Word Count
Learn what word count means in content creation and SEO. Discover optimal word count ranges, why it matters for AI monitoring, and how content length affects se...

Content length is the measurement of digital content size using various metrics including word count, character count, bytes, and kilobytes. It represents how much information is contained in a piece of content and is crucial for both SEO performance and AI citation visibility across platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Content length is the measurement of digital content size using various metrics including word count, character count, bytes, and kilobytes. It represents how much information is contained in a piece of content and is crucial for both SEO performance and AI citation visibility across platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Content length is the quantitative measurement of digital content size expressed through multiple metrics including word count, character count, bytes, and kilobytes. It represents the total volume of information contained within a piece of content, whether that’s a blog post, article, social media update, or API response. Content length serves as a fundamental metric in both traditional SEO and modern Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), influencing how search engines and AI systems evaluate content quality, relevance, and comprehensiveness. The measurement of content length varies depending on context: editorial content is typically measured in words or characters, while technical content and network transfers are measured in bytes. Understanding the different dimensions of content length is critical for content creators, marketers, and developers seeking to optimize visibility across search engines, AI platforms, and web infrastructure.
The concept of content length has evolved significantly since the early days of search engine optimization. In the 1990s and 2000s, search engines like Google began recognizing that longer, more comprehensive content often provided better answers to user queries, leading to the widespread adoption of word count as a key content metric. Early research by SEO pioneers demonstrated that pages ranking in Google’s top 10 search results averaged significantly more words than lower-ranking pages. However, the relationship between content length and rankings is more nuanced than simple correlation. According to Yoast SEO research, content length is not a direct ranking factor, but rather a proxy for content depth and topical coverage. The rise of AI-powered search systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews has introduced new dimensions to content length measurement. Research analyzing 240 million ChatGPT citations reveals that word count correlates at 0.047 with ChatGPT citations, while Perplexity shows a 0.191 correlation and Google AI Overviews shows 0.153 correlation. This indicates that different AI platforms weight content length differently in their citation algorithms. The technical measurement of content length through HTTP Content-Length headers emerged from the need to efficiently transfer data across networks, with each byte representing 8 bits of information. Today, content length encompasses multiple measurement dimensions, each serving specific purposes in content optimization, performance monitoring, and AI visibility tracking.
| Measurement Method | Unit | Primary Use Case | Example | Relevance to AI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Word Count | Words | SEO, content marketing, editorial guidelines | 1,500-2,500 words for blog posts | High—correlates with AI citations |
| Character Count | Characters (with/without spaces) | Social media, platform limits, technical specs | 280 characters for Twitter | Medium—used for platform optimization |
| Byte Count | Bytes (8-bit units) | HTTP headers, API responses, file transfers | 5,000-6,000 bytes for typical article | High—critical for network performance |
| Kilobyte (KB) | 1,024 bytes | File size measurement, bandwidth tracking | 50-100 KB for typical webpage | Medium—affects page load speed |
| Sentence Count | Sentences | Readability analysis, content structure | 50-100 sentences per article | Medium—indicates content depth |
| Paragraph Count | Paragraphs | Content organization, scannability | 10-20 paragraphs per article | Low—less direct AI impact |
| Reading Time | Minutes | User experience, content expectations | 7-10 minutes for 1,600-word article | Low—derived from word count |
Content length operates across multiple technical and editorial dimensions, each serving distinct purposes in content delivery and optimization. At the most fundamental level, word count measures the number of individual words in a piece of content, providing a straightforward metric for editorial planning and SEO strategy. A typical blog post of 1,600 words translates to approximately 7 minutes of reading time, based on average reading speeds of 200-250 words per minute. Character count extends this measurement to include every letter, number, space, and punctuation mark, making it essential for platforms with strict character limits like Twitter (280 characters) or Facebook (63,206 character limit). The distinction between character count with and without spaces is important: a 1,000-word article typically contains 5,000-6,000 characters without spaces and 6,000-7,000 characters with spaces included.
At the technical level, HTTP Content-Length headers measure response body size in bytes, where one byte equals 8 bits of binary data. When a server sends an HTTP response, it includes a Content-Length header specifying the exact number of bytes in the response body, allowing clients to know precisely how much data to expect. For example, a response with Content-Length: 5000 indicates the body contains exactly 5,000 bytes. This measurement is critical for efficient data transfer, caching mechanisms, and proxy server operations. The relationship between character count and byte count depends on character encoding: in UTF-8 encoding (the most common standard), ASCII characters occupy 1 byte each, while special characters and non-Latin scripts may occupy 2-4 bytes. Therefore, a 1,000-character string might be 1,000 bytes in ASCII but 1,500-2,000 bytes in UTF-8 with special characters.
Kilobytes (KB) represent 1,024 bytes and are commonly used to measure file sizes and bandwidth consumption. A typical webpage of 50-100 KB includes HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and images. Understanding these technical measurements is essential for web performance optimization, as larger content sizes require more bandwidth and longer load times. Modern web development practices emphasize Core Web Vitals, which include metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), both influenced by content size and delivery efficiency.
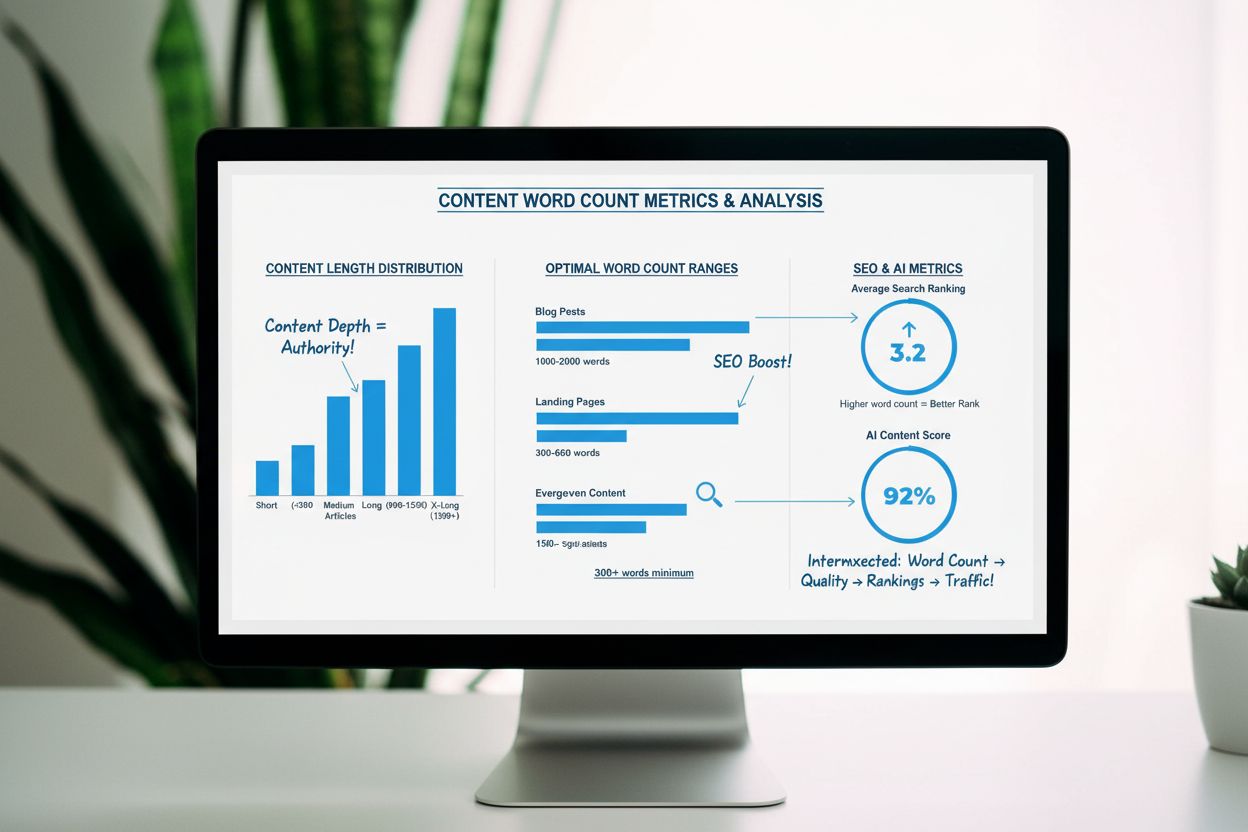
The practical implications of content length extend far beyond simple word counting. Research from HubSpot indicates that the ideal SEO content length ranges from 2,100 to 2,400 words, though they’ve observed shorter blogs with less than 1,500 words performing well in specific contexts. Hook Agency research suggests the optimal blog length for SEO in 2024 ranges from 1,760 to 2,400 words. However, the critical insight is that content depth matters more than raw word count. A 1,500-word article that thoroughly answers a user’s question will outperform a 3,000-word article filled with filler content. This distinction between content length and content depth is fundamental to modern SEO strategy.
For AI citation visibility, the relationship is more complex. Research analyzing citation patterns across ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, and Perplexity reveals that each platform weights content length differently. Perplexity shows the strongest correlation between word count and citations (0.191), suggesting the platform prioritizes comprehensive, longer-form content. Google AI Overviews shows moderate correlation (0.153), while ChatGPT shows lower correlation (0.047), instead favoring domain authority and brand recognition. This means that for ChatGPT visibility, building brand authority through backlinks and mentions may be more important than simply writing longer content. The practical implication is that content optimization strategies must be platform-specific: what works for Perplexity visibility may not work for ChatGPT visibility.
Listicles and comparative content formats account for 25.37% of all AI citations across 2.6 billion analyzed citations, making these formats significantly more likely to be cited by AI systems. This suggests that content length combined with structured formatting (numbered lists, comparison tables, bullet points) creates optimal conditions for AI citation. Additionally, research shows that 40-60% of AI citations change monthly, indicating that content freshness and regular updates are essential for maintaining visibility. Organizations using AmICited to monitor their AI citation performance can track how content length changes correlate with citation frequency, enabling data-driven optimization decisions.
Different AI platforms exhibit distinct preferences for content length and structure, requiring tailored optimization approaches. ChatGPT, powered by OpenAI’s language models, shows a preference for authoritative sources and established brands over raw content length. Analysis of 240 million ChatGPT citations reveals that domain rating correlates at 0.161 with citation frequency, significantly higher than word count correlation. This suggests that ChatGPT prioritizes content from trusted, well-known sources even if that content is shorter than competitors. For ChatGPT optimization, brands should focus on building domain authority through quality backlinks, media mentions, and brand recognition rather than simply increasing word count.
Perplexity, by contrast, shows the strongest correlation between content length and citations (0.191), indicating the platform actively seeks comprehensive, detailed content. Perplexity’s research-focused positioning means it values thorough coverage of topics, making longer, more in-depth articles more likely to be cited. Additionally, Perplexity shows a strong preference for Reddit content (6.6% of total citations), suggesting that community-driven, peer-to-peer information carries significant weight. For Perplexity optimization, brands should create detailed, comprehensive content that thoroughly addresses user questions and consider engaging in relevant Reddit communities.
Google AI Overviews demonstrates a balanced approach, showing moderate correlation with content length (0.153) while also valuing diverse source types. Analysis reveals that Google AI Overviews cites Reddit (2.2%), YouTube (1.9%), Quora (1.5%), and LinkedIn (1.3%) prominently, indicating preference for user-generated content and professional networks. This suggests that for Google AI Overviews visibility, brands should maintain presence across multiple content platforms and formats, not just traditional websites. The platform’s citation patterns indicate that multi-format content (text, video, structured data) increases visibility chances.
Claude, Anthropic’s AI assistant, shows emerging patterns in citation behavior, though less research data is available compared to ChatGPT and Perplexity. Early indicators suggest Claude values factual accuracy, source transparency, and well-structured information, making content length less important than content quality and clarity. For Claude optimization, focus on clear, well-organized content with explicit source citations and fact-based claims.
Effective content length optimization requires moving beyond simple word count targets to embrace a strategic, platform-aware approach. The first step is conducting a content audit to understand current content lengths across your site and comparing them to top-ranking competitors. Tools like Yoast SEO provide automated checks for minimum word count thresholds: regular posts should exceed 300 words, cornerstone content should exceed 900 words, and product descriptions should exceed 200 words. However, these are minimum thresholds, not targets—the actual optimal length depends on search intent and topic complexity.
For SEO optimization, follow these implementation guidelines: First, match content length to search intent. Informational queries typically require longer, more comprehensive content (1,500-2,500 words), while navigational queries may need only 300-500 words. Second, prioritize content depth over length. Structure content to answer all related questions a user might have, using clear headings, bullet points, and tables to organize information. Third, avoid content overlap by ensuring each piece of content has a distinct focus and doesn’t duplicate information from other pages. Fourth, update content regularly to maintain freshness signals—research shows that 40-60% of AI citations change monthly, making regular updates essential.
For AI citation optimization, implement these practices: First, structure content in semantic chunks with self-contained answers to specific questions. Each section should be extractable and understandable independently, making it easier for AI systems to cite relevant portions. Second, use listicles and comparative formats when appropriate, as these formats account for 25.37% of AI citations. Third, implement comprehensive structured data using schema markup (FAQPage, HowTo, Product, etc.) to help AI systems understand and extract content. Fourth, optimize for multiple platforms by creating content that works across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude, recognizing that each platform has different preferences.
For technical optimization, ensure proper HTTP Content-Length headers are set correctly on your server. Incorrect Content-Length values can cause truncated responses, connection timeouts, and poor user experience. Use tools like cURL or browser developer tools to verify that Content-Length headers match actual response body sizes. Additionally, optimize page load speed by minimizing content size through compression, lazy loading, and efficient image optimization—larger content sizes directly impact Core Web Vitals and user experience.
The definition and importance of content length are undergoing significant transformation as AI systems become more sophisticated and prevalent. The emergence of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) as a distinct discipline from traditional SEO reflects this shift. While traditional SEO focused on optimizing for keyword matching and link authority, GEO emphasizes content comprehensiveness, semantic clarity, and extractability. This evolution suggests that future content length optimization will prioritize depth and structure over raw word count.
Research from Profound analyzing 240 million ChatGPT citations reveals that citation patterns are highly volatile, with 40-60% of citations changing monthly. This volatility indicates that content length alone is insufficient for sustained AI visibility—continuous optimization, regular updates, and platform-specific strategies are essential. As AI systems become more sophisticated, they may develop more nuanced understanding of content quality, potentially reducing the importance of length as a proxy for quality. However, in the near term (2025-2026), content length remains a significant factor in AI citation performance.
The integration of AI monitoring platforms like AmICited into content strategy workflows represents a major shift in how organizations approach content optimization. Rather than relying on traditional SEO metrics like rankings and traffic, forward-thinking organizations now track AI citation frequency, citation authority, and sentiment across multiple AI platforms. This data-driven approach enables real-time optimization decisions: if a piece of content receives citations from Perplexity but not ChatGPT, the organization can analyze the differences and adjust strategy accordingly.
Future developments in content length optimization will likely include: First, platform-specific content strategies becoming standard practice, with organizations creating different content versions optimized for different AI platforms. Second, semantic content measurement replacing simple word count, with AI systems evaluating content based on semantic depth and information density rather than word count. Third, real-time citation tracking becoming integrated into content management systems, allowing writers to see immediately how content changes affect AI visibility. Fourth, multimodal content optimization becoming essential, as AI systems increasingly incorporate video, images, and structured data alongside text. Finally, content freshness automation will likely become more sophisticated, with AI-assisted tools helping maintain content relevance without requiring complete rewrites.
The strategic implication for organizations is clear: content length optimization must evolve from a static, one-time consideration to a dynamic, continuous process. Organizations that implement comprehensive AI citation monitoring and adjust content strategy based on real-time data will maintain competitive advantage as AI search becomes increasingly important. The future of content length optimization is not about hitting arbitrary word count targets, but about creating comprehensive, well-structured, platform-optimized content that serves both human readers and AI systems effectively.
Word count measures the number of individual words in content, while character count includes every letter, number, space, and punctuation mark. For example, a 1,000-word article might contain 6,000-7,000 characters depending on word length and spacing. Character count is more precise for technical specifications like HTTP headers and API responses, while word count is the standard metric for SEO and content marketing purposes.
Content length influences SEO through multiple mechanisms: longer content provides more opportunities to include target keywords and related terms, enables better internal linking, and signals topical depth to search engines. Research shows that pages ranking in Google's top 10 average around 1,500-2,000 words, though content depth matters more than raw word count. However, content length is not a direct ranking factor—quality and relevance are paramount.
Optimal lengths vary significantly: blog posts typically perform best at 1,600-2,500 words, social media posts at 40-280 characters depending on platform, product descriptions at 200+ words, and landing pages at 300-1,000 words. Research indicates that Facebook posts under 40 characters earn 86% more engagement, while tweets of 100 characters receive 17% more engagement. The key is matching content length to user intent and platform expectations.
AI platforms show distinct preferences for content length: Perplexity and Google AI Overviews prioritize content length with correlation coefficients of 0.191 and 0.153 respectively, while ChatGPT shows lower correlation (0.047) but favors domain authority. Research analyzing 240 million ChatGPT citations reveals that word count and sentence count are among the strongest positive correlations for AI visibility, with longer, more comprehensive content receiving more citations across platforms.
HTTP Content-Length headers measure response body size in bytes, not words or characters. This technical metric tells clients exactly how much data to expect in network transfers. For example, a 1,000-word article might be 5,000-6,000 bytes depending on character encoding. This is distinct from editorial content length but equally important for web performance, caching, and API communication.
For AI citation optimization, focus on content depth and comprehensiveness rather than arbitrary word counts. Research shows listicles and comparative content formats account for 25.37% of all AI citations. Structure content in semantic chunks with clear answers, use 1,500-2,500 words for comprehensive coverage, include tables and bullet points for easy extraction, and ensure content directly answers user questions. Platforms like AmICited track how content length correlates with citation frequency across AI systems.
For SEO and content marketing, use word count as the primary metric. For technical specifications and API responses, measure in bytes or kilobytes. For social media, character count is essential due to platform limits. For readability analysis, sentence count and paragraph length matter. For AI citation tracking, combine word count with semantic depth metrics. Different measurement approaches serve different optimization goals and platform requirements.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn what word count means in content creation and SEO. Discover optimal word count ranges, why it matters for AI monitoring, and how content length affects se...

Content depth is the comprehensive coverage of a topic with detailed sections, expert insights, and data. Learn how content depth impacts AI citations, rankings...

Community discussion on optimal content length for AI search visibility. Writers and strategists share data on what length gets cited and whether word count mat...