Google Gemini
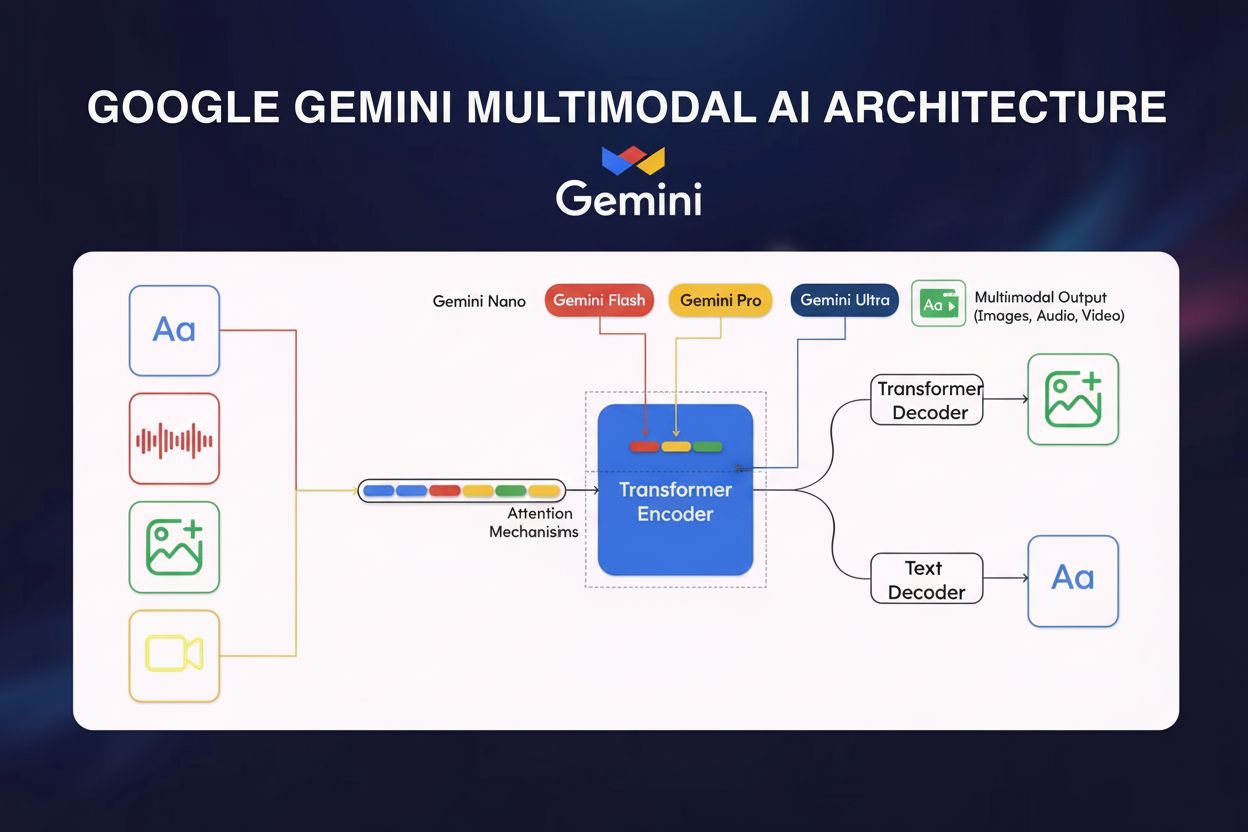
Google Gemini is a multimodal AI model by Google DeepMind that processes text, images, audio, and video. Learn its architecture, capabilities, and impact on AI ...
Google Bard is Google’s conversational AI service powered by LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications) and later PaLM 2, designed to engage in natural language conversations and provide real-time information. Originally launched in 2023 as an experimental chatbot, Bard was rebranded to Gemini in February 2024, representing Google’s answer to OpenAI’s ChatGPT in the generative AI landscape.
Google Bard is Google's conversational AI service powered by LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications) and later PaLM 2, designed to engage in natural language conversations and provide real-time information. Originally launched in 2023 as an experimental chatbot, Bard was rebranded to Gemini in February 2024, representing Google's answer to OpenAI's ChatGPT in the generative AI landscape.
Google Bard is a conversational AI service developed by Google that leverages advanced large language models to engage in natural, human-like dialogue with users. Originally launched in February 2023 as an experimental chatbot powered by LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications), Bard was designed to combine the breadth of the world’s knowledge with the power and creativity of Google’s proprietary language models. The service was rebranded to Gemini in February 2024, reflecting Google’s strategic evolution and integration of more powerful models including PaLM 2 and Gemini Pro. Bard represents Google’s direct response to the rapid adoption of ChatGPT and other generative AI systems, positioning itself as a more integrated, real-time-aware alternative within Google’s ecosystem. The platform demonstrates Google’s commitment to democratizing access to advanced AI capabilities while maintaining focus on accuracy, safety, and responsible AI development.
Google’s journey toward creating Bard began well before the public launch of ChatGPT. In 2017, Google published the groundbreaking Transformer research paper, which became the foundational architecture for modern large language models. Two years later, in 2021, Google unveiled LaMDA, a specialized language model designed specifically for dialogue applications. This early investment in conversational AI technology positioned Google to respond quickly when ChatGPT gained mainstream attention in late 2022. CEO Sundar Pichai announced Bard on February 6, 2023, during a strategic AI presentation that emphasized Google’s long-standing commitment to AI research and development. The announcement came amid significant competitive pressure from Microsoft’s partnership with OpenAI and the integration of ChatGPT into Bing Search. However, Bard’s launch was marked by a notable setback when the AI provided factually incorrect information during a live demonstration, stating that the James Webb Space Telescope took the first images of an exoplanet when this discovery actually occurred in 2004. This error resulted in a $100 billion drop in Google’s stock value and highlighted the critical importance of accuracy in AI systems. Despite this initial stumble, Google continued refining Bard, eventually transitioning the service to more advanced models and ultimately rebranding it as Gemini to reflect its evolution and expanded capabilities.
The technical foundation of Google Bard evolved significantly from its initial launch to its current iteration as Gemini. LaMDA, the original powering model, is a Transformer-based neural language model with up to 137 billion parameters, trained on 1.56 trillion words of dialogue and web text. This specialized architecture was designed to understand the nuances of human conversation, recognize context across extended exchanges, and generate responses that maintain conversational coherence. LaMDA’s training approach focused specifically on dialogue applications, enabling it to handle open-ended questions, maintain context through multi-turn conversations, and adapt to different conversational styles. When Google introduced PaLM 2 in 2023, it represented a significant advancement with improved multilingual capabilities, enhanced reasoning abilities, and superior coding proficiency. PaLM 2 demonstrated better performance across multiple benchmarks compared to its predecessors, offering more nuanced understanding of complex topics and improved ability to handle specialized domains. The transition to Gemini Pro and Gemini Ultra further enhanced these capabilities, with Gemini Ultra demonstrating superior performance on reasoning tasks, mathematics, and code generation compared to GPT-4. These models employ reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) and tree search techniques to improve response quality and alignment with user intent. The architecture enables Bard to process information from multiple modalities, including text, images, video, and code, making it a truly multimodal AI system.
Google Bard offers a comprehensive suite of capabilities that extend far beyond simple question-answering. The platform excels at natural language understanding and generation, allowing users to engage in fluid conversations about virtually any topic. Bard can summarize complex information from web sources, distilling lengthy articles, research papers, and documents into concise, digestible summaries. The creative content generation capabilities enable users to request poems, stories, scripts, emails, and other written formats in various styles and tones. Code generation and debugging represent another powerful feature, with Bard capable of writing functional code in multiple programming languages, explaining code logic, and identifying bugs in existing implementations. The real-time web search integration distinguishes Bard from many competitors, allowing it to access current information and provide up-to-date responses with source citations. Language translation across more than 100 languages enables global communication and content localization. Voice command support makes Bard accessible to users who prefer hands-free interaction, particularly valuable for accessibility and multitasking scenarios. The multi-turn conversation capability allows users to ask follow-up questions and build on previous responses, maintaining context throughout extended dialogues. Additionally, Bard offers response modification features that let users adjust tone, length, and style without requiring entirely new prompts, streamlining the refinement process.
| Feature | Google Bard (Gemini) | ChatGPT | Claude | Perplexity AI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Model | Gemini Pro/Ultra | GPT-3.5/GPT-4 | Claude 3 | Proprietary LLM |
| Real-time Internet Access | Yes (free tier) | Premium only | Limited | Yes |
| Data Training Cutoff | Continuously updated | April 2024 (GPT-4) | April 2024 | Continuously updated |
| Multimodal Capabilities | Text, images, video, code | Text, images, voice | Text, images | Text, web results |
| Integration with Google Services | Extensive (Docs, Sheets, Gmail) | Limited | None | None |
| Voice Commands | Yes | Yes (mobile app) | No | No |
| Free Tier Availability | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Premium Pricing | Gemini Advanced ($20/month) | ChatGPT Plus ($20/month) | Claude Pro ($20/month) | Perplexity Pro ($20/month) |
| Language Support | 40+ languages | 50+ languages | 40+ languages | 40+ languages |
| Conversation Retention | Up to 3 years | Limited history | Limited history | Session-based |
| Source Citations | Yes, with links | Limited | Yes | Yes, with sources |
| Code Generation | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
| Creative Writing | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
The process by which Google Bard generates responses involves sophisticated natural language processing and machine learning inference. When a user submits a prompt, Bard first performs intent recognition, analyzing the query to understand what the user is actually seeking. This step is crucial because users often phrase requests in ambiguous or indirect ways. For example, a question about “the best way to learn piano” could be seeking information about instructors, online courses, practice techniques, or instrument selection. Bard’s intent recognition helps disambiguate such queries. Next, Bard engages in information retrieval, accessing its training knowledge and, when necessary, performing real-time web searches to gather current information. The system then applies context understanding, considering the conversation history and any previous exchanges to ensure responses remain coherent and relevant. The response generation phase involves the model predicting the most likely next tokens based on patterns learned during training, building responses word-by-word or phrase-by-phrase. Throughout this process, Bard applies safety filters and alignment techniques to ensure responses are accurate, helpful, and free from harmful content. The system can generate multiple response drafts, allowing users to compare different approaches to the same question. This multi-draft capability leverages the model’s ability to explore different response paths, providing users with diverse perspectives and writing styles. Finally, Bard includes source attribution, citing the web sources it consulted when generating responses, enabling users to verify information and explore topics more deeply.
One of Google Bard’s most significant advantages is its deep integration with Google’s suite of productivity tools. Users can seamlessly export content generated in Bard directly to Google Docs, enabling efficient content creation workflows where ideas generated in conversation can be immediately formatted and refined in a document editor. Google Sheets integration allows Bard to generate tables, analyze data, and create spreadsheets, making it valuable for data-driven tasks and business intelligence applications. Gmail integration enables users to draft emails within Bard and send them directly, streamlining communication workflows. Google Maps integration provides location-based information and travel planning capabilities within the conversational interface. Google Drive integration allows Bard to access and analyze documents stored in the cloud, enabling more personalized and contextual responses based on user-specific information. Beyond Google’s native services, Bard has expanded its ecosystem through partnerships with external platforms. Google announced integrations with Kayak for travel planning, OpenTable for restaurant reservations, ZipRecruiter for job searching, Instacart for grocery shopping, Wolfram Alpha for computational knowledge, and Khan Academy for educational content. These integrations transform Bard from a standalone chatbot into a comprehensive AI assistant that can take action across multiple platforms and services. This ecosystem approach creates significant switching costs and increases user engagement, as Bard becomes increasingly embedded in users’ daily workflows and productivity routines.
As Google Bard and its successor Gemini become primary sources of information for millions of users, the implications for brand visibility and reputation management have become increasingly critical. Unlike traditional search engines that display multiple results, AI chatbots like Bard provide single, authoritative-sounding responses that users may accept without verification. When Bard cites a brand, provides product information, or mentions a company in response to user queries, this represents a form of AI-generated brand mention that differs fundamentally from traditional search visibility. Organizations must now monitor how their brands appear in AI-generated responses across multiple platforms including Bard/Gemini, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and Google AI Overviews. The challenge is that AI mention tracking requires different methodologies than traditional SEO monitoring. While search engines display multiple results allowing brands to compete for visibility, AI systems may mention only one or two brands in response to a query, making inclusion or exclusion from AI responses particularly consequential. Research indicates that 82 million monthly active users access Gemini (formerly Bard) as of Q2 2025, representing a 370% growth from earlier periods. This massive user base means that accurate representation in Bard’s responses directly impacts brand awareness, credibility, and customer acquisition. Companies should implement AI monitoring tools to track brand mentions, verify accuracy of information provided by Bard, and identify opportunities to improve their visibility in AI-generated responses. This emerging discipline of AI brand monitoring complements traditional SEO and represents a critical component of modern digital marketing strategy.
The transition from Google Bard to Gemini in February 2024 represented more than a simple name change; it reflected a fundamental strategic shift in how Google positioned its AI capabilities. The rebrand consolidated Google’s fragmented AI product portfolio under a unified Gemini brand, which now encompasses multiple model variants including Gemini Nano, Gemini Pro, and Gemini Ultra. This consolidation strategy aimed to reduce consumer confusion and create a clearer value proposition across different use cases and price points. Gemini Nano targets on-device applications with lower computational requirements, Gemini Pro serves as the standard offering for most users, and Gemini Ultra represents the most capable model reserved for premium users and enterprise applications. The rebrand also coincided with the introduction of Gemini Advanced, a premium subscription tier offering access to Gemini Ultra and additional features. This pricing structure mirrors ChatGPT’s successful freemium model, with a free tier providing access to capable models and a premium tier ($20 per month) offering access to the most advanced capabilities. The transition demonstrated Google’s commitment to competing directly with OpenAI in the consumer AI market while maintaining its enterprise focus. Additionally, the rebrand enabled Google to distance Bard from its early launch missteps and present a fresh, more polished product to the market. The Gemini branding also extended beyond the chatbot to encompass Google’s broader AI strategy, including integration into Android devices, Google Search, and other Google services, creating a more cohesive ecosystem narrative.
Google Bard/Gemini possesses several distinctive advantages that differentiate it from competing AI services. The real-time internet access on the free tier provides current information without requiring a premium subscription, a significant advantage over ChatGPT’s free version. The seamless integration with Google services creates a productivity advantage for users already embedded in the Google ecosystem, reducing friction in workflows and increasing switching costs. The multimodal capabilities enable processing of text, images, video, and code, providing versatility across diverse use cases. The conversation retention capability, allowing users to access conversations from up to three years prior, supports long-term project continuity and knowledge management. The source attribution and fact-checking features address concerns about AI hallucinations by providing transparency about information sources. The voice command support and mobile app availability ensure accessibility across devices and use cases. The multiple draft responses feature allows users to compare different approaches without requiring new prompts. Additionally, Bard’s integration with Google’s research infrastructure, including access to Google DeepMind’s latest advances, ensures continuous improvement and access to cutting-edge AI capabilities. These advantages position Bard/Gemini as a particularly strong choice for users prioritizing current information, productivity integration, and multimodal capabilities.
Despite its strengths, Google Bard/Gemini faces several notable limitations that users should understand. AI hallucinations, where the system generates plausible-sounding but factually incorrect information, remain a persistent challenge despite improvements in accuracy. The system can confidently provide false information, particularly regarding specialized topics, recent events, or niche domains where training data may be sparse. Limited creative control in some applications means users cannot always achieve the exact tone, style, or perspective they desire without multiple iterations. Potential biases inherited from training data can influence responses, particularly on controversial or sensitive topics. Privacy and security concerns persist despite Google’s assurances, with users rightfully questioning how their conversation data is stored, used, and protected. The limited integration with non-Google services compared to ChatGPT’s extensive plugin ecosystem restricts functionality for users relying on specialized tools. Language availability limitations, with Gemini Pro currently available primarily in English despite broader language support for earlier versions, restrict global accessibility. The dependency on internet connectivity for real-time information access means Bard cannot function offline, unlike some alternative solutions. Additionally, accuracy verification requirements mean users must fact-check important information before relying on it, adding friction to workflows where speed is critical. These limitations suggest that Bard/Gemini, while powerful, should be used as one tool among many rather than as a sole source of truth for critical decisions.
The future of Google Bard/Gemini appears poised for significant expansion and integration across Google’s product portfolio. Google has indicated plans to deepen integration with Google Search, potentially transforming how users discover information by combining traditional search results with AI-generated summaries and insights. The AI Overviews feature in Google Search represents an early manifestation of this strategy, providing AI-generated answers alongside traditional search results. Continued model improvements through advances in training techniques, larger datasets, and architectural innovations will likely enhance accuracy, reasoning capabilities, and multimodal processing. Enterprise-focused features including advanced security, compliance, and customization options will expand Bard/Gemini’s appeal to business users and organizations. Expanded integrations with third-party services beyond the current partnerships will increase Bard’s utility as a central AI assistant. Localization efforts will extend language support and cultural adaptation, making Bard/Gemini accessible to users worldwide. The emergence of specialized variants tailored to specific industries or use cases (healthcare, finance, legal, etc.) will likely follow, similar to how ChatGPT has spawned industry-specific implementations. Agentic capabilities enabling Bard to take autonomous actions across multiple systems represent a frontier that Google is actively exploring. The competitive landscape will continue to intensify as OpenAI, Anthropic, and other players advance their own capabilities, driving continuous innovation. For organizations and individuals, staying informed about Bard/Gemini’s evolution and maintaining awareness of how the platform represents their brands in AI-generated responses will become increasingly important as these systems become primary information sources for billions of users globally.
Google Bard and ChatGPT are both conversational AI systems, but they differ significantly in their underlying technology and capabilities. Bard uses Google's PaLM 2 model and has real-time internet access on its free version, allowing it to provide current information, while ChatGPT's free version lacks internet access and relies on training data from 2021. Bard excels at research and fact-checking with up-to-date information, whereas ChatGPT is often praised for more creative and nuanced text generation. Both support multiple languages and can handle various tasks, but Bard integrates seamlessly with Google services like Docs and Gmail, while ChatGPT offers more third-party plugins and integrations.
LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications) is the foundational technology that powers Google Bard's conversational abilities. LaMDA is a Transformer-based neural language model with up to 137 billion parameters, trained on 1.56 trillion words of dialogue and web text. This specialized architecture enables Bard to understand context, recognize patterns in conversational exchanges, and generate contextually appropriate responses that feel natural and human-like. LaMDA's design focuses specifically on dialogue applications, making it particularly effective at maintaining conversation flow and understanding nuanced user intent across diverse topics.
In February 2024, Google rebranded Bard to Gemini as part of a strategic consolidation of its AI product portfolio. The rebrand reflected Google's evolution of the AI service with more powerful models, including Gemini Pro and the advanced Gemini Ultra. This unified naming strategy helped Google present a cohesive AI vision across all its products and services. The transition also marked the introduction of Gemini Advanced, a premium tier offering access to the most capable Gemini Ultra model, positioning the service more competitively against other enterprise AI solutions.
Yes, Google Bard has real-time internet access capabilities, which is one of its key advantages over ChatGPT's free version. Bard can search the web and retrieve current information, making it particularly useful for queries about recent events, current stock prices, latest news, and trending topics. This real-time access ensures that responses are based on the most recent data available, rather than relying on static training data. Users can see sources cited in Bard's responses, and the system can provide links to relevant articles and websites for further exploration.
Google Bard serves multiple business applications including customer support automation, content creation and ideation, email marketing campaign development, e-learning and personalized tutoring, market research and competitive analysis, and code generation for software development. Businesses can leverage Bard to streamline workflows by integrating it with Google Workspace tools, automate responses to frequently asked questions, generate creative content ideas, analyze complex data, and provide personalized recommendations. The ability to access real-time information makes it particularly valuable for research-intensive tasks and staying updated with market trends.
While Google Bard prioritizes accuracy by accessing real-time web information and including source citations in responses, it can still produce inaccurate or misleading information, a phenomenon known as AI hallucinations. Google acknowledges this limitation and recommends users fact-check important information before relying on it entirely. The company has implemented quality assurance measures and continues to improve Bard's ability to recognize when it lacks sufficient information. Users should verify critical information through reliable sources, particularly for complex topics or specialized domains where errors could have significant consequences.
Google Bard is accessible through multiple platforms including the web browser at bard.google.com, iOS and Android mobile applications, and integration within the Google app on iOS. Users need a personal Google Account or Google Workspace account to access Bard, though Family Link accounts and Google Workspace for Education accounts for users under 18 cannot access the service. The service supports modern browsers including Chrome, Safari, Firefox, Opera, and Edge. Currently, Bard is available in over 40 languages, though the latest Gemini Pro version is primarily available in English, Japanese, and Korean.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Google Gemini is a multimodal AI model by Google DeepMind that processes text, images, audio, and video. Learn its architecture, capabilities, and impact on AI ...

Learn what Google-Extended is, how it works, and whether you should block it in your robots.txt. Understand the difference between AI training control and AI Ov...
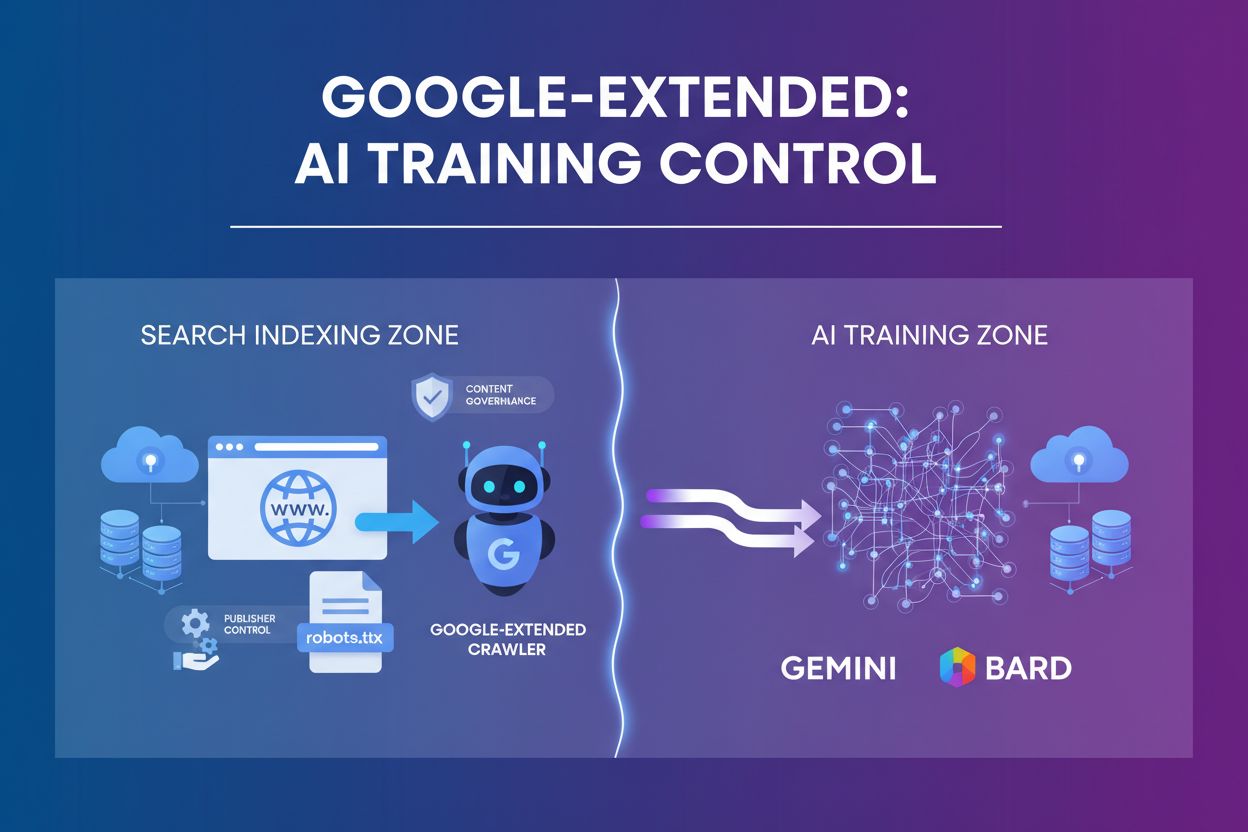
Learn about Google-Extended, the user-agent token that lets publishers control whether their content is used for AI training in Gemini and Vertex AI. Understand...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.