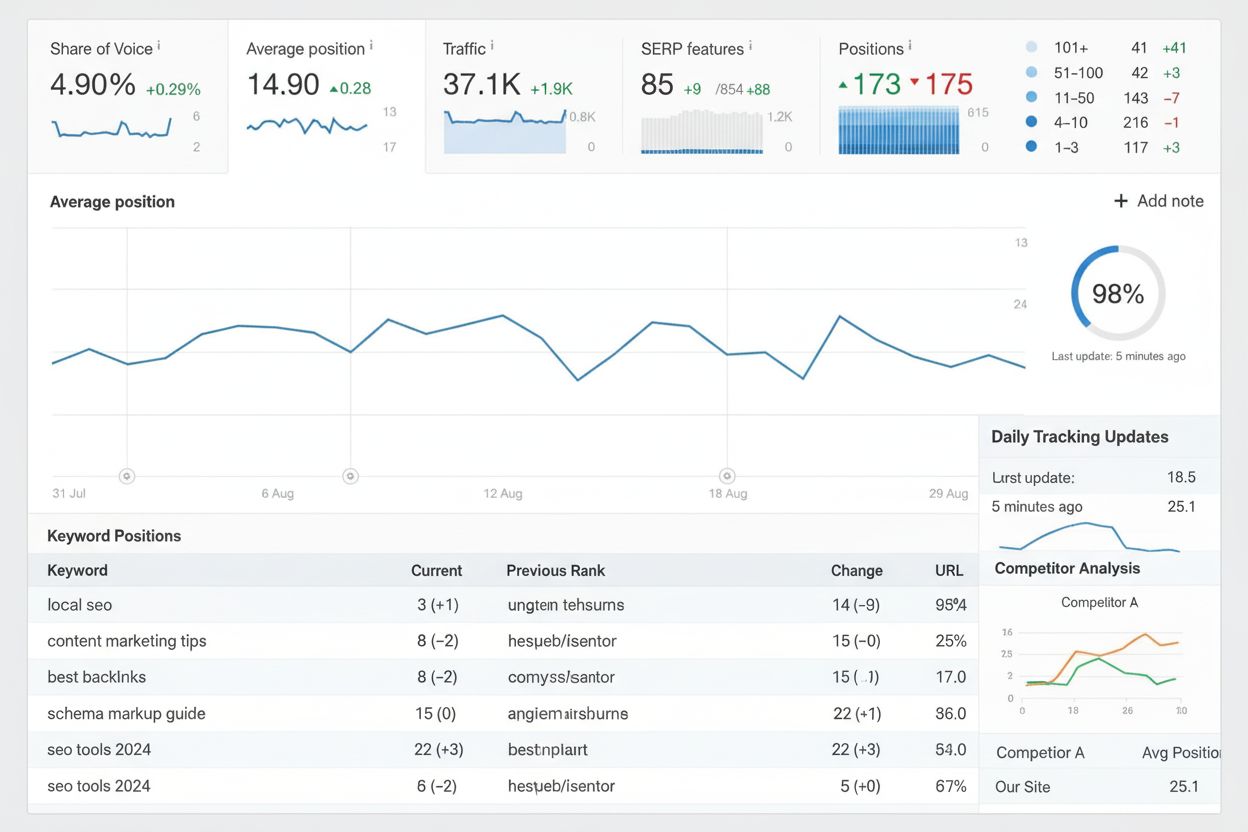
Rank Tracking
Rank tracking monitors keyword positions in search results over time. Learn how it works, why it matters for SEO, and how to use rank tracking tools effectively...

Goal tracking is the systematic process of setting specific objectives, continuously monitoring progress against measurable metrics, and evaluating outcomes to ensure alignment with organizational or personal targets. It involves using key performance indicators (KPIs), regular check-ins, and data-driven insights to maintain accountability and drive achievement of defined goals.
Goal tracking is the systematic process of setting specific objectives, continuously monitoring progress against measurable metrics, and evaluating outcomes to ensure alignment with organizational or personal targets. It involves using key performance indicators (KPIs), regular check-ins, and data-driven insights to maintain accountability and drive achievement of defined goals.
Goal tracking is the systematic and continuous process of setting specific, measurable objectives, monitoring progress against defined metrics, and evaluating outcomes to ensure alignment with organizational or personal targets. It represents far more than simply recording what you want to achieve—it is an active, data-driven discipline that transforms aspirations into actionable plans with clear accountability mechanisms. Goal tracking involves establishing key performance indicators (KPIs), conducting regular progress reviews, and making informed adjustments based on real-time data and insights. This practice is fundamental to both personal development and organizational success, serving as the bridge between strategic planning and actual execution. By implementing robust goal tracking systems, individuals and teams maintain focus, enhance motivation, and significantly increase the likelihood of achieving their most important objectives.
The concept of goal tracking has evolved significantly over the past several decades, rooted in foundational management theories and behavioral psychology. The Goal Setting Theory, developed by Locke and Latham in 1981, established that specific, challenging goals lead to higher performance than vague or easy goals. Research from this seminal work confirmed that over 90% of goal-setting studies demonstrate positive effects on performance and achievement. Throughout the 1990s and 2000s, organizations began implementing structured frameworks like Management by Objectives (MBO), which emphasized cascading goals throughout organizational hierarchies. A meta-analysis of 70 studies by Rodgers and Hunter found that MBO programs led to productivity gains in 68 of those studies, validating the business case for systematic goal tracking. In recent years, the emergence of Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) frameworks has revolutionized how companies approach goal tracking, with 98% of organizations reporting improved clarity around goals and performance when adopting OKRs. The integration of artificial intelligence and advanced analytics has further transformed goal tracking, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive insights, and automated adjustments that were previously impossible.
A comprehensive goal tracking system comprises several essential components that work together to ensure success. The first component is clear goal definition, which requires establishing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives. Rather than vague aspirations like “improve performance,” effective goals state precisely what will be accomplished, such as “increase user activation rate by 25% within the next quarter.” The second component is metric selection and KPI definition, which involves identifying the specific data points that will measure progress. Organizations typically use 5-7 KPIs to manage and track progress effectively, combining quantitative metrics (revenue, completion rates, customer satisfaction scores) with qualitative measures (feedback, observations, team sentiment). The third component is regular monitoring and check-ins, which research shows should occur at least weekly to serve as an effective early warning system. The fourth component is transparent communication, ensuring that all stakeholders understand goals, progress, and any necessary adjustments. Finally, adaptive management allows for goal refinement when circumstances change, preventing organizations from pursuing outdated or irrelevant objectives. These components create a dynamic system that maintains relevance and effectiveness throughout the goal cycle.
| Framework/Method | Primary Focus | Review Frequency | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMART Goals | Specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, time-bound objectives | Quarterly | Individual and team goals | Clear structure and simplicity |
| OKRs (Objectives & Key Results) | Ambitious objectives with measurable key results | Weekly check-ins, quarterly reviews | Organizational alignment and strategy execution | Drives transparency and alignment across teams |
| KPI Dashboards | Real-time tracking of key performance indicators | Daily/Weekly | Operational performance monitoring | Immediate visibility into metrics |
| Management by Objectives (MBO) | Cascading goals from top-down organizational structure | Annual/Quarterly | Hierarchical organizations | Clear accountability chains |
| Balanced Scorecard | Multi-perspective performance measurement (financial, customer, internal, learning) | Monthly/Quarterly | Strategic performance management | Holistic view of organizational health |
| Agile Goal Tracking | Iterative, flexible goal adjustment based on sprints | Weekly sprints | Software development and fast-moving teams | Adaptability and rapid iteration |
The technical implementation of goal tracking systems has become increasingly sophisticated with the advent of specialized software platforms and AI-powered analytics. Modern goal tracking systems typically operate through integrated dashboards that aggregate data from multiple sources, providing real-time visibility into progress metrics. These systems utilize event tracking capabilities to monitor specific user actions and milestones that contribute to goal achievement. For example, a SaaS company might track events such as feature adoption rates, user activation completion, or customer onboarding milestones. The technical architecture of effective goal tracking systems includes data collection mechanisms that capture relevant metrics automatically, reducing manual entry and improving accuracy. Advanced systems employ automated reporting features that generate progress summaries without requiring manual compilation, saving significant time for managers and team leaders. Integration capabilities are critical, allowing goal tracking systems to connect seamlessly with existing tools such as CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, analytics tools, and HRIS systems. This integration ensures that all relevant data flows into the goal tracking system, providing a unified view of performance. Additionally, modern goal tracking platforms include customizable dashboards that allow users to display the metrics and visualizations most relevant to their specific objectives, enhancing clarity and engagement.
The strategic value of goal tracking extends far beyond simple performance measurement—it fundamentally shapes organizational culture and business outcomes. Research demonstrates that employees working with clearly defined goals are 3.6 times more likely to remain committed to their organization and 14.2 times more likely to feel inspired at work. Organizations implementing structured goal tracking frameworks report 98% improved clarity around goals and performance, with 90% experiencing enhanced communication and strategy implementation. The financial impact is equally compelling: a meta-analysis of 70 studies found that Management by Objectives programs led to productivity gains in 68 studies, while the Sears Holding Company experienced an impressive 8.5% increase in sales per hour (from $14.44 to $15.67) within 18 months of consistently implementing OKRs across 20,000 employees. Beyond productivity metrics, goal tracking improves decision-making by providing data-driven insights into what is working and what requires adjustment. Organizations that review goals quarterly generate 31% greater returns than those reviewing annually, demonstrating the tangible business value of regular monitoring and adaptation. Furthermore, goal tracking enables early identification of performance issues, allowing for timely interventions before problems escalate. This proactive approach to performance management reduces costly mistakes, prevents resource waste, and ensures that organizational efforts remain aligned with strategic priorities.
In the emerging landscape of AI-driven search and content discovery, goal tracking takes on new significance for organizations concerned with their brand presence and visibility. As AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude increasingly influence how information is discovered and presented, companies must establish clear goals for how their brand appears in these AI responses. Goal tracking in this context involves monitoring specific metrics such as brand mention frequency, domain citation rates, URL appearances in AI-generated responses, and the sentiment of AI-generated content about your brand. Organizations can set ambitious yet achievable goals such as “increase brand mentions in Perplexity responses by 40% within six months” or “ensure our domain appears in the top three sources for AI-generated answers about our industry.” Platforms like AmICited enable this specialized form of goal tracking by providing real-time monitoring of brand appearances across multiple AI systems, allowing organizations to measure progress toward their AI visibility objectives. This integration of goal tracking with AI monitoring represents a critical evolution in how companies manage their digital presence, recognizing that AI systems are now primary discovery mechanisms for many users. By establishing clear goals for AI visibility and tracking progress systematically, organizations can optimize their content strategy, improve their competitive positioning, and ensure their brand receives appropriate visibility in the AI-driven information ecosystem.
Successful goal tracking implementation requires adherence to proven best practices that maximize effectiveness and adoption. The first best practice is writing down goals, which research shows increases the likelihood of achievement by 42%. Visualization of goals further enhances success, with 59% of people who visualize their goals feeling more confident and more likely to achieve them. The second best practice is establishing clear timelines and deadlines, as those who set time-bound goals and report progress weekly are 40% more likely to succeed than those who don’t. The third best practice is sharing goals with others, which increases the likelihood of success to 70%, compared to only 35% for those who keep goals private. This transparency creates accountability and enables support from colleagues and stakeholders. The fourth best practice is regular progress reviews, with quarterly reviews generating significantly better results than annual reviews. During these reviews, organizations should evaluate both the objective measure of progress (altitude—where are we?) and the subjective assessment (attitude—how do we feel about achieving this goal?). The fifth best practice is involving employees in goal setting, which research shows leads to significantly higher levels of innovative behavior and commitment. When employees participate in defining goals, they develop greater ownership and understanding of why those goals matter. The sixth best practice is maintaining flexibility and adaptability, recognizing that goals may need adjustment as circumstances change. Supervisors who adjust goals according to changing priorities see employees become 6.7 times more motivated to take action. Finally, organizations should celebrate milestones and achievements, as acknowledging progress reinforces positive behavior and maintains motivation throughout the goal cycle.
Contemporary goal tracking platforms incorporate several essential features that distinguish effective systems from basic tracking tools. Customizable dashboards allow users to display the specific metrics and visualizations most relevant to their goals, ensuring that important information is always visible and accessible. Automated reporting capabilities generate progress summaries, trend analyses, and performance reports without requiring manual compilation, saving significant time and reducing errors. Real-time progress monitoring provides immediate visibility into goal status, enabling quick identification of issues and opportunities for course correction. Integration capabilities ensure seamless data flow from other business systems, creating a unified view of performance across the organization. Collaboration features facilitate communication about goals, progress, and challenges, fostering transparency and enabling teams to support one another. Alert and notification systems automatically flag when goals are at risk or when significant milestones are achieved, ensuring that attention is directed to critical issues. Historical tracking and analytics maintain records of goal progress over time, enabling analysis of trends and patterns that inform future goal setting. Mobile accessibility allows managers and team members to check progress and provide updates from anywhere, supporting remote and distributed teams. Customizable KPI definitions enable organizations to track metrics specific to their industry, business model, and strategic priorities. These features collectively create systems that are not only effective at tracking progress but also engaging and user-friendly, encouraging consistent adoption and engagement.
The future of goal tracking is being shaped by several converging trends that will fundamentally transform how organizations monitor and manage objectives. Artificial intelligence and machine learning will increasingly automate goal setting and adjustment, analyzing historical data and market conditions to recommend optimal goals and predict achievement likelihood. Predictive analytics will enable organizations to identify risks and opportunities earlier in the goal cycle, allowing for proactive adjustments rather than reactive responses. Real-time personalization will allow goal tracking systems to adapt to individual preferences and working styles, improving engagement and effectiveness. The integration of goal tracking with AI monitoring platforms will become standard practice, as organizations recognize the importance of tracking brand presence and visibility across AI systems. Blockchain and distributed ledger technologies may enable more transparent and tamper-proof goal tracking, particularly in contexts where accountability and verification are critical. Natural language processing will make goal definition and progress reporting more intuitive and conversational, reducing the friction of traditional goal management processes. Emotional intelligence and sentiment analysis will be incorporated into goal tracking systems, recognizing that motivation and team morale are critical factors in goal achievement. As remote and distributed work becomes increasingly prevalent, goal tracking systems will evolve to better support asynchronous communication and collaboration across time zones. Organizations will increasingly recognize that goal tracking is not merely an administrative function but a strategic capability that directly influences competitive positioning and business outcomes. The convergence of these trends suggests that future goal tracking systems will be more intelligent, adaptive, personalized, and integrated with broader business intelligence and AI monitoring capabilities, enabling organizations to achieve unprecedented levels of strategic alignment and execution excellence.
Goal setting is the initial process of defining what you want to achieve, while goal tracking is the ongoing process of monitoring progress toward those goals. Goal setting establishes the destination, whereas goal tracking ensures you stay on course and make adjustments as needed. Both are essential components of a complete goal management system, with tracking providing the accountability and visibility necessary to transform aspirations into measurable results.
Research shows that goals should be tracked at least weekly, with formal reviews conducted quarterly for optimal results. Companies that review goals quarterly generate 31% greater returns than those reviewing annually. Weekly tracking serves as an early warning system to identify when goals are off-track, while quarterly reviews allow for strategic adjustments and realignment with changing business priorities. Regular tracking frequency significantly increases the likelihood of goal achievement.
Key metrics in goal tracking include Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), which measure progress toward specific objectives. Common KPIs include completion rates, quality scores, customer satisfaction metrics, revenue targets, and employee engagement levels. Effective goal tracking systems typically use 5-7 KPIs to manage progress, combining both quantitative metrics (numbers and percentages) and qualitative measures (feedback and observations) to provide comprehensive visibility into goal achievement.
Goal tracking improves performance by providing clarity, accountability, and data-driven insights. Research indicates that employees with clearly defined goals are 3.6 times more likely to stay committed to their organization and 14.2 times more likely to feel inspired at work. Goal tracking enables early identification of performance issues, facilitates timely interventions, and helps teams maintain focus on strategic priorities. Organizations using structured goal tracking frameworks like OKRs report 98% improved clarity around goals and 90% enhanced communication.
AI enhances goal tracking by automating data collection, providing real-time progress monitoring, and generating predictive insights. AI-powered systems can analyze performance patterns, identify risks before they become critical, suggest goal adjustments based on changing conditions, and reduce administrative burden through automated reporting. AI also helps reduce bias in performance evaluation by using objective metrics rather than subjective impressions, enabling more fair and data-driven goal management across organizations.
Goal tracking can be integrated with AI monitoring platforms to track brand mentions, domain appearances, and URL citations across AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. By setting specific goals for brand visibility metrics and monitoring progress through these platforms, organizations can measure the effectiveness of their AI presence strategy. This integration enables real-time tracking of how often your brand appears in AI responses and helps optimize content for better AI citation and visibility.
Common obstacles include lack of clarity in goal definition, insufficient resource allocation, poor communication across teams, and resistance to regular reviews and adjustments. Research shows that only 16% of employees clearly understand their company's priorities, and 80% of organizations fail to track their business goals effectively. Additionally, many organizations struggle with goal alignment across departments and lack the flexibility to adjust goals when circumstances change, leading to wasted resources and missed opportunities.
Goal tracking significantly boosts employee engagement by providing visibility into progress and creating a sense of accomplishment. Employees who set goals are 14.2 times more likely to feel inspired, 3.6 times more likely to remain committed, and 6.7 times more likely to feel proud of their organization. Regular progress tracking and celebration of milestones reinforce positive behavior, maintain momentum, and foster a culture of accountability. When employees see tangible progress toward meaningful objectives, motivation and job satisfaction increase substantially.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Rank tracking monitors keyword positions in search results over time. Learn how it works, why it matters for SEO, and how to use rank tracking tools effectively...
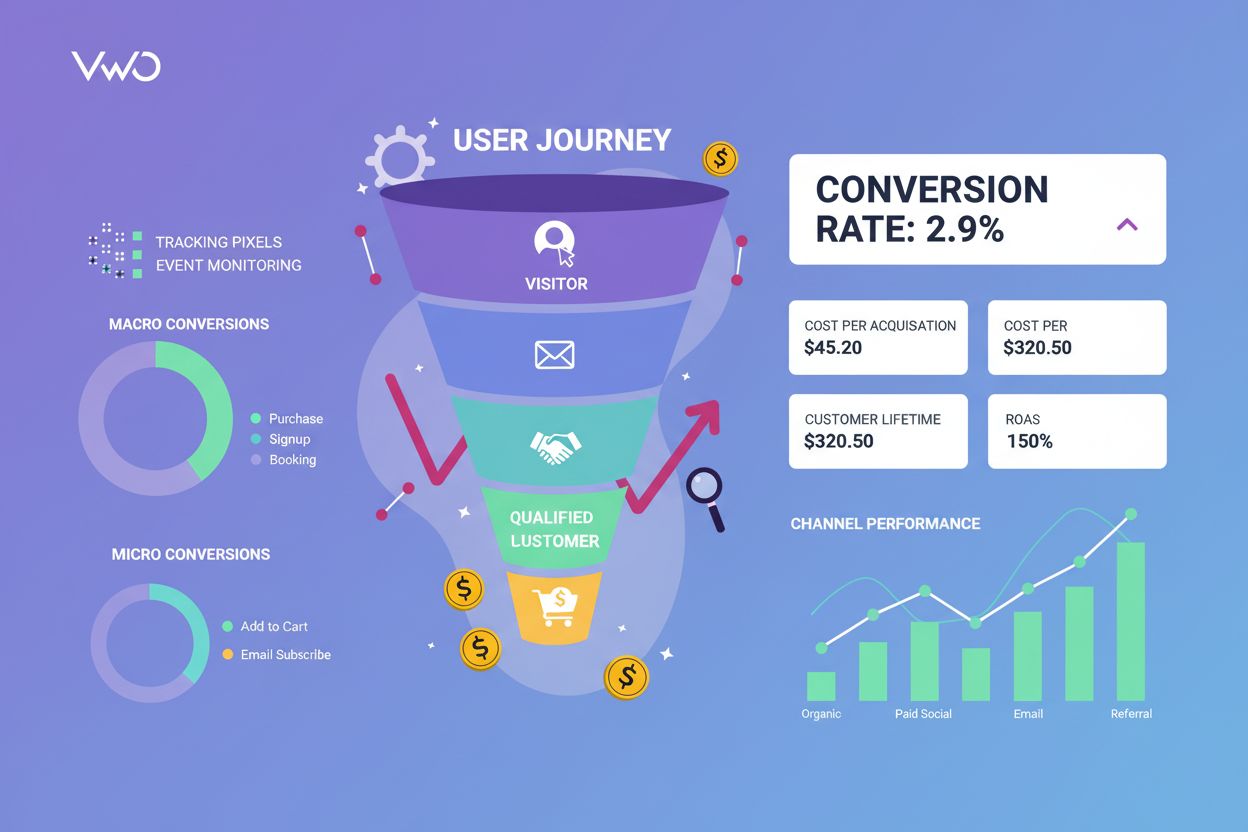
Conversion tracking monitors user actions toward business goals. Learn how to measure conversions, track metrics, and optimize marketing ROI with comprehensive ...
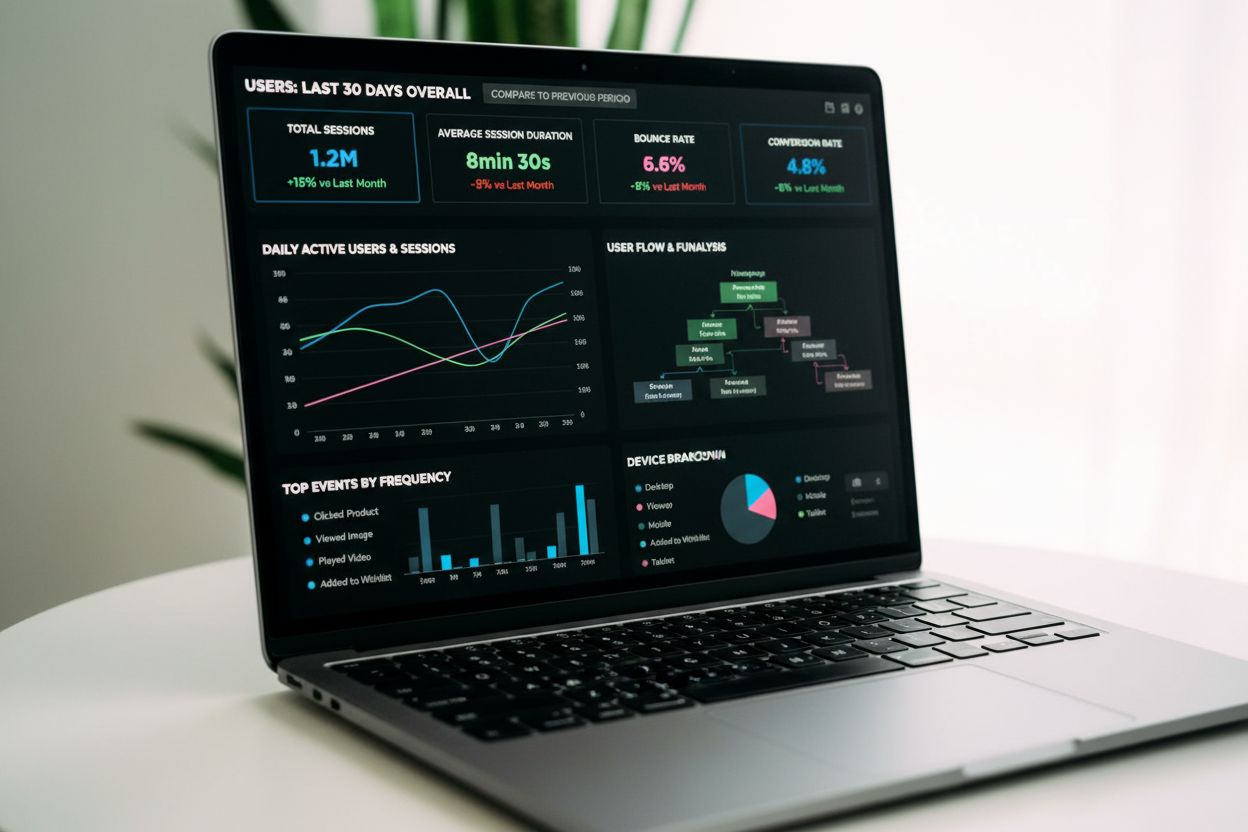
Event tracking captures and records user interactions on digital platforms. Learn how event tracking works, its importance for analytics, and how it drives data...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.