
How to Fix Keyword Cannibalization for AI Search Engines
Learn how to identify and fix keyword cannibalization issues affecting your visibility in AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. Discover conso...
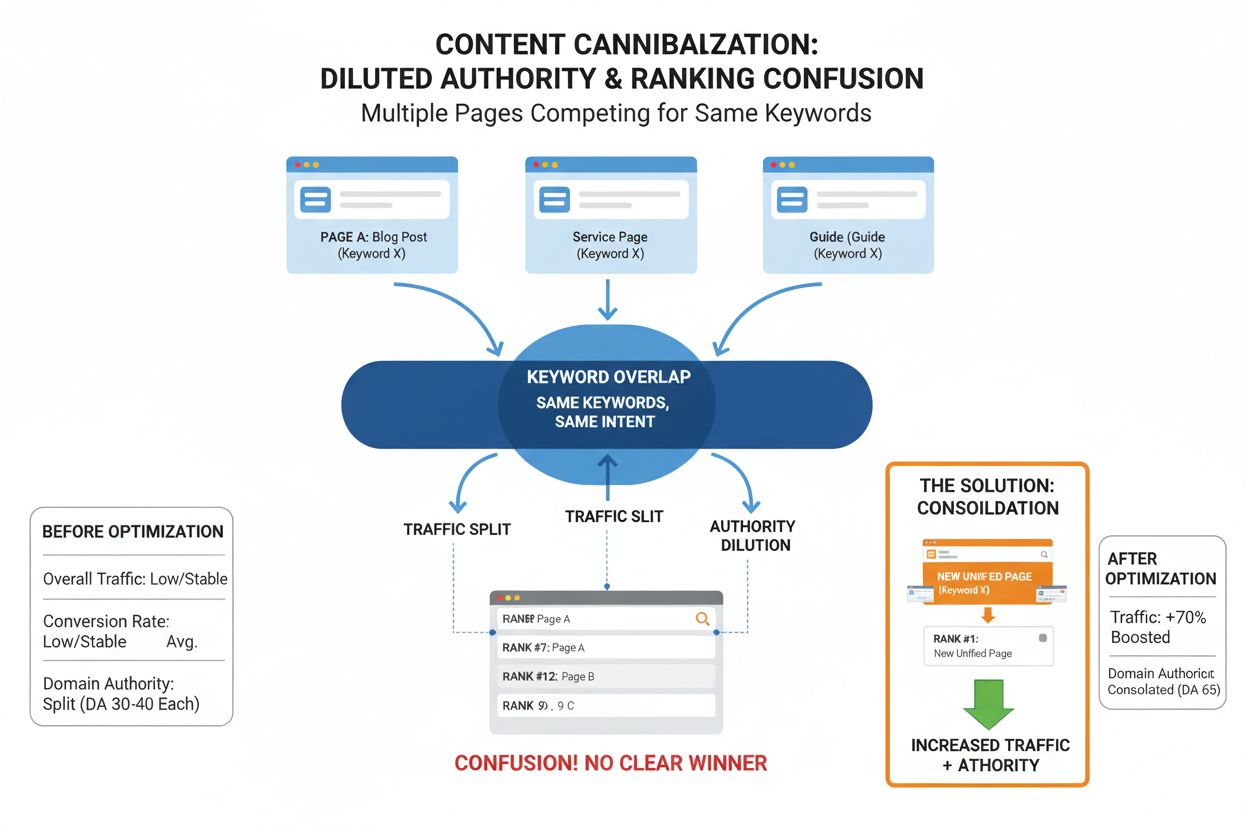
Content cannibalization occurs when multiple pages on a website target the same or similar keywords and fulfill comparable search intent, causing these pages to compete against each other in search results and diluting their individual ranking potential. This internal competition confuses search engines about which page should rank highest, resulting in lower visibility and reduced organic traffic for all affected pages.
Content cannibalization occurs when multiple pages on a website target the same or similar keywords and fulfill comparable search intent, causing these pages to compete against each other in search results and diluting their individual ranking potential. This internal competition confuses search engines about which page should rank highest, resulting in lower visibility and reduced organic traffic for all affected pages.
Content cannibalization is a critical SEO issue that occurs when multiple pages on a website target the same or very similar keywords and fulfill comparable search intent, causing these pages to compete directly against each other in search engine results. Rather than working together to strengthen your domain’s authority, cannibalized pages fragment your ranking potential by splitting the authority signals, relevance indicators, and backlink equity that would otherwise concentrate on a single, authoritative page. This internal competition creates confusion for search engines, which struggle to determine which page is most relevant for a given query, ultimately resulting in lower rankings for all competing pages. The term “cannibalization” is particularly apt because these pages essentially consume each other’s ranking potential, leaving your website weaker than if you had consolidated the content strategically.
The concept of keyword cannibalization emerged as a recognized SEO challenge in the early 2000s when search engines began refining their algorithms to better understand topical relevance and content quality. As websites grew larger and content libraries expanded, marketers and SEO professionals noticed that publishing multiple articles on similar topics didn’t necessarily increase visibility—in fact, it often decreased it. Google’s algorithm evolution, particularly with updates like Panda (2011) and subsequent core algorithm refinements, made search engines increasingly sophisticated at identifying and penalizing sites with duplicate or near-duplicate content. Today, with over 78% of enterprises using AI-driven content monitoring tools to track their online presence, understanding and preventing content cannibalization has become essential for maintaining competitive search visibility. The rise of AI search platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews has added another dimension to this problem—cannibalized content doesn’t just hurt traditional SEO rankings; it also fragments your brand’s authority in AI-generated responses, making it less likely that AI systems will cite your most authoritative pages.
When search engines encounter multiple pages targeting the same keyword, they employ sophisticated algorithms to determine relevance and authority. However, this process creates several technical challenges that directly harm your SEO performance. Authority dilution occurs because backlinks, internal links, and other ranking signals get distributed across multiple pages instead of consolidating on a single authoritative resource. For example, if external websites link to your site using the anchor text “best coffee makers,” those links might point to different pages on your domain, fragmenting the authority that would otherwise make one page dominant. Additionally, crawl budget waste becomes a significant issue—search engines allocate limited resources to crawl your website, and when multiple similar pages exist, crawlers spend time indexing redundant content instead of discovering new, unique pages. This is particularly problematic for large websites where crawl budget is already constrained. The ranking fluctuation that results from cannibalization means your pages may take turns ranking for the same keyword, with positions constantly shifting as search engines test which page is most relevant. This instability makes it nearly impossible to build consistent organic traffic from target keywords.
| Aspect | Content Cannibalization | Duplicate Content | Thin Content | Keyword Stuffing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Issue | Multiple pages compete for same keywords | Identical or near-identical pages exist | Pages lack sufficient depth and value | Excessive keyword repetition for ranking |
| Search Intent | Same or very similar | Identical | Varies | Intentionally manipulative |
| Authority Impact | Diluted across pages | Consolidated to canonical | Weak across all pages | Penalized by algorithms |
| User Experience | Confusing with similar options | Redundant results | Unsatisfying and incomplete | Poor readability and trust |
| Primary Cause | Poor planning and strategy | Technical issues or CMS problems | Rushed or low-effort creation | Black-hat SEO tactics |
| Best Fix | Consolidate and redirect | Canonical tags or 301 redirects | Expand and improve content | Remove or rewrite entirely |
| Detection Method | GSC Performance report, site: search | Plagiarism checkers, GSC | Manual review, readability tools | Keyword density analysis |
| Severity Level | High | High | Medium | Critical |
Content cannibalization extends far beyond technical SEO metrics—it directly impacts your bottom line through reduced organic traffic, lower conversion rates, and wasted content creation resources. When your pages compete with each other instead of working together, you lose the compounding effect of a well-organized content ecosystem. A 466% increase in clicks was documented when one website consolidated cannibalized content through strategic 301 redirects, demonstrating the tangible business value of addressing this issue. From a brand monitoring perspective, particularly relevant for platforms like AmICited that track domain appearances in AI search results, cannibalization becomes even more critical. When multiple pages on your site target the same topic, AI systems may cite different pages inconsistently, fragmenting your brand’s authority and making it harder for AI platforms to recognize you as the definitive source on a topic. This inconsistency in AI citations can significantly impact your visibility in emerging search channels where brand authority and topical expertise are increasingly important ranking factors.
Identifying content cannibalization requires a systematic approach using both free and premium tools. Google Search Console provides the most accessible starting point—navigate to the Performance report, filter by a specific query, and check the “Pages” tab to see which URLs are receiving impressions and clicks for that keyword. If multiple pages appear for the same query, you’ve likely identified a cannibalization issue. The site: operator in Google (e.g., site:yourdomain.com “your keyword”) quickly reveals all pages your domain has indexed for a specific term. For more comprehensive analysis, Semrush’s Cannibalization Report automatically identifies pages competing for the same keywords across your entire site, providing detailed metrics on rankings, traffic, and performance trends. Ahrefs and Nightwatch offer similar functionality with additional insights into keyword difficulty and search volume. When analyzing potential cannibalization, examine not just keyword overlap but also search intent alignment—pages targeting the same keyword but serving different user intents (informational vs. transactional, for example) may not constitute true cannibalization. However, pages with identical or nearly identical search intent targeting the same keyword almost always represent a cannibalization problem requiring intervention.
The most effective solution for content cannibalization is consolidation with 301 redirects, which involves merging multiple similar pages into one comprehensive resource and redirecting all traffic from the weaker pages to the stronger one. This approach concentrates all authority signals on a single page, dramatically improving its ranking potential. When selecting which page to consolidate into, prioritize the page with the highest search rankings, most organic traffic, strongest backlink profile, and best engagement metrics. After consolidation, ensure you remove the redirected URLs from your XML sitemap and update all internal links to point directly to the consolidated page rather than through redirects. An alternative approach is intent repositioning, where you keep multiple pages but reposition each to target a different search intent or long-tail keyword variation. For example, instead of having three pages all targeting “email marketing,” you could have one for “email marketing basics” (informational), one for “best email marketing tools” (commercial), and one for “how to set up email marketing” (navigational). This requires significant content rewriting but allows you to maintain multiple pages without cannibalization. For pages that must coexist due to business requirements, internal linking optimization can help by strategically directing link equity to your primary page using consistent anchor text, while using different anchor text for secondary pages. Canonical tags can also signal preference to search engines when you have multiple versions of similar content that must remain indexed.
Preventing content cannibalization from occurring in the first place is far more efficient than fixing it after the fact. The foundation of prevention is comprehensive keyword mapping—maintain a master spreadsheet documenting which keywords each page targets, what search intent it serves, and how it differs from related pages. This living document should be consulted before creating any new content to ensure you’re not duplicating existing coverage. Establish a content governance process where new content ideas are reviewed against existing pages to identify potential overlaps before writing begins. Define a unique search intent for every page by asking: What specific problem does this page solve? What should readers take away? Pages with similar keywords can coexist peacefully if they clearly serve different purposes. Implement a content calendar that includes target keywords and search intents, making it easy to spot conflicts before publication. For larger organizations, establish cross-team communication protocols to ensure that blog writers, product teams, and other content creators aren’t unknowingly creating duplicate content. Use SEO tools with monitoring capabilities to set up alerts for emerging cannibalization issues, allowing you to catch problems early before they impact rankings. Regularly audit your site’s internal linking structure to ensure links are distributed strategically, with your most important pages receiving the most internal link equity.
E-commerce websites face unique cannibalization challenges due to product variations, filters, and faceted navigation. A single product might have multiple URLs for different color or size options, each potentially targeting the same keywords. The solution involves using canonical tags to consolidate these variations to a primary product page, or implementing parameter handling in Google Search Console to tell search engines which URL parameters create unique content and which are just filters. For multi-location businesses, cannibalization can occur when each location has its own page targeting the same service keywords. This is actually acceptable if each page’s content is genuinely unique to that location—for example, a dental practice with multiple offices can have separate pages for each location, each optimized for local keywords. However, if the content is identical except for location names, consolidation or canonical tags are necessary. Marketplace platforms and SaaS companies with multiple product tiers often struggle with cannibalization when different product pages target overlapping keywords. The solution is to clearly differentiate each page’s target audience and use long-tail keywords specific to each product tier or use case.
As AI search platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude become increasingly important for brand visibility, content cannibalization takes on new significance. These AI systems rely on topical authority and content consolidation to determine which sources to cite. When your website has multiple pages competing for the same keywords, AI systems may cite different pages inconsistently or fail to recognize you as an authoritative source on a topic. This fragmentation of authority becomes particularly problematic as AI-driven content monitoring becomes standard practice for tracking brand mentions across search channels. Forward-thinking organizations are already using platforms like AmICited to monitor how their consolidated, authoritative content appears in AI-generated responses, recognizing that preventing cannibalization isn’t just about traditional SEO—it’s about establishing clear topical authority that AI systems can reliably cite. The evolution of search toward AI-powered answers makes the consolidation of cannibalized content even more critical, as these systems reward sites with clear, authoritative coverage of topics rather than fragmented, competing pages. As search engines continue to prioritize E-E-A-T signals (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), maintaining a clean, non-cannibalized content structure becomes essential for demonstrating genuine expertise. Organizations that proactively address cannibalization now will be better positioned to maintain visibility across both traditional search and emerging AI search channels, while those that ignore this issue risk losing authority and visibility as search continues to evolve.
Content cannibalization directly harms SEO rankings by splitting authority signals across multiple pages targeting the same keyword. When search engines encounter multiple pages competing for the same query, they struggle to determine which page is most relevant, often resulting in lower rankings for all competing pages. Research shows that consolidating cannibalized content can increase clicks by up to 466%, demonstrating the significant impact on search visibility and organic traffic performance.
Keyword cannibalization specifically refers to multiple pages targeting identical or very similar keywords, while content cannibalization is broader and encompasses pages with overlapping topics regardless of exact keyword matching. Content cannibalization focuses on thematic overlap and similar search intent, whereas keyword cannibalization is strictly about keyword duplication. Both issues harm SEO performance, but content cannibalization can occur even when pages use slightly different keywords if they serve the same user intent.
You can identify content cannibalization using Google Search Console by checking the Performance report and filtering by query to see which pages rank for the same keywords. Use the site: operator in Google (site:yourdomain.com keyword) to find all pages targeting specific terms. SEO tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, and Nightwatch offer cannibalization reports that automatically detect multiple pages competing for the same keywords, making identification faster and more comprehensive for larger websites.
Content cannibalization typically results from poor keyword mapping and planning, lack of content strategy alignment across teams, and overcomplicated site architecture. Without a clear keyword-to-URL mapping, teams may unknowingly create multiple pages targeting the same terms. Rapid content creation without checking existing pages, faceted navigation in e-commerce sites, and paginated content series can also generate duplicate or near-duplicate pages that compete for rankings.
The most effective solution is consolidating similar pages into one comprehensive resource and implementing 301 redirects from the weaker pages to the stronger one. Alternatively, you can reposition each page to target different search intents or long-tail keyword variations. For pages that must coexist, optimize internal linking to direct authority to your primary page and use canonical tags to signal preference to search engines. Regular content audits help catch and address cannibalization issues before they significantly impact rankings.
Yes, content cannibalization negatively impacts user experience by confusing visitors with multiple similar pages covering the same topic. Users may struggle to determine which page contains the most relevant or up-to-date information, leading to higher bounce rates and lower conversion rates. This confusion also reduces trust in your content quality, as visitors may perceive the duplication as poor site organization or outdated information management.
Content cannibalization becomes increasingly important in the context of AI search monitoring platforms like AmICited, which track brand and domain appearances across AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. When multiple pages on your site compete for the same keywords, it dilutes the authority of your brand's presence in AI-generated responses. Consolidating cannibalized content strengthens your domain's topical authority, making it more likely that AI systems will cite your most authoritative page rather than fragmenting citations across multiple weaker pages.
You should conduct content cannibalization audits at least quarterly, or more frequently if you publish content regularly. For large websites with continuous content creation, monthly audits are recommended to catch issues early before they impact rankings. After implementing fixes, monitor your rankings and traffic for 8-12 weeks to measure the impact of consolidation or repositioning efforts. Ongoing monitoring through tools like Google Search Console helps identify emerging cannibalization issues before they become significant problems.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn how to identify and fix keyword cannibalization issues affecting your visibility in AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. Discover conso...
Learn what AI content cannibalization is, how it differs from duplicate content, why it hurts rankings, and strategies to protect your content from being scrape...

Learn what content cannibalization in AI search means, how it affects your brand visibility in AI answers, and why monitoring your content overlap matters for A...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.