
How to Ensure AI Crawlers See All Your Content
Learn how to make your content visible to AI crawlers like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google's AI. Discover technical requirements, best practices, and monitoring...
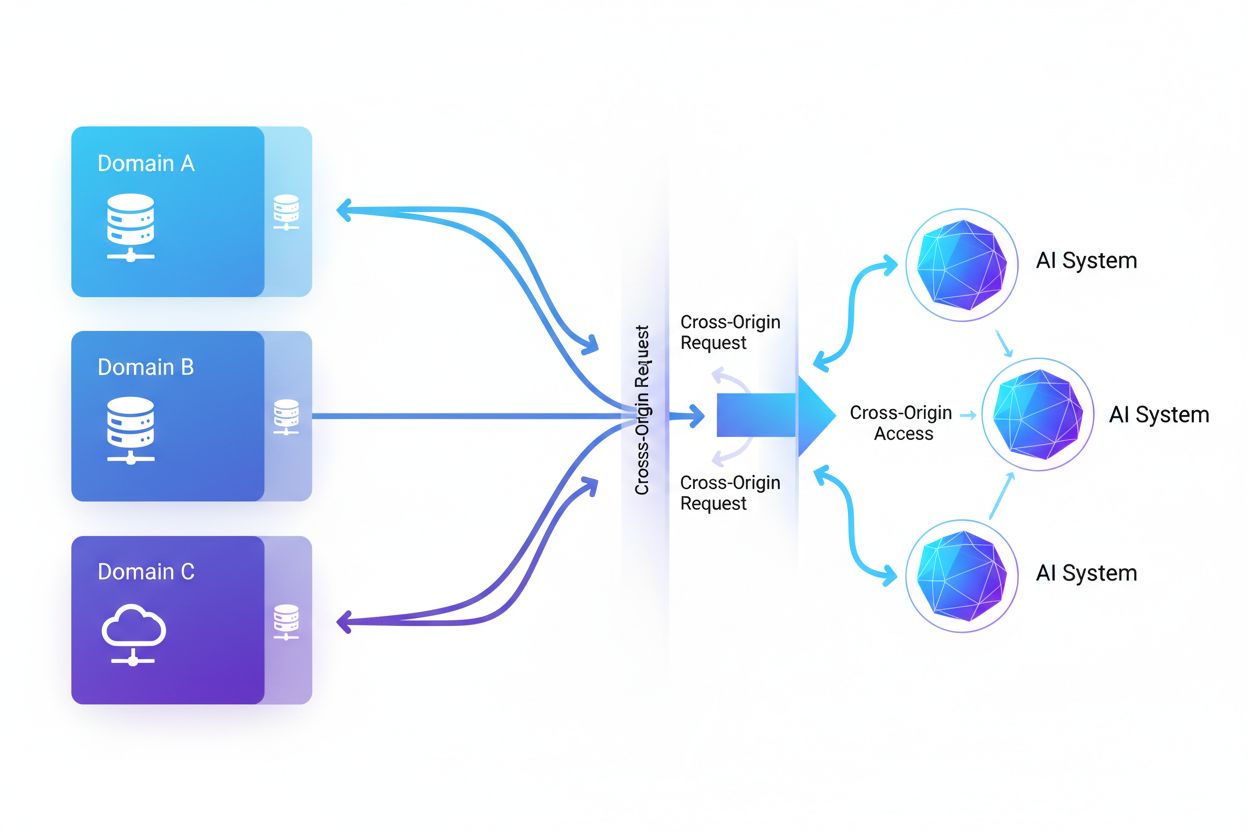
Cross-Origin AI Access refers to the ability of artificial intelligence systems and web crawlers to request and retrieve content from domains different from their origin, governed by security mechanisms like CORS. It encompasses how AI companies scale data collection for training large language models while navigating cross-origin restrictions. Understanding this concept is critical for content creators and website owners to protect intellectual property and maintain control over how their content is used by AI systems. Visibility into cross-origin AI activity helps distinguish between legitimate AI access and unauthorized scraping.
Cross-Origin AI Access refers to the ability of artificial intelligence systems and web crawlers to request and retrieve content from domains different from their origin, governed by security mechanisms like CORS. It encompasses how AI companies scale data collection for training large language models while navigating cross-origin restrictions. Understanding this concept is critical for content creators and website owners to protect intellectual property and maintain control over how their content is used by AI systems. Visibility into cross-origin AI activity helps distinguish between legitimate AI access and unauthorized scraping.
Cross-Origin AI Access refers to the ability of artificial intelligence systems and web crawlers to request and retrieve content from domains different from their origin, governed by security mechanisms like Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS). As AI companies scale their data collection efforts to train large language models and other AI systems, understanding how these systems navigate cross-origin restrictions has become critical for content creators and website owners. The challenge lies in distinguishing between legitimate AI access for search indexing and unauthorized scraping for model training, making visibility into cross-origin AI activity essential for protecting intellectual property and maintaining control over how content is used.
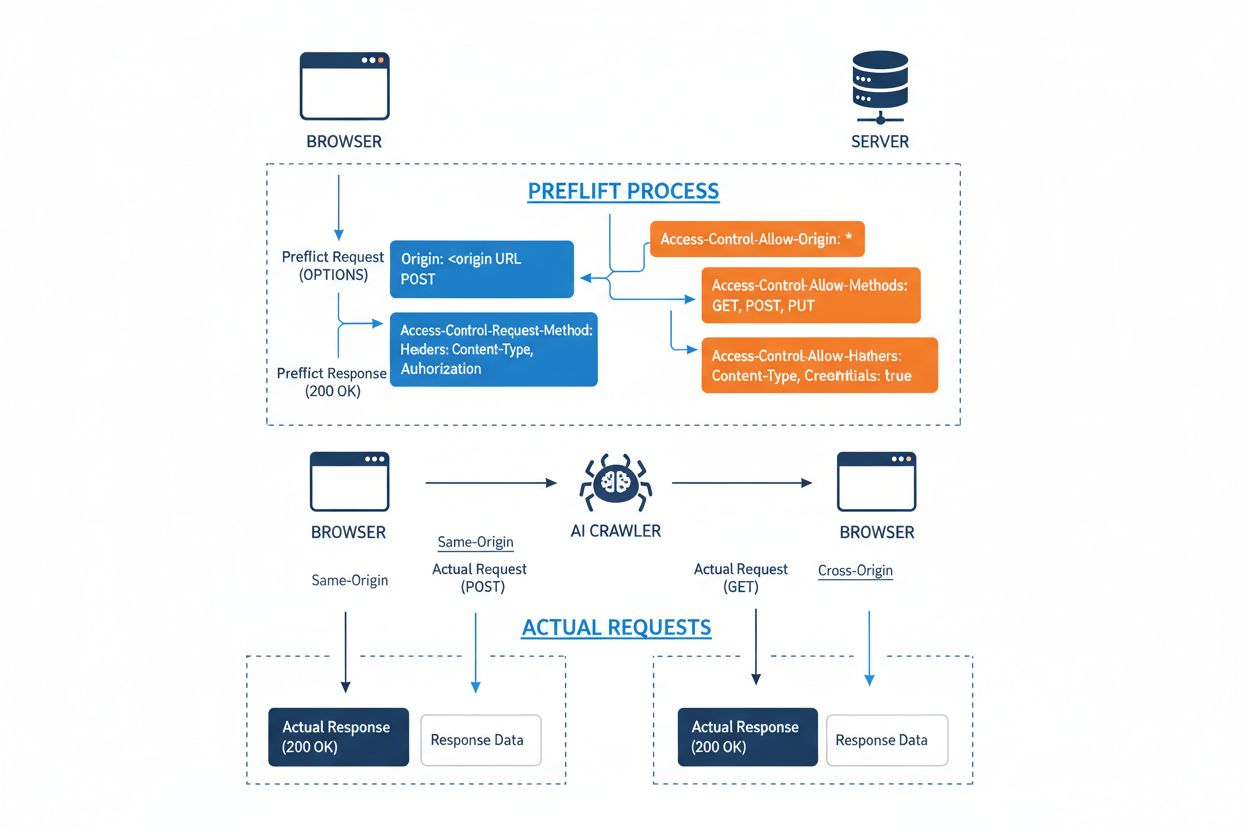
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is an HTTP-header-based security mechanism that allows servers to specify which origins (domains, schemes, or ports) can access their resources. When an AI crawler or any client attempts to access a resource from a different origin, the browser or client initiates a preflight request using the OPTIONS HTTP method to check whether the server permits the actual request. The server responds with specific CORS headers that dictate access permissions, including which origins are allowed, what HTTP methods are permitted, which headers can be included, and whether credentials like cookies or authentication tokens can be sent with the request.
| CORS Header | Purpose |
|---|---|
Access-Control-Allow-Origin | Specifies which origins can access the resource (* for all, or specific domains) |
Access-Control-Allow-Methods | Lists permitted HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.) |
Access-Control-Allow-Headers | Defines which request headers are allowed (Authorization, Content-Type, etc.) |
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials | Determines if credentials (cookies, auth tokens) can be included in requests |
Access-Control-Max-Age | Specifies how long preflight responses can be cached (in seconds) |
Access-Control-Expose-Headers | Lists response headers that clients can access |
AI crawlers interact with CORS by respecting these headers when properly configured, though many sophisticated bots attempt to circumvent these restrictions by spoofing user agents or using proxy networks. The effectiveness of CORS as a defense against unauthorized AI access depends entirely on proper server configuration and the crawler’s willingness to honor the restrictions—a critical distinction that has become increasingly important as AI companies compete for training data.
The landscape of AI crawlers accessing the web has expanded dramatically, with several major players dominating cross-origin access patterns. According to Cloudflare’s analysis of network traffic, the most prevalent AI crawlers include:
These crawlers generate billions of requests monthly, with some like Bytespider and GPTBot accessing the majority of the internet’s publicly available content. The sheer volume and aggressive nature of this activity has prompted major platforms including Reddit, Twitter/X, Stack Overflow, and numerous news organizations to implement blocking measures.
Misconfigured CORS policies create significant security vulnerabilities that AI crawlers can exploit to access sensitive data without authorization. When servers set Access-Control-Allow-Origin: * without proper validation, they inadvertently permit any origin—including malicious AI scrapers—to access resources that should be restricted. A particularly dangerous configuration occurs when Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true is combined with wildcard origin settings, allowing attackers to steal authenticated user data by making cross-origin requests that include session cookies or authentication tokens.
Common CORS misconfigurations include dynamically reflecting the Origin header directly into the Access-Control-Allow-Origin response without validation, which effectively allows any origin to access the resource. Overly permissive allow-lists that fail to properly validate domain boundaries can be exploited through subdomain attacks or prefix manipulation. Additionally, many organizations fail to implement proper validation of the Origin header itself, making them vulnerable to spoofed requests. The consequences of these vulnerabilities extend beyond data theft to include unauthorized training of AI models on proprietary content, competitive intelligence gathering, and violation of intellectual property rights—risks that tools like AmICited.com help organizations monitor and quantify.
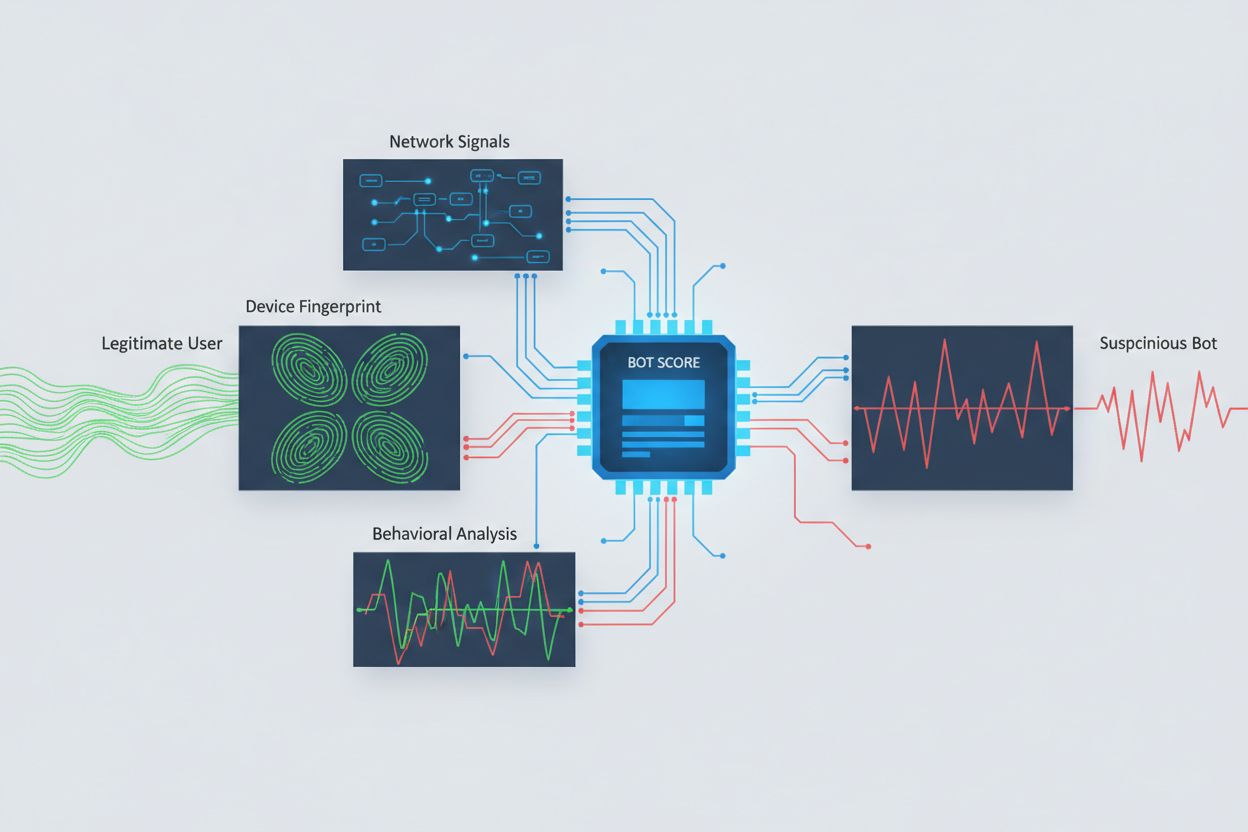
Identifying AI crawlers attempting cross-origin access requires analyzing multiple signals beyond simple user agent strings, which are trivially spoofed. User agent analysis remains a first-line detection method, as many AI crawlers identify themselves through specific user agent strings like “GPTBot/1.0” or “ClaudeBot/1.0,” though sophisticated crawlers deliberately mask their identity by impersonating legitimate browsers. Behavioral fingerprinting analyzes how requests are made—examining patterns like request timing, the sequence of pages accessed, the presence or absence of JavaScript execution, and interaction patterns that differ fundamentally from human browsing behavior.
Network signal analysis provides deeper detection capabilities by examining TLS handshake signatures, IP reputation, DNS resolution patterns, and connection characteristics that reveal bot activity even when user agents are spoofed. Device fingerprinting aggregates dozens of signals including browser version, screen resolution, installed fonts, operating system details, and JA3 TLS fingerprints to create unique identifiers for each request source. Advanced detection systems can identify when multiple sessions originate from the same device or script, catching distributed scraping attempts that try to evade rate-limiting by spreading requests across many IP addresses. Organizations can leverage these detection methods through security platforms and monitoring services to gain visibility into which AI systems are accessing their content and how they’re attempting to circumvent restrictions.
Organizations employ multiple complementary strategies to block or control cross-origin AI access, recognizing that no single method provides complete protection:
User-agent: GPTBot followed by Disallow: /) provides a polite but voluntary mechanism; effective for well-behaved crawlers but easily ignored by determined scrapersThe most effective defense combines multiple layers, as determined attackers will exploit weaknesses in any single-method approach. Organizations must continuously monitor which blocking methods are working and adapt as crawlers evolve their evasion techniques.
Effective management of cross-origin AI access requires a comprehensive, layered approach that balances security with operational needs. Organizations should implement a tiered strategy beginning with basic controls like robots.txt and user agent filtering, then progressively add more sophisticated detection and blocking mechanisms based on observed threats. Continuous monitoring is essential—tracking which AI systems are accessing your content, how frequently they’re making requests, and whether they’re respecting your restrictions provides the visibility needed to make informed decisions about access policies.
Documentation of access policies should be clear and enforceable, with explicit terms of service that prohibit unauthorized scraping and specify consequences for violations. Regular audits of CORS configurations help identify misconfigurations before they’re exploited, while maintaining an updated inventory of known AI crawler user agents and IP ranges enables rapid response to new threats. Organizations should also consider the business implications of blocking AI access—some AI crawlers provide value through search indexing or legitimate partnerships, so policies should distinguish between beneficial and harmful access patterns. Implementing these practices requires coordination between security, legal, and business teams to ensure policies align with organizational goals and regulatory requirements.
Specialized tools and platforms have emerged to help organizations monitor and control cross-origin AI access with greater precision and visibility. AmICited.com provides comprehensive monitoring of how AI systems reference and access your brand across GPTs, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI platforms, offering visibility into which AI models are using your content and how frequently your brand appears in AI-generated responses. This monitoring capability extends to tracking cross-origin access patterns and understanding the broader ecosystem of AI systems interacting with your digital properties.
Beyond monitoring, Cloudflare offers bot management features with one-click blocking of known AI crawlers, leveraging machine learning models trained on network-wide traffic patterns to identify bots even when they spoof user agents. AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall) provides customizable rules for blocking specific user agents and IP ranges, while Imperva offers advanced bot detection combining behavioral analysis with threat intelligence. Bright Data specializes in understanding bot traffic patterns and can help organizations distinguish between different types of crawlers. The choice of tools depends on organizational size, technical sophistication, and specific requirements—from simple robots.txt management for small sites to enterprise-grade bot management platforms for large organizations handling sensitive data. Regardless of tool selection, the fundamental principle remains: visibility into cross-origin AI access is the foundation for effective control and protection of digital assets.
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) is a security mechanism that controls which origins can access resources on a server. Cross-Origin AI Access specifically refers to how AI systems and crawlers interact with CORS to request content from different domains. While CORS is the technical framework, Cross-Origin AI Access describes the practical challenge of managing AI crawler behavior within that framework, including detection and blocking of unauthorized AI access.
Most well-behaved AI crawlers identify themselves through specific user agent strings like 'GPTBot/1.0' or 'ClaudeBot/1.0' that clearly indicate their purpose. However, many sophisticated crawlers deliberately spoof user agents by impersonating legitimate browsers like Chrome or Safari to bypass user agent-based blocking. This is why advanced detection methods using behavioral fingerprinting and network signal analysis are necessary to identify bots regardless of their claimed identity.
robots.txt provides a voluntary mechanism to request that crawlers respect access restrictions, and well-behaved AI crawlers like GPTBot generally honor these directives. However, robots.txt is not enforceable—determined scrapers can simply ignore it. Many AI companies have been caught bypassing robots.txt restrictions, making it a necessary but insufficient defense that should be combined with technical blocking methods like user agent filtering, rate limiting, and device fingerprinting.
Misconfigured CORS policies can allow unauthorized AI crawlers to access sensitive data, steal authenticated user information through credential-enabled requests, and scrape proprietary content for unauthorized AI model training. The most dangerous configurations combine wildcard origin settings with credential permissions, effectively allowing any origin to access protected resources. These misconfigurations can lead to intellectual property theft, competitive intelligence gathering, and violation of content licensing agreements.
Detection requires analyzing multiple signals beyond user agent strings. You can examine server logs for known AI crawler user agents, implement behavioral fingerprinting to identify bots by their interaction patterns, analyze network signals like TLS handshakes and DNS patterns, and use device fingerprinting to identify distributed scraping attempts. Tools like AmICited.com provide comprehensive monitoring of how AI systems reference your brand, while platforms like Cloudflare offer machine learning-based bot detection that identifies even spoofed crawlers.
No single method provides complete protection, so a layered approach is most effective. Start with robots.txt and user agent filtering for basic defense, add rate limiting to reduce impact, implement device fingerprinting to catch sophisticated bots, and consider authentication or paywalls for sensitive content. The most effective organizations combine multiple techniques and continuously monitor which methods are working, adapting as crawlers evolve their evasion techniques.
No. While major companies like OpenAI and Anthropic claim to respect robots.txt and CORS restrictions, investigations have revealed that many AI crawlers bypass these restrictions. Perplexity AI was caught spoofing user agents to bypass blocks, and research shows that OpenAI and Anthropic crawlers have been observed accessing content despite explicit robots.txt disallow rules. This inconsistency is why technical blocking methods and legal enforcement are increasingly necessary.
AmICited.com provides comprehensive monitoring of how AI systems reference and access your brand across GPTs, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI platforms. It tracks which AI models are using your content, how frequently your brand appears in AI-generated responses, and provides visibility into the broader ecosystem of AI systems interacting with your digital properties. This monitoring helps you understand the scope of AI access and make informed decisions about your content protection strategy.
Get complete visibility into which AI systems are accessing your brand across GPTs, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other platforms. Track cross-origin AI access patterns and understand how your content is being used in AI training and inference.

Learn how to make your content visible to AI crawlers like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google's AI. Discover technical requirements, best practices, and monitoring...
Learn how to manage AI crawler access to your website content. Understand the difference between training and search crawlers, implement robots.txt controls, an...

Learn how cross-platform AI publishing distributes content across multiple channels optimized for AI discovery. Understand PESO channels, automation benefits, a...