
How Do AI Models Decide What to Cite in AI Answers
Learn how AI models like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini select sources to cite. Understand the citation mechanisms, ranking factors, and optimization strategie...
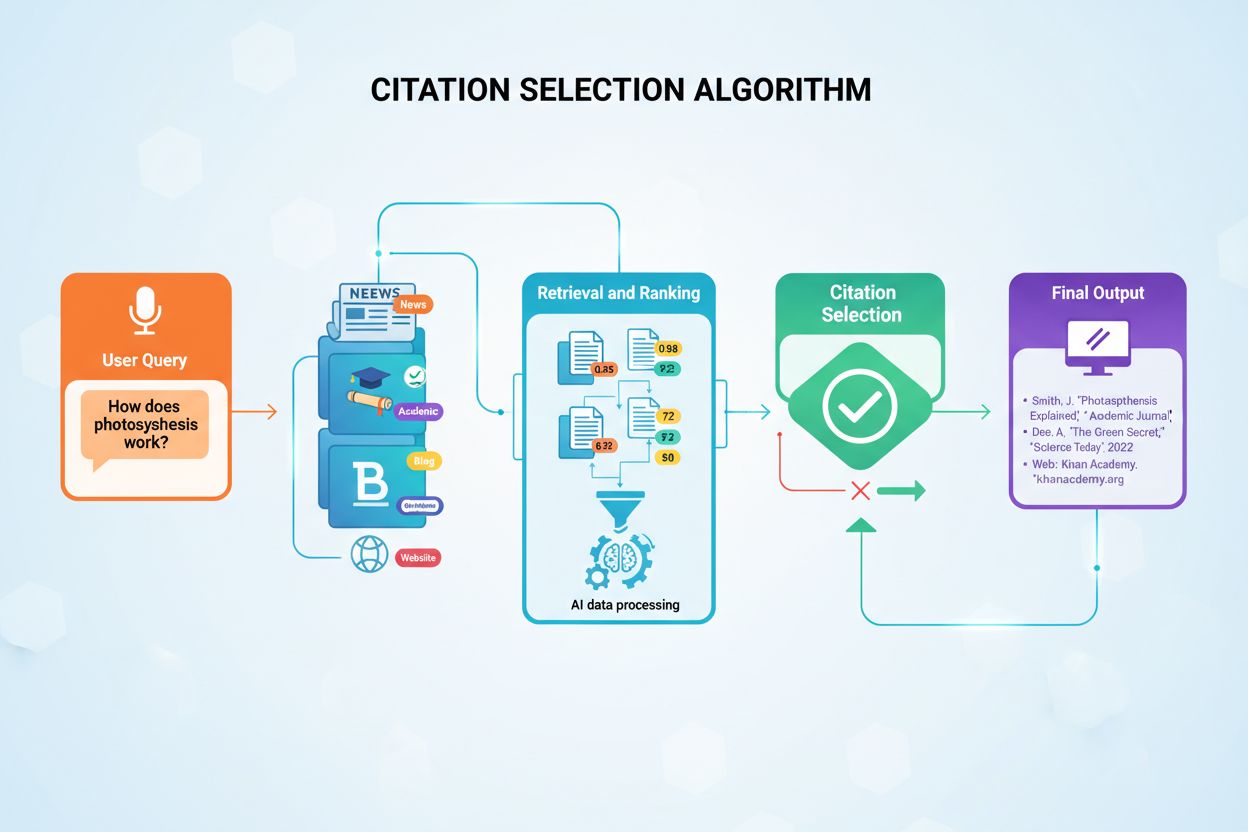
The computational mechanism that determines which sources an AI system references when generating responses. These algorithms operate within retrieval-augmented generation systems to identify, rank, and cite the most relevant and authoritative sources from vast information databases, directly impacting content visibility in AI-driven information landscapes.
The computational mechanism that determines which sources an AI system references when generating responses. These algorithms operate within retrieval-augmented generation systems to identify, rank, and cite the most relevant and authoritative sources from vast information databases, directly impacting content visibility in AI-driven information landscapes.
A citation selection algorithm is the computational mechanism that determines which sources an AI system references when generating responses to user queries. These algorithms operate within retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems to identify, rank, and ultimately cite the most relevant and authoritative sources from vast information databases. Understanding how these algorithms work is critical for modern content creators and marketers because citation visibility directly impacts brand authority, audience reach, and the discoverability of content in an AI-driven information landscape.
Citation selection operates through a multi-stage process within RAG architectures, beginning with a retrieval stage that identifies candidate sources, followed by a ranking stage that evaluates relevance and quality, and concluding with a generation stage where the AI produces responses with selected citations. The algorithmic choices made during these stages vary significantly across AI providers, as demonstrated by the following citation patterns:
| AI Provider | Citation Rate | Top Source | Concentration Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI | ~19% | Reuters | Very High (Gini: 0.83) |
| ~8% | India Times | Moderate (Gini: 0.69) | |
| Perplexity | ~8% | BBC | High (Gini: 0.77) |
This table reveals that OpenAI cites sources substantially more frequently than competitors, while all providers demonstrate concentration bias, where a small number of elite sources receive a disproportionate share of citations. The variation in top sources and concentration levels indicates that each provider’s algorithm weighs different factors when making citation decisions, creating distinct visibility opportunities and challenges for content creators across platforms.
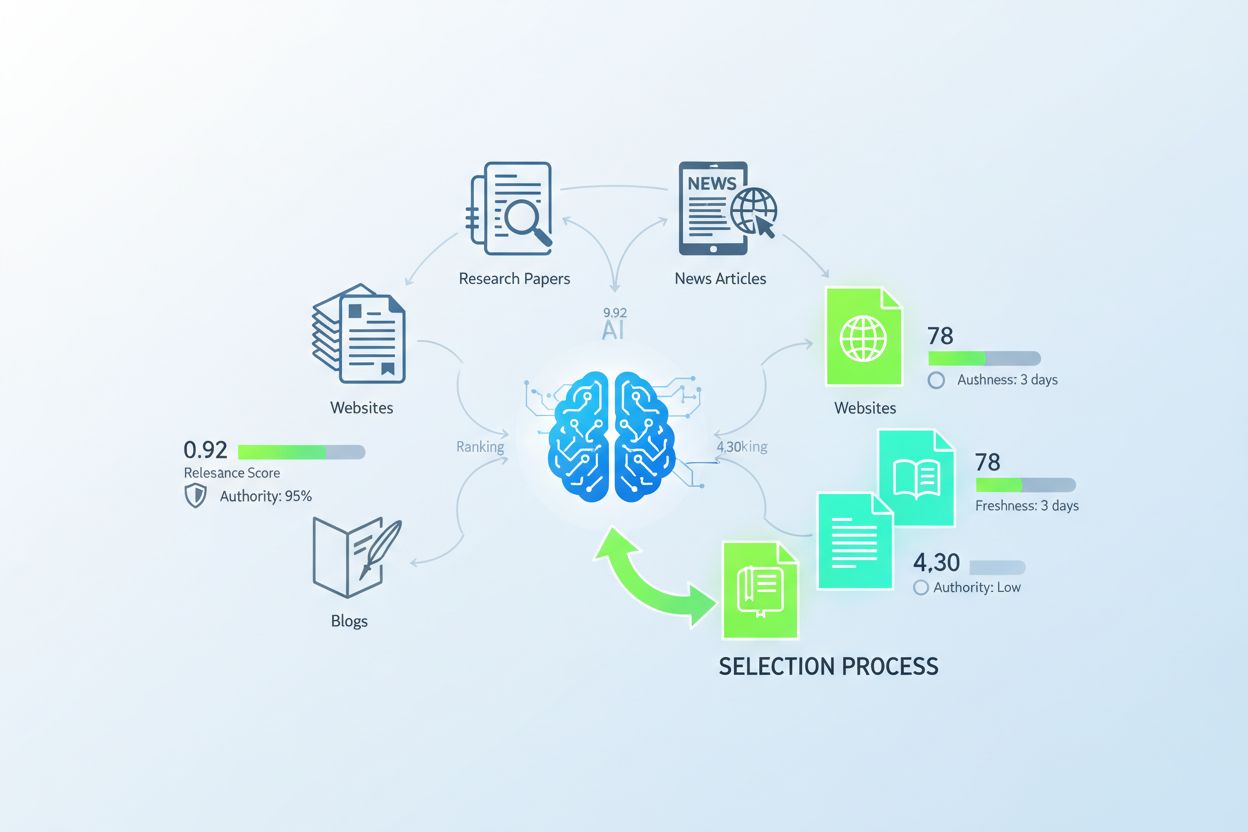
Citation selection is influenced by six primary factors that shape which sources receive algorithmic preference:
• Semantic Relevance — The algorithm prioritizes sources whose content most closely matches the semantic meaning and context of the user’s query, using advanced language models to assess conceptual alignment rather than simple keyword matching.
• Domain Authority — Established, reputable domains with strong backlink profiles and historical credibility receive preferential treatment, as algorithms recognize institutional trust signals built over time.
• Content Freshness — Recent publications and updated information are weighted more heavily, particularly for time-sensitive topics, ensuring that citations reflect current knowledge rather than outdated perspectives.
• Source Diversity — Algorithms attempt to balance citations across multiple sources to avoid over-reliance on single outlets, though this factor is often outweighed by concentration bias toward elite publications.
• Quality Metrics — High-quality sources demonstrate superior citation rates, with OpenAI citing quality sources at 96.2%, Google at 92.2%, and Perplexity at 89.7%, indicating that content quality is a decisive algorithmic factor.
• Structural Accessibility — Sources with clear metadata, proper formatting, and easily extractable information are more likely to be selected, as algorithms can more reliably parse and verify their content.
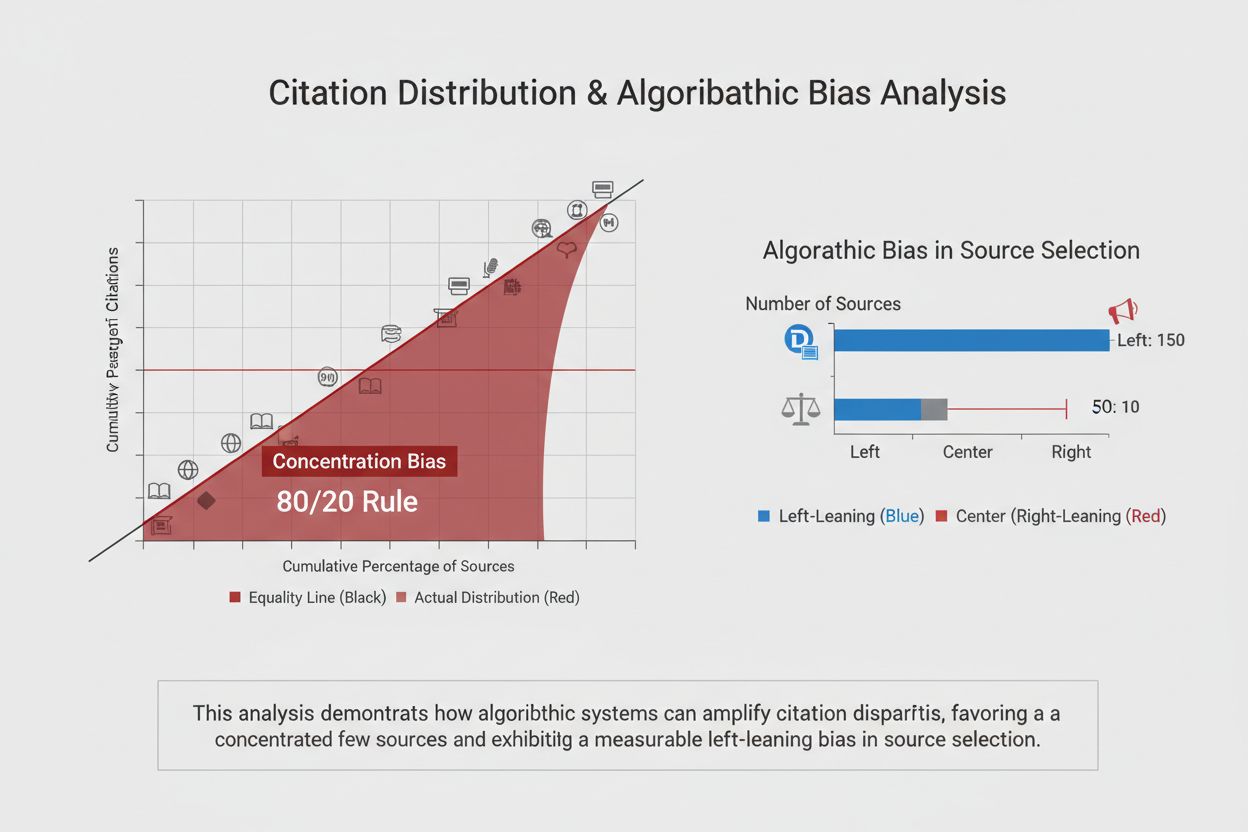
Citation selection algorithms exhibit measurable biases that significantly impact which sources gain visibility in AI-generated responses. Concentration bias is the most pronounced pattern, where elite news sources like Reuters, BBC, and India Times receive citations far exceeding their proportional representation in available information, creating a winner-take-most dynamic that marginalizes emerging publishers and niche experts. Beyond concentration, political bias appears consistently across all major AI providers, with a documented left-leaning tendency in source selection that reflects both training data composition and algorithmic design choices. The preference for high-quality sources is not inherently problematic—OpenAI’s 96.2% quality citation rate demonstrates that algorithms successfully identify authoritative content—but this preference becomes problematic when quality metrics correlate with established institutional power rather than actual accuracy or expertise. These biases collectively mean that content creators face an algorithmic gatekeeping system where visibility depends not only on content quality but also on institutional positioning and alignment with algorithmic preferences.
Citation selection and paraphrasing represent two distinct strategies that AI systems employ when incorporating source material into responses, each triggered by different algorithmic conditions. Citation selection occurs when the algorithm determines that direct attribution adds credibility, provides specific evidence, or enhances user trust—typically for factual claims, recent news, or expert opinions where source verification matters. Paraphrasing is chosen when the algorithm judges that rewording source material better serves the user’s needs, such as when simplifying complex information, integrating insights from multiple sources, or avoiding redundancy with previously cited material. The decision between these approaches depends on factors including query type, source quality, content specificity, and the algorithmic assessment of whether attribution or synthesis better serves the user’s information needs. Understanding this distinction is crucial for content creators because it means that high-quality content may be incorporated into AI responses through paraphrasing without direct citation, making citation monitoring essential for capturing your complete AI visibility footprint.
Citation selection has become a critical factor in content visibility and SEO strategy because AI-generated responses now mediate how millions of users discover and evaluate information. When your content receives citations in AI responses, it gains exposure to users actively seeking answers, establishes authority through algorithmic validation, and drives qualified traffic from users who trust AI recommendations. The concentration bias documented in citation patterns means that visibility is not evenly distributed—sources that achieve algorithmic preference gain exponential reach advantages, while sources outside the preferred tier struggle for visibility regardless of content quality. For content creators and marketers, this creates a new competitive dynamic where traditional SEO optimization must be complemented by strategies specifically designed to improve citation selection likelihood. Organizations that understand and optimize for citation selection gain a significant advantage in the AI-mediated information landscape, as citations serve as both a traffic driver and a powerful credibility signal that influences user perception and engagement.
Improving your citation selection likelihood requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses the algorithmic factors influencing source selection. First, prioritize semantic clarity and relevance by ensuring your content directly addresses specific questions and topics with precise language that AI systems can easily match to user queries. Second, build domain authority through consistent publication, quality backlinks, and established expertise signals that algorithms recognize as credibility markers. Third, maintain content freshness by regularly updating articles, publishing timely analysis, and ensuring your information reflects current developments in your field. Fourth, optimize content structure with clear metadata, proper formatting, and easily extractable information that algorithms can reliably parse and cite. To effectively track and optimize your citation performance across AI platforms, AmICited.com provides comprehensive monitoring that reveals exactly which sources are citing your content, how frequently citations occur, and which AI providers are driving visibility to your work. By combining these optimization strategies with AmICited.com’s monitoring capabilities, content creators can measure their citation performance, identify improvement opportunities, and systematically increase their visibility in AI-generated responses—transforming citation selection from an opaque algorithmic process into a manageable component of your content strategy.
Citation selection occurs when AI systems directly attribute information to specific sources, adding credibility and enabling user verification. Paraphrasing happens when AI rewrites source material without direct attribution, typically to simplify complex information or integrate insights from multiple sources. Both approaches serve different purposes depending on the query type and content specificity.
Different AI providers use distinct algorithms, training data, and retrieval mechanisms that influence source selection. OpenAI, Google, and Perplexity each have different citation rates and preferences for specific sources, creating unique visibility opportunities and challenges for content creators across platforms.
Yes, you can improve citation likelihood by optimizing content quality, structure, freshness, and semantic clarity. Building domain authority through backlinks and consistent publication, maintaining updated information, and ensuring clear metadata all increase the probability that AI systems will select your content for citation.
Citation bias stems from multiple sources including training data composition, algorithmic design choices, and the availability of structured information. Concentration bias occurs because algorithms prefer established, authoritative sources, while political bias reflects both the sources available in training data and how algorithms weight different credibility signals.
Citations in AI-generated responses drive qualified traffic from users actively seeking answers, establish algorithmic credibility validation, and influence user perception of your authority. The concentration bias in citation patterns means that achieving algorithmic preference creates exponential reach advantages compared to sources outside the preferred tier.
AmICited.com provides comprehensive monitoring that reveals exactly which sources are citing your content, how frequently citations occur, and which AI providers are driving visibility. This monitoring capability transforms citation selection from an opaque process into a measurable component of your content strategy.
Citation selection and traditional SEO are complementary but distinct. While traditional SEO focuses on search engine rankings, citation selection determines visibility in AI-generated responses. Content that ranks well in traditional search often receives more citations, but optimization strategies differ between the two approaches.
AI systems assess authority through multiple signals including domain history, backlink profiles, institutional credibility, publication frequency, and quality metrics. Established news outlets and recognized institutions receive preferential treatment because algorithms recognize these as credibility markers built over time.
Track exactly which sources are citing your content across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI platforms. Understand your citation patterns and optimize your visibility in AI-generated responses.

Learn how AI models like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini select sources to cite. Understand the citation mechanisms, ranking factors, and optimization strategie...

Learn what citation optimization for AI is and how to optimize your content to be cited by ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google Gemini, and other AI search engines.

Learn what makes content citation-worthy for AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overview. Discover the key characteristics, optimization strateg...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.