
Conversational SEO
Learn what Conversational SEO is, how it differs from traditional SEO, and why citation-based visibility matters for AI systems like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perple...
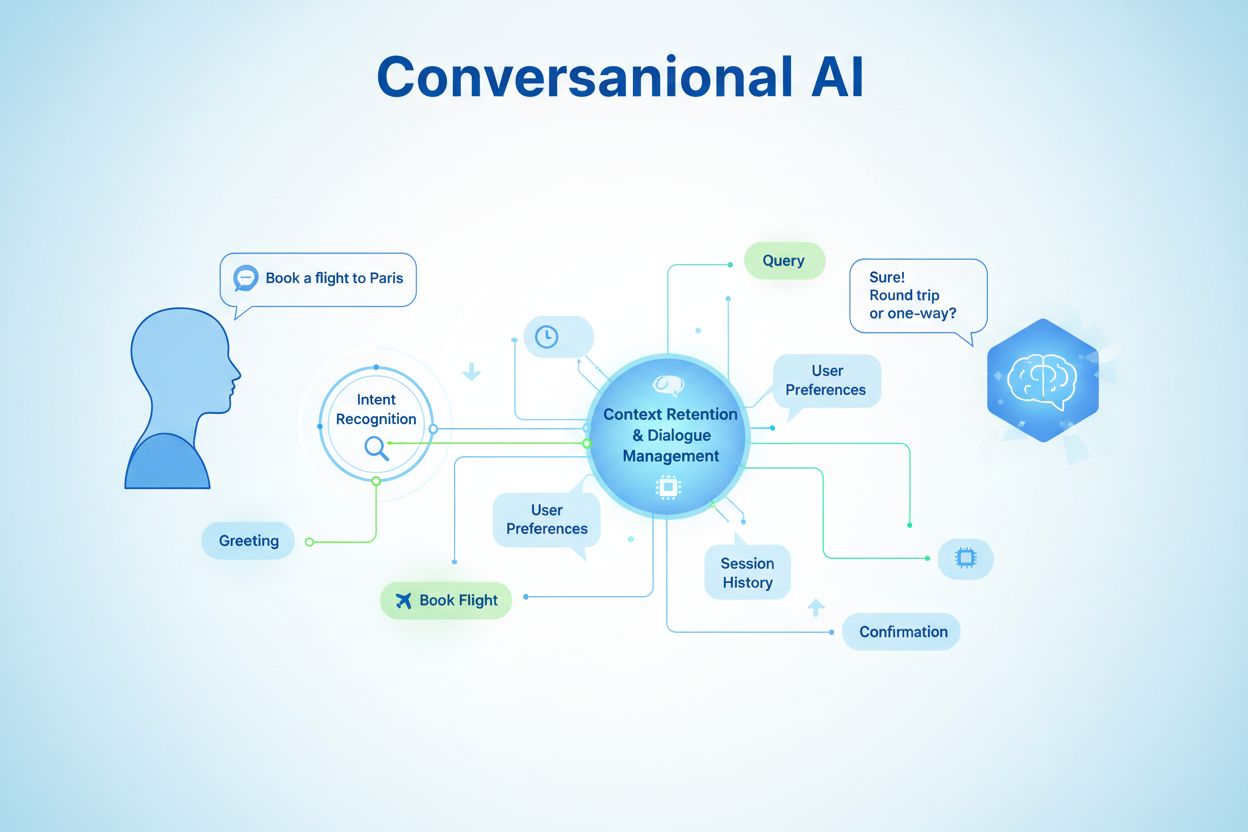
Conversational content mapping is a strategic framework for organizing and structuring content to enable natural, multi-turn dialogue between users and AI systems. Unlike traditional linear content architecture, it treats information as interconnected dialogue nodes that respond to user intent and context, ensuring AI systems can reference content accurately within conversational flows.
Conversational content mapping is a strategic framework for organizing and structuring content to enable natural, multi-turn dialogue between users and AI systems. Unlike traditional linear content architecture, it treats information as interconnected dialogue nodes that respond to user intent and context, ensuring AI systems can reference content accurately within conversational flows.
Conversational content mapping is a strategic framework for organizing and structuring content to enable natural, multi-turn dialogue between users and AI systems. Unlike traditional content architecture that presents information in linear, hierarchical structures, conversational content mapping treats information as interconnected dialogue nodes that respond to user intent and context. This approach recognizes that modern AI interactions—particularly in GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews—require content to be flexible, contextually aware, and capable of handling dynamic conversation flows. The distinction matters because AI systems must understand not just what users ask, but why they’re asking it, what they already know, and where the conversation might naturally progress. Conversational content mapping ensures that when an AI system references your content, it does so in a way that feels natural within the conversation while maintaining accuracy and relevance. This methodology has become essential as AI systems increasingly serve as primary information access points, making it critical for organizations to understand how their content flows through conversational interfaces rather than traditional search results.

| Component | Definition | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intent Recognition | The system’s ability to identify what the user actually wants to accomplish | Ensures responses address the user’s true need rather than literal question | User asks “How do I fix my password?” but intends to regain account access |
| Context Retention | Maintaining information from previous exchanges within a conversation | Allows follow-up questions to reference earlier statements without repetition | User mentions their industry in message 1; system recalls this in message 5 |
| Dialogue Flow | The logical progression and branching paths of conversation | Guides users naturally through information discovery and problem-solving | Conversation branches into troubleshooting vs. feature explanation based on user response |
| Fallback Handling | Predefined responses when the system cannot match user input to known intents | Prevents conversation breakdown and maintains user confidence | System offers clarifying questions or escalation options when uncertain |
Traditional chatbot scripts rely on rigid decision trees and predetermined response paths, while conversational content mapping embraces flexibility and natural language understanding. Key differences include:
Dialogue management is the intelligent orchestration layer that decides what happens next in a conversation. It processes user input, evaluates current context, retrieves relevant content, and determines the most appropriate response while maintaining conversation coherence. This system operates in real-time, analyzing not just the current message but the entire conversation history to ensure responses feel contextually appropriate and logically connected. Dialogue management handles critical functions like recognizing when users interrupt with new topics, managing topic switches gracefully, and deciding whether to answer immediately or request clarification. It prevents common conversational failures such as repeating information already provided, contradicting earlier statements, or pursuing irrelevant tangents. By maintaining a conversation state model, dialogue management ensures that multi-turn exchanges feel like genuine dialogue rather than isolated Q&A exchanges. This becomes particularly important for AI monitoring purposes, as proper dialogue management ensures that content citations remain accurate and contextually appropriate throughout extended conversations, directly impacting how AI systems like GPTs and Perplexity represent your brand and content.
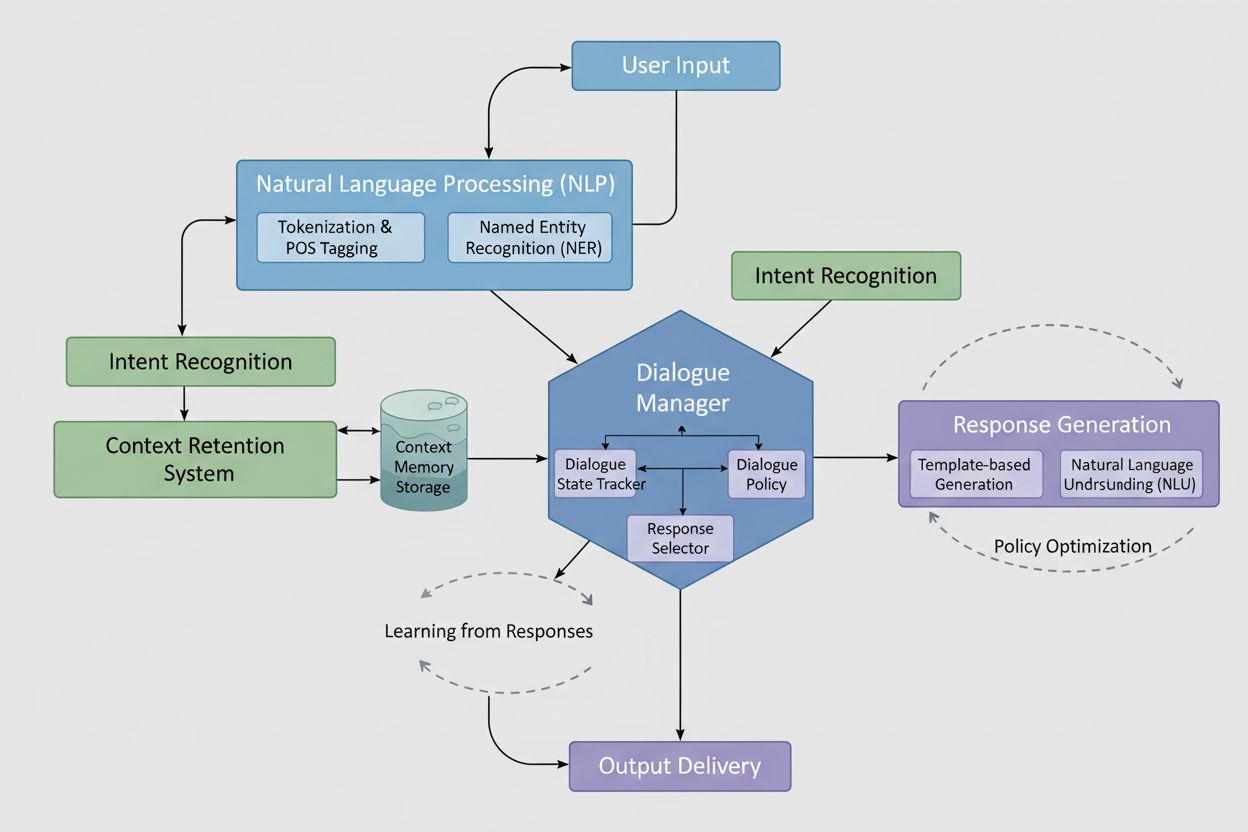
Effective multi-turn conversation design begins with a comprehensive content audit to identify which information pieces naturally support extended dialogue. Organizations must analyze their existing content to determine high-volume user intents—the questions and topics users repeatedly ask about—and map how these intents interconnect. This involves creating conversation path diagrams that show how users typically progress from initial questions through follow-ups, clarifications, and related topics. Content must be modularized into discrete, reusable units that can be combined in various sequences depending on conversation flow, rather than locked into single-use articles or pages. Edge cases require special attention; teams should identify unusual questions, controversial topics, or scenarios where users might request information outside normal parameters, then develop appropriate handling strategies. Testing and optimization occur continuously through conversation analytics, examining where users drop off, where they ask clarifying questions, and where they express confusion. Personalization strategies should account for user expertise levels, industry context, and previous interactions, allowing the same content to be presented differently based on conversation context. This approach ensures that whether a user reaches your content through direct search or through an AI system’s conversational interface, the experience remains coherent, helpful, and properly attributed.
Conduct a Comprehensive Content Audit: Inventory all existing content and categorize it by user intent, identifying gaps where content doesn’t exist for common questions and redundancies where multiple pieces address the same intent.
Define Use Cases and User Personas: Document specific scenarios where users interact with your content, including their goals, expertise levels, and typical conversation patterns to inform content structure decisions.
Map Intent-to-Content Relationships: Create detailed mappings showing which content pieces address which intents, how intents relate to each other, and which content should be referenced in follow-up exchanges.
Build Fallback Logic and Escalation Paths: Develop clear protocols for handling unrecognized intents, including clarifying questions, related topic suggestions, and escalation procedures when the system cannot adequately respond.
Test Across Multiple Conversation Scenarios: Simulate realistic multi-turn conversations, testing how content flows across different user paths, ensuring consistency and accuracy regardless of conversation direction.
Optimize Based on Interaction Data: Continuously analyze conversation logs to identify where users struggle, where content fails to satisfy intent, and where improvements can enhance dialogue quality and user satisfaction.
Proper conversational content mapping directly improves how AI systems reference and represent your content. When content is structured for conversational flow, AI systems can more accurately understand context and provide more precise citations, reducing the risk of misrepresentation or hallucination. This becomes critical for organizations monitoring their presence in AI-generated answers across GPTs, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and similar platforms. Well-mapped conversational content creates clear attribution trails, making it easier for AI systems to identify and cite your original sources rather than paraphrasing or combining information inaccurately. For AmICited.com’s mission of monitoring how AI systems answer questions and cite sources, conversational content mapping represents a fundamental shift in how brands should prepare their content for the AI era. Organizations that implement proper mapping gain visibility into how their content flows through conversational AI systems, enabling better brand monitoring and ensuring accurate representation. Additionally, conversational mapping helps identify when AI systems misuse or misattribute content, providing data points for content monitoring strategies and helping organizations understand their actual reach and influence in AI-generated responses.
Challenge: Unexpected User Inputs and Out-of-Scope Questions Solution: Implement robust intent classification with confidence thresholds and develop comprehensive fallback strategies that gracefully handle unrecognized queries through clarifying questions or related topic suggestions rather than failing silently.
Challenge: Maintaining Consistency at Scale Solution: Create detailed content guidelines and intent definitions that ensure consistent responses across different conversation paths, using version control and regular audits to catch inconsistencies before they reach users.
Challenge: Balancing Structure with Flexibility Solution: Design modular content components that can be combined flexibly while maintaining underlying structural consistency, allowing natural variation without sacrificing coherence or accuracy.
Challenge: Managing Complex Context Across Long Conversations Solution: Implement context summarization techniques that extract and retain essential information from earlier exchanges without storing entire conversation histories, reducing computational overhead while maintaining relevance.
Challenge: Preventing AI Hallucinations and Fabrications Solution: Ground conversational content in verified source material, implement fact-checking mechanisms, and design fallback responses that acknowledge uncertainty rather than generating plausible-sounding but potentially false information.
Agentic AI and autonomous decision-making will increasingly enable conversational systems to take actions on behalf of users—not just provide information—requiring content mapping to extend beyond dialogue into task execution workflows. Multimodal content mapping will integrate text, images, video, and interactive elements into conversational flows, allowing AI systems to reference and present diverse content types naturally within dialogue. Emotional intelligence in conversations will become more sophisticated, with systems recognizing user frustration, confusion, or satisfaction and adapting content presentation and tone accordingly. Personalized content models will move beyond simple user segmentation to create truly individualized conversation experiences, where content structure and presentation adapt to each user’s learning style, expertise, and preferences. Real-time adaptation will allow conversational systems to modify content mapping on-the-fly based on user feedback and interaction patterns, continuously optimizing dialogue quality without requiring manual intervention. These trends suggest that conversational content mapping will evolve from a static framework into a dynamic, adaptive system that learns and improves continuously, fundamentally changing how organizations prepare content for AI-mediated interactions.
Traditional chatbot scripts follow rigid decision trees with predetermined response paths, while conversational content mapping embraces flexibility and natural language understanding. Conversational mapping adapts to unexpected user inputs, maintains context across multiple turns, and understands underlying user intent rather than just matching keywords. This creates more fluid, human-like interactions that feel responsive and intelligent.
Context retention maintains information from previous exchanges within a conversation, allowing follow-up questions to reference earlier statements without requiring users to repeat themselves. The system stores essential information from earlier messages and recalls it when relevant, creating coherent dialogue that feels natural and responsive to the user's evolving needs.
Intent recognition identifies what users actually want to accomplish, not just what they literally ask. This ensures responses address the user's true need rather than providing surface-level answers. For example, a user asking 'How do I fix my password?' actually intends to regain account access, which the system recognizes and addresses accordingly.
Businesses should conduct a comprehensive content audit by inventorying existing content and categorizing it by user intent. This involves identifying gaps where content doesn't exist for common questions, finding redundancies where multiple pieces address the same intent, and analyzing conversation logs to see where users struggle or drop off in interactions.
Key metrics include conversation completion rates, user satisfaction scores, intent recognition accuracy, context retention effectiveness, and escalation frequency. Organizations should also track where users ask clarifying questions, where they express confusion, and analyze conversation logs to identify improvement opportunities in dialogue quality.
When content is structured for conversational flow, AI systems can more accurately understand context and provide more precise citations. Well-mapped conversational content creates clear attribution trails, making it easier for AI systems to identify and cite original sources rather than paraphrasing or combining information inaccurately, reducing hallucination risks.
Various platforms support conversational content mapping including Rasa for dialogue management, Engati for chatbot flow building, Sprinklr for conversational analytics, and Call Center Studio for omnichannel conversation management. These tools provide visual flow builders, intent classification, context management, and analytics capabilities needed for effective implementation.
Conversation flows should be continuously optimized based on interaction data and user feedback. Organizations should conduct regular audits to identify where users struggle, analyze conversation logs for patterns, and implement improvements iteratively. This ongoing optimization ensures dialogue quality improves over time and content remains relevant to evolving user needs.
Conversational content mapping ensures your brand is accurately represented in AI-generated answers. Use AmICited to track how GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews cite your content across conversational interactions.

Learn what Conversational SEO is, how it differs from traditional SEO, and why citation-based visibility matters for AI systems like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perple...
Learn what content mapping is and how aligning content with buyer journey stages drives engagement, conversions, and customer loyalty. Comprehensive guide for B...

Learn how to create comprehensive content optimized for AI systems, including depth requirements, structure best practices, and formatting guidelines for AI sea...