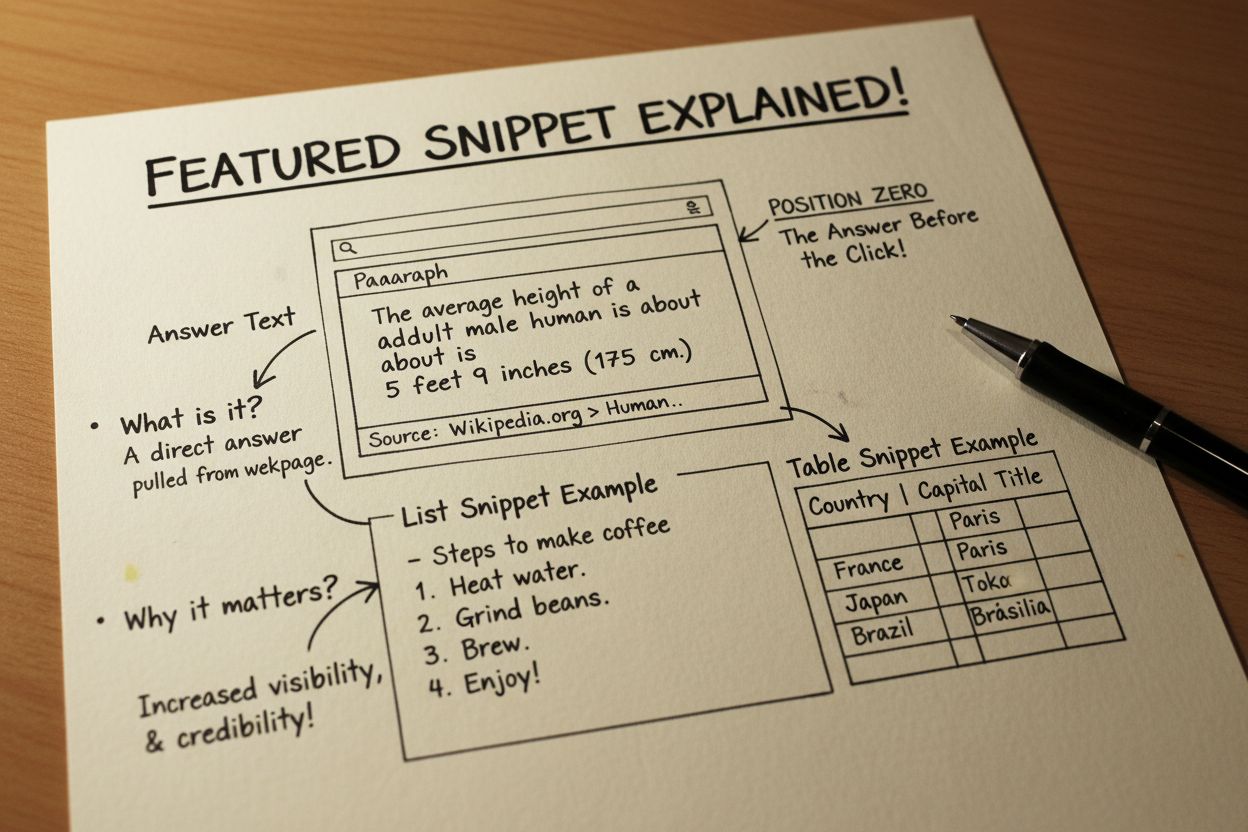
Featured Snippet
Learn what featured snippets are, how they work in Google search results, their impact on CTR, and strategies to optimize your content for position zero visibil...

A featured image is the primary visual representation of a post, page, or article that appears at the top of content and across various platforms including social media, search results, and content feeds. It serves as a visual anchor that represents the content’s theme, mood, or subject matter, and is essential for user engagement, SEO optimization, and social media sharing.
A featured image is the primary visual representation of a post, page, or article that appears at the top of content and across various platforms including social media, search results, and content feeds. It serves as a visual anchor that represents the content's theme, mood, or subject matter, and is essential for user engagement, SEO optimization, and social media sharing.
A featured image is the primary visual representation assigned to a post, page, or article within a content management system, most commonly WordPress. It serves as the main image that represents the content’s theme, mood, or subject matter and appears across multiple locations including the top of individual posts, blog archive pages, homepage feeds, and social media platforms. The featured image is distinct from other images within the content body—it is specifically designated to represent the entire piece of content at a glance. This visual element has become essential in modern web design, where approximately 65% of users are visual learners who prefer images to text. Featured images function as both a design element and a functional tool that influences user engagement, click-through rates, and search engine optimization performance.
The concept of featured images emerged with the rise of WordPress as a dominant content management system in the mid-2000s. As websites became increasingly visual and social media platforms gained prominence, the need for a standardized way to represent content visually became apparent. WordPress introduced the featured image functionality to allow theme developers to display representative images in consistent, predictable ways across different page layouts. This innovation addressed a critical gap: without featured images, websites had no reliable method to control which image would appear when content was shared on social media platforms. Today, featured images are considered a standard best practice across all major CMS platforms including Shopify, Wix, Squarespace, and custom-built websites. Research from HubSpot indicates that articles with images receive 94% more views than articles without images, demonstrating the significant impact of visual content on user engagement. The evolution of featured images has paralleled the growth of social media sharing, with platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn now relying on Open Graph meta tags to pull featured image data for social previews.
Featured images operate through a combination of database storage, metadata assignment, and template rendering. When you set a featured image in WordPress, the system stores the image file in the media library and creates a post-meta relationship linking the image to the specific post or page. The featured image is then referenced through template tags like get_the_post_thumbnail() in classic themes or through the featured image block in block themes. The optimal featured image dimensions are 1200 x 628 pixels, which provides the ideal aspect ratio for social media sharing while maintaining clarity across desktop and mobile devices. This size is specifically calculated to prevent image distortion on platforms like Facebook (which uses 1200 x 630 pixels) and Twitter (which uses 1024 x 512 pixels). File size should ideally remain under 5MB, though most images should be compressed to 100-300KB for optimal page load performance. Featured images support multiple file formats including JPEG (best for photographs), PNG (best for graphics with transparency), and WebP (modern format offering superior compression). The image must include proper metadata including alt text (for accessibility and SEO), descriptive file names (using hyphens, not underscores), and captions that provide context to both users and search engines.
| Element | Featured Image | Header Image | Thumbnail Image | Social Media Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Represents entire post/page content | Decorative site-wide header element | Small preview in archives/feeds | Social platform preview |
| Typical Dimensions | 1200 x 628 pixels | 1920 x 400 pixels (varies) | 300 x 200 pixels | 1200 x 630 pixels |
| Display Location | Top of post, archives, feeds | Top of website pages | Blog listings, search results | Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn |
| SEO Impact | High (with proper optimization) | Low to moderate | Moderate | Indirect (drives traffic) |
| Metadata Requirements | Alt text, file name, description | Alt text, file name | Alt text, file name | Open Graph tags |
| Customization | Per post/page | Site-wide or section-wide | Theme-dependent | Platform-specific |
| User Engagement | Directly influences click-through | Affects brand perception | Drives archive page clicks | Critical for social shares |
| Mobile Responsiveness | Essential for mobile UX | Important for responsive design | Automatically scaled | Platform-dependent |
Featured images significantly influence SEO performance when properly optimized. Search engines like Google use featured images to better understand content context and topic relevance. The image file name should match your target keyword or content topic—for example, naming an image “best-coffee-brewing-methods.jpg” rather than “image-001.jpg” provides valuable semantic information to search engines. Alt text is equally critical, serving dual purposes: it provides accessibility for screen reader users and gives search engines explicit information about image content. Studies show that websites implementing proper image alt text experience a 7-10% improvement in organic search visibility. Featured images also contribute to rich snippets in search results, where Google may display your featured image alongside the page title and meta description. This visual enhancement significantly increases click-through rates—research indicates that search results with images receive 30% higher CTR compared to text-only results. Additionally, featured images support schema markup implementation, particularly the ImageObject schema, which helps search engines catalog and understand images more effectively. When featured images are optimized with proper dimensions, compression, and metadata, they contribute to improved Core Web Vitals scores, particularly the Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) metric, which directly impacts search rankings.
The relationship between featured images and social media sharing is fundamental to modern content distribution. When content is shared on platforms like Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, or WhatsApp, these platforms use Open Graph meta tags to extract and display featured image data. The og:image tag specifically pulls the featured image URL to create rich preview cards that appear in social feeds. Without a properly configured featured image and Open Graph tags, social platforms may select random images from your content or display no image at all, resulting in significantly lower engagement. Research from Cronbay indicates that posts with optimized Open Graph previews generate up to 3x more shares compared to posts without proper image optimization. The featured image dimensions must be carefully considered for each platform: Facebook recommends 1200 x 630 pixels, Twitter uses 1024 x 512 pixels for summary cards with large images, and LinkedIn displays 1200 x 627 pixels. Featured images also work in conjunction with Twitter Cards, an alternative metadata system that allows more granular control over how content appears when shared on Twitter. When a featured image is properly optimized with compelling visual design and relevant content representation, it serves as a visual call-to-action that encourages users to click through from social media to your website, directly impacting traffic and conversion metrics.
Different content management systems and website builders handle featured images with varying levels of sophistication. WordPress, the most widely used CMS powering 43% of all websites, offers native featured image functionality with extensive customization options through themes and plugins. WordPress block themes provide visual controls for featured image styling, while classic themes require CSS modifications. Shopify uses featured images for product pages and blog posts, with specific dimension requirements (1024 x 1024 pixels for products). Wix and Squarespace offer drag-and-drop featured image management with automatic optimization. HubSpot CMS integrates featured images with its content management and marketing automation tools, allowing dynamic image selection based on content attributes. Elementor, a popular WordPress page builder, provides advanced featured image controls including overlay effects, duotone filters, and responsive sizing options. For Hugo CMS and static site generators, featured images are typically managed through front matter metadata, allowing developers to specify image paths and dimensions programmatically. Each platform has different optimal dimensions and implementation methods, making it essential to understand your specific platform’s requirements. Additionally, many platforms now support AI-generated featured images, allowing users to create images directly within the CMS using generative AI tools, streamlining the content creation workflow.
Featured images directly influence user behavior and engagement metrics across multiple touchpoints. On blog archive pages and homepage feeds, featured images serve as visual anchors that help users quickly scan and identify content of interest. Research from the Content Marketing Institute demonstrates that articles with relevant featured images receive 94% more total views compared to articles without images. Featured images also reduce cognitive load—users can understand content topic and relevance in milliseconds by viewing an image, rather than reading headlines and descriptions. This visual processing advantage translates to higher click-through rates, with studies showing that featured images can increase CTR by 30-50% depending on visual quality and relevance. On mobile devices, featured images become even more critical, as they occupy significant screen real estate and serve as the primary visual element users encounter before deciding whether to engage with content. Featured images also influence bounce rate and time on page metrics; compelling featured images encourage users to stay on pages longer and explore related content. Additionally, featured images contribute to social proof and brand trust—professional, high-quality featured images signal content credibility and authority, while poorly designed or irrelevant images damage brand perception. The psychological impact of featured images extends to color psychology, where specific colors in featured images can influence user emotions and decision-making, making strategic color selection an important optimization consideration.
The featured image landscape is evolving rapidly with emerging technologies and changing user behaviors. AI-generated featured images are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with tools like DALL-E, Midjourney, and platform-native AI image generators allowing creators to generate custom featured images without design skills or stock photo subscriptions. This democratization of image creation is expected to increase featured image usage and customization across all content types. Dynamic featured images that change based on user context, device type, or personalization data are emerging as a next-generation approach, allowing different featured images to display to different audience segments. Video featured images and animated GIFs are gaining traction as platforms increasingly support motion content in preview cards, offering higher engagement potential than static images. The integration of featured images with AI content monitoring platforms like AmICited is creating new opportunities for tracking how featured images appear in AI-generated responses and generative search results. As AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews become primary discovery mechanisms, the importance of featured images in these contexts will grow significantly. Responsive image formats using WebP and AVIF are becoming standard, offering superior compression and faster load times. Additionally, the rise of voice search and visual search technologies means featured images will play increasingly important roles in content discoverability beyond traditional text-based search. The future of featured images will likely involve greater integration with schema markup, structured data, and semantic web technologies, enabling machines to understand and utilize featured images with unprecedented sophistication.
In the context of AI-powered content discovery and generative search, featured images serve as critical visual identifiers for brand and content attribution. Platforms like AmICited monitor how content appears in AI-generated responses across systems including ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude. Featured images, when properly optimized with metadata and schema markup, help ensure accurate visual representation of your content in these AI systems. As generative AI systems increasingly incorporate images alongside text in their responses, the quality and relevance of featured images become essential for brand recognition and content attribution. Featured images with clear, descriptive alt text and proper schema markup are more likely to be selected and displayed by AI systems when referencing your content. This emerging importance of featured images in AI contexts represents a significant shift from traditional SEO, where featured images were primarily optimization tools for human users and search engines. Organizations using AI monitoring tools can track which featured images are most frequently displayed in AI responses, providing valuable insights into content performance and brand visibility in generative search results. The integration of featured image optimization with AI citation tracking represents a new frontier in content strategy, where visual elements become as important as textual content for ensuring proper attribution and visibility in AI-generated responses.
The recommended featured image size is 1200 x 628 pixels, which works optimally across most WordPress themes and social media platforms. This dimension ensures clarity on desktop and mobile devices while maintaining proper aspect ratios. However, the exact size may vary depending on your specific theme, so always check your theme's documentation for recommended dimensions to avoid pixelation or distortion.
Featured images improve SEO by providing search engines with visual context about your content through alt text, file names, and schema markup. When properly optimized with descriptive alt text and relevant file names, featured images help search engines understand content better, potentially leading to rich snippets and improved click-through rates. Additionally, featured images enhance user experience, which indirectly supports SEO performance through increased engagement signals.
Featured images are directly used by Open Graph meta tags to control how content appears when shared on social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn. The og:image tag pulls the featured image URL to display in social media previews. Without a properly set featured image, social platforms may select random images from your content or display no image at all, significantly reducing click-through rates and engagement.
Yes, featured images can significantly impact page load speed if not properly optimized. Large, uncompressed images slow down your site, frustrating users and potentially harming SEO rankings. To maintain performance, compress images before uploading, use appropriate file formats (JPEG for photos, PNG for graphics), and ensure file sizes don't exceed 5MB. Many WordPress plugins like Smush or ShortPixel can automatically optimize images without sacrificing quality.
Block themes offer more visual control over featured images through the site editor, allowing you to add overlays, adjust sizing, and customize display across templates with point-and-click functionality. Classic themes require CSS code modifications to change featured image appearance. Block themes provide greater flexibility for designers and non-developers, while classic themes require more technical knowledge to customize featured image styling and behavior.
Featured images serve as visual identifiers for content when it appears in AI-generated responses, search results, and social media shares. Platforms like AmICited track how featured images are displayed alongside brand mentions in AI responses from ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Properly optimized featured images with descriptive metadata help ensure accurate visual representation of your content in AI systems and improve brand recognition in generative search results.
Creating unique featured images for each post is strongly recommended for better engagement and SEO performance. Unique images help differentiate content, improve click-through rates on social media, and provide better visual context to search engines. However, maintaining consistent styling, color schemes, and design elements across featured images helps establish brand identity and visual coherence across your content library.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn what featured snippets are, how they work in Google search results, their impact on CTR, and strategies to optimize your content for position zero visibil...

Learn what custom images and original visual content are, their importance for brand identity, SEO, and AI search visibility. Discover how custom visuals differ...

Main Content (MC) is the primary material on a webpage that fulfills its purpose. Learn how MC quality affects SEO rankings, E-E-A-T signals, and AI monitoring ...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.