Content Freshness Signals
Learn how content freshness signals work in AI systems. Understand timestamps, modification dates, and technical indicators that influence AI citations and visi...
A freshness signal is a ranking factor that evaluates how recently a web page was published or significantly updated, influencing its visibility in search results and AI-generated responses. Search engines and AI platforms prioritize fresh content for time-sensitive queries where recency directly impacts information accuracy and relevance.
A freshness signal is a ranking factor that evaluates how recently a web page was published or significantly updated, influencing its visibility in search results and AI-generated responses. Search engines and AI platforms prioritize fresh content for time-sensitive queries where recency directly impacts information accuracy and relevance.
Freshness signal is a ranking factor that search engines and AI platforms use to evaluate how recently a web page was published or significantly updated, and how this recency should influence its visibility in search results and AI-generated responses. The freshness signal measures content timeliness through multiple indicators including publication date, modification date, update frequency, and the volume of content changes. This signal became particularly important after Google’s 2011 Freshness Algorithm update, which fundamentally changed how search results are ranked for time-sensitive queries. Today, freshness signals play an even more critical role in AI search platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews, where content decay happens significantly faster than traditional search. Understanding freshness signals is essential for any organization seeking visibility across both traditional search and emerging AI search channels, as the recency of your content directly impacts whether your brand gets cited when AI systems answer user questions.
The concept of content freshness in search ranking emerged gradually before becoming formalized through Google’s 2011 Freshness Algorithm update. Prior to this update, Google’s ranking systems treated all content relatively equally regardless of publication date, assuming that older, more established content was inherently more authoritative. However, this approach created problems for users seeking current information—a five-year-old article about smartphone technology would rank alongside brand-new reviews of the latest models, despite being largely obsolete. The Freshness Algorithm changed this paradigm by introducing time as a relevance measure, enabling Google to surface content that was literally up-to-the-minute relevant for queries where recency mattered. Google’s official announcement stated that the update impacted approximately 35% of all search queries, with noticeable effects on 6-10% of searches. This represented one of the most significant algorithmic shifts in search history, demonstrating that freshness had become a core ranking principle rather than a minor signal.
The infrastructure enabling the Freshness Algorithm came from Google’s Caffeine update, released five months earlier in 2010. Caffeine fundamentally transformed Google’s indexing infrastructure, enabling the search engine to process and index web content at unprecedented scale and speed. Before Caffeine, Google’s indexing system operated on a batch-processing model that could take weeks to fully crawl and index the web. Caffeine introduced continuous, real-time indexing that could detect and process new content within minutes of publication. This technological foundation made the Freshness Algorithm possible—without the ability to rapidly detect and index new content, Google couldn’t effectively prioritize fresh results. The combination of Caffeine’s infrastructure and the Freshness Algorithm’s logic created a system where breaking news could rank within hours of publication, and regularly updated content could maintain top positions indefinitely.
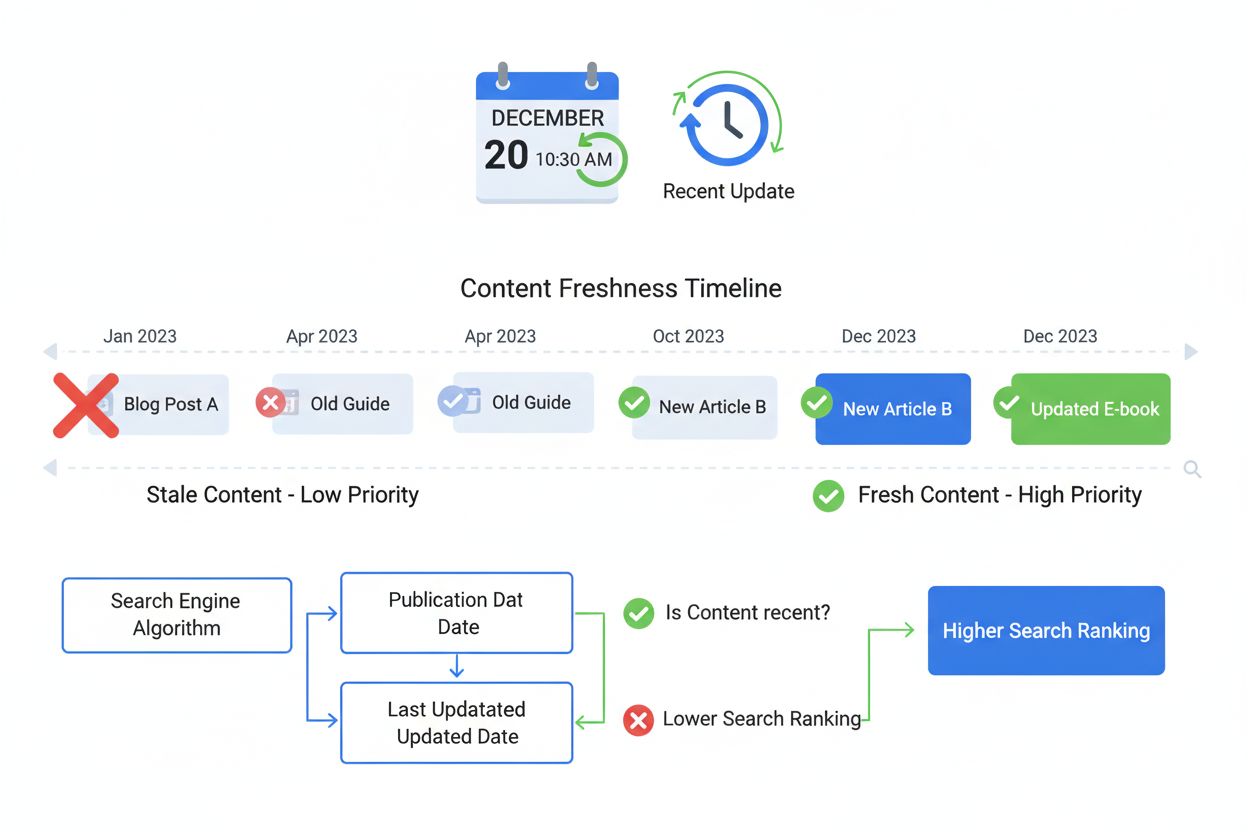
Search engines employ sophisticated methodologies to assess content freshness, moving far beyond simple publication date comparisons. Google’s freshness measurement considers multiple signals that collectively determine a page’s freshness score. The page inception date—when a page was first indexed by Google—provides the baseline. However, more important than initial publication is the modification date, which indicates when the page was last substantially changed. Google distinguishes between minor edits (fixing typos, correcting links) and major updates (rewriting sections, adding new content, restructuring information). Only significant changes contribute meaningfully to freshness signals; cosmetic edits don’t reset the freshness clock. The frequency of updates matters substantially—pages that change regularly signal ongoing maintenance and relevance, while pages that never change suggest abandonment. The volume of content change also factors in; adding an entire new section signals more freshness than updating a single sentence. Additionally, the freshness of backlinks pointing to your page influences your freshness score—links from recently updated, high-freshness sites transfer some of that freshness signal to your page.
Research from Moz and other SEO authorities has documented these freshness measurement factors through extensive analysis of ranking patterns. Pages showing consistent update patterns across multiple signals achieve substantially higher freshness scores than pages with sporadic or minimal changes. Interestingly, the relationship between freshness and ranking isn’t linear—a page updated daily doesn’t necessarily rank twice as well as one updated weekly. Instead, freshness signals interact with other ranking factors like relevance, authority, and user experience. A highly authoritative page updated monthly might outrank a low-authority page updated daily, demonstrating that freshness amplifies existing authority rather than replacing it. This nuanced relationship explains why some older content continues ranking well despite newer alternatives—if the older content maintains regular updates and strong authority signals, it can compete effectively against fresher but less authoritative alternatives.
| Aspect | Traditional Search (Google) | AI Search (ChatGPT/Perplexity) | Evergreen Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Update Frequency Impact | Weekly updates maintain strong signals | 2-3 day updates required for top visibility | Monthly updates sufficient |
| Content Age Tolerance | Pages 6+ months old still rank well | Content older than 30 days shows decay | Age irrelevant if regularly updated |
| Citation Preference | Average cited content age: 1,432 days | Average cited content age: 1,064 days | Not a primary ranking factor |
| Decay Timeline | Gradual decline over months | Rapid decline within days | No decay pattern |
| Update Type Required | Substantial changes needed | Any meaningful update helps | Minimal updates needed |
| Ranking Impact | 6% of algorithm (2025 data) | ~35% of ranking factors | Minimal direct impact |
| Query Types Affected | News, trends, products, recurring events | All query types (more aggressive) | Historical, foundational topics |
| Measurement Method | Publication date, modification date, update frequency | Real-time content analysis, recency scoring | Not actively measured |
The technical implementation of freshness signals involves sophisticated algorithms that analyze temporal patterns in content and user behavior. Search engines use timestamp metadata embedded in HTML to identify publication and modification dates, though they also employ content analysis to detect changes even when metadata isn’t explicitly provided. When a crawler revisits a page, it compares the current version against previously cached versions, identifying what changed, how much changed, and when the change occurred. This comparison happens at the HTML level, analyzing actual content differences rather than relying solely on date tags. Pages that show genuine content modifications receive freshness credit, while pages where only the date changed without content updates receive no credit—search engines have become sophisticated enough to detect this manipulation.
Query-level freshness evaluation represents another crucial mechanism. Search engines don’t apply freshness uniformly to all queries; instead, they analyze each query to determine whether freshness is relevant. Queries containing temporal indicators (“2025,” “latest,” “new,” “recent,” “this year”) trigger freshness evaluation. Queries about evergreen topics (“how to tie a tie,” “photosynthesis definition,” “recipe for chocolate cake”) don’t trigger freshness evaluation. Search engines use machine learning models trained on historical click data to predict whether users searching a particular query prefer fresh or established content. This prediction happens in milliseconds, allowing the search engine to adjust ranking algorithms on a per-query basis. A query for “iPhone 16 review” triggers aggressive freshness weighting, while “iPhone history” doesn’t. This dynamic approach explains why freshness importance varies so dramatically across different search queries.
Temporal decay functions model how content value decreases over time for time-sensitive topics. These mathematical functions assign higher relevance scores to recently published content while gradually reducing scores for older content. The decay rate varies by topic—news content decays rapidly (within hours), product reviews decay moderately (within weeks), and evergreen content doesn’t decay at all. Search engines implement different decay functions for different content categories, allowing them to handle the diverse freshness requirements across the entire web. A page about “best smartphones 2025” decays rapidly as the year progresses and new models release, while a page about “smartphone history” maintains constant value regardless of time passage.
The importance of freshness signals in AI search far exceeds their importance in traditional Google search, creating a fundamental shift in content strategy requirements. Research analyzing over 129,000 ChatGPT citations reveals that AI platforms cite content averaging 1,064 days old, compared to 1,432 days for traditional Google search results—representing 25.7% fresher content on average. This preference for recency reflects how AI models work: they synthesize information from multiple sources to create comprehensive answers, and they prioritize recent sources to ensure accuracy and relevance. When an AI system answers a question about “best project management tools 2025,” it will heavily weight sources published or updated in 2024-2025, largely ignoring articles from 2022 or earlier regardless of their authority or quality.
Perplexity AI demonstrates the most aggressive freshness requirements of any major platform. Research tracking Perplexity visibility shows that content begins losing visibility within 2-3 days without updates, and visibility drops substantially after one week without changes. This creates a fundamentally different content maintenance requirement compared to Google, where pages can maintain top rankings for months without updates. For Perplexity optimization, brands targeting high-visibility topics must implement update schedules of every 2-3 days, adding new information, refreshing statistics, incorporating recent examples, or expanding existing sections. This intensive maintenance requirement explains why Perplexity visibility correlates so strongly with content freshness—the platform essentially forces continuous content improvement as the price of visibility.
ChatGPT and Google AI Overviews show less aggressive freshness requirements than Perplexity but still prioritize recent content more heavily than traditional Google search. ChatGPT’s search capabilities perform real-time web searches, meaning even newly published content can achieve citations if it provides exceptional answers. Google AI Overviews draw primarily from pages already ranking in traditional search results, so traditional SEO freshness requirements apply, but AI Overviews show preference for fresher content within the ranked set. For brands seeking AI visibility across multiple platforms, implementing weekly update schedules for priority content maintains strong visibility while remaining operationally feasible.
Google’s Freshness Algorithm identified three distinct categories of queries deserving fresh content, each with different freshness requirements and update patterns. Recent events queries include breaking news, trending topics, and current developments where users explicitly seek the latest information. A search for “Ukraine conflict latest developments” clearly indicates the user wants the most recent news, not historical background. Search engines prioritize content published within hours or days for these queries, making real-time news coverage essential for visibility. Content about recent events becomes stale rapidly—an article published yesterday about today’s news is already outdated. For brands covering news-related topics, maintaining real-time publishing capabilities and rapid update processes is essential for freshness signal optimization.
Regularly recurring events include annual conferences, seasonal sports competitions, election cycles, and other predictable events that happen on regular schedules. A search for “Super Bowl 2025” clearly indicates interest in the current year’s event, not historical Super Bowls. Content about recurring events requires strategic updates aligned with event cycles—updating Super Bowl content annually, conference content yearly, and election content every four years. The freshness requirement isn’t continuous but rather synchronized with event timing. Brands can plan content updates around predictable event schedules, making this category more manageable than breaking news while still requiring deliberate freshness management.
Frequently updated topics include product reviews, technology news, market trends, and other subjects where information changes regularly but without specific event triggers. A search for “best email marketing software” indicates interest in current options with current pricing, features, and user experiences. Content about frequently updated topics requires regular refreshes—monthly or quarterly updates for most product reviews, weekly updates for rapidly evolving technology topics. Unlike breaking news (which requires immediate response) or recurring events (which follow predictable schedules), frequently updated topics require ongoing maintenance based on how rapidly the topic evolves. Brands must monitor their topic area and update content whenever significant changes occur—new product releases, pricing changes, feature updates, or competitive shifts.
The relationship between freshness signals and E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) has become increasingly important in modern search ranking. Fresh content signals trustworthiness by demonstrating that an organization actively maintains and updates its information. When users encounter a page about “best marketing tools 2025” published in 2023 and never updated, they question whether the information remains accurate. Conversely, a page showing “Last Updated: January 2025” with recent examples and current pricing signals that the organization cares about accuracy and maintains current information. This trust signal extends to AI systems, which increasingly use freshness as a proxy for reliability—if an organization updates content regularly, the content is more likely to be accurate and trustworthy.
Author expertise signals strengthen when combined with content freshness. An expert who publishes content and then never updates it appears less engaged with their field than an expert who regularly updates content with new insights and developments. Freshness demonstrates ongoing expertise maintenance—the author stays current with industry developments and incorporates new knowledge into existing content. This is particularly important for technical fields, business topics, and any area where knowledge evolves rapidly. An expert in artificial intelligence who published an article about AI in 2020 and never updated it appears less credible than one who regularly updates the article with new developments, research findings, and emerging trends.
Authority building through consistent content updates creates compounding advantages. Pages that receive regular updates tend to attract more backlinks, generate more engagement, and receive more social mentions—all signals that reinforce authority. Additionally, regular updates signal to search engines that a page is important enough to maintain, which influences crawl frequency and ranking priority. Search engines allocate more crawl budget to frequently updated pages, ensuring new content gets indexed quickly. This creates a virtuous cycle: fresh content attracts more engagement, which attracts more links, which increases authority, which improves rankings, which drives more traffic, which justifies further investment in content maintenance.
Implementing effective freshness signal optimization requires strategic planning that balances content quality with update frequency. The first step involves query analysis to determine which of your target keywords require freshness optimization. Examine the top 10-20 search results for each target keyword and note their publication dates. If most results are from the past month, freshness is critical for that keyword. If results span multiple years with older content ranking well, freshness matters less. This analysis reveals which content requires aggressive update schedules and which can maintain longer update cycles. Create a spreadsheet tracking target keywords, current ranking positions, average result age, and freshness requirements. This becomes your roadmap for content maintenance prioritization.
Content refresh scheduling should align with freshness requirements identified in your analysis. Establish tiered update schedules: Tier 1 (critical freshness required) updates every 2-3 days, Tier 2 (moderate freshness) updates weekly, Tier 3 (minimal freshness) updates monthly, and Tier 4 (evergreen) updates quarterly or as needed. Assign responsibility for each tier—perhaps your news team handles Tier 1, marketing team handles Tier 2, and content team handles Tier 3. Use content management system scheduling features to automate publication of updated content. Many platforms allow you to schedule updates in advance, ensuring consistent publication even during busy periods. Document your update schedule and track compliance to ensure consistency.
Meaningful update practices distinguish legitimate freshness optimization from manipulation. Each update should add genuine value: new statistics with current dates, recent examples replacing outdated ones, expanded sections addressing emerging questions, or revised explanations reflecting current best practices. Avoid the common mistake of changing only the publication date without content changes—search engines detect this manipulation and may penalize your site. Instead, make substantive changes that improve the page for users. Add a “Last Updated” date prominently near the article top, along with a brief changelog noting what changed: “Updated January 2025: Added new case study, refreshed statistics, expanded mobile optimization section.” This transparency helps both users and search engines understand that updates are genuine improvements rather than manipulation.
Content monitoring systems help identify when updates are needed. Set up Google Alerts for your target keywords to monitor when new information emerges. Subscribe to industry newsletters and news sources covering your topic area. Monitor competitor content to identify when they publish new information you should address. Use tools like Semrush or Ahrefs to track ranking changes for your target keywords—sudden drops often indicate freshness decay. When you notice ranking declines for previously strong pages, prioritize those for updates. This reactive approach complements your proactive update schedule, ensuring you address both planned updates and emerging freshness needs.
The definition and application of freshness signals continues evolving as search technology advances and user behavior changes. Real-time content integration represents an emerging frontier where search engines increasingly incorporate live data—current pricing, real-time inventory, breaking news, live event scores—directly into search results. This trend suggests freshness requirements will intensify for certain content categories. Brands selling products will need to maintain real-time pricing and inventory information. News organizations will need to publish updates within minutes of developments. Financial services will need to update market data continuously. This evolution creates both challenges (more intensive content maintenance) and opportunities (competitive advantage for brands that implement real-time systems).
Personalized freshness evaluation is emerging as AI systems increasingly customize responses based on individual user context. Rather than applying uniform freshness requirements across all users, AI platforms may weight freshness differently based on user preferences, search history, and stated interests. A user who frequently searches for breaking news might receive fresher content in their results, while a user researching historical topics might receive older, more established sources. This personalization means content freshness becomes less about absolute recency and more about relevance to specific user segments. Brands will need to create content serving diverse freshness preferences—maintaining both breaking news content for current-focused users and comprehensive evergreen content for research-focused users.
Multimodal freshness signals will expand as search engines increasingly process images, videos, and audio alongside text. A video published recently with current examples will signal freshness differently than a text article. Infographics with current data will carry freshness signals. Podcast episodes discussing recent developments will demonstrate topical currency. This expansion means freshness optimization extends beyond text content to all content formats. Brands will need to maintain fresh visual assets, update video content, and produce timely audio content to maintain comprehensive freshness signals across all content types.
Semantic freshness understanding represents another evolution where search engines move beyond simple date-based freshness to understanding conceptual freshness. Rather than just measuring when content was published, systems will evaluate whether content addresses current concepts, recent developments, and emerging trends. Content about “artificial intelligence” published in 2020 might be considered stale not because of its age but because it doesn’t address recent developments like large language models, generative AI, and current AI applications. This semantic approach to freshness will reward content that stays conceptually current even if not constantly updated, while penalizing content that becomes conceptually outdated despite recent publication dates.
For organizations using platforms like AmICited to monitor brand mentions in AI search, freshness signals directly impact citation frequency and visibility. AI systems cite fresh content more frequently, meaning brands that maintain updated content achieve higher visibility in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude responses. When monitoring your brand’s AI search presence, freshness becomes a key variable to track alongside citation frequency. If your brand’s AI visibility declines while competitors’ visibility increases, content staleness may be the culprit. Conversely, implementing aggressive content refresh schedules often correlates with increased AI citations, demonstrating the direct relationship between freshness and AI visibility.
Citation tracking combined with freshness analysis reveals optimization opportunities. If your brand appears in AI responses but less frequently than competitors, analyze whether your content is fresher or staler than competitors’ content. If competitors update their content weekly while you update monthly, that difference likely explains citation frequency gaps. Use freshness as a competitive benchmarking metric—track not just whether you’re cited but how your content freshness compares to competitors. This analysis guides content strategy decisions: if freshness is your competitive weakness, implementing more aggressive update schedules becomes a priority. If your content is fresher but still receives fewer citations, other factors (authority, comprehensiveness, structure) may need attention.
Seasonal freshness patterns emerge when monitoring AI citations over time. Content about seasonal topics (holiday shopping, summer travel, tax preparation) shows predictable freshness patterns—visibility peaks as the season approaches and declines afterward. Understanding these patterns helps allocate content maintenance resources efficiently. Rather than maintaining constant updates for seasonal content year-round, focus updates on the months leading up to peak season. This seasonal approach to freshness optimization balances resource constraints with visibility requirements, ensuring you maintain freshness when it matters most for your business.
+++
Freshness signal is a ranking factor that search engines and AI platforms use to evaluate how recently a web page was published or significantly updated, and how this recency should influence its visibility in search results and AI-generated responses. The freshness signal measures content timeliness through multiple indicators including publication date, modification date, update frequency, and the volume of content changes. This signal became particularly important after Google’s 2011 Freshness Algorithm update, which fundamentally changed how search results are ranked for time-sensitive queries. Today, freshness signals play an even more critical role in AI search platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews, where content decay happens significantly faster than traditional search. Understanding freshness signals is essential for any organization seeking visibility across both traditional search and emerging AI search channels, as the recency of your content directly impacts whether your brand gets cited when AI systems answer user questions.
The concept of content freshness in search ranking emerged gradually before becoming formalized through Google’s 2011 Freshness Algorithm update. Prior to this update, Google’s ranking systems treated all content relatively equally regardless of publication date, assuming that older, more established content was inherently more authoritative. However, this approach created problems for users seeking current information—a five-year-old article about smartphone technology would rank alongside brand-new reviews of the latest models, despite being largely obsolete. The Freshness Algorithm changed this paradigm by introducing time as a relevance measure, enabling Google to surface content that was literally up-to-the-minute relevant for queries where recency mattered. Google’s official announcement stated that the update impacted approximately 35% of all search queries, with noticeable effects on 6-10% of searches. This represented one of the most significant algorithmic shifts in search history, demonstrating that freshness had become a core ranking principle rather than a minor signal.
The infrastructure enabling the Freshness Algorithm came from Google’s Caffeine update, released five months earlier in 2010. Caffeine fundamentally transformed Google’s indexing infrastructure, enabling the search engine to process and index web content at unprecedented scale and speed. Before Caffeine, Google’s indexing system operated on a batch-processing model that could take weeks to fully crawl and index the web. Caffeine introduced continuous, real-time indexing that could detect and process new content within minutes of publication. This technological foundation made the Freshness Algorithm possible—without the ability to rapidly detect and index new content, Google couldn’t effectively prioritize fresh results. The combination of Caffeine’s infrastructure and the Freshness Algorithm’s logic created a system where breaking news could rank within hours of publication, and regularly updated content could maintain top positions indefinitely.
Search engines employ sophisticated methodologies to assess content freshness, moving far beyond simple publication date comparisons. Google’s freshness measurement considers multiple signals that collectively determine a page’s freshness score. The page inception date—when a page was first indexed by Google—provides the baseline. However, more important than initial publication is the modification date, which indicates when the page was last substantially changed. Google distinguishes between minor edits (fixing typos, correcting links) and major updates (rewriting sections, adding new content, restructuring information). Only significant changes contribute meaningfully to freshness signals; cosmetic edits don’t reset the freshness clock. The frequency of updates matters substantially—pages that change regularly signal ongoing maintenance and relevance, while pages that never change suggest abandonment. The volume of content change also factors in; adding an entire new section signals more freshness than updating a single sentence. Additionally, the freshness of backlinks pointing to your page influences your freshness score—links from recently updated, high-freshness sites transfer some of that freshness signal to your page.
Research from Moz and other SEO authorities has documented these freshness measurement factors through extensive analysis of ranking patterns. Pages showing consistent update patterns across multiple signals achieve substantially higher freshness scores than pages with sporadic or minimal changes. Interestingly, the relationship between freshness and ranking isn’t linear—a page updated daily doesn’t necessarily rank twice as well as one updated weekly. Instead, freshness signals interact with other ranking factors like relevance, authority, and user experience. A highly authoritative page updated monthly might outrank a low-authority page updated daily, demonstrating that freshness amplifies existing authority rather than replacing it. This nuanced relationship explains why some older content continues ranking well despite newer alternatives—if the older content maintains regular updates and strong authority signals, it can compete effectively against fresher but less authoritative alternatives.
| Aspect | Traditional Search (Google) | AI Search (ChatGPT/Perplexity) | Evergreen Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Update Frequency Impact | Weekly updates maintain strong signals | 2-3 day updates required for top visibility | Monthly updates sufficient |
| Content Age Tolerance | Pages 6+ months old still rank well | Content older than 30 days shows decay | Age irrelevant if regularly updated |
| Citation Preference | Average cited content age: 1,432 days | Average cited content age: 1,064 days | Not a primary ranking factor |
| Decay Timeline | Gradual decline over months | Rapid decline within days | No decay pattern |
| Update Type Required | Substantial changes needed | Any meaningful update helps | Minimal updates needed |
| Ranking Impact | 6% of algorithm (2025 data) | ~35% of ranking factors | Minimal direct impact |
| Query Types Affected | News, trends, products, recurring events | All query types (more aggressive) | Historical, foundational topics |
| Measurement Method | Publication date, modification date, update frequency | Real-time content analysis, recency scoring | Not actively measured |
The technical implementation of freshness signals involves sophisticated algorithms that analyze temporal patterns in content and user behavior. Search engines use timestamp metadata embedded in HTML to identify publication and modification dates, though they also employ content analysis to detect changes even when metadata isn’t explicitly provided. When a crawler revisits a page, it compares the current version against previously cached versions, identifying what changed, how much changed, and when the change occurred. This comparison happens at the HTML level, analyzing actual content differences rather than relying solely on date tags. Pages that show genuine content modifications receive freshness credit, while pages where only the date changed without content updates receive no credit—search engines have become sophisticated enough to detect this manipulation.
Query-level freshness evaluation represents another crucial mechanism. Search engines don’t apply freshness uniformly to all queries; instead, they analyze each query to determine whether freshness is relevant. Queries containing temporal indicators (“2025,” “latest,” “new,” “recent,” “this year”) trigger freshness evaluation. Queries about evergreen topics (“how to tie a tie,” “photosynthesis definition,” “recipe for chocolate cake”) don’t trigger freshness evaluation. Search engines use machine learning models trained on historical click data to predict whether users searching a particular query prefer fresh or established content. This prediction happens in milliseconds, allowing the search engine to adjust ranking algorithms on a per-query basis. A query for “iPhone 16 review” triggers aggressive freshness weighting, while “iPhone history” doesn’t. This dynamic approach explains why freshness importance varies so dramatically across different search queries.
Temporal decay functions model how content value decreases over time for time-sensitive topics. These mathematical functions assign higher relevance scores to recently published content while gradually reducing scores for older content. The decay rate varies by topic—news content decays rapidly (within hours), product reviews decay moderately (within weeks), and evergreen content doesn’t decay at all. Search engines implement different decay functions for different content categories, allowing them to handle the diverse freshness requirements across the entire web. A page about “best smartphones 2025” decays rapidly as the year progresses and new models release, while a page about “smartphone history” maintains constant value regardless of time passage.
The importance of freshness signals in AI search far exceeds their importance in traditional Google search, creating a fundamental shift in content strategy requirements. Research analyzing over 129,000 ChatGPT citations reveals that AI platforms cite content averaging 1,064 days old, compared to 1,432 days for traditional Google search results—representing 25.7% fresher content on average. This preference for recency reflects how AI models work: they synthesize information from multiple sources to create comprehensive answers, and they prioritize recent sources to ensure accuracy and relevance. When an AI system answers a question about “best project management tools 2025,” it will heavily weight sources published or updated in 2024-2025, largely ignoring articles from 2022 or earlier regardless of their authority or quality.
Perplexity AI demonstrates the most aggressive freshness requirements of any major platform. Research tracking Perplexity visibility shows that content begins losing visibility within 2-3 days without updates, and visibility drops substantially after one week without changes. This creates a fundamentally different content maintenance requirement compared to Google, where pages can maintain top rankings for months without updates. For Perplexity optimization, brands targeting high-visibility topics must implement update schedules of every 2-3 days, adding new information, refreshing statistics, incorporating recent examples, or expanding existing sections. This intensive maintenance requirement explains why Perplexity visibility correlates so strongly with content freshness—the platform essentially forces continuous content improvement as the price of visibility.
ChatGPT and Google AI Overviews show less aggressive freshness requirements than Perplexity but still prioritize recent content more heavily than traditional Google search. ChatGPT’s search capabilities perform real-time web searches, meaning even newly published content can achieve citations if it provides exceptional answers. Google AI Overviews draw primarily from pages already ranking in traditional search results, so traditional SEO freshness requirements apply, but AI Overviews show preference for fresher content within the ranked set. For brands seeking AI visibility across multiple platforms, implementing weekly update schedules for priority content maintains strong visibility while remaining operationally feasible.
Google’s Freshness Algorithm identified three distinct categories of queries deserving fresh content, each with different freshness requirements and update patterns. Recent events queries include breaking news, trending topics, and current developments where users explicitly seek the latest information. A search for “Ukraine conflict latest developments” clearly indicates the user wants the most recent news, not historical background. Search engines prioritize content published within hours or days for these queries, making real-time news coverage essential for visibility. Content about recent events becomes stale rapidly—an article published yesterday about today’s news is already outdated. For brands covering news-related topics, maintaining real-time publishing capabilities and rapid update processes is essential for freshness signal optimization.
Regularly recurring events include annual conferences, seasonal sports competitions, election cycles, and other predictable events that happen on regular schedules. A search for “Super Bowl 2025” clearly indicates interest in the current year’s event, not historical Super Bowls. Content about recurring events requires strategic updates aligned with event cycles—updating Super Bowl content annually, conference content yearly, and election content every four years. The freshness requirement isn’t continuous but rather synchronized with event timing. Brands can plan content updates around predictable event schedules, making this category more manageable than breaking news while still requiring deliberate freshness management.
Frequently updated topics include product reviews, technology news, market trends, and other subjects where information changes regularly but without specific event triggers. A search for “best email marketing software” indicates interest in current options with current pricing, features, and user experiences. Content about frequently updated topics requires regular refreshes—monthly or quarterly updates for most product reviews, weekly updates for rapidly evolving technology topics. Unlike breaking news (which requires immediate response) or recurring events (which follow predictable schedules), frequently updated topics require ongoing maintenance based on how rapidly the topic evolves. Brands must monitor their topic area and update content whenever significant changes occur—new product releases, pricing changes, feature updates, or competitive shifts.
The relationship between freshness signals and E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) has become increasingly important in modern search ranking. Fresh content signals trustworthiness by demonstrating that an organization actively maintains and updates its information. When users encounter a page about “best marketing tools 2025” published in 2023 and never updated, they question whether the information remains accurate. Conversely, a page showing “Last Updated: January 2025” with recent examples and current pricing signals that the organization cares about accuracy and maintains current information. This trust signal extends to AI systems, which increasingly use freshness as a proxy for reliability—if an organization updates content regularly, the content is more likely to be accurate and trustworthy.
Author expertise signals strengthen when combined with content freshness. An expert who publishes content and then never updates it appears less engaged with their field than an expert who regularly updates content with new insights and developments. Freshness demonstrates ongoing expertise maintenance—the author stays current with industry developments and incorporates new knowledge into existing content. This is particularly important for technical fields, business topics, and any area where knowledge evolves rapidly. An expert in artificial intelligence who published an article about AI in 2020 and never updated it appears less credible than one who regularly updates the article with new developments, research findings, and emerging trends.
Authority building through consistent content updates creates compounding advantages. Pages that receive regular updates tend to attract more backlinks, generate more engagement, and receive more social mentions—all signals that reinforce authority. Additionally, regular updates signal to search engines that a page is important enough to maintain, which influences crawl frequency and ranking priority. Search engines allocate more crawl budget to frequently updated pages, ensuring new content gets indexed quickly. This creates a virtuous cycle: fresh content attracts more engagement, which attracts more links, which increases authority, which improves rankings, which drives more traffic, which justifies further investment in content maintenance.
Implementing effective freshness signal optimization requires strategic planning that balances content quality with update frequency. The first step involves query analysis to determine which of your target keywords require freshness optimization. Examine the top 10-20 search results for each target keyword and note their publication dates. If most results are from the past month, freshness is critical for that keyword. If results span multiple years with older content ranking well, freshness matters less. This analysis reveals which content requires aggressive update schedules and which can maintain longer update cycles. Create a spreadsheet tracking target keywords, current ranking positions, average result age, and freshness requirements. This becomes your roadmap for content maintenance prioritization.
Content refresh scheduling should align with freshness requirements identified in your analysis. Establish tiered update schedules: Tier 1 (critical freshness required) updates every 2-3 days, Tier 2 (moderate freshness) updates weekly, Tier 3 (minimal freshness) updates monthly, and Tier 4 (evergreen) updates quarterly or as needed. Assign responsibility for each tier—perhaps your news team handles Tier 1, marketing team handles Tier 2, and content team handles Tier 3. Use content management system scheduling features to automate publication of updated content. Many platforms allow you to schedule updates in advance, ensuring consistent publication even during busy periods. Document your update schedule and track compliance to ensure consistency.
Meaningful update practices distinguish legitimate freshness optimization from manipulation. Each update should add genuine value: new statistics with current dates, recent examples replacing outdated ones, expanded sections addressing emerging questions, or revised explanations reflecting current best practices. Avoid the common mistake of changing only the publication date without content changes—search engines detect this manipulation and may penalize your site. Instead, make substantive changes that improve the page for users. Add a “Last Updated” date prominently near the article top, along with a brief changelog noting what changed: “Updated January 2025: Added new case study, refreshed statistics, expanded mobile optimization section.” This transparency helps both users and search engines understand that updates are genuine improvements rather than manipulation.
Content monitoring systems help identify when updates are needed. Set up Google Alerts for your target keywords to monitor when new information emerges. Subscribe to industry newsletters and news sources covering your topic area. Monitor competitor content to identify when they publish new information you should address. Use tools like Semrush or Ahrefs to track ranking changes for your target keywords—sudden drops often indicate freshness decay. When you notice ranking declines for previously strong pages, prioritize those for updates. This reactive approach complements your proactive update schedule, ensuring you address both planned updates and emerging freshness needs.
The definition and application of freshness signals continues evolving as search technology advances and user behavior changes. Real-time content integration represents an emerging frontier where search engines increasingly incorporate live data—current pricing, real-time inventory, breaking news, live event scores—directly into search results. This trend suggests freshness requirements will intensify for certain content categories. Brands selling products will need to maintain real-time pricing and inventory information. News organizations will need to publish updates within minutes of developments. Financial services will need to update market data continuously. This evolution creates both challenges (more intensive content maintenance) and opportunities (competitive advantage for brands that implement real-time systems).
Personalized freshness evaluation is emerging as AI systems increasingly customize responses based on individual user context. Rather than applying uniform freshness requirements across all users, AI platforms may weight freshness differently based on user preferences, search history, and stated interests. A user who frequently searches for breaking news might receive fresher content in their results, while a user researching historical topics might receive older, more established sources. This personalization means content freshness becomes less about absolute recency and more about relevance to specific user segments. Brands will need to create content serving diverse freshness preferences—maintaining both breaking news content for current-focused users and comprehensive evergreen content for research-focused users.
Multimodal freshness signals will expand as search engines increasingly process images, videos, and audio alongside text. A video published recently with current examples will signal freshness differently than a text article. Infographics with current data will carry freshness signals. Podcast episodes discussing recent developments will demonstrate topical currency. This expansion means freshness optimization extends beyond text content to all content formats. Brands will need to maintain fresh visual assets, update video content, and produce timely audio content to maintain comprehensive freshness signals across all content types.
Semantic freshness understanding represents another evolution where search engines move beyond simple date-based freshness to understanding conceptual freshness. Rather than just measuring when content was published, systems will evaluate whether content addresses current concepts, recent developments, and emerging trends. Content about “artificial intelligence” published in 2020 might be considered stale not because of its age but because it doesn’t address recent developments like large language models, generative AI, and current AI applications. This semantic approach to freshness will reward content that stays conceptually current even if not constantly updated, while penalizing content that becomes conceptually outdated despite recent publication dates.
For organizations using platforms like AmICited to monitor brand mentions in AI search, freshness signals directly impact citation frequency and visibility. AI systems cite fresh content more frequently, meaning brands that maintain updated content achieve higher visibility in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude responses. When monitoring your brand’s AI search presence, freshness becomes a key variable to track alongside citation frequency. If your brand’s AI visibility declines while competitors’ visibility increases, content staleness may be the culprit. Conversely, implementing aggressive content refresh schedules often correlates with increased AI citations, demonstrating the direct relationship between freshness and AI visibility.
Citation tracking combined with freshness analysis reveals optimization opportunities. If your brand appears in AI responses but less frequently than competitors, analyze whether your content is fresher or staler than competitors’ content. If competitors update their content weekly while you update monthly, that difference likely explains citation frequency gaps. Use freshness as a competitive benchmarking metric—track not just whether you’re cited but how your content freshness compares to competitors. This analysis guides content strategy decisions: if freshness is your competitive weakness, implementing more aggressive update schedules becomes a priority. If your content is fresher but still receives fewer citations, other factors (authority, comprehensiveness, structure) may need attention.
Seasonal freshness patterns emerge when monitoring AI citations over time. Content about seasonal topics (holiday shopping, summer travel, tax preparation) shows predictable freshness patterns—visibility peaks as the season approaches and declines afterward. Understanding these patterns helps allocate content maintenance resources efficiently. Rather than maintaining constant updates for seasonal content year-round, focus updates on the months leading up to peak season. This seasonal approach to freshness optimization balances resource constraints with visibility requirements, ensuring you maintain freshness when it matters most for your business.
Google measures freshness through multiple signals including page inception date (when first indexed), the amount of change to updated pages (larger changes signal more freshness), the number of changes to core content (main body changes matter more than metadata adjustments), the rate of page changes (frequent updates signal higher freshness), the rate of new page creation on your site, and the freshness of backlinks pointing to your page. These signals combine to create a freshness score that influences ranking for time-sensitive queries.
No, freshness signals apply selectively based on query type. Google's algorithm identifies three categories of queries deserving freshness: recent events (trending news and breaking stories), regularly recurring events (annual conferences, elections, sports seasons), and frequently updated topics (product reviews, technology news, market trends). For evergreen content like recipes, historical facts, or foundational guides, freshness has minimal impact on rankings. Understanding whether your target queries require freshness is essential for determining content update strategy.
AI platforms like ChatGPT and Perplexity prioritize freshness far more aggressively than traditional Google search. Research shows content decay happens within 2-3 days on Perplexity without updates, compared to weeks or months on Google. AI platforms cite content averaging 1,064 days old versus 1,432 days for traditional search results—25.7% fresher on average. This creates a critical difference: while Google rewards regular updates, AI platforms demand constant content refreshes to maintain visibility, making content maintenance a more intensive requirement for AI search optimization.
Updating content means making substantive changes to the actual page content—adding new sections, revising existing information, incorporating recent examples, or expanding explanations. Changing the publication date without content updates is considered artificial freshness manipulation that search engines detect and penalize. Google explicitly warns against changing dates without meaningful content changes, as this provides no actual value to users. Legitimate freshness comes from genuine content improvements that make pages more accurate, comprehensive, and valuable.
Update frequency depends on content type and platform priorities. For AI search optimization, update priority content every 2-3 days. For traditional Google search, weekly updates maintain strong freshness signals for time-sensitive topics. Evergreen content benefits from monthly reviews and updates. The key is matching update frequency to query type—news and trending topics need daily attention, product reviews need weekly updates, and foundational guides need monthly maintenance. Consistency matters more than frequency; regular, predictable updates signal reliability better than sporadic changes.
Yes, older content can rank exceptionally well if regularly updated and maintained. Content age alone doesn't determine ranking—freshness signals measure update recency, not publication date. A page published five years ago but updated weekly will have stronger freshness signals than a page published last month never updated. This creates opportunity: instead of constantly creating new content, strategically updating and refreshing existing high-performing pages maintains and improves rankings while preserving accumulated authority, backlinks, and user engagement.
For platforms like AmICited that track brand mentions in AI responses, freshness signals directly impact citation frequency. AI systems cite fresher content more frequently, meaning brands that maintain updated content achieve higher visibility in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI responses. Monitoring freshness alongside citation tracking reveals whether declining AI visibility stems from content staleness or other factors. Brands can use freshness optimization as a strategic lever to improve AI search presence, particularly important as AI platforms increasingly dominate search behavior.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn how content freshness signals work in AI systems. Understand timestamps, modification dates, and technical indicators that influence AI citations and visi...

Learn how to balance evergreen and news content for maximum AI visibility. Discover freshness strategies that work with ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity.

Learn how to update content for AI freshness with technical signals, structural changes, and refresh strategies that keep your brand visible in ChatGPT, Perplex...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.