
How Do I Optimize Support Content for AI?
Learn essential strategies to optimize your support content for AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Discover best practices for clarit...
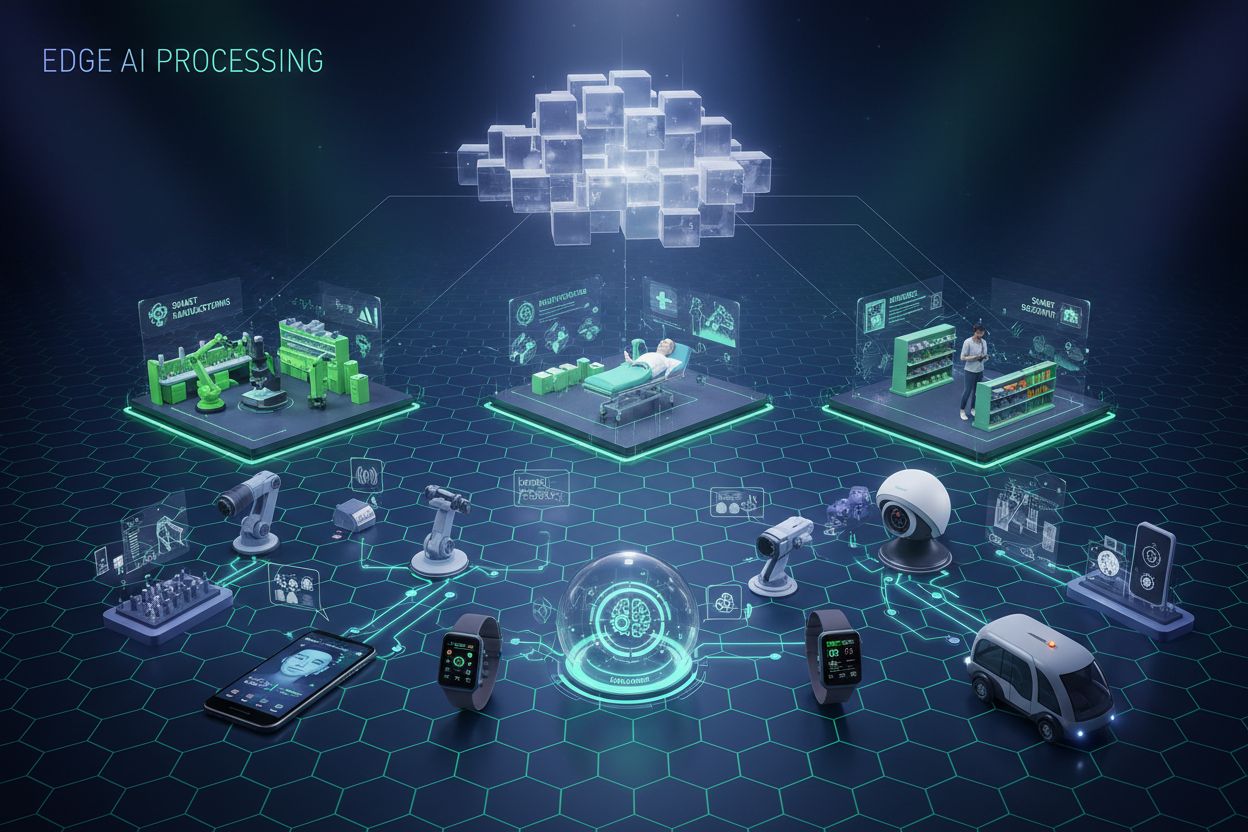

Edge AI Processing refers to the deployment of artificial intelligence algorithms directly on local devices or edge servers, enabling real-time data processing and analysis without constant reliance on cloud infrastructure. This approach reduces latency, enhances data privacy, and enables immediate decision-making for applications like brand monitoring, IoT devices, and autonomous systems.
Edge AI Processing refers to the deployment of artificial intelligence algorithms directly on local devices or edge servers, enabling real-time data processing and analysis without constant reliance on cloud infrastructure. This approach reduces latency, enhances data privacy, and enables immediate decision-making for applications like brand monitoring, IoT devices, and autonomous systems.
Edge AI Processing represents a paradigm shift in artificial intelligence deployment, where computational tasks execute directly on edge devices—such as smartphones, IoT sensors, cameras, and embedded systems—rather than relying exclusively on centralized cloud servers. This approach processes data at the source, enabling immediate analysis and decision-making without transmitting raw information to distant data centers. Unlike traditional cloud AI, which sends data to remote servers for processing and returns results after network latency, edge AI brings intelligence to the periphery of networks where data originates. The processing occurs on local hardware with embedded machine learning models, allowing devices to operate autonomously and make real-time decisions. Edge AI combines lightweight neural networks, optimized algorithms, and specialized hardware accelerators to deliver AI capabilities within strict resource constraints. This distributed intelligence model fundamentally changes how organizations approach data privacy, system responsiveness, and infrastructure costs. By processing sensitive information locally, edge AI eliminates the need to transmit potentially confidential data across networks, addressing growing privacy concerns in regulated industries.
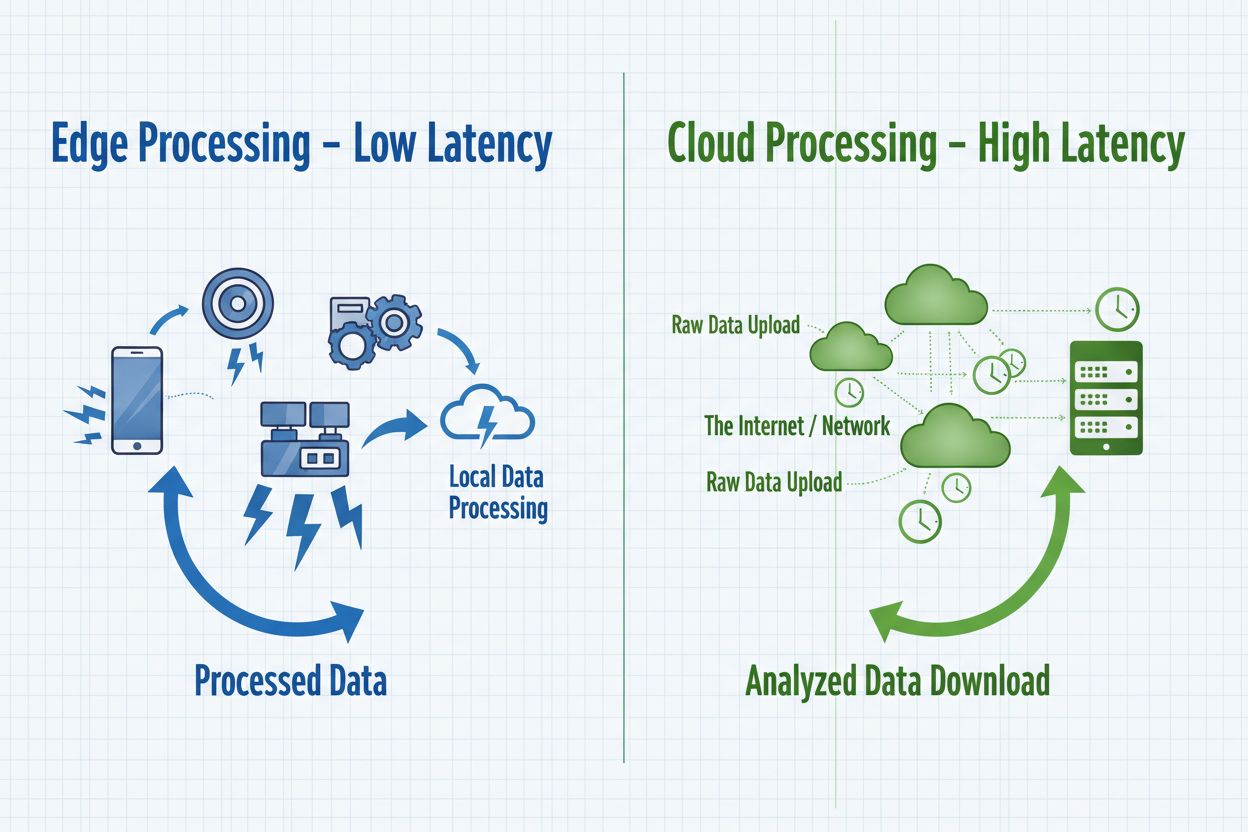
Edge AI and cloud AI represent complementary approaches to artificial intelligence deployment, each with distinct advantages suited to different use cases and organizational requirements. Cloud AI excels at handling massive datasets, training complex models, and performing computationally intensive tasks that benefit from centralized processing power and unlimited scalability. However, cloud solutions introduce inherent latency as data travels across networks, making them unsuitable for applications requiring immediate responses. Edge AI prioritizes speed and responsiveness by processing information locally, enabling sub-millisecond decision-making critical for autonomous systems and real-time monitoring applications. The choice between these approaches depends on specific requirements: cloud AI suits batch processing, model training, and applications where slight delays are acceptable, while edge AI serves real-time applications, privacy-sensitive operations, and scenarios with unreliable network connectivity. Organizations increasingly adopt hybrid architectures that leverage both paradigms—using edge devices for immediate processing and cloud infrastructure for model training, analytics, and long-term data storage. Understanding these fundamental differences helps organizations architect solutions that balance performance, security, and operational efficiency.
| Aspect | Edge AI | Cloud AI |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Sub-millisecond response times; immediate local processing | 50-500ms+ due to network transmission and server processing |
| Bandwidth | Minimal data transmission; processes locally | High bandwidth requirements; transmits raw data continuously |
| Security & Privacy | Data remains local; reduced exposure to breaches | Data travels across networks; centralized storage creates single point of failure |
| Computational Power | Limited by device hardware; optimized lightweight models | Unlimited scalability; handles complex models and massive datasets |
| Scalability | Scales horizontally across distributed devices | Scales vertically with server infrastructure; centralized management |
Edge AI systems comprise four essential technical components that work together to deliver intelligent processing at the network periphery. The inference engine executes pre-trained machine learning models on edge devices, performing predictions and classifications without requiring cloud connectivity. These engines utilize optimized frameworks like TensorFlow Lite, ONNX Runtime, and PyTorch Mobile that compress models to fit within device memory constraints while maintaining acceptable accuracy levels. The hardware accelerators—including GPUs, TPUs, and specialized AI chips—provide the computational power necessary to run neural networks efficiently on resource-constrained devices. Edge devices employ model optimization techniques such as quantization, pruning, and knowledge distillation to reduce model size and computational requirements without significantly degrading performance. The data management layer handles local data collection, preprocessing, and selective transmission of relevant insights to cloud systems for aggregation and long-term analysis. Finally, the connectivity module manages intermittent network connections, enabling devices to operate offline while synchronizing data when connectivity becomes available.
Edge AI Processing enables unprecedented capabilities in real-time brand recommendations and AI output monitoring, directly supporting organizations’ need to track and verify AI decision-making at the point of execution. Retail applications leverage edge AI to deliver personalized product recommendations instantly as customers browse, analyzing behavior patterns locally without transmitting sensitive shopping data to external servers. Real-time monitoring of AI outputs becomes feasible when inference occurs on edge devices, allowing organizations to immediately detect anomalies, biased predictions, or model drift before recommendations reach customers. This localized processing creates audit trails and decision logs that support compliance requirements and enable brands to understand exactly why specific recommendations were generated. Edge AI monitoring systems can flag suspicious patterns—such as recommendations that disproportionately favor certain products or demographics—enabling rapid intervention and model adjustment. For brand safety and reputation management, edge-based AI monitoring ensures that automated systems operate within defined parameters and align with brand values before customer-facing deployment. The ability to monitor AI outputs in real-time at the edge transforms how organizations maintain quality control over algorithmic decision-making, supporting transparency initiatives and building customer trust through verifiable AI governance.

Edge AI Processing delivers substantial advantages across multiple dimensions that address critical organizational challenges in modern digital environments. Reduced latency stands as the primary benefit, enabling applications requiring immediate responses—autonomous vehicles making split-second navigation decisions, industrial robots responding to safety hazards, or medical devices detecting critical patient conditions. Enhanced privacy emerges as a secondary advantage, as sensitive data remains on local devices rather than traversing networks or residing in centralized cloud storage, addressing GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulatory requirements. Bandwidth optimization reduces network congestion and associated costs by processing data locally and transmitting only relevant insights rather than raw information streams. Offline functionality allows edge devices to continue operating and making intelligent decisions even when network connectivity fails, critical for remote locations and mission-critical applications. Improved reliability results from distributed processing—system failures on individual edge devices don’t cascade across entire infrastructure, and local processing continues regardless of cloud service availability. Cost efficiency emerges through reduced cloud computing expenses, as organizations process data locally rather than paying for continuous cloud infrastructure and data transmission. Scalability advantages manifest differently than cloud systems; edge AI scales horizontally across distributed devices without requiring centralized infrastructure expansion, making it ideal for IoT deployments spanning thousands of devices.
Edge AI Processing transforms operations across diverse industries by enabling intelligent decision-making at the point of data generation. Manufacturing facilities deploy edge AI for predictive maintenance, analyzing equipment vibrations and thermal patterns locally to predict failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Healthcare providers utilize edge AI in medical imaging devices that perform preliminary analysis locally, enabling faster diagnosis while protecting patient privacy by keeping sensitive medical data on-premises. Retail environments implement edge AI for inventory management, customer behavior analysis, and personalized recommendations delivered instantly without cloud latency. Autonomous vehicles depend entirely on edge AI, processing sensor data from cameras, lidar, and radar locally to make real-time navigation and safety decisions within milliseconds. Smart home systems leverage edge AI to recognize voice commands, detect security threats, and automate routines without transmitting audio or video to cloud servers. Security and surveillance applications use edge AI to detect anomalies, identify threats, and trigger alerts locally, reducing false positives through intelligent filtering before transmitting alerts to monitoring centers. Agricultural operations employ edge AI on IoT sensors to monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health, making irrigation and fertilization decisions locally while minimizing data transmission costs across rural areas with limited connectivity.
Despite substantial advantages, Edge AI Processing faces significant technical and operational challenges that organizations must address during implementation. Power consumption remains a critical constraint, as running neural networks on battery-powered devices drains energy rapidly, limiting deployment duration and requiring careful model optimization to balance accuracy with efficiency. Computational limitations restrict the complexity of models deployable on edge devices; organizations must choose between deploying simplified models with reduced accuracy or accepting longer inference times on resource-constrained hardware. Model management complexity increases substantially in distributed environments, as updating models across thousands of edge devices requires robust versioning, rollback capabilities, and mechanisms to ensure consistency across the fleet. Data heterogeneity presents challenges when edge devices operate in diverse environments with varying data characteristics, potentially causing models trained on centralized datasets to perform poorly on local data distributions. Debugging and monitoring difficulties emerge from the distributed nature of edge systems, making it challenging to diagnose failures, understand model behavior, and collect comprehensive performance metrics across geographically dispersed devices. Security vulnerabilities on edge devices create attack surfaces, as compromised devices could execute malicious code or manipulate local models, requiring robust security measures and regular updates. Integration complexity with existing cloud infrastructure demands careful architectural planning to ensure edge systems effectively communicate with centralized analytics and model training pipelines.
The intersection of Edge AI Processing and AI monitoring creates powerful capabilities for organizations seeking to maintain oversight of algorithmic decision-making at scale. Traditional AI monitoring approaches struggle with cloud-based systems where latency and data transmission costs limit real-time visibility into model outputs; edge AI monitoring addresses this by enabling local analysis of predictions before they impact customers. Output verification systems deployed on edge devices can immediately validate predictions against business rules, detect anomalies, and flag decisions requiring human review before execution. This localized monitoring approach supports brand safety initiatives by ensuring that AI-generated recommendations, content decisions, and customer interactions align with organizational values and compliance requirements. Edge-based monitoring systems generate detailed audit trails documenting why specific decisions were made, supporting transparency requirements and enabling post-hoc analysis of algorithmic behavior. Bias detection mechanisms operating at the edge can identify when models produce disproportionate outcomes across demographic groups, enabling rapid intervention before biased recommendations reach customers. The combination of edge AI and monitoring creates a feedback loop where local decision logs inform model retraining, ensuring that systems continuously improve while maintaining oversight of their behavior. Organizations implementing edge AI monitoring gain unprecedented visibility into algorithmic decision-making, transforming AI from a black box into a transparent, auditable system that supports both performance optimization and responsible AI governance.
Edge AI Processing stands at the forefront of technological evolution, with emerging trends reshaping how organizations deploy and manage distributed intelligence. Federated learning represents a transformative approach where edge devices collaboratively train models without transmitting raw data to centralized servers, enabling privacy-preserving machine learning at scale. 5G network expansion will dramatically accelerate edge AI adoption by providing reliable, low-latency connectivity that enables seamless synchronization between edge devices and cloud infrastructure while maintaining local processing advantages. Specialized hardware development continues advancing, with manufacturers creating increasingly efficient AI chips optimized for specific edge applications, improving performance-per-watt metrics critical for battery-powered devices. Market projections indicate explosive growth, with the global edge AI market expected to reach $15.7 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 38.3% from 2023 to 2030. TinyML (machine learning on microcontrollers) emerges as a significant trend, enabling AI capabilities on devices with minimal memory and processing power, expanding edge AI applications to previously impossible use cases. Containerization and orchestration technologies like Kubernetes are adapting to edge environments, enabling organizations to manage distributed edge deployments with the same tools and processes used for cloud infrastructure. The convergence of these trends suggests a future where intelligent processing occurs seamlessly across distributed networks, with edge devices handling real-time decisions while cloud systems provide training, aggregation, and long-term analytics.
Successfully deploying Edge AI Processing requires careful planning across multiple dimensions to ensure systems deliver expected performance and business value. Model selection represents the first critical decision, requiring organizations to evaluate available pre-trained models, assess their accuracy on target use cases, and determine whether custom model development is necessary. Optimization strategies must balance model accuracy against device constraints, employing quantization, pruning, and architecture search techniques to create models that fit within hardware limitations while maintaining acceptable performance. Hardware selection depends on specific application requirements, computational needs, and power constraints; organizations must evaluate options ranging from general-purpose processors to specialized AI accelerators. Deployment mechanisms require robust processes for distributing models across edge devices, managing versions, and rolling back to previous versions if issues arise. Monitoring and observability systems must track model performance, detect data drift, identify anomalies, and generate alerts when systems deviate from expected behavior. Security hardening protects edge devices against unauthorized access, model theft, and malicious manipulation through encryption, authentication, and regular security updates. Integration planning ensures edge systems effectively communicate with cloud infrastructure for model updates, analytics, and long-term data storage, creating cohesive hybrid architectures that leverage advantages of both paradigms. Organizations implementing edge AI should establish clear success metrics, pilot deployments on limited scale before full rollout, and maintain flexibility to adjust strategies based on real-world performance data.
Edge AI processes data locally on devices with immediate response times (sub-millisecond latency), while Cloud AI sends data to remote servers for processing, introducing network delays. Edge AI prioritizes speed and privacy, while Cloud AI offers unlimited computational power for complex tasks.
Edge AI keeps sensitive data on local devices rather than transmitting it across networks or storing it in centralized cloud servers. This approach reduces exposure to breaches, supports GDPR and HIPAA compliance, and ensures that personal information remains under organizational control.
Edge AI achieves sub-millisecond response times by processing data locally, compared to 50-500ms or more for cloud-based systems. This dramatic latency reduction enables real-time applications like autonomous vehicles, industrial robotics, and medical devices that require immediate decision-making.
Yes, Edge AI systems can operate completely offline since processing occurs locally on devices. This offline functionality is critical for remote locations with unreliable connectivity and mission-critical applications where network failures cannot interrupt operations.
Edge AI runs on diverse devices including smartphones, IoT sensors, industrial equipment, security cameras, smartwatches, autonomous vehicles, and embedded systems. Modern edge devices range from microcontrollers with minimal resources to powerful single-board computers with specialized AI accelerators.
Edge AI processes data locally and transmits only relevant insights rather than raw information streams. This selective transmission dramatically reduces bandwidth consumption, lowering network costs and improving system performance by minimizing data transmission across networks.
Edge AI enables real-time monitoring of AI-generated recommendations and decisions at the point of execution, allowing organizations to immediately detect anomalies, verify brand safety, and ensure algorithmic outputs align with organizational values before reaching customers.
Key challenges include power consumption on battery-powered devices, computational limitations requiring model optimization, complexity of managing distributed systems, security vulnerabilities on edge devices, and integration challenges with existing cloud infrastructure.
Edge AI Processing enables instant analysis of AI outputs and brand citations. AmICited tracks how your brand appears in AI-generated content across GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews with real-time precision.

Learn essential strategies to optimize your support content for AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Discover best practices for clarit...

Learn how AI models process text through tokenization, embeddings, transformer blocks, and neural networks. Understand the complete pipeline from input to outpu...
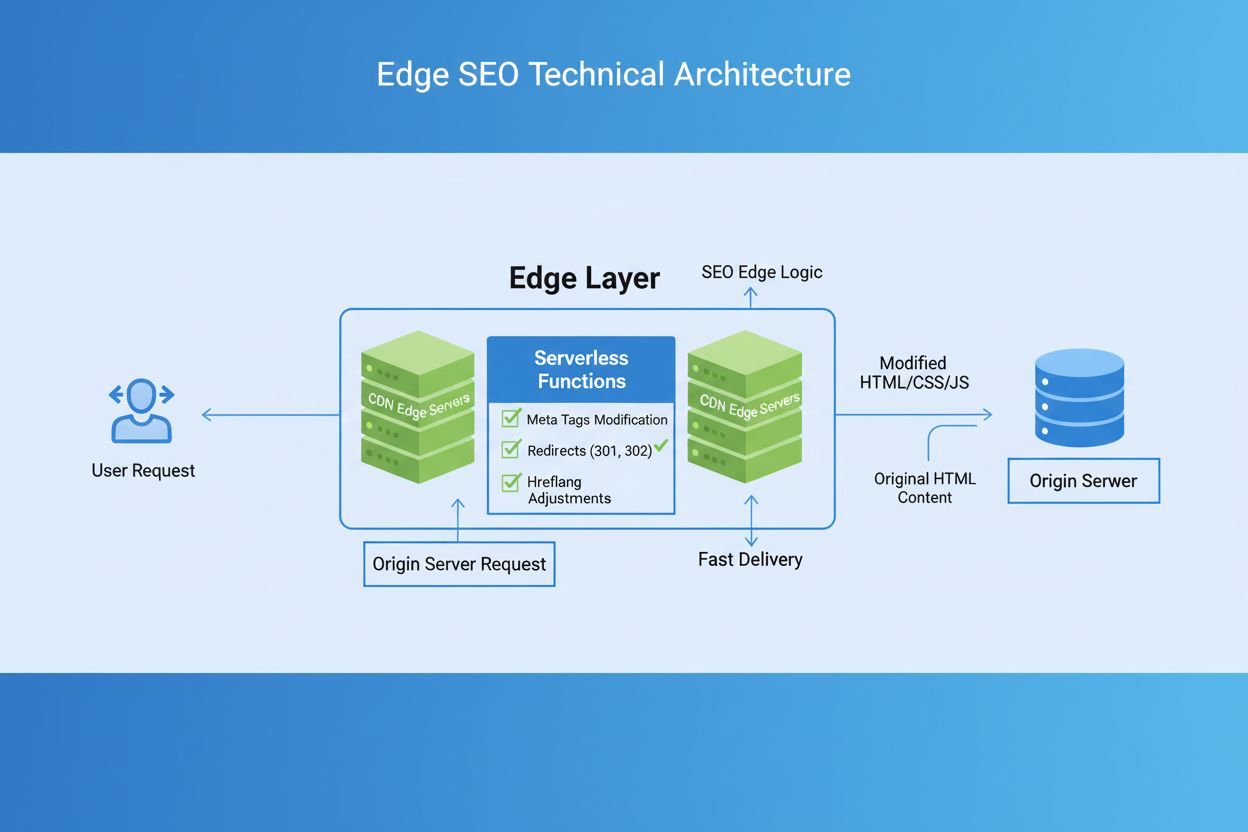
Edge SEO is the practice of implementing technical SEO changes at the network edge using serverless functions on CDNs. Learn how it improves performance, enable...