
Crawl Frequency
Crawl frequency is how often search engines and AI crawlers visit your site. Learn what affects crawl rates, why it matters for SEO and AI visibility, and how t...
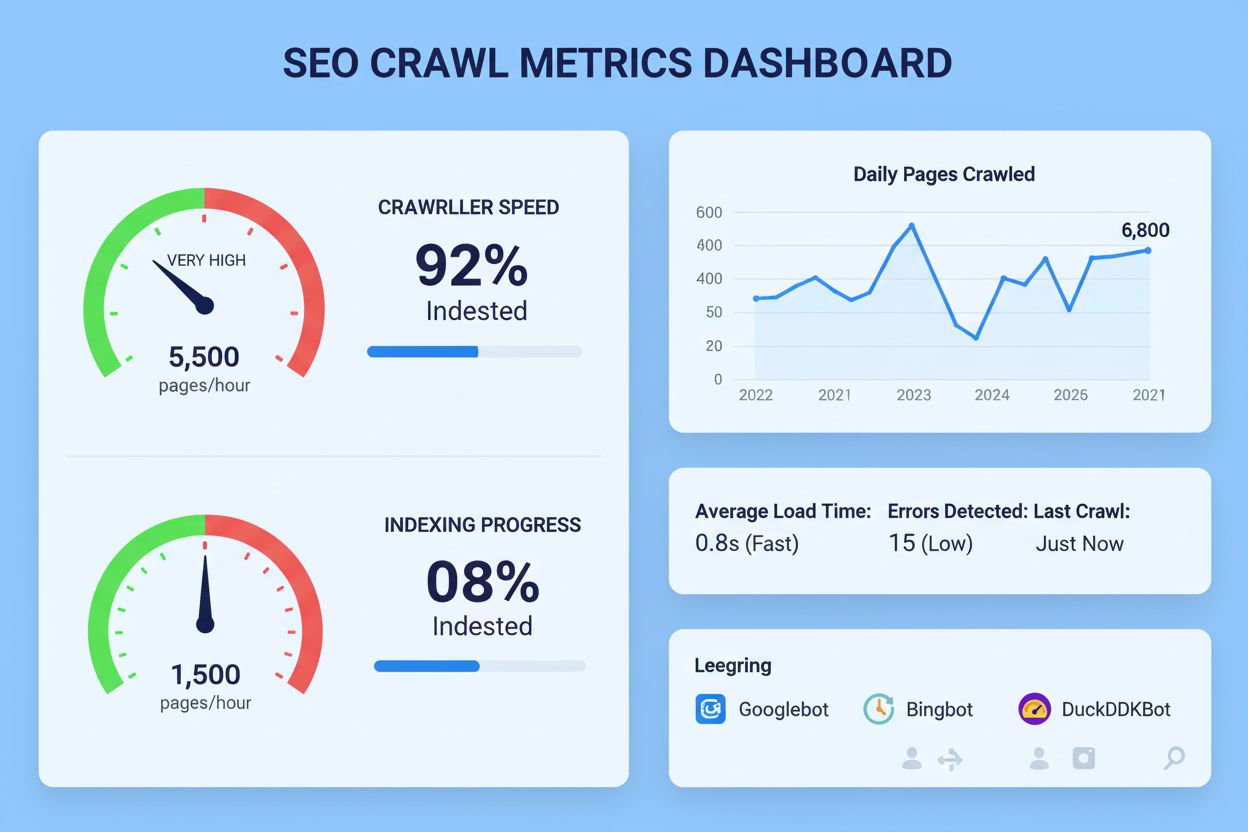
Crawl rate is the speed at which search engine bots, such as Googlebot, request and fetch pages from a website. It represents the number of URLs a search engine crawler accesses per second or per day, directly influencing how quickly new or updated content gets indexed and appears in search results.
Crawl rate is the speed at which search engine bots, such as Googlebot, request and fetch pages from a website. It represents the number of URLs a search engine crawler accesses per second or per day, directly influencing how quickly new or updated content gets indexed and appears in search results.
Crawl rate is the speed at which search engine bots, particularly Googlebot, request and fetch pages from your website. It represents the number of URLs a search engine crawler accesses per second or per day, directly influencing how quickly new or updated content gets discovered, indexed, and appears in search results. Unlike crawl budget, which defines the total number of pages a search engine will crawl, crawl rate specifically measures the velocity of that crawling activity. This metric is critical for website owners because it determines whether your content reaches search engine indexes in a timely manner, affecting both visibility and traffic potential. For large websites with thousands of pages or frequently updated content, crawl rate becomes a strategic consideration in technical SEO planning.
The concept of crawl rate emerged as search engines scaled to index billions of web pages. In the early days of the internet, search engines could crawl most websites thoroughly, but as the web expanded exponentially, Google and other search engines had to develop sophisticated algorithms to allocate their crawling resources efficiently. According to recent data from HTTP Archive, 83.9% of mobile sites and 83.5% of desktop sites return proper robots.txt responses, indicating widespread awareness of crawl management. The distinction between crawl rate and crawl budget became increasingly important as websites grew larger and more complex. Googlebot operates across multiple data centers worldwide, and its crawling behavior reflects a balance between the search engine’s desire to keep content fresh and the need to avoid overwhelming website servers. Research from Cloudflare shows that crawler traffic increased by 18% from May 2024 to May 2025, with Googlebot traffic growing by 96%, demonstrating the increasing importance of understanding and optimizing crawl behavior. For enterprises managing large digital properties, crawl rate optimization has become a core component of technical SEO strategy, directly impacting content visibility and search performance.
| Concept | Definition | Measurement | Impact on Indexing | Control Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crawl Rate | Speed at which bots fetch pages (URLs/second) | Requests per second or per day | Determines indexing speed | Indirect (optimize conditions) |
| Crawl Budget | Total pages crawled in a time period | Total URLs crawled daily/weekly | Determines coverage scope | Indirect (manage inventory) |
| Crawl Frequency | How often a specific page is revisited | Visits per page per time period | Determines freshness | Indirect (content updates) |
| Crawl Demand | Search engine’s desire to crawl your site | Algorithmic assessment | Determines priority allocation | Indirect (content quality) |
| Crawl Capacity Limit | Maximum simultaneous connections allowed | Parallel connections available | Determines maximum speed | Indirect (server capacity) |
| Indexing Speed | Time from crawl to index inclusion | Days/hours to appear in results | Direct visibility impact | Indirect (crawl optimization) |
Crawl rate operates through a sophisticated system of parallel connections and request throttling that search engines use to balance efficiency with server responsibility. When Googlebot initiates a crawl, it establishes multiple simultaneous connections to your server—typically between 4-10 parallel threads depending on your site’s capacity. Each thread makes requests at a controlled pace, measured in URLs per second, which collectively determines your overall crawl rate. The Time to First Byte (TTFB) plays a crucial role in this calculation; if your server takes 500 milliseconds to respond to each request, a crawler with 4 threads operating at 5 URLs per second maximum can theoretically crawl only 2 URLs per second per thread, resulting in actual throughput of approximately 8 URLs per second across all threads. Search engines monitor your server’s response patterns continuously, automatically adjusting the crawl rate upward when responses are fast and stable, and downward when they detect slowness or errors. HTTP status codes provide critical feedback signals—200 responses indicate healthy pages, 304 responses signal unchanged content (allowing cached versions), while 5XX errors trigger immediate crawl rate reduction to prevent server overload. This dynamic adjustment system ensures that crawl rate remains responsive to your site’s actual capacity, preventing the accidental Denial of Service (CDoS) scenarios that can occur when crawlers operate too aggressively.
The practical implications of crawl rate extend far beyond technical metrics—they directly affect your website’s competitive position in search results. A slow crawl rate means new content takes longer to appear in search results, which is particularly damaging for time-sensitive industries like news, e-commerce, and financial services where content freshness directly correlates with traffic and revenue. Research indicates that pages crawled and indexed within 24 hours capture significantly more organic traffic than those taking 3-7 days, especially for trending topics and breaking news. For e-commerce sites, a poor crawl rate can mean product updates, price changes, and inventory adjustments don’t reflect in search results quickly enough, leading to customer frustration and lost sales. Large websites with millions of pages face the most acute crawl rate challenges, as they must compete for limited crawl resources while managing complex site architectures. According to Google’s own guidance, sites with 1 million+ unique pages that update weekly, or sites with 10,000+ pages updating daily, require active crawl rate management to ensure important content receives adequate attention. The business impact becomes even more critical when considering that over 78% of enterprises now use AI-driven content monitoring tools to track their brand presence, and crawl rate directly affects how quickly your content appears in AI training datasets and subsequently in AI-generated responses across platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Different search engines and AI platforms exhibit distinct crawl rate behaviors based on their infrastructure and priorities. Googlebot, the primary search engine crawler, operates with sophisticated algorithms that adjust crawl rate based on perceived site health, content quality, and server capacity. Google’s mobile-first indexing approach means that crawl rate for mobile versions of your site often takes precedence, and mobile page speed directly influences how aggressively Googlebot crawls your desktop content. Bingbot, Microsoft’s crawler, typically operates at lower crawl rates than Googlebot but follows similar principles of respecting server capacity and adjusting based on content freshness. For AI monitoring platforms like AmICited, understanding crawl rate becomes crucial because these platforms track how quickly your website content gets indexed and subsequently appears in AI-generated responses. Perplexity, Claude, and other AI systems rely on indexed web content, meaning your crawl rate indirectly determines how quickly your brand mentions and content appear in AI citations. The emergence of GPTBot and other AI-specific crawlers has added complexity to crawl rate management; according to Cloudflare data, GPTBot traffic grew by 305% from May 2024 to May 2025, indicating that AI training data collection now represents a significant portion of overall crawl activity. Website owners must now consider not just traditional search engine crawl rates but also the crawl rates of AI training bots, which may have different patterns and priorities than search engines.
Optimizing crawl rate requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses both technical infrastructure and content strategy. First, audit your current crawl rate using Google Search Console’s Crawl Stats report, which provides detailed metrics on crawl frequency, response times, and availability issues. The report shows exactly how many requests Google makes daily, average response times, and any server errors that might be throttling crawl activity. Second, optimize your server infrastructure for speed and reliability—this is the single most impactful factor you can control. Implement caching strategies, use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs), optimize database queries, and ensure your hosting can handle peak crawl loads. Third, maintain a clean and efficient URL structure that makes it easy for crawlers to discover and navigate your content. Avoid excessive URL parameters, session identifiers, and faceted navigation that create duplicate content and waste crawl budget. Fourth, implement proper XML sitemaps that include only high-quality, indexable content and update them regularly when you publish new pages or make significant updates. Include the <lastmod> tag to signal content freshness to search engines. Fifth, strengthen your internal linking structure by ensuring important pages have multiple contextual links from authoritative pages on your site, particularly from your homepage and category pages. Sixth, use robots.txt strategically to block crawling of low-value pages like admin sections, duplicate content, and infinite scroll pages, but never block critical resources like CSS or JavaScript files that search engines need to render your pages properly.
Effective crawl rate management requires ongoing monitoring and proactive troubleshooting. Use Google Search Console’s Crawl Stats report as your primary monitoring tool, checking it weekly or biweekly to identify trends and anomalies. Look for sudden drops in crawl requests, which might indicate robots.txt issues, server errors, or content quality problems. Analyze your server logs to correlate crawl patterns with server performance metrics—if you see spikes in response times coinciding with drops in crawl requests, your server capacity is likely the limiting factor. Monitor HTTP status codes carefully; a sudden increase in 5XX errors will trigger immediate crawl rate reduction by search engines. Check for soft 404 errors, which are pages that return a 200 status code but contain little or no content—these waste crawl budget and should be fixed by returning proper 404 status codes. Examine your robots.txt file for unintended blocks that might be preventing crawlers from accessing important content or critical resources. Test your site’s performance using tools like PageSpeed Insights and GTmetrix to identify speed bottlenecks that might be limiting crawl rate. If you experience a crawl rate spike (sudden increase in crawl requests), check your Crawl Stats report to identify which crawler type is responsible—if it’s AdsBot, you may have created too many Dynamic Search Ad targets; if it’s Googlebot, you may have recently added significant new content or unblocked previously restricted sections.
The landscape of crawl rate is evolving rapidly as AI systems become increasingly important to content discovery and brand visibility. The rise of AI-specific crawlers like GPTBot represents a fundamental shift in how content gets discovered and distributed, with these crawlers now accounting for a significant portion of overall crawl activity. This trend suggests that crawl rate optimization will increasingly need to account for multiple crawler types with different priorities and behaviors, not just traditional search engines. The integration of crawl rate monitoring into AI citation tracking platforms like AmICited indicates that businesses now need to understand crawl rate not just for search visibility but for AI visibility—ensuring their content appears in AI-generated responses and citations. As AI systems become more sophisticated in their content sourcing, crawl rate will become an even more critical factor in determining brand presence across the AI-powered search landscape. Future developments may include more granular crawl rate controls, allowing website owners to specify different crawl rates for different crawler types or content categories. The emergence of real-time indexing technologies may eventually reduce the importance of crawl rate by enabling near-instantaneous content discovery, but this remains years away for most websites. For now, crawl rate optimization remains a core technical SEO practice that directly impacts both traditional search visibility and emerging AI visibility, making it essential for any organization serious about maintaining a strong digital presence. Organizations that master crawl rate optimization today will be better positioned to capitalize on future developments in search and AI-powered content discovery.
Crawl rate refers to the speed at which search engines crawl your pages (URLs per second), while crawl budget is the total number of pages a search engine will crawl within a specific time period. Think of crawl budget as the total allocation and crawl rate as how fast that allocation is being used. Both work together to determine how efficiently your site gets indexed.
Crawl rate indirectly affects SEO by determining how quickly new or updated content gets discovered and indexed. While crawl rate itself isn't a direct ranking factor, faster indexing means your content can appear in search results sooner, potentially capturing more organic traffic. Sites with poor crawl rates may experience delays in content visibility, especially for time-sensitive information.
Key factors include server response time (TTFB), page load speed, site structure and internal linking, content freshness and update frequency, domain authority and page popularity, and server capacity. Additionally, the quality and relevance of your content affects how often search engines prioritize crawling your pages. HTTP status codes and availability issues also significantly impact crawl rate.
Use Google Search Console's Crawl Stats report to monitor crawl frequency, response times, and availability issues. Improve crawl rate by optimizing page speed, fixing broken links, maintaining updated XML sitemaps, improving internal linking structure, and ensuring your server can handle crawl requests. Avoid blocking important resources in robots.txt and consolidate duplicate content to maximize crawl efficiency.
A healthy crawl rate depends on your site size and update frequency. Large sites with frequently changing content should see consistent crawl activity, while smaller sites may be crawled less frequently. Monitor your Crawl Stats report for trends rather than absolute numbers. If new pages are indexed within 3-7 days and updates appear promptly, your crawl rate is likely healthy.
You cannot directly request Google to increase crawl rate, but you can optimize conditions that encourage it. Improve server performance and page speed, maintain fresh content with regular updates, use XML sitemaps effectively, strengthen internal linking, and ensure your site is mobile-friendly. Google automatically adjusts crawl rate based on your site's capacity and content value.
For platforms like AmICited that monitor brand mentions in AI systems, understanding crawl rate is crucial because it affects how quickly AI training data sources are updated. Faster crawl rates mean your website content is indexed more frequently, increasing the likelihood of your brand appearing in AI-generated responses and citations across platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Crawl frequency is how often search engines and AI crawlers visit your site. Learn what affects crawl rates, why it matters for SEO and AI visibility, and how t...

Crawl budget is the number of pages search engines crawl on your website within a timeframe. Learn how to optimize crawl budget for better indexing and SEO perf...
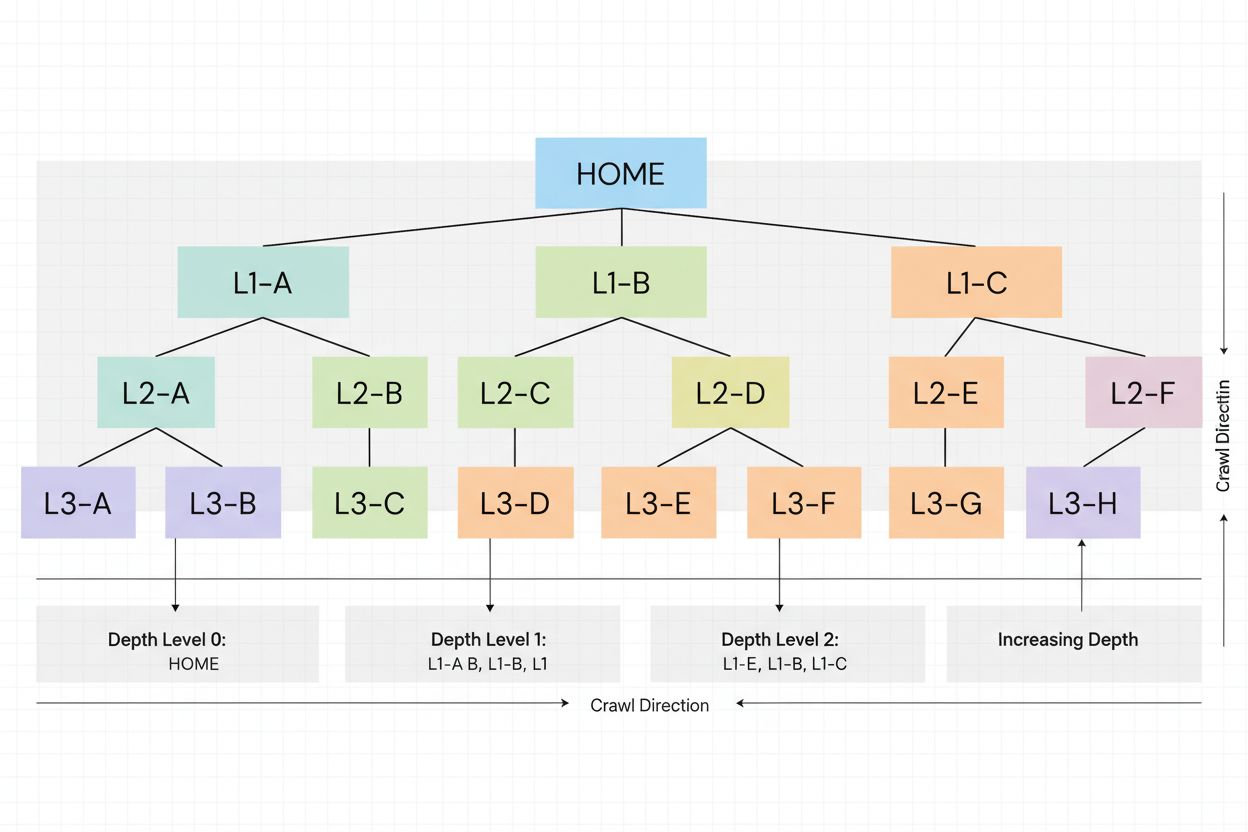
Crawl depth is how deep search engine bots navigate your site structure. Learn why it matters for SEO, how it affects indexation, and strategies to optimize cra...