AI Crawlers Explained: GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and More
Understand how AI crawlers like GPTBot and ClaudeBot work, their differences from traditional search crawlers, and how to optimize your site for AI search visib...

Bytespider is ByteDance’s web crawler that systematically collects content from websites to train artificial intelligence models and power TikTok’s recommendation algorithms. Operating primarily from Singapore, it aggressively crawls the internet to gather training data for large language models including Doubao, ByteDance’s ChatGPT competitor. The crawler is known for ignoring robots.txt directives and generating millions of requests daily, making it one of the most prevalent AI data scrapers on the web.
Bytespider is ByteDance's web crawler that systematically collects content from websites to train artificial intelligence models and power TikTok's recommendation algorithms. Operating primarily from Singapore, it aggressively crawls the internet to gather training data for large language models including Doubao, ByteDance's ChatGPT competitor. The crawler is known for ignoring robots.txt directives and generating millions of requests daily, making it one of the most prevalent AI data scrapers on the web.
Bytespider is ByteDance’s proprietary web crawler designed to systematically browse and index content across the internet for artificial intelligence model training. Operating primarily from Singapore-based infrastructure, this crawler collects vast amounts of publicly available web content to fuel the development of large language models and power ByteDance’s various AI-driven services. The crawler functions as a critical component of ByteDance’s data acquisition pipeline, enabling the company to gather training datasets at massive scale. Bytespider’s primary purpose extends beyond simple content indexing—it serves as the backbone for training AI systems including Doubao, ByteDance’s ChatGPT competitor, while simultaneously contributing to TikTok’s sophisticated recommendation algorithms. The crawler operates continuously, making millions of requests daily to websites worldwide, systematically extracting text, metadata, and structural information. Unlike traditional search engine crawlers that prioritize user experience and website guidelines, Bytespider is optimized for data collection efficiency, making it one of the most prevalent AI data scrapers on the modern internet.
| Crawler Name | Operator | Primary Purpose | Respects robots.txt | Typical Traffic Volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bytespider | ByteDance | AI model training, TikTok recommendations | No | Millions of requests daily |
| Googlebot | Search indexing, ranking | Yes | Varies by site importance | |
| ClaudeBot | Anthropic | Claude AI training data | Partial | High volume, inconsistent |
| PerplexityBot | Perplexity AI | AI search training | Yes | Moderate, growing |

Bytespider serves as the data collection engine for ByteDance’s entire ecosystem of AI-powered services, with particular emphasis on enhancing TikTok’s recommendation algorithms and training advanced language models. The crawler systematically collects web content that is then processed and used to train Doubao, ByteDance’s large language model that competes directly with OpenAI’s ChatGPT, boasting over 60 million monthly active users. The relationship between Bytespider’s data collection and TikTok’s recommendation system is symbiotic—the crawler gathers diverse content patterns and user engagement signals from across the web, which inform the machine learning models that determine what content appears in users’ feeds. This data collection process operates at an unprecedented scale, with Bytespider accounting for nearly 90% of all AI crawler traffic on many websites, demonstrating ByteDance’s aggressive investment in AI infrastructure. The collected data encompasses text, images, metadata, and structural information from millions of websites, creating comprehensive training datasets that improve model accuracy and relevance. ByteDance’s strategic approach treats Bytespider as a critical competitive advantage, enabling rapid iteration and improvement of AI systems across its product portfolio.
Key AI systems powered by Bytespider data:
Bytespider has earned a reputation as an aggressive web crawler due to its deliberate disregard for standard web protocols and its massive request volume. Unlike most reputable AI crawlers that respect robots.txt directives—a standard file webmasters use to communicate crawler access preferences—Bytespider actively ignores these guidelines, treating them as optional rather than binding. The crawler generates millions of requests daily to individual domains, with typical crawling rates of approximately 5 requests per second per targeted website, creating significant server strain. Bytespider employs sophisticated evasion tactics to circumvent detection and rate-limiting mechanisms, including rotating IP addresses and masking its identity to appear as legitimate user traffic rather than automated bot activity. When websites attempt to block Bytespider by its user agent string, the crawler’s origin IP geolocation shifts from China to Singapore, suggesting coordinated infrastructure management designed to maintain access despite blocking attempts. This aggressive behavior reflects ByteDance’s prioritization of data collection over website performance considerations, fundamentally distinguishing Bytespider from search engine crawlers that balance their own needs with website operator interests.
The aggressive crawling behavior of Bytespider creates substantial challenges for website operators, manifesting in multiple dimensions of infrastructure strain and security concerns. Websites hosting Bytespider traffic experience significant bandwidth consumption, with millions of daily requests consuming server resources that could otherwise serve legitimate user traffic and improve website performance for actual visitors. The server strain caused by Bytespider’s activity translates directly into increased power consumption and carbon footprint, as data centers must allocate additional computational resources to process crawler requests, creating environmental costs that benefit only ByteDance’s AI training objectives. Security implications extend beyond simple resource exhaustion—the crawler’s evasion tactics and refusal to respect standard protocols raise concerns about potential exploitation of security vulnerabilities or unauthorized access attempts to sensitive areas of websites. Many organizations have made the strategic decision to block Bytespider entirely, recognizing that the crawler provides no tangible value to their business while consuming resources and potentially exposing their infrastructure to risks. The fundamental trade-off facing website operators is whether to allow their content to contribute to AI model training (potentially improving AI systems that may compete with their own services) or to protect their infrastructure and content from unauthorized scraping.

Website operators have several technical options available to block or limit Bytespider’s access, though effectiveness varies depending on implementation sophistication and the crawler’s evasion capabilities. The simplest approach involves configuring your website’s robots.txt file with specific directives targeting Bytespider’s user agent, though this method provides only a courtesy request rather than a hard technical block, as Bytespider frequently ignores these guidelines. More robust blocking strategies employ firewall rules and IP-based filtering to prevent Bytespider’s requests from reaching your servers, though this requires ongoing maintenance as the crawler rotates through different IP addresses and geolocation origins. Rate limiting at the server or application level can restrict the number of requests any single user agent or IP address can make within a specified time period, effectively throttling Bytespider’s crawling rate even if complete blocking isn’t feasible. Behavioral analytics approaches use machine learning to identify and classify bot traffic patterns, distinguishing Bytespider from legitimate user traffic based on request characteristics, timing patterns, and interaction behaviors. Monitoring tools like Dark Visitors provide real-time visibility into which crawlers are accessing your website, allowing you to verify whether your blocking attempts are effective and adjust strategies accordingly.
# Example robots.txt configuration to block Bytespider
User-agent: Bytespider
Disallow: /
# Alternative: Block all AI data scrapers
User-agent: Bytespider
User-agent: ClaudeBot
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
# Selective blocking: Allow crawling of specific directories
User-agent: Bytespider
Disallow: /private/
Disallow: /admin/
Allow: /public/
The emergence of aggressive AI crawlers like Bytespider raises fundamental questions about content ownership, attribution, and the ethical foundations of AI model training in the digital age. Content creators face a dilemma: their original work may be incorporated into AI training datasets without explicit consent, compensation, or clear attribution, potentially enabling AI systems to generate outputs that compete with or diminish the value of the original content. The lack of transparency regarding how Bytespider-collected content is used, modified, or attributed in AI-generated responses creates uncertainty about whether creators will receive recognition or benefit from their intellectual property’s contribution to AI advancement. Conversely, some organizations recognize that AI-powered discovery represents an emerging channel for brand awareness and product visibility, as AI chatbots and search systems increasingly serve as primary information sources for users seeking recommendations and information. The balance between protecting content and enabling AI progress remains unresolved, with different stakeholders advocating for stronger creator protections, clearer attribution standards, or unrestricted data access to accelerate AI development. From an SEO perspective, blocking Bytespider might reduce your representation in AI-generated responses and AI-powered search results, potentially affecting discoverability as users increasingly turn to AI systems as alternatives to traditional search engines. The broader conversation about responsible AI data collection, ethical web scraping practices, and fair compensation for content creators will likely shape internet governance and AI regulation for years to come, making decisions about Bytespider blocking part of a larger strategic consideration about your brand’s relationship with emerging AI technologies.
Bytespider is ByteDance's web crawler designed to collect training data for artificial intelligence models, particularly large language models (LLMs) like Doubao. The crawler systematically browses websites to gather content that helps improve AI systems and powers TikTok's recommendation algorithms. It also contributes to ByteDance's broader AI infrastructure and content discovery systems.
Bytespider is considered aggressive because it ignores robots.txt directives that websites use to control crawler access, generates millions of requests per day to individual domains, and employs tactics to evade detection and rate limiting. Unlike most reputable crawlers that respect website guidelines, Bytespider prioritizes data collection over website performance, causing significant server strain and bandwidth consumption.
You can block Bytespider by adding specific rules to your robots.txt file using the user agent 'Bytespider'. However, since Bytespider often ignores robots.txt, you may need to implement additional measures such as firewall rules, IP blocking, rate limiting at the server level, or using bot management solutions. Tools like Dark Visitors can help you monitor and verify whether blocking attempts are effective.
Blocking Bytespider has minimal direct impact on traditional search engine optimization since it's not a search engine crawler. However, if your content is used to train AI models that power AI search engines and chatbots, blocking Bytespider might reduce your representation in AI-generated responses, potentially affecting discoverability through AI-powered search platforms in the future.
According to Dark Visitors data, approximately 16% of the world's top 1,000 websites actively block Bytespider in their robots.txt files. This relatively low blocking rate suggests that many websites either allow the crawler or are unaware of its presence. However, the actual blocking rate may be higher when including firewall-level and server-level restrictions not visible in robots.txt.
Bytespider generates enormous amounts of traffic, with studies showing it accounts for nearly 90% of all AI crawler traffic on some websites. Individual domains can receive millions of requests from Bytespider daily, with typical crawling rates of approximately 5 requests per second. This makes it one of the most significant sources of bot traffic on the internet.
Bytespider is operated by ByteDance, which is TikTok's parent company, but it's not exclusively TikTok's crawler. While it does collect data to improve TikTok's recommendation algorithms, Bytespider primarily serves ByteDance's broader AI infrastructure, including training data for Doubao (ByteDance's LLM) and other AI systems. It's a company-wide tool rather than a platform-specific crawler.
Bytespider typically focuses on publicly available content for training data collection. However, like other sophisticated crawlers, it may attempt to access password-protected areas, API endpoints, or content behind paywalls depending on ByteDance's objectives and technical capabilities. Most reputable crawlers respect authentication barriers, but the scope of Bytespider's access attempts may vary based on specific data collection goals.
Track mentions of your brand across AI-powered platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. AmICited helps you understand how AI systems are using your content and ensures proper attribution.

Understand how AI crawlers like GPTBot and ClaudeBot work, their differences from traditional search crawlers, and how to optimize your site for AI search visib...

Learn which AI crawlers to allow or block in your robots.txt. Comprehensive guide covering GPTBot, ClaudeBot, PerplexityBot, and 25+ AI crawlers with configurat...
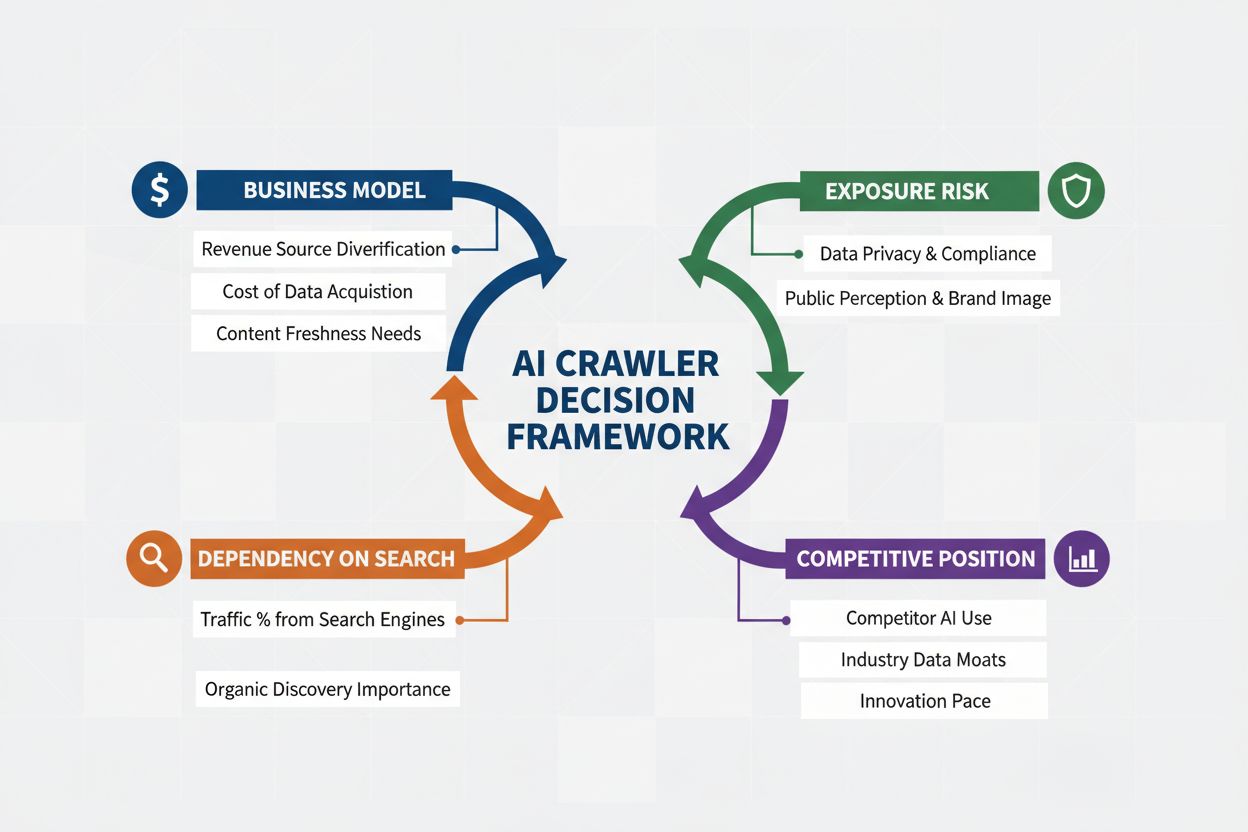
Learn how to make strategic decisions about blocking AI crawlers. Evaluate content type, traffic sources, revenue models, and competitive position with our comp...