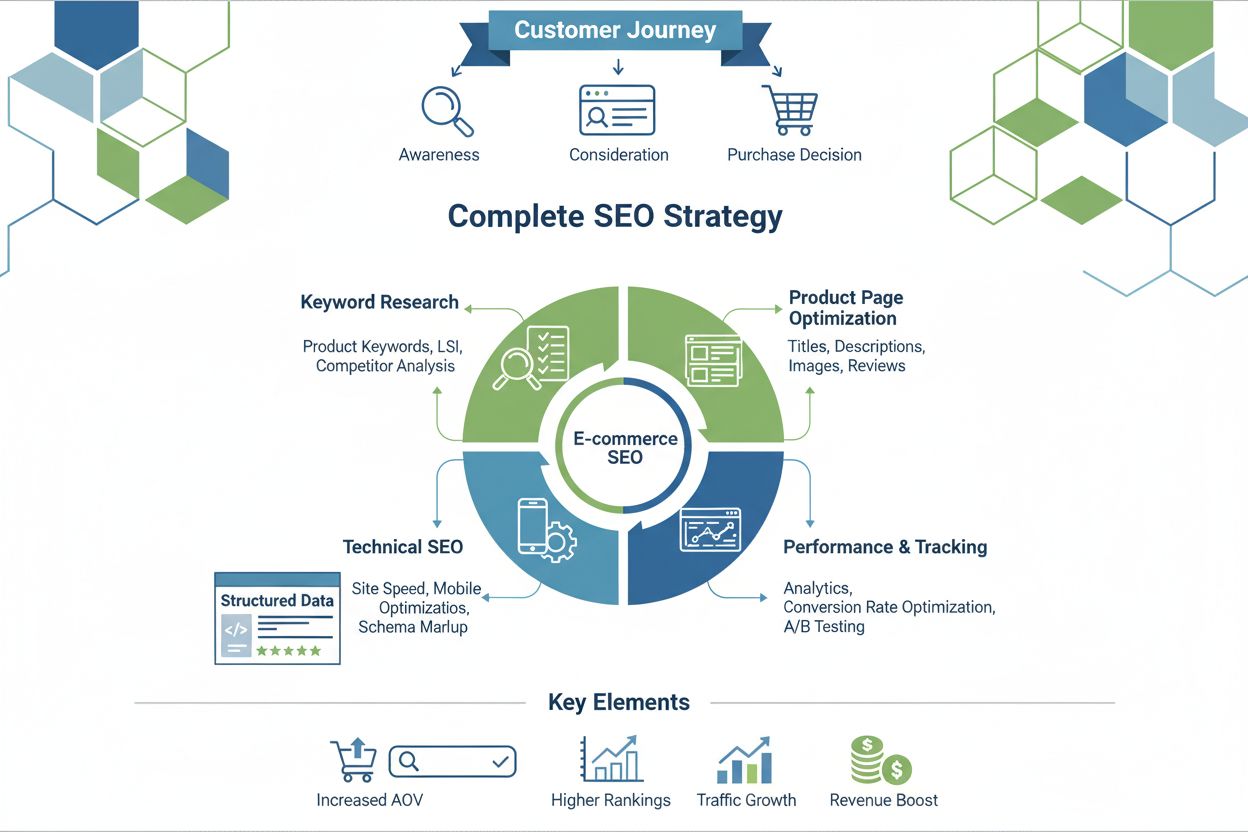
Ecommerce SEO
Ecommerce SEO is the optimization of online stores for search visibility. Learn keyword research, product page optimization, technical SEO, and conversion strat...

Enterprise SEO refers to search engine optimization strategies specifically designed for large organizations with complex website structures, multiple pages (often thousands or millions), and diverse target audiences. It involves coordinated efforts across multiple departments, advanced technical optimization, and sophisticated tools to manage scale, complexity, and long-term organic growth.
Enterprise SEO refers to search engine optimization strategies specifically designed for large organizations with complex website structures, multiple pages (often thousands or millions), and diverse target audiences. It involves coordinated efforts across multiple departments, advanced technical optimization, and sophisticated tools to manage scale, complexity, and long-term organic growth.
Enterprise SEO is the practice of optimizing large, complex websites with thousands or millions of pages for search engine visibility and organic traffic. Unlike traditional SEO, which focuses on smaller websites with simpler structures, Enterprise SEO addresses the unique challenges of managing search optimization across massive digital footprints, multiple departments, diverse product lines, and often global markets. Enterprise organizations—such as Fortune 500 companies, large ecommerce platforms, and multinational corporations—require specialized strategies, advanced tools, and cross-functional teams to implement SEO at scale. The primary goal of Enterprise SEO is to improve search rankings, increase organic traffic, and drive revenue while managing the complexity of thousands of pages, multiple stakeholders, and competing business priorities.
The emergence of Enterprise SEO as a distinct discipline reflects the evolution of search engine optimization from a tactical, page-level practice to a strategic, organization-wide initiative. As websites grew from hundreds to millions of pages, traditional SEO approaches—designed for small businesses and niche websites—became insufficient. According to research from Backlinko, GitHub alone has over 78 million pages indexed in Google, illustrating the scale at which modern enterprises operate. The complexity of managing such vast digital properties necessitated the development of specialized methodologies, tools, and team structures.
Enterprise SEO emerged in the early 2010s as organizations recognized that organic search was a critical driver of revenue and brand visibility. Studies show that 91% of marketers reported that SEO had a positive impact on their website performance and marketing goals in 2024, according to Conductor’s State of Organic Marketing survey. Furthermore, SEO delivers an average 825% ROI across all verticals, with leads from search engines closing at 14.6% compared to just 1.7% for outbound leads. These compelling statistics drove enterprises to invest heavily in dedicated SEO programs, specialized platforms, and expert teams.
The rise of Enterprise SEO also coincided with the increasing sophistication of search algorithms. Google’s shift toward E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) signals, the introduction of Core Web Vitals as ranking factors, and the emphasis on user experience meant that enterprises needed to coordinate optimization efforts across technical, content, and design teams. Additionally, the emergence of AI-powered search features like Google AI Overviews has created new challenges for enterprise organizations, requiring them to monitor brand visibility not just in traditional search results but across AI-generated summaries and citations.
| Aspect | Traditional SEO | Enterprise SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Website Scale | 100-1,000 pages | 1,000+ to millions of pages |
| Organization Size | Micro to small firms (1-49 employees) | Medium to large enterprises (250+ employees) |
| Content Strategy | Bottom-of-funnel (BOF) content focused on conversions | All-funnel content (top, middle, bottom) |
| Keyword Focus | Long-tail keywords with lower search volume | Head terms, branded keywords, and global keywords |
| Team Structure | Individual, freelancer, or small agency | Cross-functional teams (content, dev, design, marketing, PR) |
| Tools Required | Basic tools (Yoast, Ahrefs basic, Screaming Frog free) | Enterprise platforms (Semrush Enterprise, Conductor, BrightEdge, Google Analytics 360) |
| Monthly Budget | $500-$5,000 | $50,000-$500,000+ |
| Implementation Timeline | Weeks to months | Months to years |
| Primary Challenge | Limited resources and authority | Coordination, scale, and complexity |
| ROI Timeline | 3-6 months | 6-12 months (peak results in year 2-3) |
Enterprise SEO requires sophisticated approaches to managing technical challenges that simply do not exist at smaller scales. One of the most critical issues is crawl budget optimization—the number of pages Google will crawl and index on a website within a given timeframe. For a site with millions of pages, an inefficient crawl budget means that important pages may not be indexed, directly impacting visibility and traffic. Enterprise organizations must implement strategic site architecture, XML sitemaps, internal linking structures, and server optimization to ensure that Google’s crawlers prioritize high-value pages.
Duplicate content represents another significant challenge in Enterprise SEO. Large ecommerce sites, for example, often generate thousands of product pages with similar or identical content. Without proper management using canonical tags, 301 redirects, and parameter handling, search engines may penalize the site or dilute ranking power across duplicate versions. According to research from Ahrefs, 94% of all pages have zero backlinks, and many enterprise sites struggle with internal content duplication that further weakens their SEO performance.
Page bloat—the accumulation of low-quality, outdated, or unnecessary pages—is endemic to enterprise websites. Old product pages, archived content, search result pages accidentally indexed, and redundant category pages can consume crawl budget and dilute site authority. Managing page bloat requires ongoing audits, strategic removal or consolidation of pages, and clear governance around content lifecycle management. This is particularly important because only 33% of websites pass Google’s Core Web Vitals assessment, and page bloat often contributes to performance issues that harm rankings.
Creating and managing content at enterprise scale requires fundamentally different approaches than traditional SEO. Enterprise SEO demands a content governance framework that defines roles, responsibilities, workflows, and quality standards across the organization. Without clear governance, content creation becomes chaotic, leading to inconsistent messaging, duplicate content, and missed optimization opportunities.
Successful enterprise content strategies typically involve targeted keyword research that identifies thousands of relevant terms across multiple product categories, markets, and customer segments. Unlike small businesses that might target 50-100 keywords, enterprises often manage portfolios of 10,000+ keywords. This requires advanced keyword research tools and data-driven prioritization to focus efforts on terms with the highest commercial value and achievable ranking potential.
Content diversification is essential in Enterprise SEO. Rather than relying solely on blog posts, enterprises create comprehensive content ecosystems including product pages, category pages, comparison guides, whitepapers, case studies, webinars, videos, and infographics. According to HubSpot, companies with blog content experience an average of 126% higher lead growth, but enterprises amplify this by creating content across multiple formats and distribution channels. The challenge lies in maintaining quality and relevance across thousands of content pieces while ensuring each page is optimized for its target keywords and user intent.
Link building in Enterprise SEO operates at a different scale and sophistication level than traditional link building. While small websites might acquire 5-10 backlinks per month, enterprise sites can leverage their brand authority to build links at scale. According to Backlinko, the #1 result in Google has an average of 3.8x more backlinks than positions 2-10, and 96% of websites in Google’s top 10 have more than 1,000 links from unique domains.
Enterprise organizations can capitalize on unlinked brand mentions—instances where other websites mention the brand without linking to it. A popular brand might receive 500+ unlinked mentions monthly, each representing a potential backlink opportunity. By systematically identifying and reaching out to these mentions, enterprises can build high-quality links at scale. Additionally, enterprises can leverage digital PR, guest posting, original research, and content partnerships to earn links from authoritative sources.
Internal linking strategy is particularly important in Enterprise SEO. With thousands of pages, a well-planned internal linking architecture can distribute link equity strategically, improve crawlability, and establish topical relevance. Enterprise sites often implement programmatic internal linking—automated systems that generate contextual links between related pages—to scale this effort across millions of pages. This approach ensures that important pages receive sufficient internal link authority while maintaining natural, user-focused linking patterns.
One of the most underestimated aspects of Enterprise SEO is the organizational and political complexity of implementing changes across multiple departments. Unlike a small business where the owner can make quick decisions, enterprises must navigate approval processes, competing priorities, and departmental silos. Team buy-in is critical to success, and SEO leaders must effectively communicate the value of SEO recommendations to stakeholders in development, design, product, marketing, and executive leadership.
Successful Enterprise SEO programs establish clear governance structures and cross-functional workflows. The adaptive triad approach—temporary teams of 3-5 people from different departments focused on solving specific problems—has proven effective for enterprises. These teams might include an SEO specialist, a content strategist, a developer, and a designer, working together to implement a major site redesign or launch a new product category with SEO optimization built in from the start.
Enterprise SEO also requires sophisticated change management. When recommending a site architecture redesign or implementing new technical standards, SEO leaders must demonstrate the business value, address concerns from other departments, and provide clear implementation timelines. According to Conductor’s research, 57% of enterprises rated limited SEO in-house skills as the most challenging obstacle, while 43% reported limited SEO budget as a major constraint. Overcoming these barriers requires strong leadership, data-driven recommendations, and effective stakeholder communication.
Enterprise SEO demands enterprise-grade tools and platforms that can handle massive data volumes, provide advanced analytics, and integrate with existing systems. While small businesses can use basic SEO tools, enterprises require specialized platforms like Semrush Enterprise, Conductor, BrightEdge, and Botify. These platforms offer features specifically designed for enterprise scale, including:
Additionally, enterprises often invest in Google Analytics 360 (starting at $50,000+ annually), Google Search Console integrations, and custom data warehousing solutions to consolidate SEO data with other business metrics. The total technology investment for enterprise SEO can easily exceed $100,000+ annually, reflecting the complexity and scale of the operation.
Enterprise SEO requires sophisticated measurement frameworks that connect organic search performance to business outcomes. Unlike traditional SEO, which might track simple metrics like rankings and traffic, Enterprise SEO must demonstrate ROI through revenue attribution, cost savings, and competitive advantage.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for Enterprise SEO include organic traffic growth, keyword rankings (particularly for high-value head terms), conversion rates from organic search, cost-per-acquisition (CPA) compared to other channels, and return on ad spend (ROAS) when comparing organic to paid search. According to FirstPageSage, SEO delivers an average 825% ROI across all verticals, with B2B SaaS companies reporting a 702% average SEO ROI and ecommerce brands generating a 317% SEO ROI.
Attribution modeling is critical in enterprise environments where customers often interact with multiple touchpoints before converting. Multi-touch attribution models help enterprises understand the role of organic search in the customer journey, particularly for awareness and consideration-stage content. Additionally, enterprises should track brand lift, market share gains, and competitive positioning to understand the full impact of SEO investments beyond direct revenue attribution.
The landscape of Enterprise SEO is rapidly evolving in response to emerging technologies and changing search behavior. AI-powered search represents one of the most significant shifts, with platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude increasingly influencing how users discover information. According to SparkToro, 27.2% of U.S. searches now end without a click, as AI Overviews provide instant answers that reduce the need to visit external websites.
This shift has profound implications for Enterprise SEO. Organizations must now optimize not just for traditional search rankings but for AI citations and mentions. This requires ensuring that content is authoritative, well-structured, and easily extractable by AI systems. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) are emerging as critical disciplines within Enterprise SEO, requiring enterprises to adapt their content strategies to be visible and cited by AI systems.
Additionally, voice search optimization, visual search, and video SEO are becoming increasingly important for enterprises. With 58% of consumers using voice search daily and over 1.5 billion people using Google Lens monthly, enterprises must optimize for these emerging search modalities. Furthermore, the rise of AI-assisted content creation and automation is transforming how enterprises produce and optimize content at scale, with 56% of marketers already using AI in digital marketing and 65% of companies reporting better SEO results with AI.
The future of Enterprise SEO will likely involve greater integration of AI tools, more sophisticated attribution modeling, increased focus on brand authority and E-E-A-T signals, and adaptation to AI-powered search platforms. Enterprises that successfully navigate these changes will maintain competitive advantage in organic search, while those that fail to adapt risk losing visibility as search behavior continues to evolve.
The primary difference is scale and complexity. Traditional SEO targets small to medium-sized websites with fewer pages and simpler structures, while Enterprise SEO manages large websites with thousands or millions of pages across multiple departments. Enterprise SEO requires advanced tools, larger teams, higher budgets (often $50,000+ monthly), and strategies that address cross-functional coordination, whereas traditional SEO can be managed by individuals or small teams with basic tools.
Enterprise websites face unique challenges that standard SEO approaches cannot address effectively. These include managing crawl budgets across millions of pages, preventing duplicate content issues, coordinating SEO across multiple departments, implementing changes at scale, and targeting both high-volume head terms and long-tail keywords. Enterprise SEO platforms and specialized strategies are necessary to handle this complexity and ensure consistent optimization across the entire digital footprint.
Enterprise SEO budgets vary significantly but typically range from $50,000 to $500,000+ annually, depending on website size, complexity, and goals. Costs include specialized tools (some costing $50,000+ per year like Google Analytics 360), dedicated teams (content writers, developers, SEO specialists, analysts), and ongoing optimization efforts. The investment reflects the scale of operations and the need for enterprise-grade solutions to manage thousands of pages effectively.
Enterprise SEO requires premium or enterprise versions of specialized tools including Semrush Enterprise, Ahrefs Enterprise, Conductor, BrightEdge, Google Analytics 360, and Screaming Frog (paid versions). These tools provide advanced features for tracking thousands of keywords, analyzing millions of pages, automating reporting, and identifying technical issues at scale. Many enterprises also use custom solutions and APIs to integrate SEO data with their existing systems.
Enterprise SEO success depends heavily on cross-functional collaboration between SEO, content, development, design, product, and marketing teams. Effective team structures include hierarchical models (with specialized roles), pod structures (cross-functional teams by product or vertical), and market-specific structures (for global organizations). Clear roles, communication channels, and governance processes are essential to ensure SEO recommendations are implemented promptly and consistently across the organization.
Major challenges include managing massive page volumes and crawl budgets, preventing duplicate content across thousands of pages, coordinating changes across multiple departments, securing stakeholder buy-in, maintaining content quality at scale, and adapting to algorithm updates across complex site structures. Additionally, enterprises must balance SEO priorities with other business objectives and manage the complexity of multiple teams working on different aspects of the website simultaneously.
Enterprise SEO typically requires 6-12 months to show positive ROI, with peak results often appearing in the second or third year of implementation. The longer timeline reflects the complexity of optimizing large sites, the need for comprehensive technical audits, content creation at scale, and the time required for search engines to crawl and index millions of pages. However, some quick wins in technical SEO and on-page optimization can show results within 3-6 months.
Enterprise SEO delivers exceptional ROI, with studies showing 22:1 return on SEO spend and an average 825% ROI across all verticals. SEO leads close at 14.6% compared to 1.7% for outbound leads, making organic search 8.5x more effective. Over 91% of marketers report that SEO positively impacts website performance, and 50% rate SEO as the top ROI channel. The long-term nature of SEO means returns compound over time, making it one of the most cost-effective marketing investments.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Ecommerce SEO is the optimization of online stores for search visibility. Learn keyword research, product page optimization, technical SEO, and conversion strat...
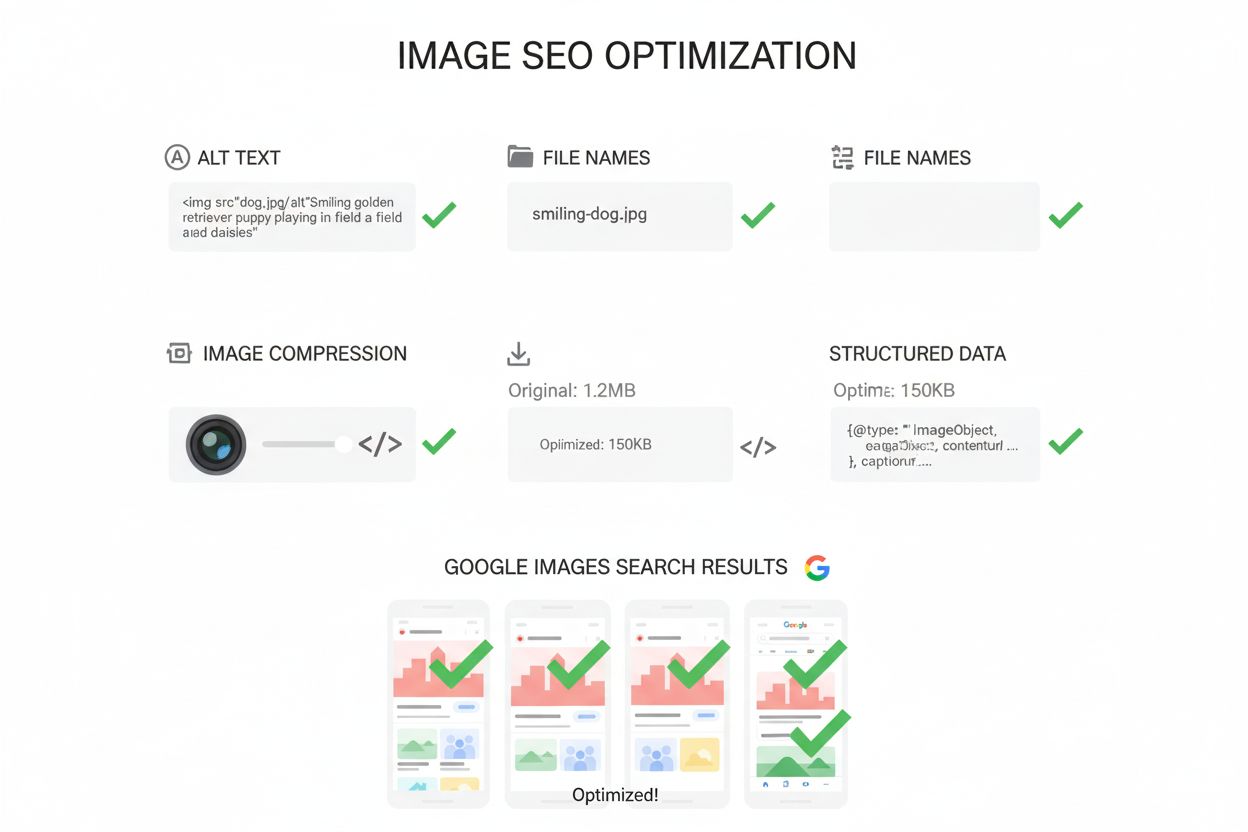
Image SEO optimizes images for search visibility through alt text, file names, compression, and structured data. Learn how to improve rankings in Google Images ...
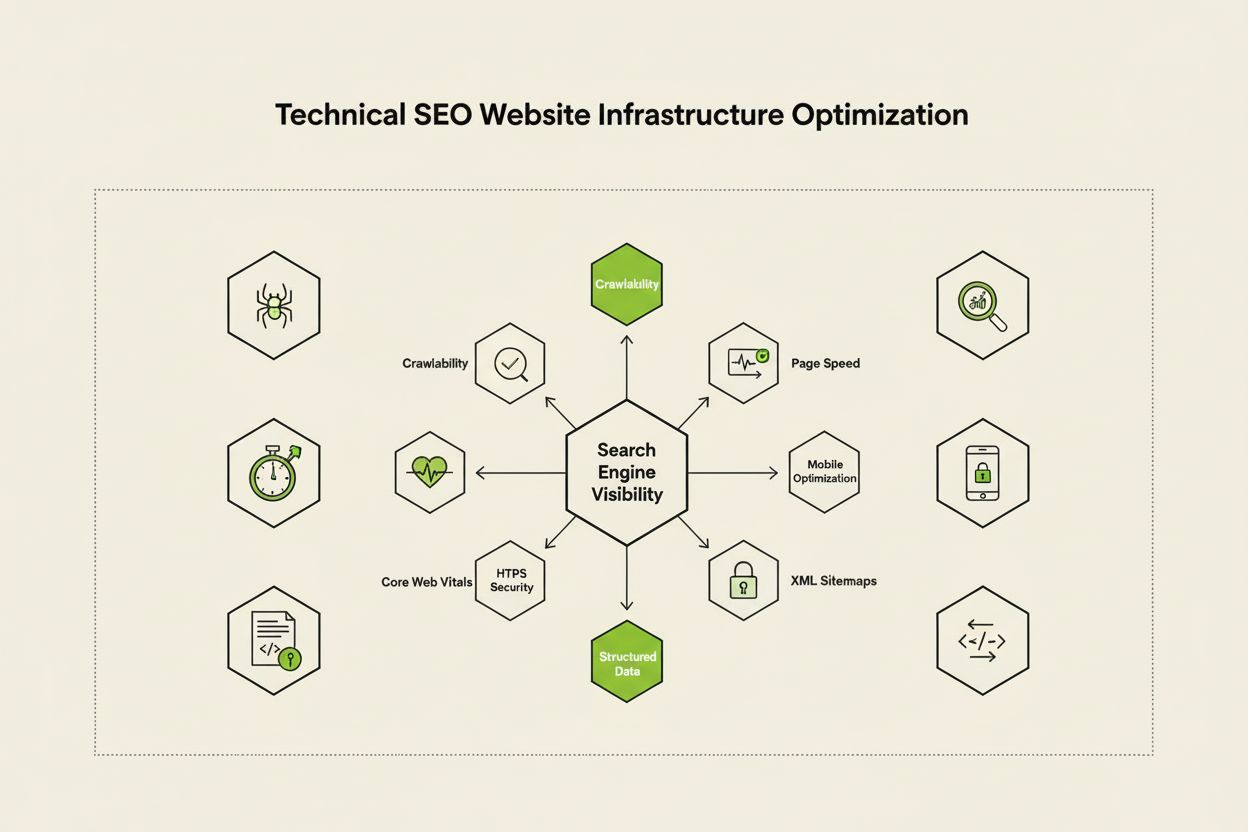
Technical SEO optimizes website infrastructure for search engine crawling, indexing, and ranking. Learn crawlability, Core Web Vitals, mobile optimization, and ...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.