
Google Trends
Google Trends is a free analytics tool that measures search interest over time and location. Learn how it works, its applications in marketing, SEO, and AI moni...
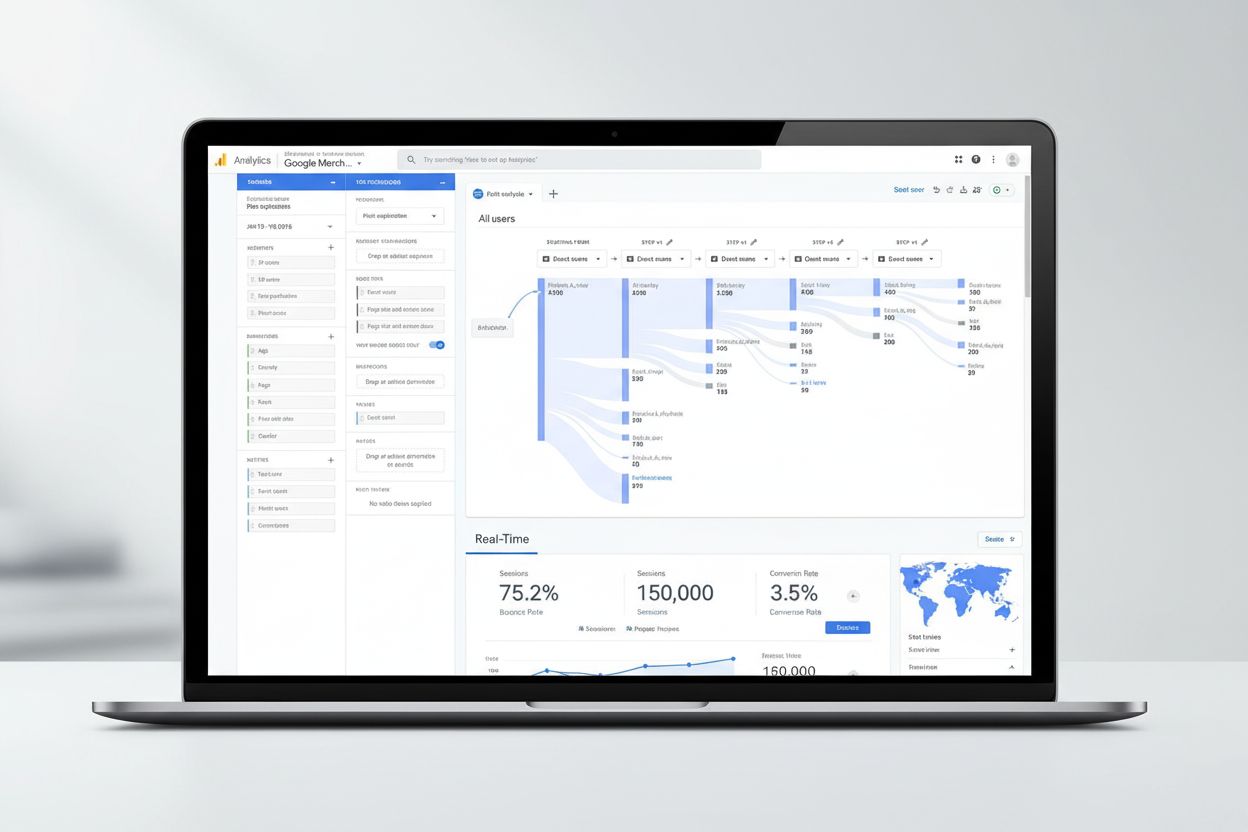
Google Analytics is a free web analytics platform that collects, processes, and reports website and app traffic data to provide insights into user behavior, marketing performance, and business metrics. It uses JavaScript tracking code to measure user interactions and generates actionable reports for optimizing digital presence and marketing ROI.
Google Analytics is a free web analytics platform that collects, processes, and reports website and app traffic data to provide insights into user behavior, marketing performance, and business metrics. It uses JavaScript tracking code to measure user interactions and generates actionable reports for optimizing digital presence and marketing ROI.
Google Analytics is a free, web-based analytics platform offered by Google that collects, processes, and reports data about website and mobile app traffic. It provides comprehensive insights into how users interact with digital properties, enabling businesses to understand visitor behavior, measure marketing effectiveness, and optimize their online presence. The platform uses JavaScript tracking code deployed on websites to capture user interactions in real-time, which are then aggregated and processed into actionable reports. Google Analytics serves as a foundational tool for digital marketing, SEO optimization, and business intelligence, helping organizations of all sizes make data-driven decisions about their online strategies.
Google Analytics was first launched in 2005 as a free alternative to expensive enterprise analytics solutions, fundamentally democratizing access to website performance data. The platform evolved significantly over nearly two decades, with major updates introducing new features and capabilities. In October 2020, Google released Google Analytics 4 (GA4), representing the most substantial transformation in the platform’s history by shifting from a session-based to an event-based data model. This evolution reflected changing digital landscapes where users interact across multiple devices and platforms, requiring more sophisticated tracking mechanisms. Today, over 44 million websites utilize Google Analytics, making it the dominant web analytics platform globally, with approximately 55.49% of all websites using the service. The platform’s continuous evolution demonstrates Google’s commitment to addressing emerging challenges in digital measurement, privacy regulations, and the need for cross-platform attribution in an increasingly complex digital ecosystem.
The functioning of Google Analytics relies on a sophisticated data collection and processing pipeline that begins with the implementation of tracking code. Website owners must add a small JavaScript measurement code (also called a tracking tag or pixel) to each page they wish to monitor. When a user visits a page containing this code, it automatically captures pseudonymous information about their session, including their browser type, device, operating system, language settings, and traffic source. The tracking code functions as a web beacon or web bug, collecting data through browser cookies that enable the system to recognize returning visitors and track their behavior across multiple sessions. This collected data is packaged and transmitted to Google’s servers where it undergoes processing, aggregation, and organization based on predefined criteria such as device type, geographic location, and traffic channel. Once processed, the data is stored in an immutable database, meaning historical data cannot be modified—a critical consideration for data governance and compliance. The entire process typically completes within hours, with data appearing in reports and dashboards for user analysis and decision-making.
Google Analytics supports measurement of over 200 different metrics, each providing specific quantitative insights into website performance. The most fundamental metrics include Users (unique or new visitors), Sessions (groups of user interactions occurring within a 30-minute window), Pageviews (total number of pages viewed), Bounce Rate (percentage of visitors who view only a single page), Average Session Duration (mean time spent on the site per session), and Conversion Rate (percentage of visitors completing desired actions). Beyond these standard metrics, GA4 introduced engagement metrics that measure active user participation, event count tracking for specific user actions, and key events (formerly called conversions) that represent important business objectives. Dimensions complement metrics by providing qualitative context—examples include geographic location, browser type, device category, traffic source, and user demographics. Understanding the relationship between dimensions and metrics is essential for proper data interpretation; for instance, analyzing average session duration (metric) segmented by geographic region (dimension) reveals how user engagement varies across different countries. This framework enables sophisticated analysis and custom reporting tailored to specific business questions and analytical needs.
| Feature | Google Analytics 4 | Universal Analytics | Adobe Analytics | Mixpanel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Model | Event-based | Session-based | Event-based | Event-based |
| Cost | Free | Free (deprecated) | Enterprise pricing | Freemium model |
| Parameters per Event | Up to 25 unique | 3 pre-defined | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Cross-Device Tracking | Advanced | Limited | Advanced | Advanced |
| Real-Time Reporting | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Machine Learning | Built-in predictive models | Limited | Advanced AI features | Behavioral analytics |
| Privacy Features | IP anonymization default | Optional | GDPR-compliant | Privacy-focused |
| Integration Ecosystem | Google Marketing Platform | Google Marketing Platform | Adobe Experience Cloud | Third-party integrations |
| Learning Curve | Moderate | Moderate | Steep | Moderate |
| Best For | Small to mid-size businesses | Legacy implementations | Large enterprises | Product analytics |
Google Analytics 4 represents a fundamental reimagining of how digital analytics operates, moving away from the session-centric approach of Universal Analytics toward a comprehensive event-based architecture. This shift enables more granular tracking of user interactions, where every action—from page views to button clicks to video plays—is captured as an individual event with associated parameters. GA4’s event-based model provides superior flexibility for businesses with complex user journeys, allowing up to 25 unique parameters per event compared to Universal Analytics’ limitation of 3 pre-defined parameters. The platform incorporates machine learning capabilities that automatically detect patterns, surface actionable insights, and generate predictive models for user behavior and conversion likelihood. GA4 also emphasizes privacy-safe measurement through features like default IP anonymization, which prevents Google from storing users’ full IP addresses, and enhanced data controls that align with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. The platform’s integration with Google BigQuery enables seamless export of raw analytics data for advanced analysis, custom modeling, and integration with other business intelligence tools. Additionally, GA4 provides improved cross-device tracking through machine learning models that recognize the same user across different devices, offering a more complete picture of the customer journey in an increasingly multi-device world.
The collection of user data through Google Analytics operates within an increasingly complex regulatory environment shaped by privacy legislation and user expectations. GDPR compliance requires that organizations obtain explicit user consent before deploying analytics tracking code, implement transparent privacy policies, and provide users with rights to access, modify, or delete their data. GA4 addresses these requirements through privacy-by-default features, including automatic IP anonymization and configurable data retention settings that allow organizations to specify how long data is stored before deletion. However, some European regulators have raised concerns about data transfers from the European Union to Google’s servers in the United States, necessitating additional safeguards such as Standard Contractual Clauses or supplementary encryption measures. Organizations must also account for users who disable cookies, employ ad blockers, or use privacy-focused browsers and VPNs, which can result in data sampling and incomplete tracking. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and similar state-level regulations impose additional requirements for data transparency and user rights. Best practices for compliance include implementing cookie consent management platforms, maintaining detailed data processing agreements with Google, conducting privacy impact assessments, and regularly auditing analytics implementations to ensure adherence to evolving regulatory requirements.
Google Analytics functions as the central measurement hub within the Google Marketing Platform, seamlessly integrating with advertising and marketing automation tools to provide unified insights across channels. Integration with Google Ads allows bidirectional data flow—analytics conversions can be imported into Google Ads for automated bidding optimization, while Google Ads performance data appears directly within analytics reports. Similarly, Display & Video 360 and Search Ads 360 integrations enable marketers to view advertising performance alongside website and app metrics, facilitating comprehensive attribution modeling that reveals how different touchpoints contribute to conversions. The connection to Google Search Console provides insights into organic search performance, showing which search queries drive traffic and how that traffic translates into on-site actions. Google Tag Manager integration simplifies tracking code deployment by allowing marketers to manage tags without requiring developer intervention, reducing implementation time and complexity. For enterprise users, Analytics 360 offers deeper integrations with Google Cloud services, including direct connections to BigQuery for advanced data analysis, and integration with Looker for sophisticated data visualization and business intelligence. Third-party integrations extend functionality further—Salesforce Marketing Cloud integration enables email marketing performance analysis within analytics, while connections to CRM systems, e-commerce platforms, and customer data platforms create a unified view of customer interactions across the entire business ecosystem.
Google Analytics provides a comprehensive suite of features designed to address diverse analytical needs across organizations. Real-time reporting allows marketers to monitor website activity as it happens, enabling rapid response to traffic spikes, technical issues, or campaign performance anomalies. Acquisition reports reveal how users discover websites through paid search, organic search, social media, email, and direct traffic, helping optimize marketing spend allocation. Engagement reports identify which content drives user interaction and conversions, informing content strategy and website optimization efforts. Monetization reports track revenue generation through e-commerce transactions, subscriptions, or advertising, providing visibility into business performance. Funnel exploration visualizes the steps users take toward conversion goals, identifying drop-off points where user experience improvements could increase conversion rates. Audience segmentation enables creation of custom user groups based on behavior, demographics, or acquisition source, facilitating targeted analysis and personalized marketing. Predictive capabilities leverage machine learning to forecast user behavior, such as predicting which users are likely to make purchases or churn, enabling proactive retention and acquisition strategies. Custom reporting allows creation of tailored dashboards and reports that align with specific business metrics and KPIs, ensuring stakeholders access the most relevant data for their roles and responsibilities.
Successful Google Analytics implementation requires careful planning and configuration to ensure accurate data collection and meaningful insights. The initial setup involves creating a Google Analytics account (distinct from a Gmail account), establishing properties for each website or app, and obtaining the unique tracking ID or measurement ID for GA4. The JavaScript tracking code must be deployed on every page requiring measurement, typically through the website’s header or footer, or via Google Tag Manager for centralized management. Critical configuration decisions include defining conversion goals that align with business objectives, setting up custom dimensions and metrics for business-specific measurements, and implementing filters to exclude internal traffic from analytics reports. Organizations should establish data governance policies specifying who can access analytics data, what modifications are permitted, and how data is used for decision-making. Event tracking configuration requires identifying key user interactions beyond standard pageviews—such as video plays, form submissions, or product interactions—and implementing code to capture these events. Audience creation based on user behavior enables segmentation for remarketing campaigns and personalized marketing. Regular data quality audits should verify that tracking code is functioning correctly, data is flowing as expected, and reports accurately reflect business activity. Documentation of implementation decisions, custom configurations, and data definitions ensures consistency and facilitates knowledge transfer across teams.
In the emerging landscape of AI-generated search results and conversational AI platforms, Google Analytics provides foundational website traffic measurement but requires supplementation with specialized AI citation tracking tools. While Google Analytics captures users arriving from traditional search engines and direct traffic, it cannot directly measure how often a brand or domain appears as a source citation in responses from ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, or Claude. This gap represents a critical blind spot for modern digital marketing, as AI systems increasingly influence user discovery and brand perception. Organizations leveraging Google Analytics alongside AI citation monitoring platforms like AmICited gain comprehensive visibility into their digital presence—understanding both direct website traffic and indirect brand mentions within AI-generated content. This integrated approach enables measurement of brand authority in AI systems, identification of content that resonates with AI training data, and optimization of content strategy to improve AI citation likelihood. The combination of traditional analytics and AI citation tracking provides a complete picture of how brands reach audiences through both conventional and emerging discovery mechanisms, informing content strategy, SEO optimization, and overall digital marketing effectiveness in an AI-augmented information landscape.
The future trajectory of Google Analytics reflects broader trends in digital measurement, privacy regulation, and the shift toward first-party data strategies. Google’s ongoing deprecation of third-party cookies and emphasis on privacy-safe measurement through machine learning models indicates a fundamental transformation in how analytics platforms will operate. Cookieless tracking alternatives, including server-side tracking and first-party data collection, will become increasingly important as browser privacy protections strengthen. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into analytics platforms will accelerate, with predictive capabilities, automated insights, and AI-driven recommendations becoming standard features rather than premium offerings. Cross-platform measurement will continue evolving to address the fragmented digital landscape where users interact across websites, apps, social media, and emerging platforms. The rise of AI-generated search results and conversational AI systems creates new measurement challenges and opportunities, requiring analytics platforms to adapt for tracking brand visibility in AI responses. Organizations should anticipate increased regulatory scrutiny of data collection practices, necessitating more sophisticated privacy compliance mechanisms and transparency measures. The strategic imperative for businesses is to view Google Analytics as one component of a comprehensive measurement ecosystem that includes AI citation tracking, customer data platforms, and business intelligence tools—enabling holistic understanding of how brands reach, engage, and convert audiences across all discovery and interaction channels in an increasingly complex digital environment.
Google Analytics collects data through a small piece of JavaScript tracking code that must be added to each page of a website. When a user visits a page containing this code, it captures pseudonymous information about their interactions, including pageviews, clicks, form submissions, and other events. This data is then sent to Google's servers where it is processed, aggregated, and stored in a database for analysis and reporting.
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) uses an event-based data model that tracks individual user interactions as separate events, while Universal Analytics measured sessions and pageviews. GA4 allows up to 25 unique parameters per event compared to Universal Analytics' 3 pre-defined parameters. GA4 also provides better cross-device tracking, enhanced privacy features with IP anonymization by default, and improved machine learning capabilities for predictive insights and behavioral modeling.
Key metrics include Users (unique visitors), Sessions (groups of interactions within 30 minutes), Pageviews (total pages viewed), Bounce Rate (percentage of single-page visits), Average Session Duration (time spent on site), Conversion Rate (goal completions), and Traffic Source (how users arrived). GA4 also tracks engagement metrics, event counts, and provides custom metrics based on specific business needs and goals.
Google Analytics 4 requires explicit user consent before collecting data due to GDPR regulations. Businesses must implement cookie consent mechanisms and inform users about data collection practices. GA4 includes privacy-safe features like IP anonymization by default and allows data retention settings. However, some European regulators have raised concerns about data transfers to the US, so organizations should implement additional privacy measures and consider supplementary tools for full GDPR compliance.
Google Analytics tracks the entire customer journey from initial acquisition through conversion, allowing marketers to understand which channels and campaigns drive the most valuable traffic. By measuring goal completions, revenue attribution, and customer lifetime value, businesses can calculate ROI for each marketing channel. Integration with Google Ads and other advertising platforms enables automated bidding optimization and audience creation based on analytics insights.
Dimensions are qualitative attributes or labels used to describe and organize data, such as geographic location, browser type, or traffic source. Metrics are quantitative measurements of data, such as pageviews, bounce rate, or average session duration. Reports combine dimensions and metrics to provide comprehensive analysis—for example, measuring average session duration (metric) across different regions (dimension).
Yes, Google Analytics can track mobile app traffic through the Google Analytics for Firebase SDK. This allows businesses to measure app installations, user engagement, in-app purchases, and other events. Firebase integration provides real-time reporting, audience creation, and integration with Google Ads for app promotion campaigns, offering similar insights to website analytics but tailored for mobile applications.
Google Analytics integrates seamlessly with Google Ads, Display & Video 360, Search Ads 360, Google Tag Manager, Google Search Console, and Google BigQuery. It also connects with third-party platforms like Salesforce Marketing Cloud and Google Ad Manager. These integrations allow data sharing, audience creation, conversion tracking, and unified reporting across multiple marketing channels and platforms.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Google Trends is a free analytics tool that measures search interest over time and location. Learn how it works, its applications in marketing, SEO, and AI moni...
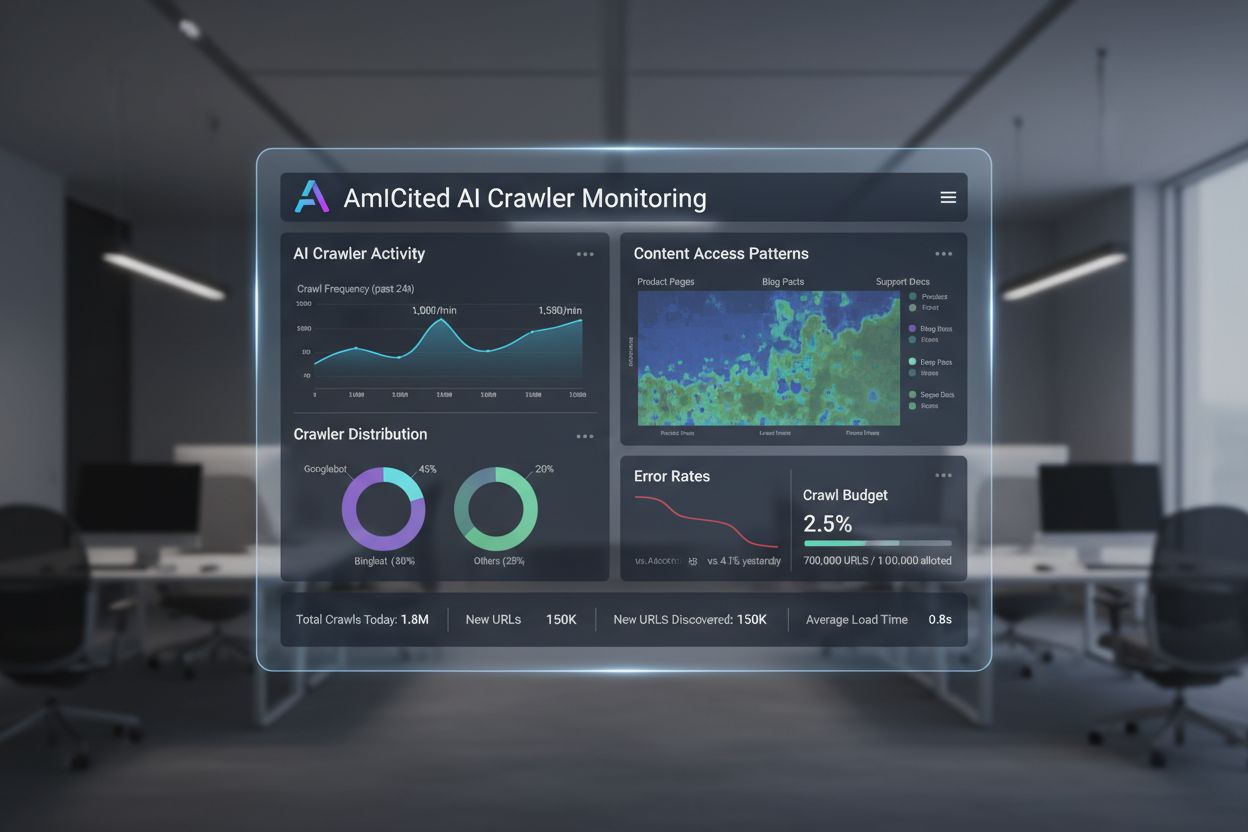
Learn what AI crawl analytics is and how server log analysis tracks AI crawler behavior, content access patterns, and visibility in AI-powered search platforms ...

Learn how to track and monitor AI traffic from ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini and other AI platforms in Google Analytics 4. Discover 4 proven methods to identify A...