
How Thorough Should Content Be for AI Citations?
Learn the optimal content depth, structure, and detail requirements for getting cited by ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI. Discover what makes content citatio...

Content specifically designed to be referenced and linked by AI systems in their responses. Citation-worthy content combines authority, structure, freshness, and factual density to make it the preferred choice for AI systems when generating answers. It represents a fundamental shift from traditional SEO toward visibility in AI-powered search results.
Content specifically designed to be referenced and linked by AI systems in their responses. Citation-worthy content combines authority, structure, freshness, and factual density to make it the preferred choice for AI systems when generating answers. It represents a fundamental shift from traditional SEO toward visibility in AI-powered search results.
Citation-worthy content is material that AI systems, particularly large language models (LLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems, actively select and reference when generating responses to user queries. In the AI era, this concept has become fundamental to digital visibility and authority. Unlike traditional SEO, which focuses on search engine rankings, citation-worthiness determines whether your content appears in AI-generated answers, summaries, and recommendations. Citation signals include how frequently AI systems retrieve your content, the context in which it appears, and whether it’s presented as a primary source or supporting evidence. The distinction matters because AI citations drive traffic, establish expertise, and influence how information is synthesized across the internet. As AI systems become primary information discovery tools for millions of users, understanding what makes content citation-worthy has shifted from optional to essential for publishers, researchers, and organizations seeking visibility in AI-powered search results.
AI systems employ sophisticated retrieval mechanisms to identify and prioritize sources for citations. Most modern AI platforms use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), a process that combines vector embeddings, semantic search, and ranking algorithms to find relevant content before generating responses. When a user asks a question, the system converts the query into mathematical representations, searches across indexed content, and retrieves the most semantically relevant documents. The ranking considers multiple factors: content freshness, domain authority, semantic alignment with the query, and historical citation patterns. Different platforms implement these mechanisms with varying emphasis on different signals.
| Platform | Citation Method | Top Sources | Key Signals |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT | Vector search + ranking | News sites, academic databases, Wikipedia | Recency, authority, semantic relevance |
| Perplexity | Real-time web search + RAG | News, blogs, research papers | Freshness (65% target past year), domain trust |
| Google AI Overview | Knowledge Graph + web index | Wikipedia (26.3%), Reddit (40.1%), news | Entity recognition, structured data, consensus |
| Claude | Contextual retrieval + filtering | Academic sources, documentation, news | Accuracy signals, source diversity, expertise |
The retrieval pipeline typically involves three stages: candidate generation (finding potentially relevant documents), ranking (scoring candidates by relevance and authority), and filtering (removing low-quality or contradictory sources). Perplexity’s emphasis on freshness explains why 65% of AI bot hits target content published within the past year. Google’s AI Overview shows strong preference for Wikipedia (26.3% of citations) and Reddit (40.1%), reflecting how these platforms’ structured data and community validation signal reliability. Understanding these mechanisms reveals that citation-worthiness isn’t about gaming algorithms—it’s about creating content that genuinely serves the retrieval system’s goal of providing accurate, relevant answers.
Citation-worthy content possesses five essential attributes that make AI systems prioritize it for retrieval and reference:
• Authority: Content created by recognized experts, established organizations, or verified sources with demonstrated credibility in their domain. AI systems evaluate authority through domain history, author credentials, institutional affiliation, and citation patterns from other authoritative sources.
• Structure: Well-organized content with clear hierarchies, semantic HTML markup, descriptive headings, and logical flow. Structured content is easier for AI systems to parse, understand, and extract relevant information from specific sections.
• Freshness: Recent publication dates and regular updates signal that information remains current and accurate. AI systems weight recent content more heavily, particularly for topics where information changes frequently (news, technology, research).
• Factual Density: High concentration of verifiable facts, statistics, data points, and specific examples rather than filler or promotional language. Content with original research, citations, and quantifiable claims demonstrates substantive value.
• Semantic Relevance: Deep topical alignment with user queries, including related concepts, synonyms, and contextual information. Content that comprehensively addresses a topic’s various dimensions ranks higher in semantic search than narrowly focused material.
These characteristics work synergistically. A piece of content with strong authority but poor structure may be retrieved but not effectively cited. Conversely, beautifully structured content from an unknown source lacks the trust signals AI systems require. The most citation-worthy content excels across all five dimensions, creating a compound effect that makes it the obvious choice for AI systems seeking reliable, comprehensive answers.
AI systems evaluate trustworthiness through multiple interconnected signals that collectively determine whether content merits citation. Domain authority remains a primary factor, measured through the age of the domain, historical consistency, and the quality of inbound links. Older, established domains with decades of publishing history receive higher trust scores than newly created sites, regardless of content quality. Backlink profile serves as a trust multiplier—content linked from other authoritative sources signals that the broader information ecosystem recognizes its value. However, AI systems distinguish between natural editorial links and manipulative link schemes, using sophisticated analysis to identify authentic endorsements.
Expert attribution significantly boosts citation-worthiness. Content explicitly authored by named experts with verifiable credentials, professional affiliations, or publication history receives higher trust scores. AI systems cross-reference author names against academic databases, professional directories, and publication records to validate expertise claims. Knowledge graphs provide another critical trust signal—when content aligns with structured information in Google’s Knowledge Graph or similar systems, it gains credibility through association with verified facts. E-E-A-T signals (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) have become increasingly important as AI systems adopt evaluation frameworks similar to Google’s search quality guidelines. Content demonstrating clear expertise, transparent sourcing, and author accountability consistently outperforms anonymous or poorly attributed material. Organizations can strengthen these signals by publishing author bios with credentials, maintaining consistent publishing standards, securing links from recognized institutions, and ensuring content aligns with established knowledge bases.
The way content is structured directly impacts whether AI systems can effectively extract, understand, and cite it. Semantic HTML provides explicit meaning to content elements, helping AI systems understand the relationship between different parts of your text. Proper heading hierarchy (H1 for main topic, H2 for major sections, H3 for subsections) creates a logical outline that AI systems use to navigate and extract relevant passages. Paragraph optimization involves keeping paragraphs between 40-60 words on average—long enough to develop a complete thought but short enough for AI systems to identify self-contained, quotable chunks. This length allows AI systems to extract meaningful passages without including excessive context.
Self-contained chunks are critical for citation-worthiness. Each section should be understandable independently, allowing AI systems to cite a specific paragraph without requiring readers to understand surrounding content. This means avoiding excessive cross-references, defining terms locally rather than assuming prior knowledge, and ensuring each section delivers complete information on its topic. Subheadings should be descriptive and specific rather than generic, helping AI systems understand what each section covers. Lists and tables break up dense text and create structured data that AI systems can easily parse and reference.
<article>
<h1>Citation-Worthy Content in the AI Era</h1>
<section>
<h2>Understanding Citation Mechanisms</h2>
<p>Citation-worthy content is material that AI systems actively select and reference when generating responses. This concept has become fundamental to digital visibility in the AI era.</p>
<h3>How RAG Systems Work</h3>
<p>Retrieval-Augmented Generation combines vector embeddings with ranking algorithms to identify relevant sources. The system converts queries into mathematical representations and retrieves semantically aligned documents.</p>
</section>
<section>
<h2>Key Characteristics</h2>
<ul>
<li><strong>Authority:</strong> Content from recognized experts and established organizations</li>
<li><strong>Structure:</strong> Clear hierarchies with semantic HTML markup</li>
<li><strong>Freshness:</strong> Recent publication dates and regular updates</li>
</ul>
</section>
</article>
Implementing semantic HTML, maintaining proper heading hierarchy, optimizing paragraph length, and creating self-contained sections transforms content into a format that AI systems can efficiently retrieve, understand, and cite. This structural optimization doesn’t require sacrificing readability for human audiences—in fact, the same structure that helps AI systems also improves user experience.
Original research and proprietary data represent the highest-value content for AI citation. When you conduct original research, surveys, or analysis, you create information that exists nowhere else on the internet—making your content the only possible source for AI systems to cite. This exclusivity drives citation frequency dramatically. Content incorporating original statistics shows a 22% improvement in AI visibility, while content featuring direct quotations from experts or studies shows a 37% improvement. These improvements reflect how AI systems prioritize content that provides novel information or unique perspectives over derivative summaries.
Statistics and data points function as citation magnets. When your content includes specific, sourced statistics—particularly original research—AI systems preferentially cite it because the data itself becomes the answer to user queries. A user asking “What percentage of AI bot hits target recent content?” receives an answer citing the statistic directly, and if your research provided that finding, your content gets cited. Quotations from experts similarly drive citations because they provide authoritative voices and specific language that AI systems can reference. Rather than paraphrasing expert opinions, directly quoting experts (with proper attribution) makes your content more citable.
The mechanism behind this citation boost relates to how AI systems evaluate content value. Original research and data-driven content demonstrate factual density and authority simultaneously. They’re harder to produce, which signals quality. They’re more specific and quotable than general commentary. They often come from organizations with clear expertise and credibility. Building a content strategy around original research—whether through surveys, data analysis, experiments, or expert interviews—creates a sustainable competitive advantage in AI citation. Organizations that consistently publish original research become recognized sources that AI systems automatically prioritize when relevant to user queries.
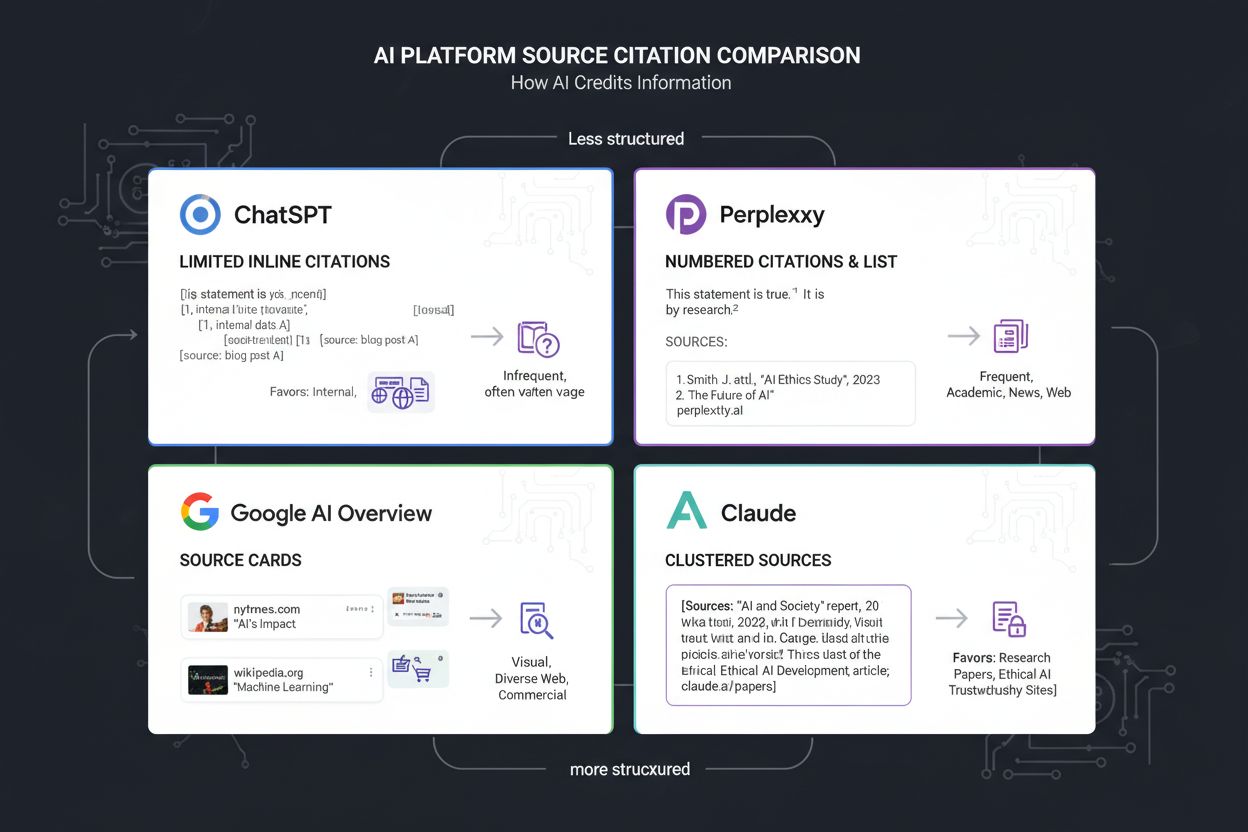
Different AI platforms exhibit distinct citation patterns reflecting their underlying architectures and design philosophies. ChatGPT prioritizes semantic relevance and authority, drawing heavily from academic sources, established news outlets, and Wikipedia. Its training data cutoff means it cannot cite very recent content, but it shows strong preference for comprehensive, well-structured articles from recognized publishers. ChatGPT’s citations tend toward authoritative sources that have been widely linked and referenced across the web.
Perplexity emphasizes freshness and real-time relevance, actively searching the current web for recent content. The platform’s citation patterns show that 65% of AI bot hits target content from the past year, reflecting its design as a real-time research tool. Perplexity cites news articles, blog posts, and research papers published recently, making it ideal for topics where current information matters. Its algorithm weights recency heavily, sometimes at the expense of older but more authoritative sources.
Google AI Overview demonstrates strong structural preferences, heavily citing Wikipedia (26.3% of citations) and Reddit (40.1% of citations). This pattern reflects Google’s reliance on structured data and community-validated information. Wikipedia’s consistent formatting and knowledge graph integration make it easily parseable. Reddit’s upvote system provides quality signals that Google’s systems recognize. Google AI Overview also cites news sources and official websites, but shows less preference for independent blogs compared to other platforms.
Claude shows the most balanced approach, citing diverse sources including academic papers, news articles, blogs, and documentation. Claude appears to weight source diversity and accuracy signals heavily, sometimes citing less obvious sources if they provide more accurate or nuanced information. Claude’s citations tend toward sources that demonstrate clear expertise and transparent reasoning.
Understanding these platform differences allows content creators to optimize strategically. Content targeting Perplexity should emphasize freshness and real-time relevance. Content for ChatGPT should focus on comprehensive authority and semantic depth. Content for Google AI Overview benefits from structured data and community engagement. Content for Claude should emphasize accuracy, nuance, and transparent expertise.
Implementing citation-worthy content requires systematic optimization across multiple dimensions. Here are actionable strategies that directly improve AI visibility:
Implement Schema Markup: Add structured data using Schema.org vocabulary, particularly Article, NewsArticle, ScholarlyArticle, and FAQPage schemas. This markup helps AI systems understand content type, publication date, author credentials, and content structure. Include author information with credentials, publication dates, and content sections in your schema implementation.
Create FAQ Sections: Organize content with FAQ format using proper schema markup. AI systems frequently cite FAQ sections because they provide concise, directly relevant answers to specific questions. Each FAQ item should address a distinct query that users might ask, with answers between 50-150 words.
Build Topic Clusters: Create comprehensive content clusters where a pillar article covers a broad topic and cluster articles address specific subtopics, all internally linked. This structure signals topical authority to AI systems and increases the likelihood that at least one piece in your cluster gets cited for any related query.
Maintain Content Freshness: Establish a regular update schedule for existing content, particularly for topics where information changes frequently. Update publication dates when making substantial revisions, and add new data, statistics, or examples to keep content current. AI systems weight recently updated content more heavily than static content.
Develop Original Research Programs: Commit to publishing original research, surveys, or data analysis on a regular schedule. This creates exclusive content that only your organization can cite, building a sustainable citation advantage. Share research findings across multiple content formats (articles, infographics, datasets) to maximize citation opportunities.
Optimize for Semantic Relevance: Use natural language that covers related concepts, synonyms, and contextual information. Rather than keyword stuffing, write comprehensively about your topic, naturally incorporating related terms and concepts. This semantic depth helps AI systems understand your content’s relevance to diverse queries.
These strategies work synergistically. Schema markup makes content easier for AI systems to parse. FAQ sections provide quotable answers. Topic clusters signal authority. Content freshness keeps material relevant. Original research creates citation magnets. Semantic optimization ensures broad relevance. Implementing all six creates a compound effect that significantly improves AI citation rates.
Tracking AI citations requires different tools and methodologies than traditional SEO analytics. Citation tracking tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, and specialized AI monitoring platforms now include features for tracking appearances in AI-generated responses. These tools monitor when your content appears in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overview, and other AI systems, providing data on citation frequency and context. Set up regular monitoring to track which pieces of content get cited most frequently and for which queries.
Key metrics to monitor include citation frequency (how often your content appears in AI responses), citation context (whether you’re cited as primary source or supporting evidence), query coverage (which search queries trigger your citations), and traffic attribution (how much referral traffic comes from AI systems). Brand search volume correlation represents the strongest predictor of AI visibility, with a 0.334 correlation coefficient—meaning that building brand recognition directly improves AI citation rates. Monitor branded search volume alongside AI citations to understand this relationship.
Testing methodology involves running identical queries across different AI platforms and documenting which sources appear in responses. Create a testing framework that covers your target keywords and queries, running tests monthly to track changes in citation patterns. Document not just whether your content appears, but in what context—whether it’s cited as the primary source, supporting evidence, or mentioned in passing. This granular data reveals which content types and topics generate the strongest AI visibility.
Establish baseline metrics before implementing optimization strategies, then measure improvements over 3-6 month periods. AI citation patterns change more slowly than traditional search rankings, so patience is essential. Track metrics that matter: citation frequency, traffic from AI systems, and brand visibility. These measurements reveal whether your optimization efforts are working and where to focus future content development.
Many organizations pursuing AI citation-worthiness make predictable mistakes that undermine their efforts. Keyword stuffing remains a persistent error—the assumption that repeating target keywords will improve AI visibility. AI systems evaluate semantic meaning rather than keyword frequency, so keyword stuffing actually reduces citation-worthiness by making content less readable and less semantically coherent. Focus on natural language that comprehensively addresses topics rather than forcing keywords into unnatural positions.
Over-emphasizing backlinks represents another misconception. While backlinks remain important trust signals, they’re not the primary driver of AI citations. Content with fewer backlinks but stronger semantic relevance, better structure, and higher factual density often outperforms heavily linked but poorly written content. AI systems evaluate backlinks as one signal among many, not as the dominant ranking factor.
Publishing thin content expecting AI systems to cite it is fundamentally misguided. AI systems prioritize comprehensive, substantive content that thoroughly addresses topics. Thin content—brief articles with minimal information, few examples, and shallow coverage—rarely gets cited because it doesn’t provide sufficient value. Invest in depth and comprehensiveness rather than publishing numerous shallow articles.
Ignoring freshness signals causes content to become invisible to AI systems that prioritize recent information. Content published years ago without updates gradually loses citation visibility, particularly for topics where information changes frequently. Establish update schedules and refresh content regularly to maintain AI visibility.
Assuming all AI platforms work identically leads to misaligned optimization efforts. Different platforms have different citation patterns, source preferences, and ranking signals. Content optimized only for ChatGPT may not perform well on Perplexity or Google AI Overview. Develop platform-aware strategies that account for these differences while maintaining core quality standards across all platforms.
Citation-worthy content is optimized for AI systems to reference and cite in their responses, while traditional SEO content focuses on ranking in search engine results. Citation-worthy content emphasizes authority, structure, freshness, and factual density to make it the preferred choice for AI systems. While good SEO content may rank well, it may not be cited by AI systems if it lacks these specific characteristics.
You can track AI citations using specialized monitoring tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, or dedicated AI visibility platforms. Alternatively, manually test your target queries across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overview, and Claude to see if your content appears in their responses. AmICited.com provides comprehensive monitoring across multiple AI platforms to track your brand's citation frequency and context.
No. While Google rankings correlate with AI citations (approximately 0.65 correlation), they don't guarantee citations. AI systems evaluate different signals than traditional search engines. Content can rank well in Google but not be cited by AI systems if it lacks proper structure, freshness, or factual density. Conversely, content on page 4 of Google results can be heavily cited by AI systems if it provides superior answers.
Brand search volume is the strongest predictor of AI citations (0.334 correlation), significantly outperforming backlinks. While backlinks remain important trust signals, they're not the primary driver of AI visibility. Focus on building brand recognition, creating authoritative content, and establishing expertise in your domain. These factors drive AI citations more effectively than pursuing backlinks alone.
Update content every 48-72 hours for maximum freshness signals, though this isn't always practical. At minimum, establish a quarterly review schedule to update statistics, add new examples, and refresh information. Content published within the past year receives 65% of AI bot hits, while content updated within 2 years receives 79%. Stale content gradually loses citation visibility regardless of historical authority.
Yes, absolutely. The fundamentals overlap significantly—both require quality content, proper structure, and authority signals. However, AI optimization emphasizes freshness, semantic relevance, and factual density more heavily than traditional SEO. The best approach is to build a strong SEO foundation while adding AI-specific optimizations like schema markup, FAQ sections, and original research.
Wikipedia represents approximately 26.3% of all LLM citations, making it the second-most cited source after Reddit (40.1%). Wikipedia's consistent structure, knowledge graph integration, and community validation make it easily parseable by AI systems. While creating a Wikipedia page requires meeting notability guidelines, ensuring your organization is mentioned in relevant Wikipedia articles can significantly boost AI visibility.
Track metrics including citation frequency across AI platforms, referral traffic from AI systems, brand search volume, and brand sentiment in AI responses. While AI citations may not drive direct traffic like traditional search results, they establish authority and influence how information is synthesized about your brand. Monitor these metrics over 3-6 month periods, as AI citation patterns change more slowly than traditional search rankings.
Track how often your brand is cited by ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI systems. Get real-time insights into your AI visibility and optimize your content strategy accordingly.

Learn the optimal content depth, structure, and detail requirements for getting cited by ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI. Discover what makes content citatio...

Learn what AI citations are, how they work across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI, and why they matter for your brand's visibility in generative search engin...
Discover which content formats get cited most by AI models. Analyze data from 768,000+ AI citations to optimize your content strategy for ChatGPT, Perplexity, a...