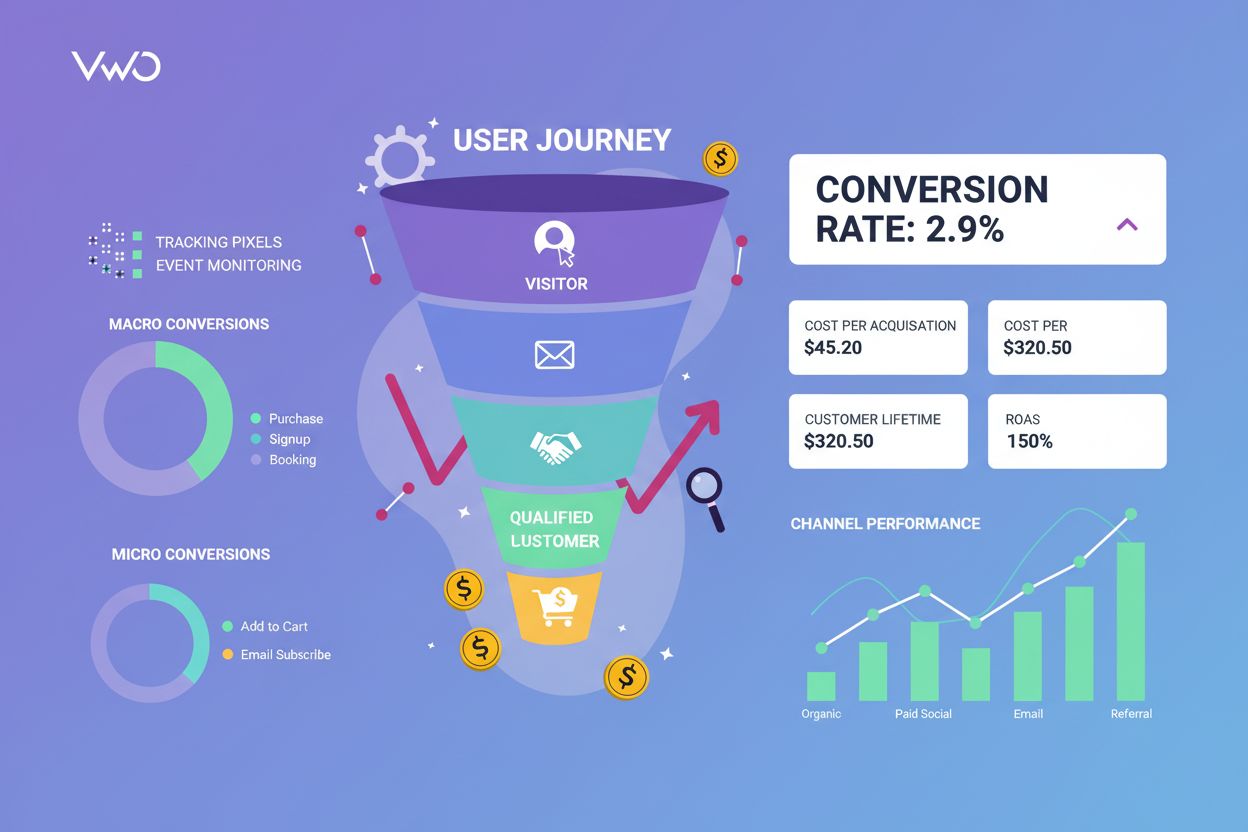
Conversion Tracking
Conversion tracking monitors user actions toward business goals. Learn how to measure conversions, track metrics, and optimize marketing ROI with comprehensive ...
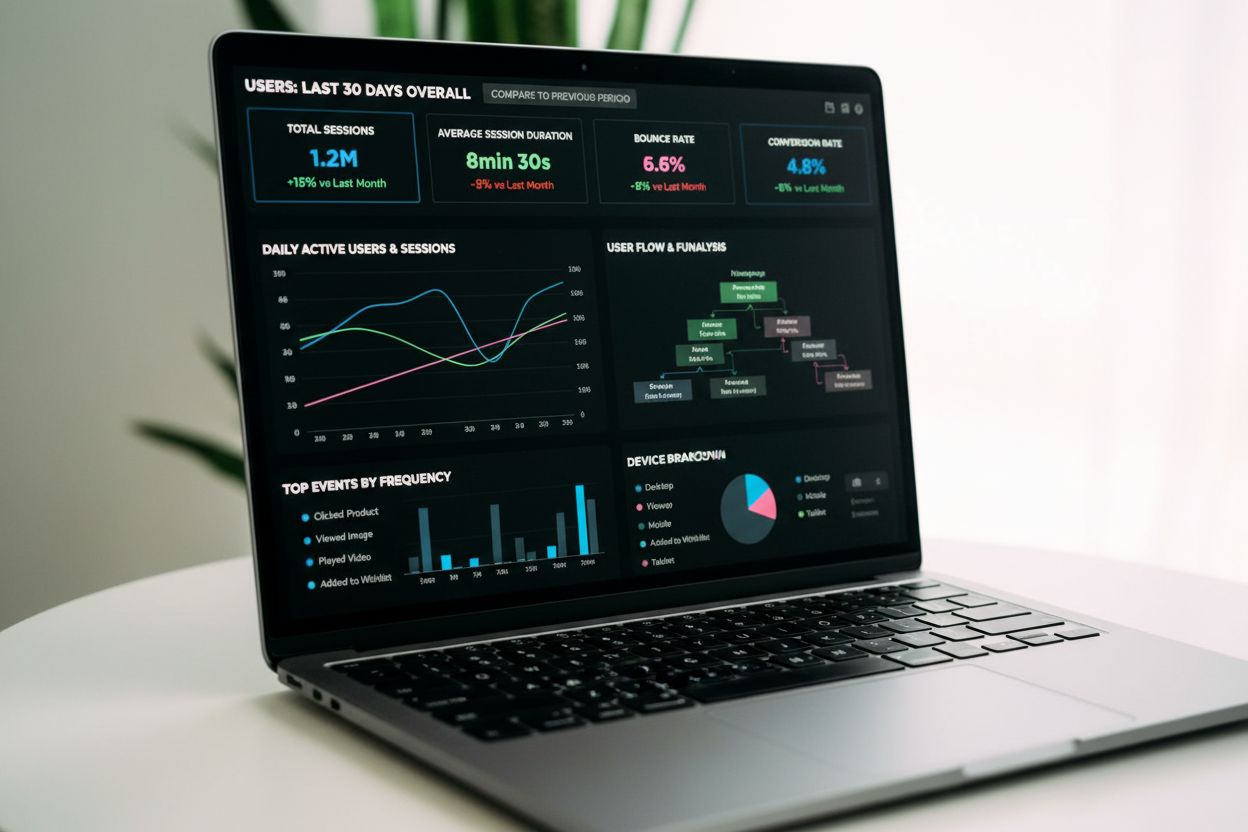
Event tracking is the process of capturing and recording specific user interactions on websites, mobile apps, and digital platforms. Each action—such as clicks, form submissions, purchases, or page views—is timestamped and analyzed to provide insights into user behavior, engagement patterns, and product performance.
Event tracking is the process of capturing and recording specific user interactions on websites, mobile apps, and digital platforms. Each action—such as clicks, form submissions, purchases, or page views—is timestamped and analyzed to provide insights into user behavior, engagement patterns, and product performance.
Event tracking is the systematic process of capturing, recording, and analyzing specific user interactions on digital platforms including websites, mobile applications, and web-based software. Each interaction—whether a button click, form submission, video play, page view, or purchase—is treated as a discrete “event” and is timestamped with associated metadata. This granular data collection enables organizations to understand precisely how users engage with their digital products, identify behavioral patterns, and make informed decisions about product optimization and marketing strategy. Unlike traditional analytics that measure aggregate metrics like page views or session duration, event tracking provides actionable insights into the “why” and “how” of user behavior, transforming raw interaction data into strategic business intelligence.
Event tracking emerged as a critical analytics discipline in the early 2000s as web analytics evolved beyond simple page counting. Initially, tools like Google Analytics introduced basic event tracking capabilities, but the methodology gained prominence with the rise of product analytics platforms such as Mixpanel and Amplitude in the 2010s. These platforms recognized that understanding user behavior at the event level was essential for product development, user retention, and conversion optimization. Today, over 78% of enterprises utilize some form of event tracking to monitor user interactions, according to industry research. The discipline has become foundational to data-driven decision-making across product management, marketing, and user experience teams. As digital products have become increasingly complex, event tracking has evolved to support real-time analysis, machine learning integration, and privacy-compliant data collection. The shift toward server-side event tracking represents the latest evolution, addressing privacy concerns while maintaining data quality and enabling more sophisticated attribution modeling.
Event tracking implementation involves several interconnected components working in concert to capture and process user interactions. At the most basic level, tracking code (typically JavaScript for web applications or SDKs for mobile apps) is embedded within the digital product to detect and record user actions. When a user triggers an event—such as clicking a button or submitting a form—the tracking code captures relevant parameters including the event name, category, action, label, value, timestamp, and user identifier. This data is then transmitted to an analytics backend, either through client-side tracking (where data is sent directly from the user’s browser) or server-side tracking (where data is processed on your servers before transmission). Modern implementations increasingly favor server-side tracking because it provides better data accuracy, improved privacy compliance, and reduced reliance on third-party cookies. The collected events are stored in databases optimized for time-series data, enabling rapid querying and analysis. Advanced implementations incorporate event validation schemas to ensure data quality, preventing malformed or incomplete events from corrupting analytics datasets. Organizations typically use tools like Google Tag Manager to manage tracking code without requiring constant developer intervention, allowing marketers and product managers to configure events through user-friendly interfaces.
| Aspect | Client-Side Tracking | Server-Side Tracking | Hybrid Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Accuracy | Moderate (affected by ad blockers, browser restrictions) | High (server-controlled, more reliable) | High (combines both methods) |
| Privacy Compliance | Challenging (relies on third-party cookies) | Excellent (first-party data, GDPR/CCPA friendly) | Excellent (flexible implementation) |
| Implementation Complexity | Low (simple JavaScript snippets) | High (requires backend infrastructure) | Medium (requires coordination) |
| Real-Time Capabilities | Excellent (immediate transmission) | Good (slight latency possible) | Excellent (optimized routing) |
| Cost | Low (minimal server resources) | Medium-High (requires infrastructure) | Medium (balanced approach) |
| Popular Tools | Google Analytics, Mixpanel, Heap | Segment, RudderStack, mParticle | Custom implementations, enterprise platforms |
| Best For | Small-medium businesses, simple tracking | Enterprise, privacy-sensitive industries | Complex, multi-channel operations |
The strategic value of event tracking extends far beyond simple data collection—it fundamentally transforms how organizations understand and optimize their digital products. Companies implementing comprehensive event tracking report 25-40% improvements in user engagement metrics within the first year, according to product analytics research. By tracking specific user actions, product teams can identify which features drive retention, which onboarding flows convert most effectively, and where users encounter friction. Marketing teams leverage event data to understand which campaigns and content attract high-value users, enabling more efficient budget allocation. For e-commerce businesses, event tracking on actions like “add to cart,” “view product,” and “complete purchase” reveals the precise points where customers abandon their journeys, allowing targeted interventions. Financial services companies use event tracking to monitor regulatory compliance interactions, while SaaS platforms track feature adoption to identify at-risk customers before churn occurs. The competitive advantage gained through event tracking is substantial: organizations that deeply understand user behavior through event-level analytics can iterate faster, make more confident product decisions, and ultimately deliver superior user experiences. This data-driven approach has become table stakes in competitive markets, with companies lacking robust event tracking falling behind competitors who leverage behavioral insights for continuous optimization.
In the context of AI-powered search and monitoring platforms, event tracking takes on additional significance for brand visibility and citation tracking. As AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude increasingly generate responses that cite or reference specific brands and content, organizations need to track not only how users interact with their own digital properties but also how their brand appears within AI-generated content. AmICited represents a new category of monitoring tools that extends traditional event tracking concepts to the AI domain, recording when and how your brand is mentioned in AI responses. This creates a comprehensive picture: traditional event tracking shows you how users interact with your website or app, while AI citation tracking reveals how your brand is being referenced in AI-generated answers. Together, these tracking mechanisms provide complete visibility into your digital presence. For example, a software company might track that 45% of users who discover them through an AI recommendation complete a trial signup (event tracking), while simultaneously monitoring that their brand appears in 12% of AI responses about their product category (AI citation tracking). This dual perspective enables more sophisticated marketing strategies and helps organizations understand the full customer journey in an AI-augmented search landscape.
Successful event tracking requires careful planning and disciplined execution to avoid common pitfalls that undermine data quality and actionability. The first critical step is developing a comprehensive tracking plan that documents which events matter most to your business objectives. Rather than tracking every possible interaction—which creates noise and performance overhead—organizations should focus on events that directly indicate user engagement, conversion progress, or feature adoption. Best practices include establishing consistent naming conventions for events (such as “user_signup_completed” rather than “signup” or “new_user”), defining clear event parameters, and documenting the business rationale for each tracked event. Teams should implement data validation mechanisms to catch malformed events before they corrupt analytics datasets. Privacy compliance requires explicit attention: organizations must obtain user consent, implement transparent data handling practices, and provide users with options to control their data. Performance optimization is essential—poorly implemented tracking can slow websites and apps, degrading user experience. Modern best practices favor server-side tracking where feasible, as it reduces client-side overhead and improves data reliability. Organizations should also establish data governance policies defining who can access event data, how long it’s retained, and how it’s used. Regular audits of tracking implementations help identify gaps, redundancies, or compliance issues before they become problems.
Modern event tracking systems have evolved beyond simple data collection to enable sophisticated analytical capabilities that drive strategic business decisions. Machine learning algorithms can analyze historical event patterns to predict which users are at risk of churning, enabling proactive retention interventions. Cohort analysis—comparing event patterns across different user segments—reveals which types of users are most valuable and what drives their engagement. Funnel analysis visualizes the step-by-step progression through critical user journeys, highlighting conversion rates at each stage and identifying optimization opportunities. Heatmap analysis overlays event data onto user interface elements, showing which buttons, links, and content areas receive the most interaction. Attribution modeling uses event sequences to determine which marketing touchpoints and product experiences contribute most to conversions, enabling more sophisticated budget allocation. Predictive models can forecast future user behavior based on historical event patterns, such as predicting which free trial users will convert to paid customers. Session replay technology combines event data with video recordings of user sessions, providing qualitative context for quantitative patterns. These advanced applications transform event tracking from a descriptive tool (showing what happened) into a predictive and prescriptive tool (showing what will happen and what to do about it).
Event tracking continues to evolve in response to changing technological landscapes, regulatory environments, and business needs. The shift toward privacy-first tracking represents a fundamental transformation, with server-side implementations and first-party data strategies replacing third-party cookie reliance. Regulatory pressures from GDPR, CCPA, and emerging privacy laws are forcing organizations to rethink data collection and retention practices. AI-powered analytics are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with machine learning models automatically identifying significant patterns and anomalies without requiring manual analysis. The integration of event tracking with AI monitoring platforms like AmICited reflects a broader trend toward comprehensive digital presence monitoring that encompasses both direct user interactions and AI-mediated brand visibility. Cross-platform tracking is becoming more sophisticated, enabling organizations to understand user journeys that span websites, mobile apps, email, and increasingly, AI-generated content. Real-time personalization powered by event data is becoming standard, with systems that adapt user experiences based on behavioral signals in milliseconds. The emergence of composable analytics architectures allows organizations to build custom tracking solutions tailored to specific needs rather than relying on monolithic platforms. Looking forward, event tracking will likely become even more integrated with business intelligence systems, enabling automatic decision-making based on behavioral triggers. The convergence of event tracking with AI citation monitoring represents the next frontier, where organizations can understand not only how users interact with their properties but also how their brand appears in AI-generated responses—creating a truly comprehensive view of digital presence and influence in an AI-augmented world.
Page view tracking measures when users load a page, while event tracking captures specific interactions within that page, such as button clicks, form submissions, or video plays. Event tracking provides granular behavioral data that page views alone cannot offer, enabling deeper insights into user engagement and product usage patterns.
Event tracking identifies friction points in the user journey by showing where users drop off or hesitate. By analyzing these events, teams can optimize forms, simplify checkout processes, and improve CTAs. Studies show that companies using event tracking see conversion rate improvements of 15-30% through targeted optimizations based on behavioral data.
Event tracking must comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA, requiring explicit user consent and transparent data handling. Best practices include anonymizing user data, implementing consent mechanisms, and using privacy-first tracking methods. Many platforms now offer server-side tracking to reduce third-party cookie reliance while maintaining data quality.
Popular event tracking tools include Google Analytics, Mixpanel, Amplitude, Heap, and Countly. Each offers different capabilities—Google Analytics excels in web analytics, Mixpanel specializes in product analytics, and Amplitude focuses on user journey analysis. The best choice depends on your platform, budget, and specific tracking needs.
Event tracking on your website or app helps monitor how users discover and interact with your brand content. When combined with AI monitoring tools like AmICited, you can track not only direct user interactions but also how your brand appears in AI-generated responses, creating a comprehensive view of your digital presence and visibility.
Standard events are pre-defined interactions like page views and clicks that most analytics tools track automatically. Custom events are tailored to your specific business needs, such as 'feature_adoption' or 'checkout_completed.' Custom events provide deeper insights into product-specific behaviors and business metrics.
Data retention depends on your business needs and regulatory requirements. Most companies retain event data for 12-24 months for analysis and trend identification. GDPR and CCPA may require shorter retention periods or user deletion options. Consider your analytics goals and compliance obligations when setting retention policies.
Poorly implemented event tracking can impact performance, but modern tools use asynchronous tracking and batching to minimize impact. Best practices include using server-side tracking, implementing event buffering, and avoiding excessive event firing. Most well-configured event tracking systems add less than 1% performance overhead.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Conversion tracking monitors user actions toward business goals. Learn how to measure conversions, track metrics, and optimize marketing ROI with comprehensive ...
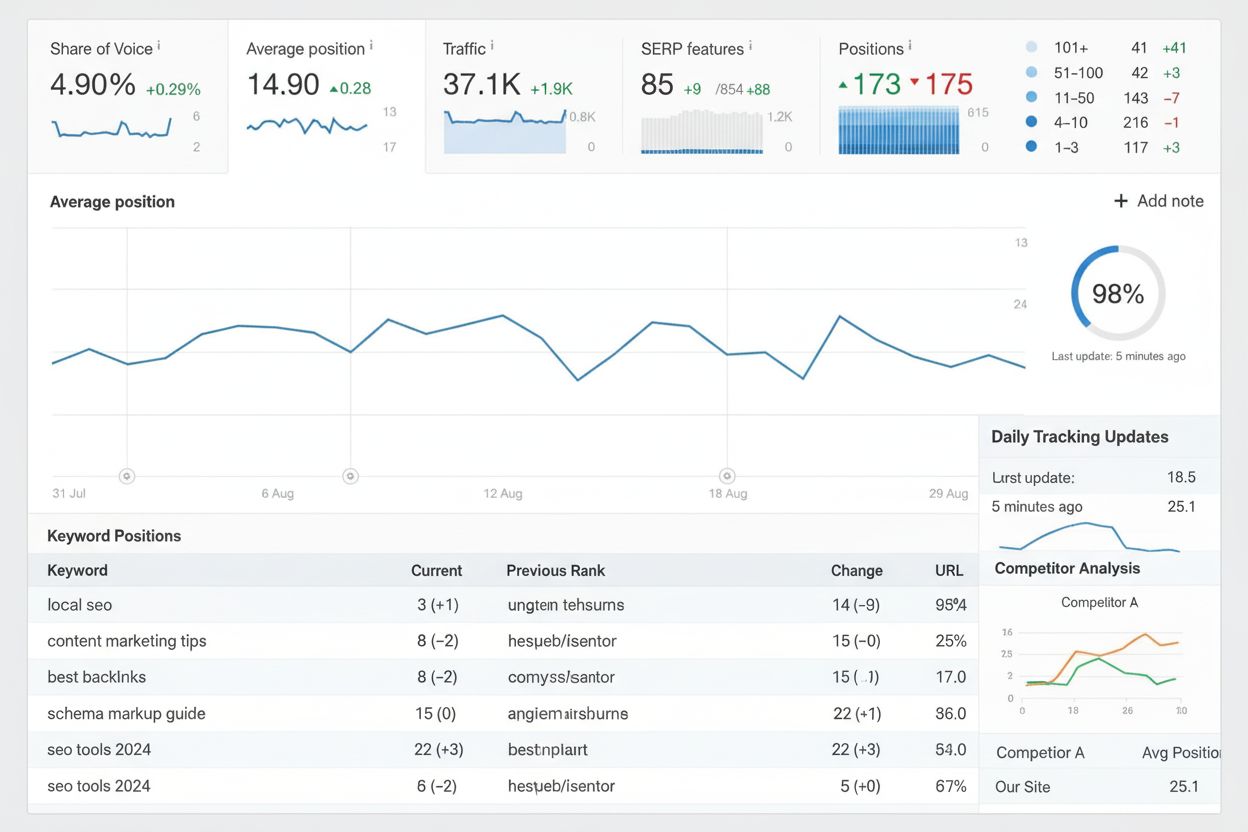
Rank tracking monitors keyword positions in search results over time. Learn how it works, why it matters for SEO, and how to use rank tracking tools effectively...
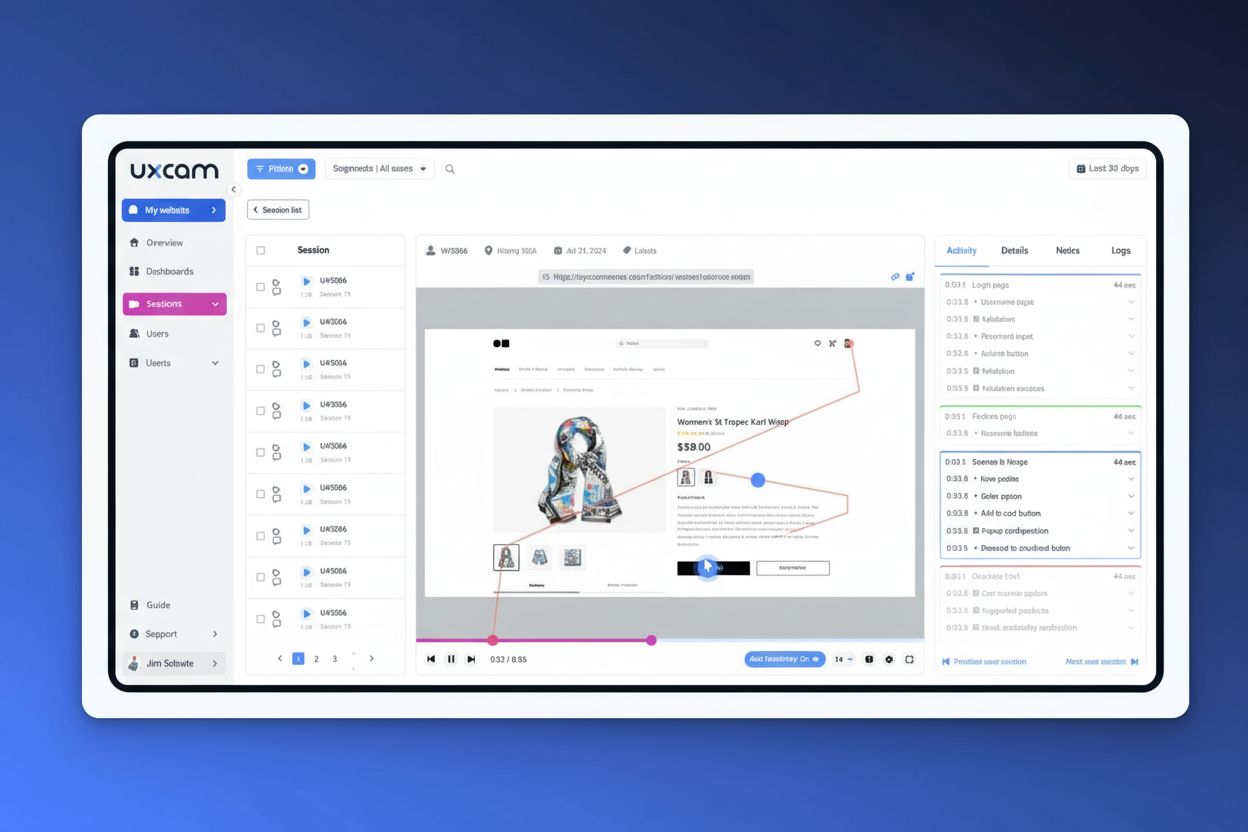
Session recording captures video of user website interactions including clicks, scrolls, and navigation. Learn how session replays work, their benefits for UX o...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.