Large sites with many pages | Indicating page relationships |
Search engines like Google use BreadcrumbList Schema to gain explicit understanding of a website’s organizational structure and how individual pages relate to one another. When a search engine crawler encounters properly implemented BreadcrumbList markup, it can immediately determine the hierarchical position of a page without having to infer relationships from URL structure or internal linking patterns alone. This explicit communication is particularly valuable because it allows search engines to understand the intended site architecture, even if the URL structure doesn’t perfectly reflect the hierarchy. For example, a page might have a URL like /products/item-12345, but the BreadcrumbList Schema can clearly indicate that this page belongs to “Home > Electronics > Computers > Laptops > Item Name”. This contextual information helps search engines better understand the page’s topic and relevance within the broader site context. Additionally, BreadcrumbList Schema improves crawlability by providing clear internal linking paths that search engine bots can follow. The schema essentially creates a map of the site’s structure, making it easier for crawlers to discover and index pages efficiently. Research indicates that websites implementing BreadcrumbList Schema experience improved crawl efficiency, with search engines able to discover and index pages more quickly. Furthermore, when BreadcrumbList Schema is properly implemented, Google and other search engines can display breadcrumb trails directly in search results, which enhances the visual appearance of your listing and provides users with additional context about the page’s position within your site. This enhanced display can lead to higher click-through rates (CTR), as users are more likely to click on results that clearly show the page’s relevance and context.
In the emerging landscape of AI search and large language models (LLMs), BreadcrumbList Schema plays an increasingly important role in content visibility and citation. Platforms like Perplexity, ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, and Claude rely on structured data to understand content relationships and provide accurate, contextual responses to user queries. Structured data like BreadcrumbList Schema creates what researchers call “chains” of information that make it easier for LLMs to grasp and recall content context. When an AI system encounters well-structured breadcrumb markup, it can better understand how a specific page fits into the broader topic landscape of a website. This improved understanding increases the likelihood that your content will be cited or referenced in AI-generated responses. According to research from Semrush and other SEO platforms, structured data appears to play a significant role in an LLM’s ability to read, understand, and serve content. Pages with comprehensive structured data implementation, including BreadcrumbList Schema, are more likely to be selected as sources for AI-generated answers. This is particularly important for AmICited users who are monitoring their brand and domain appearances across AI platforms. By implementing BreadcrumbList Schema, you’re not only optimizing for traditional search engines but also improving your visibility in AI search results. The schema helps AI systems understand your site’s topical authority and content organization, making your pages more likely to be cited when users ask questions related to your content. As AI search continues to grow—with Google AI Overviews now appearing in a significant percentage of search results—ensuring your structured data is comprehensive and accurate becomes increasingly critical for maintaining visibility across all search channels.
Implementing BreadcrumbList Schema effectively requires following several established best practices to ensure maximum benefit for both search engines and users. First, design breadcrumbs around a clear, logical hierarchy that matches the way most visitors naturally navigate your site. The breadcrumb trail should represent the actual site structure, not the user’s browsing history or arbitrary categorization. This consistency helps both search engines and users understand your site’s organization. Second, use hierarchy-based breadcrumbs rather than path-based or attribute-based breadcrumbs for primary navigation. Hierarchy-based breadcrumbs are the most stable and SEO-friendly, as they reflect your site’s permanent structure rather than temporary user behavior. Third, ensure each breadcrumb has a unique position value starting from 1 for the homepage or top-level category. Position values must be sequential integers with no gaps or duplicates. Fourth, include descriptive, user-friendly names for each breadcrumb item. The name should be concise but clear enough that users immediately understand what content they’ll find at that level. Avoid generic terms like “Page 1” or “Item A”; instead, use meaningful category names. Fifth, validate your implementation using Google’s Rich Results Test or other schema validation tools. This ensures your markup is syntactically correct and contains all required properties. Sixth, monitor your breadcrumb schema in Google Search Console’s Rich Results report to identify any errors or issues affecting your implementation. Finally, keep breadcrumbs consistent across your entire site in terms of format, separators (such as “>”, “/”, or “→”), and styling. Consistency improves user experience and helps search engines understand that your breadcrumbs follow a predictable pattern.
BreadcrumbList Schema’s impact extends beyond search engine optimization to directly influence user experience and engagement metrics. When breadcrumbs are properly implemented and displayed in search results, users gain immediate context about a page’s position within your site hierarchy. This contextual information reduces cognitive load and helps users quickly determine whether a page is relevant to their needs. Research from major ecommerce platforms shows that breadcrumb navigation significantly reduces bounce rates by providing users with easy navigation options back to parent categories or the homepage. Instead of using the browser’s back button or returning to search results, users can click on breadcrumb links to explore related content. This increased internal navigation leads to longer session durations and higher engagement metrics. Additionally, breadcrumbs improve the mobile user experience particularly significantly. On mobile devices where main navigation is often hidden behind hamburger menus, breadcrumbs provide an always-visible navigation option. Studies indicate that mobile users are more likely to use breadcrumb navigation than desktop users, making breadcrumbs especially valuable for mobile-first websites. The presence of breadcrumbs in search results also influences click-through rates (CTR). When users see a breadcrumb trail in a search result, they gain additional confidence that the page is relevant to their query. This visual confirmation can increase CTR by 5-15% depending on the industry and search context. Furthermore, breadcrumbs support internal linking strategy by creating additional pathways through your site. Each breadcrumb link is an internal link that passes authority and helps distribute page rank throughout your site. This improved internal linking structure benefits both user navigation and search engine crawlability.
The strategic importance of BreadcrumbList Schema is expected to increase significantly as AI search and large language models become more prevalent in the search landscape. Currently, approximately 45 million web domains have implemented some form of schema.org structured data, representing about 12.4% of all registered domains. However, adoption of BreadcrumbList Schema specifically remains lower than other schema types, presenting an opportunity for early adopters to gain competitive advantage. As AI systems become more sophisticated in understanding content relationships and context, the role of structured data like BreadcrumbList Schema will become increasingly critical. Future developments may include AI systems using breadcrumb information to better understand topical authority and content relationships, potentially influencing how AI-generated responses cite and reference sources. Additionally, as voice search and conversational AI continue to grow, breadcrumb schema may play a role in helping AI systems understand context in voice-based queries. The integration of BreadcrumbList Schema with other schema types—such as Article Schema, Product Schema, and Organization Schema—creates a comprehensive semantic web that AI systems can leverage for deeper understanding. Looking forward, webmasters should view BreadcrumbList Schema implementation not as a one-time technical task but as an ongoing optimization effort. Regular audits of breadcrumb implementation, monitoring of schema validation reports, and updates to reflect site structure changes will become standard practice. As competition for visibility in AI search results intensifies, the quality and accuracy of structured data implementation will increasingly differentiate successful websites from those that fail to adapt to the AI-driven search landscape.
Regular HTML breadcrumbs are visual navigation elements displayed on a webpage for users, while BreadcrumbList Schema is structured data markup that explicitly tells search engines about the breadcrumb hierarchy. HTML breadcrumbs improve user experience, but schema markup enables search engines like Google to understand and display breadcrumbs in search results, potentially improving click-through rates. Both can be implemented together for maximum benefit.
BreadcrumbList Schema helps AI systems and large language models (LLMs) understand content hierarchy and relationships between pages. Structured data creates 'chains' that make it easier for LLMs to grasp and recall content context, improving the likelihood of your content being cited in AI-generated responses. This is particularly important for platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews that rely on structured information to provide accurate answers.
A valid BreadcrumbList Schema requires at least two ListItem elements, each containing a 'position' (integer), 'name' (text label), and 'item' (URL). The position property must be unique and sequential, starting from 1. The name should be descriptive and match the breadcrumb text visible to users. The item property specifies the URL for each breadcrumb level, though it's optional for the final item.
JSON-LD is Google's preferred and most widely recommended format for BreadcrumbList Schema implementation. It's easier to implement, doesn't require changes to existing HTML structure, and is supported across all major search engines. RDFa and Microdata are also valid but less commonly used. JSON-LD adoption has reached 41% across the web, making it the industry standard for structured data implementation.
BreadcrumbList Schema does not directly impact search rankings as a ranking factor. However, it indirectly benefits SEO by improving internal linking structure, enhancing crawlability, and increasing click-through rates (CTR) when breadcrumbs appear in search results. Better CTR signals to search engines that your content is relevant and useful, which can positively influence ranking performance over time.
You can validate BreadcrumbList Schema using Google's Rich Results Test, Schema.org's Markup Validator, or SEO tools like Semrush and Ahrefs. Simply enter your page URL and the tool will check for proper implementation, missing required properties, and formatting errors. Google Search Console also provides a Rich Results report showing valid and invalid breadcrumb markup across your site.
Yes, a single page can have multiple BreadcrumbList implementations if there are multiple valid navigation paths to reach that page. This is common on ecommerce sites where products can be accessed through different category hierarchies. Each BreadcrumbList should represent a distinct path, and all implementations should be included in the page's structured data markup.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Schema markup is standardized code that helps search engines understand content. Learn how structured data improves SEO, enables rich results, and supports AI s...

Learn what Article schema is and how AI systems use it. Discover why Article schema matters for AI search visibility, implementation best practices, and how to ...

Product Schema is structured data markup that helps search engines and AI systems understand product details. Learn how to implement it for better visibility in...