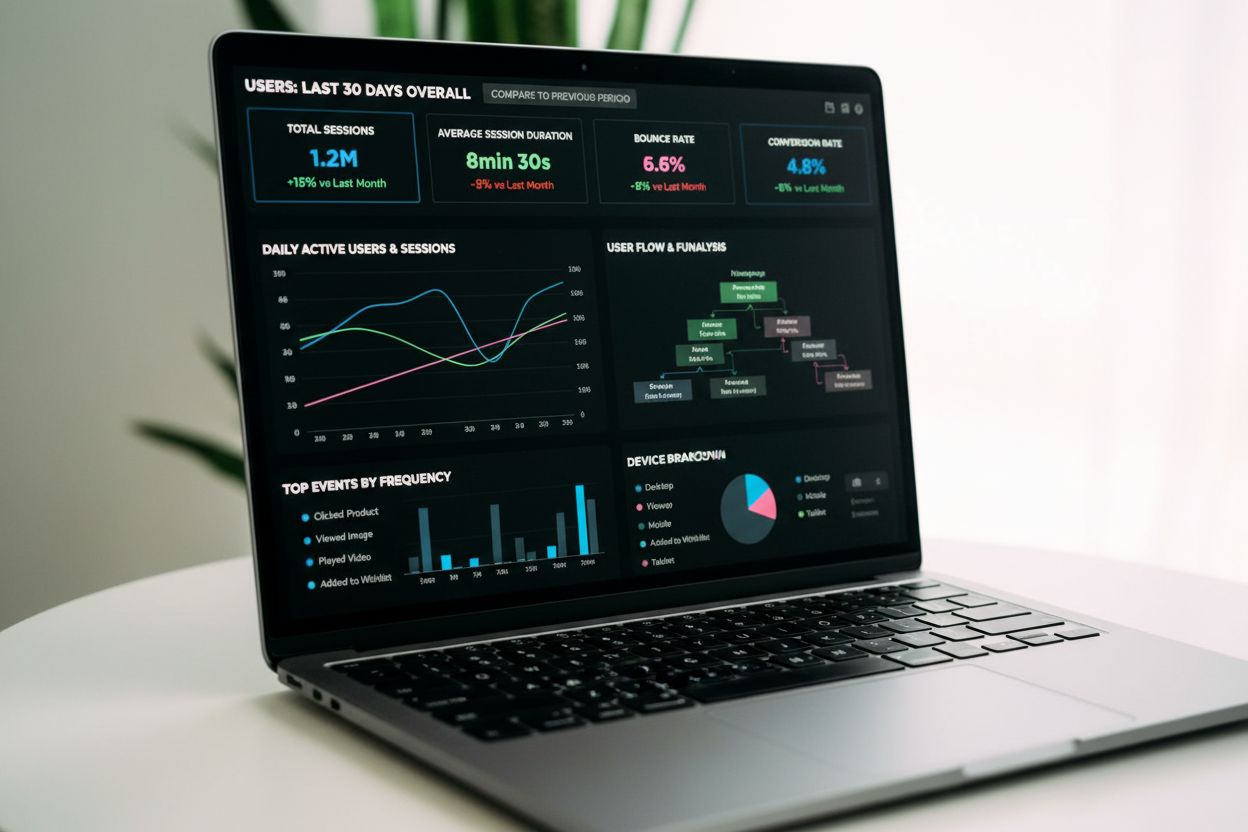
Event Tracking
Event tracking captures and records user interactions on digital platforms. Learn how event tracking works, its importance for analytics, and how it drives data...
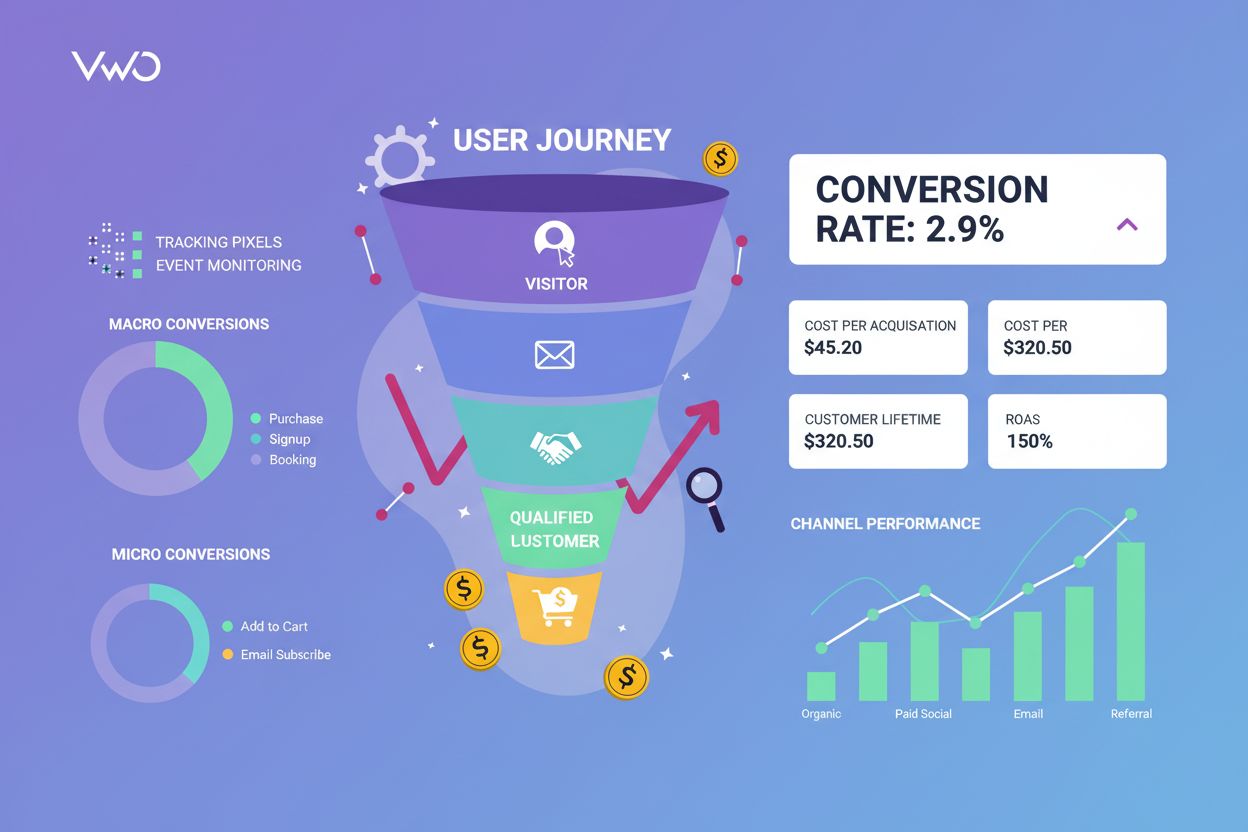
Conversion tracking is the process of monitoring and recording specific user actions that contribute to business goals, such as purchases, form submissions, signups, or downloads. It measures which marketing efforts drive meaningful results and enables data-driven optimization of campaigns and customer journeys.
Conversion tracking is the process of monitoring and recording specific user actions that contribute to business goals, such as purchases, form submissions, signups, or downloads. It measures which marketing efforts drive meaningful results and enables data-driven optimization of campaigns and customer journeys.
Conversion tracking is the systematic process of monitoring and recording specific user actions that contribute to achieving business objectives. These actions, known as conversions, represent meaningful progress toward defined goals such as completing a purchase, submitting a form, signing up for a service, downloading content, or booking a consultation. At its core, conversion tracking answers a fundamental question that every marketer must address: which marketing efforts, campaigns, and channels are actually driving results? Without conversion tracking, businesses operate with incomplete visibility into their marketing effectiveness, unable to attribute revenue to specific sources or optimize their spending with confidence. The practice has become indispensable in the digital marketing landscape, serving as the foundation for data-driven decision-making, budget allocation, and continuous performance improvement across all marketing channels and customer touchpoints.
Conversion tracking emerged as a critical practice in the early 2000s when digital marketing began to mature and businesses recognized the need to measure online campaign effectiveness beyond simple metrics like impressions and clicks. Initially, tracking relied on basic page-level analytics and simple conversion pixels placed on thank-you pages. As digital ecosystems became more complex, with multiple channels, devices, and touchpoints in the customer journey, conversion tracking evolved to become more sophisticated and comprehensive. The introduction of Google Analytics in 2005 revolutionized the field by providing accessible, detailed conversion measurement capabilities to businesses of all sizes. Over the past two decades, conversion tracking has transformed from a technical afterthought into a strategic imperative, with platforms like Google Analytics 4, Facebook Conversions API, and specialized tools like VWO and Usermaven enabling real-time, multi-channel, privacy-compliant tracking. Today, approximately 56% of marketing professionals identify conversion rate as a top key performance indicator, reflecting the central importance of conversion tracking in modern marketing strategy. The evolution continues as businesses adapt to privacy regulations, the deprecation of third-party cookies, and the rise of AI-driven marketing channels that require new approaches to measuring conversions and attribution.
Conversion tracking systems operate through several interconnected components that work together to capture, process, and analyze user behavior data. The first component is the tracking infrastructure, which includes tracking pixels, JavaScript tags, or server-side implementations that monitor user interactions across websites and applications. These technical elements are deployed through tools like Google Tag Manager (GTM), which centralizes tag management and simplifies the process of implementing tracking without requiring constant code modifications. The second component involves event definition and configuration, where businesses specify which user actions constitute conversions relevant to their goals. This requires clear alignment between marketing objectives and technical implementation, ensuring that tracked events accurately reflect business priorities. The third component is data collection and transmission, which captures conversion events in real-time and sends them to analytics platforms for processing. The fourth component encompasses attribution modeling, which assigns credit to various touchpoints and channels that contributed to conversions, helping marketers understand the true impact of their efforts. Finally, reporting and analysis tools visualize conversion data, enabling marketers to identify trends, compare performance across channels, and make informed optimization decisions. Together, these components create a comprehensive system for understanding how marketing efforts translate into business results.
Conversion tracking distinguishes between two fundamental types of conversions that serve different purposes in understanding customer behavior and optimizing marketing performance. Macro conversions represent primary business goals that directly impact revenue or core business metrics. For an ecommerce business, macro conversions include completed purchases; for a SaaS company, they include trial signups or paid plan upgrades; for a B2B service provider, they include qualified lead form submissions or demo bookings. These high-value conversions are the ultimate measure of marketing success and directly influence business profitability. Micro conversions, by contrast, are smaller, supportive actions that indicate user interest and progress toward macro conversions without representing final transactions. Examples include adding items to a shopping cart, viewing pricing pages, downloading whitepapers, watching product videos, or signing up for newsletters. While micro conversions don’t generate immediate revenue, they provide invaluable insights into user intent, engagement patterns, and potential friction points in the customer journey. By tracking both macro and micro conversions, businesses gain a complete picture of how users interact with their brand and where optimization opportunities exist. Research shows that businesses tracking both conversion types achieve significantly better results than those focusing only on final transactions, as micro conversions enable early intervention and optimization before users abandon the funnel.
| Aspect | Google Analytics 4 (GA4) | Facebook Conversions API | Server-Side Tracking | First-Party Data Tracking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Cross-device, event-based tracking | Social platform conversion measurement | Privacy-compliant, cookie-independent | Direct customer data collection |
| Cookie Dependency | Relies on cookies (first-party) | Minimal cookie reliance | No cookie dependency | No cookie dependency |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate (requires GTM or code) | Moderate (requires API setup) | High (requires server infrastructure) | Moderate (requires data collection strategy) |
| Privacy Compliance | GDPR/CCPA compatible with proper setup | GDPR/CCPA compatible | Highest privacy compliance | Highest privacy compliance |
| Real-Time Reporting | Yes, with slight delay | Yes, with slight delay | Yes, real-time | Yes, real-time |
| Attribution Modeling | Multiple models available | Limited to platform data | Customizable models | Fully customizable |
| Cost | Free with premium options | Free with API costs | Higher infrastructure costs | Variable based on implementation |
| Best For | Comprehensive web analytics | Social media ROI measurement | Enterprise privacy requirements | Direct customer relationships |
Conversion tracking implementation varies depending on business needs, technical capabilities, and privacy requirements, with several established methods available to modern marketers. Pixel-based tracking, the traditional approach, involves placing a small piece of code (a tracking pixel) on conversion pages that fires when users complete desired actions. This method is simple to implement but increasingly limited by browser privacy features and cookie restrictions. Tag-based tracking through Google Tag Manager provides more flexibility, allowing marketers to manage multiple tracking tags from a centralized interface without modifying website code directly. This approach has become industry standard for many organizations due to its ease of use and reduced dependency on developer resources. Event-based tracking, popularized by Google Analytics 4, captures specific user interactions as discrete events rather than page views, enabling more granular measurement of user behavior and conversion paths. Server-side tracking represents the most advanced approach, capturing conversion events on the server rather than the browser, which bypasses cookie restrictions and provides superior data accuracy and privacy compliance. This method is increasingly adopted by enterprises and privacy-conscious organizations. API-based tracking, used by platforms like Facebook Conversions API, allows direct transmission of conversion data from business systems to advertising platforms, enabling accurate measurement even when browser-based tracking fails. Each method has distinct advantages and limitations, and many sophisticated organizations employ multiple methods simultaneously to ensure comprehensive, accurate conversion measurement across all channels and devices.
Conversion tracking directly impacts business profitability by enabling precise measurement of marketing return on investment and guiding strategic budget allocation decisions. By tracking conversions, businesses can calculate critical metrics like Cost Per Acquisition (CPA), which reveals how much they spend to acquire each customer, and Return on Ad Spend (ROAS), which shows how much revenue each dollar of advertising generates. These metrics transform marketing from an expense category into an investment with measurable returns, enabling CFOs and business leaders to justify marketing budgets with concrete data. For example, a business with a ROAS of 5:1 generates $5 in revenue for every $1 spent on advertising, a compelling justification for continued investment. Conversion tracking also enables businesses to identify their most efficient marketing channels and campaigns, allowing them to reallocate budgets from underperforming initiatives to high-performing ones. This optimization can dramatically improve overall marketing efficiency; studies show that businesses actively optimizing based on conversion data achieve 20-30% improvements in marketing ROI within the first year. Furthermore, conversion tracking reveals the true Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) of customers acquired through different channels, enabling sophisticated decisions about acceptable acquisition costs. A channel that appears expensive based on immediate conversion costs might be highly profitable when considering long-term customer value, while another channel might appear efficient initially but generate low-value customers with poor retention. This comprehensive understanding of conversion economics enables businesses to make strategic decisions that maximize long-term profitability rather than optimizing for short-term metrics.
As artificial intelligence increasingly influences consumer decision-making through platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and Google AI Overviews, conversion tracking has evolved to encompass AI-generated content and citations. AmICited and similar AI monitoring platforms track how brands appear in AI responses and measure the conversions those citations drive, creating a new dimension of conversion tracking beyond traditional digital marketing channels. When a brand is mentioned in an AI response, users may click through to the brand’s website, leading to conversions that can be tracked and attributed to AI visibility. This represents a significant shift in how businesses must think about conversion tracking, as AI responses increasingly influence user behavior and purchasing decisions. Approximately 62% of consumers now use AI tools in their research process, making AI visibility a critical component of the customer journey. Conversion tracking in the AI context requires businesses to implement UTM parameters and tracking codes that identify traffic originating from AI platform citations, enabling attribution of conversions to specific AI mentions. This integration of AI monitoring with traditional conversion tracking creates a more complete picture of how different information sources influence customer behavior. Organizations that successfully track conversions from AI sources gain competitive advantages by understanding which AI platforms drive the most valuable traffic, enabling them to optimize their content and positioning for AI visibility. The convergence of conversion tracking and AI monitoring represents the future of digital marketing measurement, where businesses must understand conversion paths across both traditional and emerging AI-powered channels.
Conversion tracking generates numerous metrics that provide different perspectives on marketing performance and customer behavior. Conversion Rate, the percentage of visitors who complete desired actions, serves as the foundational metric for evaluating campaign effectiveness. The average conversion rate across industries is 2.9%, though this varies significantly by sector, with some industries achieving rates above 5% and others below 2%. Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) measures the average expense required to acquire each customer, enabling businesses to evaluate whether acquisition costs align with customer value. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) represents the total revenue expected from a customer across their entire relationship with the business, providing crucial context for acquisition cost decisions. Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) directly measures advertising efficiency by comparing revenue generated to advertising spend, with healthy ROAS typically ranging from 3:1 to 5:1 depending on industry and business model. Bounce Rate indicates the percentage of visitors who leave without taking any action, revealing potential issues with page relevance or user experience. Click-Through Rate (CTR) measures the percentage of users who click on ads or links, indicating creative effectiveness and audience relevance. Revenue Per Visitor (RPV) calculates average revenue generated per website visit, helping businesses understand monetization efficiency. Retention Rate measures the percentage of customers who continue engaging with the business over time, reflecting customer satisfaction and product value. Customer Churn Rate indicates the percentage of customers discontinuing their relationship with the business, serving as an early warning indicator of satisfaction or competitive issues. Net Promoter Score (NPS) measures customer willingness to recommend the business, providing insight into brand loyalty and satisfaction. Together, these metrics create a comprehensive framework for understanding conversion performance and identifying optimization opportunities.
The future of conversion tracking is being fundamentally reshaped by privacy regulations and the deprecation of third-party cookies, requiring businesses to adopt new approaches to measurement and attribution. GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California have established strict requirements for data collection and user consent, making traditional cookie-based tracking increasingly risky and unreliable. Google’s announcement of third-party cookie deprecation in Chrome, combined with similar moves by other browsers, has accelerated the shift toward privacy-compliant tracking methods. Server-side tracking has emerged as the preferred solution, capturing conversion events on business servers rather than user browsers, enabling accurate measurement without relying on cookies or fingerprinting. First-party data collection through direct customer relationships, email lists, and CRM systems provides another avenue for conversion tracking that respects privacy while maintaining measurement accuracy. Consent management platforms enable businesses to collect conversion data only from users who have explicitly consented, ensuring compliance while maintaining measurement capabilities. The shift toward privacy-compliant tracking represents not just a regulatory necessity but also a competitive advantage, as businesses that successfully implement these methods maintain accurate data while competitors struggle with data loss from cookie restrictions. Forward-thinking organizations are investing in first-party data strategies, building direct customer relationships, and implementing server-side tracking infrastructure that will remain effective regardless of future privacy regulations or browser changes. This evolution reflects a broader industry recognition that sustainable competitive advantage comes from respecting user privacy while still delivering personalized, effective marketing experiences.
Conversion tracking continues to evolve in response to technological changes, regulatory pressures, and shifting consumer behavior patterns, with several significant trends shaping the future of the discipline. AI-powered attribution is increasingly sophisticated, using machine learning algorithms to understand complex, multi-touch customer journeys and assign credit more accurately than traditional attribution models. Unified measurement platforms are consolidating data from multiple sources—web, mobile, email, social, and increasingly AI platforms—into single dashboards that provide comprehensive conversion visibility. Real-time optimization powered by conversion data enables businesses to adjust campaigns, messaging, and targeting instantly based on conversion performance rather than waiting for periodic analysis. Privacy-first measurement continues advancing, with solutions like Aggregate Reporting API and Privacy Sandbox initiatives enabling conversion measurement without individual-level tracking. Cross-device tracking is becoming more sophisticated, enabling businesses to understand how users move between devices throughout their customer journey and attribute conversions accurately across devices. Conversion rate optimization (CRO) is increasingly integrated with conversion tracking, with platforms enabling rapid testing and optimization based on real-time conversion data. AI visibility tracking through platforms like AmICited represents an emerging frontier, enabling businesses to measure conversions driven by AI-generated content and citations. The convergence of these trends suggests that future conversion tracking will be more sophisticated, privacy-compliant, real-time, and integrated across channels than ever before. Organizations that invest in modern conversion tracking infrastructure and capabilities today will be best positioned to compete effectively in this evolving landscape, maintaining accurate measurement while respecting privacy and adapting to new channels and technologies as they emerge.
Macro conversions are primary business goals like purchases or paid subscriptions that directly impact revenue, while micro conversions are smaller supportive actions like adding items to cart or downloading content that indicate user intent and move customers closer to macro conversions. Both are essential for understanding the complete customer journey and identifying optimization opportunities at each funnel stage.
Conversion tracking integrates with AI monitoring platforms like AmICited to measure how brand mentions and citations in AI responses (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Google AI Overviews) drive user actions. By tracking conversions from AI-generated content, businesses can attribute revenue and engagement to AI visibility, similar to traditional digital marketing attribution.
The average conversion rate across all industries is approximately 2.9% as of 2025, though this varies significantly by sector. For example, Google Ads conversion rates average 7.04%, while ecommerce and fashion industries typically see lower conversion rates. Understanding your industry benchmark helps set realistic conversion goals and identify optimization opportunities.
Modern conversion tracking must balance data collection with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Server-side tracking and first-party data approaches ensure accurate conversion measurement without relying on third-party cookies, which are increasingly restricted. Privacy-compliant tracking maintains data accuracy while respecting user privacy and regulatory requirements.
Conversion rate is calculated by dividing total conversions by total clicks or visitors, then multiplying by 100. For example, 100 conversions from 1,000 visitors equals a 10% conversion rate. ROAS (Return on Ad Spend) is calculated by dividing total revenue from conversions by total ad spend; a ROAS of 5 means you earn $5 for every $1 spent on advertising.
Leading conversion tracking tools include Google Analytics 4 (GA4) for event-based tracking, Google Tag Manager (GTM) for tag management, Facebook Conversions API for privacy-compliant tracking, and specialized platforms like VWO and Usermaven. The best choice depends on your business model, privacy requirements, and need for cross-platform attribution and real-time insights.
Conversion tracking provides the data foundation for marketing attribution by recording which touchpoints and channels drive conversions. Attribution models (first-touch, last-touch, linear, time-decay) then assign credit to these touchpoints, helping marketers understand which campaigns and channels truly drive ROI and optimize budget allocation accordingly.
Yes, modern conversion tracking increasingly relies on cookieless methods including server-side tracking, first-party data collection, and privacy-focused platforms. These approaches capture conversion events on the server rather than the browser, bypassing cookie restrictions while maintaining accuracy and compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Event tracking captures and records user interactions on digital platforms. Learn how event tracking works, its importance for analytics, and how it drives data...
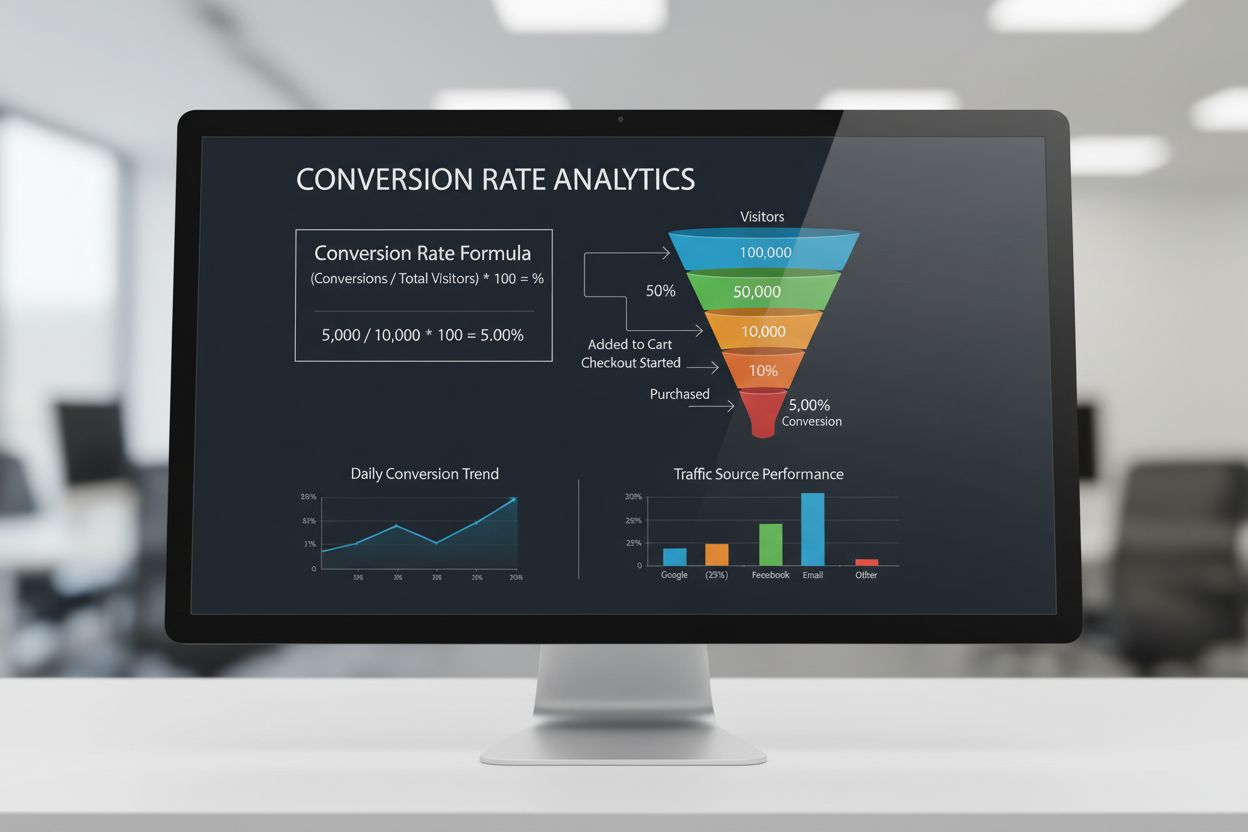
Conversion rate measures the percentage of visitors completing desired actions. Learn the formula, industry benchmarks, types, and optimization strategies for t...

Goal tracking is the systematic monitoring of specific user objectives and performance metrics. Learn how to implement effective goal tracking systems for AI mo...