
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is OpenAI's conversational AI assistant powered by GPT models. Learn how it works, its impact on AI monitoring, brand visibility, and why it matters for...

GPT-4 is OpenAI’s fourth-generation large language model and the first multimodal LLM capable of processing both text and image inputs to generate human-level responses. Released in March 2023, GPT-4 represents a significant advancement in artificial intelligence with a 128K context window, improved reasoning capabilities, and enhanced safety features compared to its predecessor GPT-3.5.
GPT-4 is OpenAI's fourth-generation large language model and the first multimodal LLM capable of processing both text and image inputs to generate human-level responses. Released in March 2023, GPT-4 represents a significant advancement in artificial intelligence with a 128K context window, improved reasoning capabilities, and enhanced safety features compared to its predecessor GPT-3.5.
GPT-4 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 4) is OpenAI’s fourth-generation large language model and represents a watershed moment in artificial intelligence development. Released in March 2023, GPT-4 is the first multimodal large language model capable of accepting both text and image inputs while generating sophisticated text outputs. Unlike its predecessor GPT-3.5, which processes only text, GPT-4 combines natural language processing with computer vision capabilities, enabling it to understand and analyze visual information alongside textual context. This breakthrough model demonstrates human-level performance across numerous professional and academic benchmarks, fundamentally changing how enterprises approach AI-driven content generation, analysis, and decision-making. The significance of GPT-4 extends beyond raw capability improvements—it represents a paradigm shift in how AI systems can interact with and understand the world.
The development of GPT-4 builds upon the transformer architecture introduced by Google researchers in 2017 through their seminal paper “Attention Is All You Need.” OpenAI’s progression from GPT-1 through GPT-4 demonstrates exponential improvements in model sophistication and capability. GPT-3, released in 2020, was trained on 175 billion parameters and established the foundation for modern large language models. However, OpenAI chose not to disclose the exact number of parameters used to train GPT-4, partially due to increased competition in the AI space and the company’s transition to a for-profit structure. Despite speculation that GPT-4 uses over 100 trillion parameters, CEO Sam Altman explicitly denied these claims. The model’s development incorporated extensive safety research, human feedback integration, and real-world testing to address concerns about misinformation, bias, and harmful outputs that plagued earlier iterations. GPT-4 represents approximately 18 months of intensive research and development following GPT-3.5’s release, incorporating lessons learned from millions of user interactions and expert consultations.
GPT-4’s architecture represents a significant departure from previous models through its adoption of a Mixture of Experts (MoE) design. This sophisticated neural network architecture employs multiple specialized sub-networks, each optimized for different types of information processing. Rather than using a single dense network like GPT-3.5, the MoE approach allows GPT-4 to efficiently route different inputs to the most appropriate expert networks, improving both performance and computational efficiency. The multimodal capability is achieved through a combination of a text encoder and a Vision Transformer (ViT) image encoder, allowing the model to process visual information with the same sophistication it applies to text. The attention mechanism in GPT-4 has been substantially improved, enabling the model to better understand relationships between distant concepts in both text and images. This architectural innovation allows GPT-4 to maintain coherence across longer sequences of information and to understand complex relationships that span multiple modalities. The model’s ability to process 128,000 tokens in its context window (compared to GPT-3.5’s 8,000-token limit) represents an 8x improvement in short-term memory capacity, enabling analysis of entire documents, lengthy conversations, and substantial code repositories without losing contextual information.
| Aspect | GPT-4 | GPT-3.5 | GPT-4 Turbo | Claude 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Modality | Text + Images | Text only | Text + Images | Text only |
| Context Window | 128K tokens | 8K tokens | 128K tokens | 100K tokens |
| Bar Exam Performance | 90th percentile | 10th percentile | 88th percentile | 88th percentile |
| Biology Olympiad | 99th percentile | 31st percentile | 97th percentile | 96th percentile |
| Safety Features | 82% less likely to respond to disallowed content | Baseline | Enhanced | Comparable |
| Factual Accuracy | 40% more accurate | Baseline | Improved | Similar |
| Parameters (Disclosed) | Not disclosed | 175 billion | Not disclosed | Not disclosed |
| Release Date | March 2023 | November 2022 | November 2023 | March 2024 |
| Real-time Internet Access | Yes (updated Sept 2023) | Limited | Yes | Yes |
| Pricing (API) | Higher cost | Lower cost | Mid-range | Competitive |
GPT-4’s vision capabilities represent one of its most transformative features, enabling applications previously impossible with text-only models. The model can perform visual question answering (VQA), where users provide an image and ask questions about its content, receiving detailed and contextually appropriate answers. Text transcription from images allows GPT-4 to digitize handwritten notes, printed documents, and screenshots with remarkable accuracy, making it invaluable for document management and accessibility applications. Object detection and identification enables GPT-4 to recognize and describe objects within images, even in complex scenes with multiple objects or varying lighting conditions. The model excels at data visualization interpretation, analyzing charts, graphs, and infographics to extract insights and explain complex data relationships in natural language. Real-world applications demonstrate GPT-4’s ability to generate functional code from hand-drawn sketches, create websites from wireframe images, and develop games from visual specifications. Companies like Be My Eyes leverage GPT-4’s vision capabilities to assist individuals with visual impairments by analyzing images in real-time. Duolingo uses GPT-4 to provide conversational language practice, while Morgan Stanley deployed a custom GPT-4 model trained on proprietary financial data to provide instant access to investment insights and wealth management information. These applications showcase how multimodal processing bridges the gap between human visual understanding and AI language capabilities.
GPT-4 demonstrates unprecedented performance across standardized academic and professional examinations. On the Uniform Bar Exam, GPT-4 scored in the 90th percentile compared to human test-takers, a dramatic improvement from GPT-3.5’s 10th percentile score. This represents the difference between a score that would qualify someone to practice law and a score that would result in failure. Similarly, on the Biology Olympiad, GPT-4 achieved the 99th percentile, compared to GPT-3.5’s 31st percentile. These benchmarks extend across multiple domains including mathematics, coding, writing, and visual reasoning. Microsoft researchers characterized GPT-4 as an “early yet still incomplete version of artificial general intelligence (AGI)”, highlighting its broad capabilities across diverse domains. The model demonstrates superior performance in specialized fields including medicine, law, psychology, and engineering. However, it’s important to note that benchmark performance doesn’t guarantee real-world accuracy, and GPT-4 can still produce hallucinations or provide incorrect information in specific contexts. The improvements in factual accuracy—40% more likely to produce factually correct responses than GPT-3.5—represent significant progress but not perfection. These performance metrics have made GPT-4 the preferred model for enterprise applications requiring high accuracy and sophisticated reasoning.
OpenAI implemented comprehensive safety measures in GPT-4 to address concerns about harmful outputs, misinformation, and bias. The model is 82% less likely to respond to requests for disallowed content compared to GPT-3.5, representing a substantial improvement in content filtering and safety guardrails. This improvement was achieved through multiple mechanisms including reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), consultations with security experts across diverse domains, and extensive real-world testing before public release. GPT-4 demonstrates improved resistance to jailbreak attempts, where users try to manipulate the model into ignoring safety guidelines. The model’s training incorporated diverse perspectives to reduce biases, though bias concerns remain an ongoing challenge in AI development. OpenAI also implemented refusal mechanisms that prevent GPT-4 from analyzing certain sensitive images, particularly those involving people, to protect privacy and prevent misuse. The 40% improvement in factual accuracy reflects better training data curation and validation processes. However, these safety improvements don’t eliminate all risks—GPT-4 can still provide unreliable medical advice, generate biased responses in certain contexts, and produce hallucinations. The model’s cybersecurity vulnerabilities, including potential CAPTCHA-solving capabilities, highlight the ongoing tension between capability and safety in advanced AI systems. Organizations deploying GPT-4 must implement additional safeguards and human oversight to ensure responsible usage aligned with their values and regulatory requirements.
The 128,000-token context window in GPT-4 represents a revolutionary improvement in how much information the model can process simultaneously. To understand this capacity, consider that one token approximately equals 0.75 words in English, meaning GPT-4 can process roughly 96,000 words at once. This is equivalent to analyzing an entire novel, a comprehensive research paper with appendices, or an extended conversation spanning hundreds of exchanges. GPT-4 Turbo, released in November 2023, maintains this full 128K context window, while earlier versions had smaller limits. The expanded context window enables several critical capabilities: users can upload entire codebases for analysis and refactoring, provide complete project documentation for context-aware assistance, and maintain coherent conversations without the model forgetting earlier discussion points. The context window improvement addresses a major limitation of GPT-3.5, which could only maintain approximately 8,000 words of context before losing information. This 16x improvement fundamentally changes how GPT-4 can be applied to complex, document-heavy tasks. However, research indicates that GPT-4’s effective context utilization may be less than the theoretical maximum, with some studies suggesting the model performs optimally with approximately 8,000-40,000 tokens of actual content, with performance degrading at the extreme ends of the context window. This phenomenon, known as the “context window illusion,” suggests that while the capacity exists, practical performance may vary based on information placement and complexity.
GPT-4 adoption across enterprises has accelerated dramatically since its release, with adoption rates reaching 57% in computer-related fields, 50% in management and business, 48% in engineering and science, and 44% in other professional roles. Organizations are deploying GPT-4 for diverse applications including customer service automation, content generation, code development, data analysis, and strategic decision-making. Financial institutions like Morgan Stanley have implemented custom GPT-4 models trained on proprietary data to enhance wealth management and investment advisory services. Healthcare organizations are exploring GPT-4’s potential for medical research, diagnostic assistance, and patient communication, though regulatory and accuracy concerns remain significant. Educational institutions leverage GPT-4 for personalized tutoring, content creation, and accessibility support. The API pricing structure for GPT-4 is higher than GPT-3.5, reflecting the increased computational resources required and the model’s superior capabilities. This pricing differential has created a market segmentation where organizations with high-accuracy requirements or complex tasks justify the premium cost, while others continue using GPT-3.5 for cost-sensitive applications. The enterprise adoption trajectory suggests that GPT-4 will become the standard for sophisticated AI applications, similar to how GPT-3.5 became ubiquitous for general-purpose tasks. However, concerns about data privacy, model hallucinations, and regulatory compliance continue to influence adoption decisions, particularly in regulated industries like finance and healthcare.
The emergence of GPT-4 as a dominant AI platform has significant implications for AI monitoring and citation tracking systems like AmICited. As enterprises increasingly rely on GPT-4 for research, content generation, and decision-making, understanding how GPT-4 cites sources and mentions brands becomes critical for SEO strategy and brand visibility. GPT-4’s multimodal capabilities mean that citations can appear in response to both text queries and image-based searches, expanding the surface area for brand mentions. The model’s 128K context window allows it to process and cite from longer documents, potentially increasing the likelihood of specific brand or domain mentions in responses. AI monitoring platforms must track GPT-4 citations across multiple dimensions: whether citations appear in text responses, whether images are analyzed and cited, the frequency of brand mentions, and the context in which citations occur. The improved factual accuracy of GPT-4 compared to GPT-3.5 means that citations are more likely to be accurate, making GPT-4 responses particularly valuable for understanding how AI systems represent your brand or domain. Organizations using AmICited can identify which content pieces are most frequently cited by GPT-4, optimize content for AI discoverability, and understand how their brand positioning differs across various AI platforms including ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude. The strategic importance of GPT-4 monitoring extends beyond vanity metrics—it provides insights into how AI systems understand and represent your industry, competitors, and market positioning.
Despite its remarkable capabilities, GPT-4 has significant limitations that organizations must understand before deployment. Hallucinations—where the model generates plausible-sounding but factually incorrect information—remain a persistent challenge, particularly in specialized domains or when the model lacks training data on specific topics. The model can confidently provide incorrect medical advice, potentially causing harm if users rely on it without professional verification. Privacy concerns arise from GPT-4’s ability to identify individuals and locations in images, raising questions about consent and data protection compliance. Bias in image analysis could lead to discriminatory outcomes, particularly affecting underrepresented demographic groups. The model’s refusal to analyze certain images, while a safety feature, limits its functionality in legitimate use cases. Cybersecurity vulnerabilities include potential exploitation for solving CAPTCHAs or generating adversarial content. The model’s knowledge cutoff (training data ending in April 2024 for recent versions) means it lacks awareness of very recent events or developments. Computational costs for running GPT-4 remain substantial, limiting accessibility for smaller organizations. The model’s tendency to produce verbose responses can be inefficient for certain applications. Additionally, GPT-4’s performance can vary significantly based on prompt engineering, with poorly constructed prompts yielding suboptimal results. Organizations must implement human oversight, fact-checking processes, and domain expertise validation to mitigate these limitations.
The trajectory of GPT-4 development suggests continued evolution toward more capable, efficient, and specialized models. OpenAI has already released GPT-4 Turbo with improved performance and lower costs, and announced GPT-4.1 with enhanced capabilities and extended context window support up to 1 million tokens. The emergence of specialized GPT-4 variants—including GPT-4o (optimized), GPT-4 mini, and GPT-4 nano—indicates a strategy of model diversification to serve different use cases and computational constraints. Future developments likely include improved multimodal capabilities with support for audio and video inputs, enhanced reasoning for complex problem-solving, and better integration with external tools and APIs. The competitive landscape is intensifying with Claude 3, Gemini, and other models challenging GPT-4’s dominance, driving innovation across the industry. Regulatory frameworks around AI are evolving, potentially imposing new requirements for transparency, explainability, and safety that will influence model development. The cost trajectory for AI models is expected to decrease as competition increases and efficiency improvements are implemented, potentially democratizing access to advanced AI capabilities. Integration with enterprise systems will likely deepen, with GPT-4 becoming embedded in productivity tools, business intelligence platforms, and specialized industry applications. The importance of AI monitoring and citation tracking will increase as organizations recognize the strategic value of understanding how AI systems represent their brands and content. The future of GPT-4 is not merely about incremental capability improvements but about fundamental shifts in how AI systems interact with information, understand context, and support human decision-making across diverse domains.
GPT-4 significantly outperforms GPT-3.5 in multiple dimensions. GPT-4 scored in the 90th percentile on the Uniform Bar Exam compared to GPT-3.5's 10th percentile, and achieved 99th percentile on the Biology Olympiad versus GPT-3.5's 31st percentile. GPT-4 is multimodal, accepting both text and image inputs, while GPT-3.5 only processes text. Additionally, GPT-4 has an 8x larger context window (64,000 words versus 8,000 words) and is 82% less likely to respond to disallowed content requests.
Multimodal refers to GPT-4's ability to understand and process multiple types of input data simultaneously, including text, images, and potentially other data formats. This allows GPT-4 to analyze images, answer questions about visual content, perform optical character recognition, and generate responses based on combined text and visual information, mimicking human-like comprehension across different sensory inputs.
GPT-4's context window is 128,000 tokens (approximately 80,000 words in English), with GPT-4 Turbo supporting the full 128K capacity. This means GPT-4 can process and maintain coherence across significantly longer documents, conversations, and code files compared to GPT-3.5's 8,000-word limit. A larger context window enables better understanding of complex documents and longer conversations without losing information.
GPT-4 excels at text generation, code writing, mathematical reasoning, visual analysis, document summarization, and complex problem-solving. It can interpret charts and infographics, transcribe text from images, detect objects, perform visual question answering, and generate code from sketches or wireframes. GPT-4 also demonstrates improved accuracy in specialized domains including law, medicine, and academic subjects.
GPT-4's advanced reasoning and multimodal capabilities make it a significant platform for AI monitoring tools like AmICited. As enterprises increasingly use GPT-4 for content generation and research, tracking brand mentions, citations, and URL appearances in GPT-4 responses becomes critical for SEO, brand management, and understanding AI-driven content distribution patterns across different AI platforms.
GPT-4 employs a Mixture of Experts (MoE) design, a neural network architecture that uses multiple specialized sub-networks (experts) to process different types of information. This approach allows GPT-4 to efficiently handle diverse tasks and scale computations, improving performance while managing computational resources more effectively than traditional dense architectures used in earlier models.
OpenAI implemented multiple safety measures in GPT-4, including training with human feedback, consultations with security experts, and real-world testing. GPT-4 is 82% less likely to respond to requests for disallowed content and 40% more likely to produce factually accurate responses than GPT-3.5. These improvements address concerns about misinformation, bias, and harmful content generation.
GPT-4 has notable limitations including potential hallucinations (generating false information), privacy concerns with image analysis, possible biases in responses, and occasional refusal to analyze sensitive images. The model can provide unreliable medical advice, may struggle with very recent information, and has cybersecurity vulnerabilities such as potential CAPTCHA-solving capabilities that could be exploited maliciously.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

ChatGPT is OpenAI's conversational AI assistant powered by GPT models. Learn how it works, its impact on AI monitoring, brand visibility, and why it matters for...
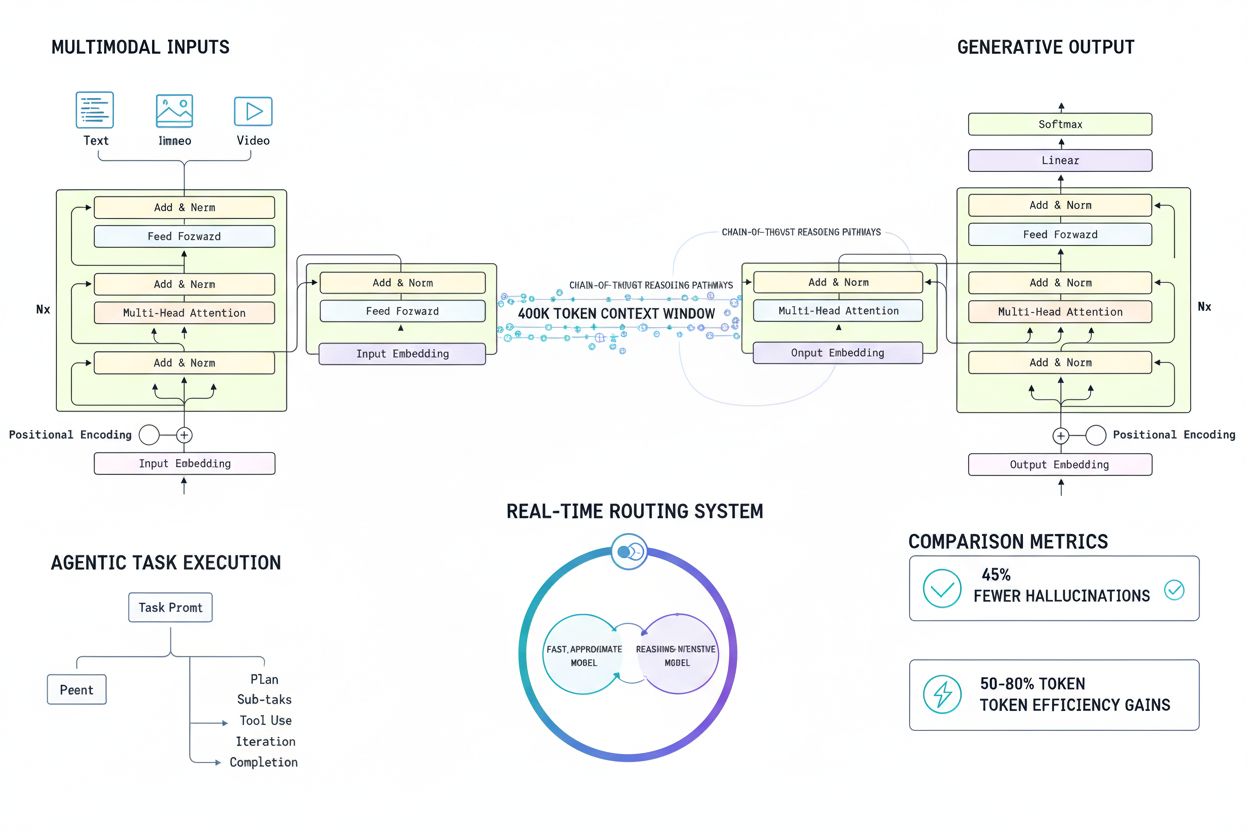
GPT-5 is OpenAI's latest LLM released August 2025, featuring 400K context window, 45% fewer hallucinations, multimodal capabilities, and unified reasoning archi...
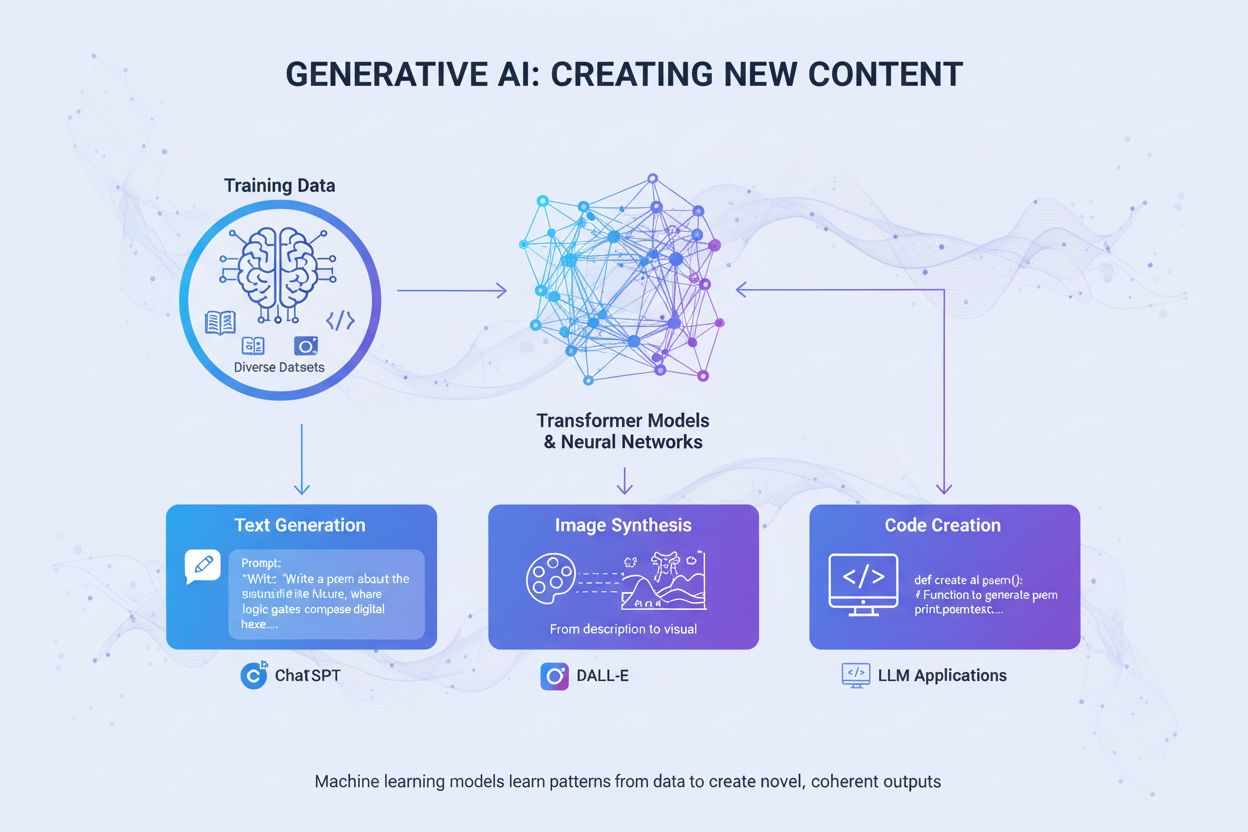
Generative AI creates new content from training data using neural networks. Learn how it works, its applications in ChatGPT and DALL-E, and why monitoring AI vi...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.