
Buyer Journey in AI Search: How AI Reshapes Discovery and Decision-Making
Explore how AI search transforms the buyer journey across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI. Learn the stages, platform differences, and strategies for visibil...

A buyer persona is a semi-fictional, detailed representation of an ideal customer based on market research, real customer data, and insights. It includes demographics, goals, pain points, motivations, and decision-making behaviors that help businesses tailor marketing strategies and product development to meet customer needs effectively.
A buyer persona is a semi-fictional, detailed representation of an ideal customer based on market research, real customer data, and insights. It includes demographics, goals, pain points, motivations, and decision-making behaviors that help businesses tailor marketing strategies and product development to meet customer needs effectively.
A buyer persona is a semi-fictional, detailed representation of an ideal customer created through market research, real customer data, and strategic insights. Unlike generic target audiences, buyer personas breathe life into customer profiles by assigning them names, ages, job titles, company backgrounds, motivations, pain points, and decision-making behaviors. These comprehensive profiles serve as tangible representations that help marketing, sales, and product teams understand who they’re trying to reach and how to communicate effectively with them. Buyer personas transform abstract customer segments into relatable characters that guide every aspect of business strategy, from content creation to product development and customer service approaches.
The concept of buyer personas emerged from the need to move beyond demographic targeting toward a more empathetic, behavior-driven understanding of customers. Rather than assuming all customers within an age range or geographic location have identical needs, buyer personas recognize that individuals have unique goals, challenges, and preferences shaped by their professional roles, personal circumstances, and industry contexts. This nuanced approach has become foundational to modern marketing, with research indicating that 71% of companies that exceed revenue and revenue goals have documented personas, compared to only 37% of companies that meet goals and 26% that miss them.
The buyer persona methodology gained prominence in the early 2000s as marketing professionals recognized the limitations of traditional demographic segmentation. Marketing strategist Alan Cooper popularized the concept through his work on user personas in software design, which was subsequently adapted for marketing and sales applications. As digital marketing evolved and customer data became more accessible through analytics platforms, CRM systems, and social media insights, buyer personas became increasingly sophisticated and data-driven. The shift from assumption-based personas to research-backed profiles marked a significant evolution in how businesses understand and serve their customers.
Today’s buyer personas benefit from unprecedented access to customer data. Companies can analyze website behavior, email engagement patterns, social media interactions, customer support conversations, and purchase history to create remarkably accurate profiles. This data-driven approach has transformed buyer personas from creative exercises into strategic business tools. According to recent research, 56% of companies generated higher quality leads using buyer personas, while 36% of companies created shorter sales cycles through persona-based strategies. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning has further enhanced persona creation, allowing businesses to identify patterns and segments that might be invisible to human analysis alone.
A comprehensive buyer persona includes multiple layers of information that collectively paint a complete picture of the ideal customer. Demographic information forms the foundation, including age, gender, education level, income, family status, and geographic location. However, truly effective buyer personas extend far beyond demographics to encompass psychographic data such as values, interests, lifestyle preferences, and personality traits. Professional information becomes particularly important in B2B contexts, including job title, industry, company size, years of experience, and reporting structure.
The most valuable buyer personas include detailed descriptions of customer pain points—the specific challenges and frustrations that keep your ideal customer awake at night. These might include operational inefficiencies, budget constraints, time management challenges, or difficulty finding solutions that meet their needs. Equally important are goals and motivations, which explain what success looks like for your persona and what drives their decision-making. Buying behaviors and preferences describe how your persona prefers to research solutions, what information sources they trust, which platforms they use, and what factors influence their purchasing decisions. Finally, effective buyer personas include information about objections and concerns, helping teams anticipate and address hesitations before they derail sales conversations.
| Aspect | Buyer Persona | Target Audience | Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) | User Persona |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Semi-fictional representation of ideal individual customer | Broad group of consumers interested in product | Profile of companies/organizations ideal for solution | Person who uses product daily |
| Focus | Individual motivations, pain points, behaviors | Demographic and psychographic characteristics | Company characteristics, revenue, industry | End-user experience and needs |
| Primary Use | Marketing messaging and content strategy | Campaign targeting and audience segmentation | Sales qualification and account selection | Product design and UX optimization |
| Detail Level | Highly detailed with personal context | General demographic information | Company-level metrics and criteria | Functional role and workflow details |
| B2B vs B2C | Used in both, more critical in B2B | More common in B2C marketing | Primarily B2B focused | Both, but especially product-focused |
| Decision-Making | Includes individual decision factors | Assumes similar preferences within group | Focuses on organizational buying criteria | Not primary focus; user, not buyer |
| Number Needed | 3-5 typical per business | 1-2 broad segments | 1-3 company profiles | Multiple per product feature |
Creating effective buyer personas requires a systematic, research-driven approach that combines quantitative and qualitative data collection methods. The first critical step involves comprehensive data gathering from multiple sources. This includes analyzing your existing customer database to identify patterns among your most valuable clients, conducting customer surveys to understand motivations and preferences, performing in-depth interviews with current customers and prospects, reviewing website analytics to see how potential customers interact with your content, examining email engagement metrics to understand what messaging resonates, and analyzing social media conversations to identify industry discussions and pain points. Sales teams provide invaluable insights about common objections, decision-making timelines, and the actual buying process, while customer support teams can articulate the most frequent problems customers face.
Once data is collected, the next phase involves identifying patterns and segments. Rather than creating personas based on assumptions, successful teams look for genuine clusters of similar customers. This might reveal that your customer base includes both budget-conscious small business owners and enterprise decision-makers with different priorities, or that some customers are early adopters while others are risk-averse. These natural groupings become the foundation for distinct buyer personas. The third phase, building detailed profiles, transforms raw data into narrative personas. This is where the semi-fictional element comes in—you assign each persona a name, create a brief backstory, and write descriptions in first person to make them feel real. A persona might be “Marketing Manager Maria,” a 35-year-old professional managing a team of three, responsible for lead generation, struggling with limited budget and multiple competing priorities, and seeking solutions that integrate with existing tools.
The final critical step is validation and refinement. Rather than treating personas as static documents, successful organizations test them against real customer behavior. If your persona predicts that customers prefer detailed technical documentation but analytics show they actually engage more with video content, that’s valuable feedback requiring persona adjustment. This iterative approach ensures buyer personas remain accurate and useful over time. Many organizations establish quarterly or semi-annual review cycles to update personas based on new customer data, market changes, and business evolution.
The business impact of well-developed buyer personas extends across every customer-facing function. In marketing, personas enable creation of highly targeted content that addresses specific pain points and motivations. Rather than creating generic messaging hoping to appeal to everyone, teams can develop distinct campaigns for each persona. This targeted approach delivers measurable results: research shows that using buyer personas in email campaigns improved open rates by 2x and clickthrough rates by 5x, while personalized emails drive 18 times more revenue than broadcast emails. Behaviorally targeted ads are twice as effective as non-targeted ads, and websites optimized for specific personas are 2-5 times more effective and easier to use by targeted users.
In sales, personas accelerate the qualification process and improve conversion rates. Sales teams equipped with detailed personas can quickly assess whether a prospect fits the ideal profile, focus conversations on relevant pain points, and tailor their pitch to address specific motivations. This results in shorter sales cycles and higher close rates. According to research, 36% of companies using buyer personas created shorter sales cycles, and 93% of companies exceeding lead and revenue goals segment their database by buyer persona. In product development, personas ensure that features and improvements address actual customer needs rather than internal assumptions. Product teams can prioritize features that solve the most critical pain points for their most valuable customer segments.
The financial impact is substantial. Customer-centric companies are 60% more profitable than companies that don’t prioritize customer understanding. One case study found that implementing buyer personas resulted in a 900% increase in length of visit, 171% increase in marketing-generated revenue, 111% increase in email open rate, and 100% increase in the number of pages visited. Another example showed 124% increased sales leads, 55% increase in organic search traffic, 97% increase in online leads, and 210% increase in North American site traffic after implementing a targeted content marketing strategy based on personas.
In the context of modern AI-driven search and content discovery, buyer personas take on additional strategic importance. As platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude become primary information sources for many professionals, understanding your buyer personas’ information-seeking behaviors becomes critical. Different personas may prefer different AI platforms based on their use cases—a researcher might favor Perplexity for its citation capabilities, while a busy executive might prefer ChatGPT for quick answers. Your buyer personas should include information about which AI platforms they use, what types of queries they submit, and what information they’re seeking.
This is where AI monitoring platforms like AmICited become valuable. By understanding your buyer personas deeply, you can optimize your content strategy to appear in AI-generated responses that your ideal customers actually see. If your primary persona is a B2B software buyer researching solutions, you’ll want your content to appear when they ask AI systems about industry-specific challenges, comparison questions, and implementation best practices. If your persona is a technical decision-maker, you might focus on appearing in responses to technical architecture and integration questions. The intersection of buyer personas and AI monitoring represents a new frontier in marketing strategy, where understanding your customer profile directly informs your visibility in AI-generated content.
Successfully implementing buyer personas requires more than creating documents—it demands organizational alignment and consistent application. Here are essential practices for maximizing persona effectiveness:
The future of buyer personas will be shaped by advancing technology, particularly artificial intelligence and machine learning. Rather than replacing human insight, AI will enhance persona creation by processing vast amounts of customer data to identify patterns and segments that might otherwise remain hidden. AI-powered persona generation tools are already emerging, capable of analyzing customer interactions across multiple touchpoints and automatically updating personas as new data arrives. This represents a shift from static, annually-updated personas to dynamic, continuously-evolving customer profiles that reflect real-time market conditions.
The integration of behavioral data will become increasingly sophisticated. Rather than relying primarily on demographic and psychographic information, future personas will incorporate detailed behavioral patterns—how customers interact with content, which resources they consult, how long they spend evaluating solutions, and what triggers their purchasing decisions. Predictive analytics will enable businesses to anticipate persona needs before customers themselves recognize them, allowing for proactive rather than reactive marketing. The rise of first-party data collection, driven by privacy regulations limiting third-party tracking, will make direct customer relationships and feedback even more valuable for persona development.
As AI search and content generation become increasingly central to how professionals find information, buyer personas will need to explicitly address AI-related behaviors and preferences. Forward-thinking organizations are already incorporating questions into their persona research about AI platform usage, preferred information formats for AI consumption, and how personas evaluate AI-generated information. The companies that successfully integrate buyer persona strategy with AI monitoring and optimization will gain significant competitive advantages in visibility and customer acquisition. The future belongs to organizations that understand not just who their customers are, but how those customers interact with AI systems and what information they seek through those channels.
A target audience is a broad group of consumers interested in your product, while a buyer persona is a detailed, semi-fictional representation of a specific ideal customer within that audience. Target audiences focus on general demographics and psychographics, whereas buyer personas dive deeper into individual motivations, pain points, job titles, company size, and decision-making processes. Buyer personas are particularly valuable in B2B marketing where multiple stakeholders influence purchasing decisions.
Most businesses should start with one primary buyer persona representing their most common customer at the top of the sales funnel, then expand to 3-5 personas covering different customer segments. According to research, 93% of companies that exceed lead and revenue goals segment their database by buyer persona. The number depends on your product complexity, market diversity, and sales cycle length. B2B companies typically need more personas than B2C companies due to multiple decision-makers.
Effective buyer personas require data from multiple sources including customer surveys, website analytics, email engagement metrics, social media insights, customer interviews, sales team feedback, support ticket analysis, and industry reports. Combining qualitative data (interviews, feedback) with quantitative data (analytics, metrics) creates the most accurate profiles. Avoid relying solely on assumptions; real customer data ensures your personas reflect actual behaviors and needs rather than guesses.
Buyer personas directly improve ROI by enabling targeted messaging that resonates with specific customer segments. Research shows that using buyer personas in email campaigns improved open rates by 2x and clickthrough rates by 5x, while personalized emails drive 18 times more revenue than broadcast emails. Personas help allocate marketing budgets more efficiently, reduce customer acquisition costs, and increase conversion rates by ensuring content and campaigns address actual customer pain points and motivations.
A buyer persona represents the person who makes the purchase decision, while a user persona represents the person who actually uses the product or service. In B2B contexts, these are often different people. For example, a CFO might be the buyer persona approving software purchase, while the marketing team members are user personas who interact with it daily. Understanding both helps businesses create messaging for decision-makers and product experiences for end-users.
Buyer personas should be reviewed and updated at least quarterly or whenever significant market changes occur. Customer preferences, industry trends, and business goals evolve, so personas must reflect current reality. Monitor actual customer interactions, sales feedback, and performance metrics to identify when personas need refinement. Some companies update personas annually as part of strategic planning, while others maintain continuous updates based on real-time data from CRM systems and analytics platforms.
Yes, AI significantly accelerates persona creation by analyzing large datasets, identifying patterns, and generating insights at scale. AI tools can process customer data from CRM systems, support tickets, website analytics, and social media to highlight common characteristics and behaviors. However, AI should enhance rather than replace human research. Combining AI-generated insights with qualitative data from customer interviews and sales team feedback creates the most accurate and actionable personas.
Buyer personas are essential for AI monitoring platforms like AmICited because they help identify which customer segments and decision-makers are most likely to encounter your brand in AI-generated responses. Understanding your personas' information-seeking behaviors, preferred platforms (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI), and pain points allows you to optimize your content strategy for AI citation. This ensures your brand appears in relevant AI responses to your ideal customers.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Explore how AI search transforms the buyer journey across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI. Learn the stages, platform differences, and strategies for visibil...
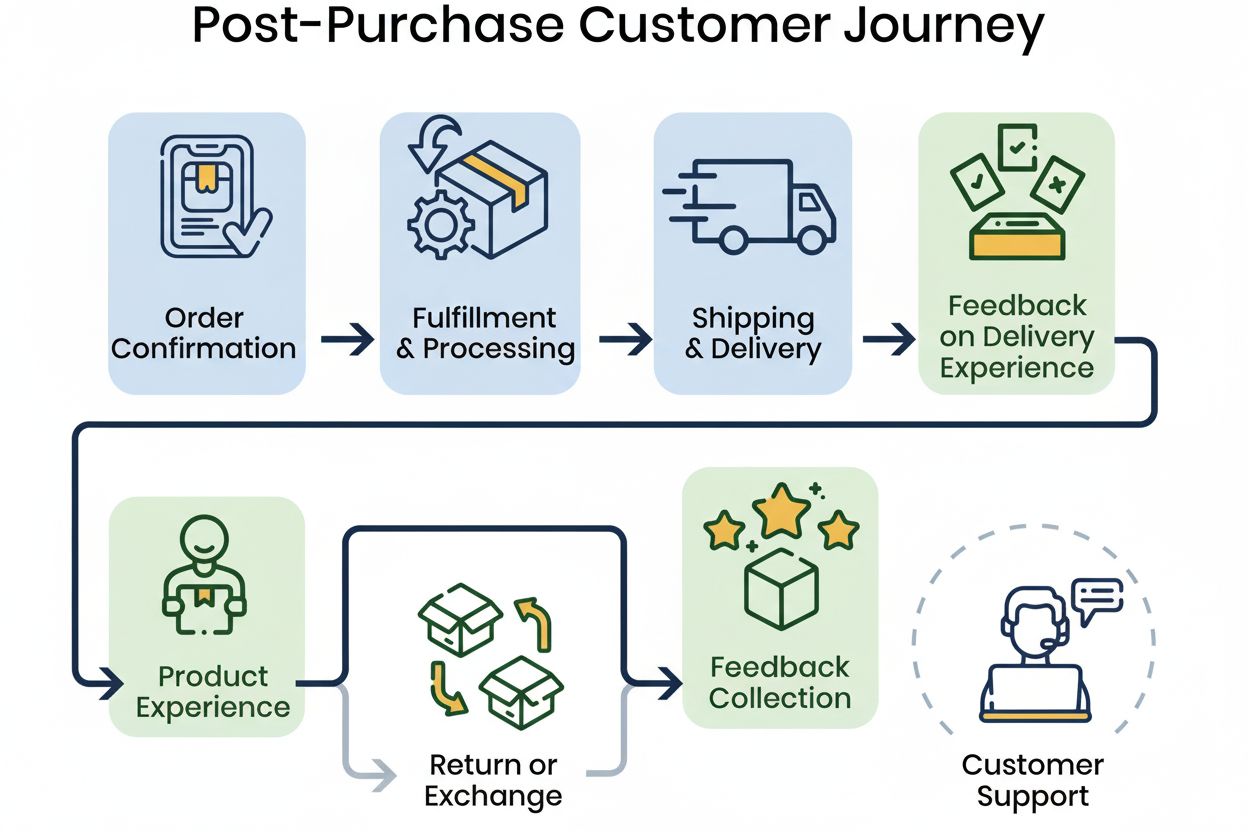
Learn what the post-purchase phase is, why it matters for customer retention and loyalty, and how to optimize every touchpoint after conversion to drive repeat ...
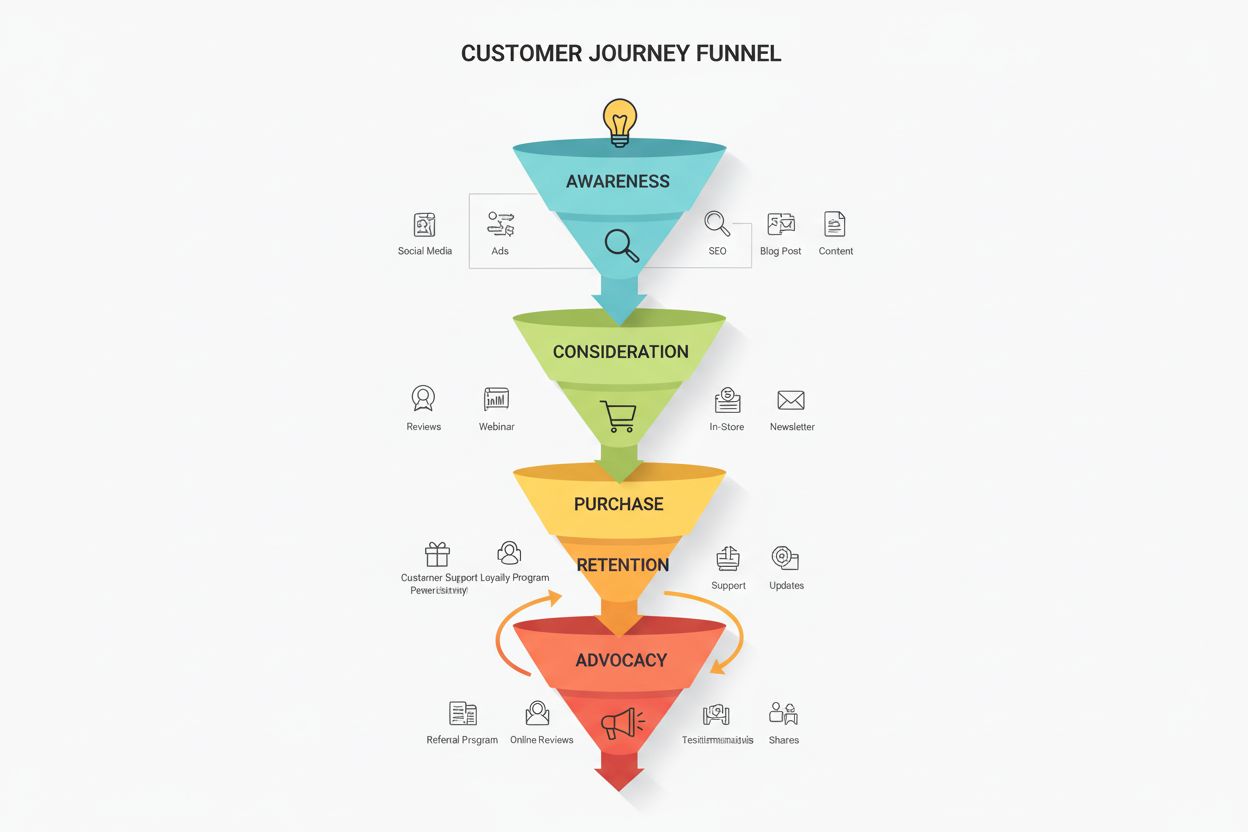
Learn what a customer journey is, explore its five key stages from awareness to advocacy, and discover how to map and optimize touchpoints for better customer e...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.