
Best Way to Format Headers for AI: Complete Guide for 2025
Learn the best practices for formatting headers for AI systems. Discover how proper H1, H2, H3 hierarchy improves AI content retrieval, citations, and visibilit...
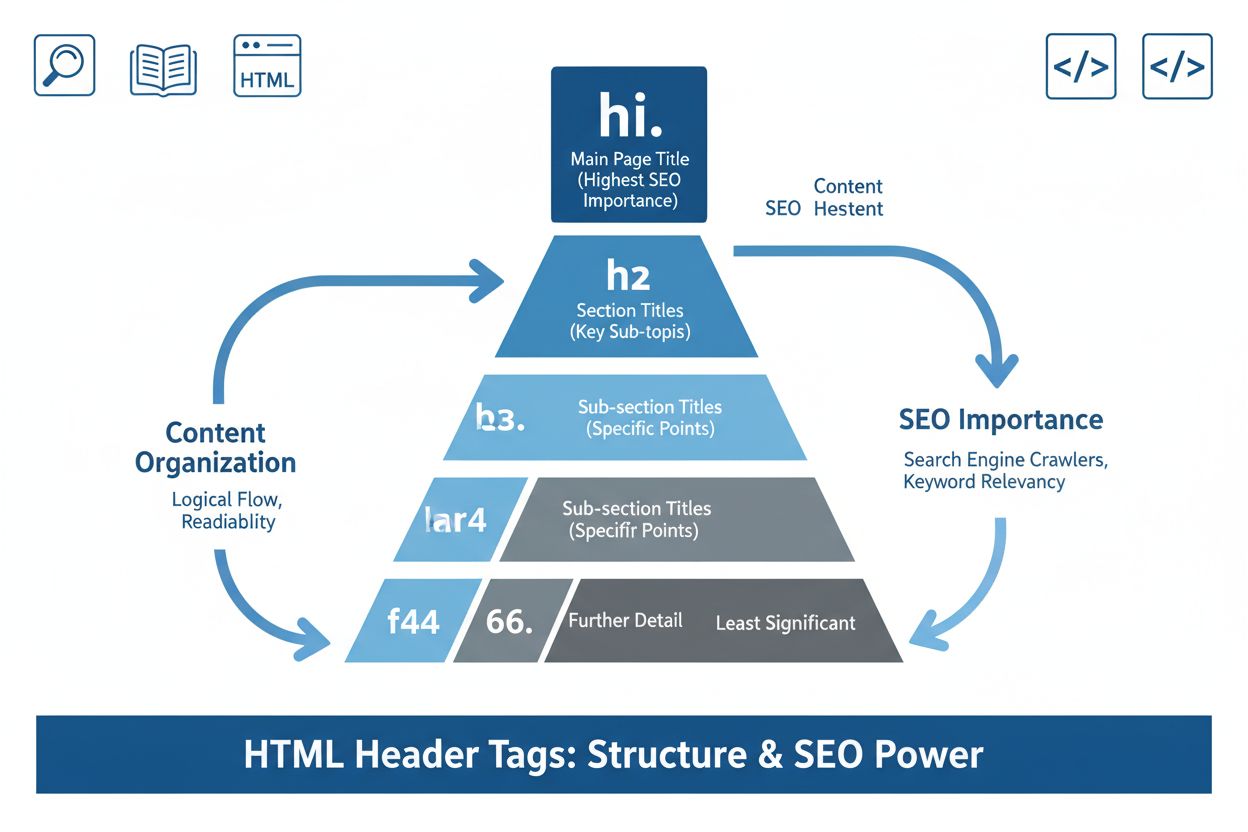
Header tags are HTML elements (
Header tags are HTML elements (<h1> through <h6>) that define hierarchical heading levels in web content, with H1 representing the most important heading and H6 the least important. They structure content for both users and search engines, improving readability, accessibility, and SEO performance.
Header tags are HTML elements that define hierarchical heading levels within web content, ranging from <h1> (most important) to <h6> (least important). These semantic HTML elements communicate the structure and organization of information to browsers, search engines, and assistive technologies. The H1 tag represents the primary heading or main topic of a page, while H2 through H6 tags create a hierarchical structure for subheadings and subsections. Header tags are fundamental to modern web design because they serve dual purposes: they enhance user experience by making content scannable and readable, and they provide critical context signals that help search engines and AI systems understand page content. Unlike simple text formatting, header tags embed meaning directly into the HTML structure, making them essential for both human visitors and machine interpretation.
Header tags have been part of HTML since the earliest versions of the specification, reflecting the web’s foundational need to structure documents hierarchically. The concept originated from academic and technical documentation practices, where clear heading hierarchies were essential for organizing complex information. As the web evolved from static documents to dynamic content platforms, header tags remained a cornerstone of semantic HTML. The introduction of HTML5 brought refinements to how header tags interact with sectioning elements like <article>, <section>, and <nav>, allowing for more sophisticated content organization. Today, header tags are recognized as critical components of both SEO and web accessibility standards. According to research from 2024-2025, approximately 93.5% of top-ranking pages use a single H1 tag, demonstrating widespread adoption of best practices. The rise of AI-powered search systems has further elevated the importance of header tags, as these systems rely on clear content structure to extract, understand, and cite information accurately.
Header tags are implemented using straightforward HTML syntax, with each level enclosed in opening and closing tags. An H1 tag appears as <h1>Main Topic</h1>, while H2 through H6 follow the same pattern with their respective numbers. The hierarchy must be logical and sequential—you should never skip levels by jumping from H1 directly to H3, as this breaks the semantic structure that both users and machines rely on. Each heading level has default CSS styling that makes it visually distinct, with H1 typically displaying at the largest font size and H6 at the smallest. However, the visual appearance should never be the primary reason for choosing a heading level; semantic meaning must take precedence. Content management systems like WordPress, Shopify, and custom platforms provide user-friendly interfaces for adding header tags without requiring direct HTML editing, though developers can also implement them manually in code. The proper structure creates a document outline that screen readers can interpret, allowing assistive technology users to navigate pages efficiently and understand content organization at a glance.
| Aspect | Header Tags (H1-H6) | Title Tag | Meta Description | Bold/Strong Tags |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Define content hierarchy and structure | Page title in browser tab and SERPs | Brief page summary in search results | Emphasize important text within content |
| Semantic Meaning | High - indicates heading hierarchy | High - defines page topic | Medium - provides context | Low - purely stylistic emphasis |
| SEO Impact | Direct - signals topic relevance | Very High - primary ranking signal | Medium - affects CTR | Minimal - no direct ranking impact |
| Accessibility | Critical - enables screen reader navigation | Important - identifies page purpose | Not used by screen readers | Useful - helps emphasize key terms |
| AI System Usage | High - used for content extraction | Very High - primary topic indicator | High - helps understand page purpose | Low - not typically extracted |
| Quantity Per Page | Multiple (1 H1, multiple H2-H6) | One per page | One per page | As needed for emphasis |
| Visual Display | Yes - different sizes for each level | Not displayed on page | Not displayed on page | Yes - bold text appearance |
| HTML Requirement | Required for proper structure | Required in <head> | Required in <head> | Optional - semantic alternative to <b> |
Header tags create a logical framework that transforms unstructured text into organized, scannable content. When users land on a page, they typically don’t read every word; instead, they scan headings to determine if the content addresses their needs. This scanning behavior is so prevalent that research shows pages with well-structured headings have significantly higher engagement rates than those without. Header tags break long blocks of text into digestible sections, reducing cognitive load and improving comprehension. For users with cognitive disabilities or those reading on mobile devices with limited screen space, clear heading hierarchies are invaluable. The H1 tag sets expectations about the page’s main topic, H2 tags introduce major sections, and H3-H6 tags provide further granularity for complex topics. This structure also benefits content creators by forcing them to think critically about information organization and logical flow. When writers use header tags properly, they naturally create better-organized content that serves both human readers and machine interpretation. The relationship between header tag structure and user experience is so significant that Google explicitly rewards well-structured content in its ranking algorithms, recognizing that good structure correlates with user satisfaction.
Search engines use header tags as semantic signals to understand page content and topic relevance. Google’s John Mueller has confirmed that header elements are a ‘really strong signal’ for interpreting what a page is about, and the search engine uses this information to match pages with relevant queries. Header tags help Google determine the primary topic (via H1), supporting topics (via H2), and specific subtopics (via H3-H6), creating a comprehensive understanding of page content. When your target keyword appears naturally in header tags, it reinforces the page’s topical relevance without requiring keyword stuffing in body text. Research from SEMrush and Moz shows that pages with well-optimized header structures tend to rank higher for their target keywords, though this correlation doesn’t necessarily indicate causation. The real value lies in how header tags improve content clarity and user experience, which are direct ranking factors. Additionally, header tags influence featured snippet acquisition—Google often pulls H2 and H3 content to create featured snippets, providing additional visibility in search results. For pages targeting multiple related keywords, strategic header tag placement allows you to address different keyword variations while maintaining natural, readable content. The SEO benefit of header tags extends beyond traditional search to AI-powered search systems, which rely heavily on clear content structure to extract and present information.
As AI systems become increasingly important in search and content discovery, header tags have taken on new significance as structural signals. AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude use header tags to understand page organization and extract relevant information for generating responses. When an AI system encounters a query, it scans indexed pages for relevant content, and header tags help it quickly identify sections most likely to contain the answer. For example, if a user asks “How do I optimize header tags for SEO?”, an AI system will look for pages with H2 or H3 tags containing keywords like “SEO optimization” or “best practices.” The clarity provided by proper header tag structure allows AI systems to extract accurate, contextually relevant information rather than relying on generic text matching. This has profound implications for content visibility in AI-powered search results. Pages with clear, well-organized header structures are more likely to be cited by AI systems because the structure makes it easier to identify and extract relevant passages. Platforms like AmICited monitor how AI systems cite and reference content across different sources, and proper header tag implementation ensures your content is correctly interpreted and attributed. As AI search continues to grow—with estimates suggesting AI-powered search will capture significant market share in coming years—the importance of header tags for content discoverability will only increase.
Implementing header tags effectively requires following established best practices that balance SEO optimization with user experience and accessibility. Use only one H1 tag per page, making it descriptive and reflective of the page’s main topic. This H1 should typically match or closely align with your page title, reinforcing the primary topic for both users and search engines. Avoid keyword stuffing in header tags; instead, write naturally for human readers while incorporating relevant keywords where they fit logically. Use H2 tags to introduce major sections of your content, with each H2 representing a distinct topic or idea. Within each H2 section, use H3 tags for subsections or related points, maintaining a logical hierarchy. Never skip heading levels—always progress from H1 to H2 to H3, rather than jumping from H1 directly to H3. Keep header tags concise, ideally under 70 characters, making them scannable and impactful. Ensure header tags accurately describe the content that follows them; misleading headers damage user trust and confuse search engines. Use consistent formatting across your website—if you use title case for H2 tags on one page, maintain that style across all pages. Finally, test your header structure using tools like Screaming Frog or browser developer tools to ensure proper hierarchy and identify any issues with missing or duplicate H1 tags.
Header tags are fundamental to web accessibility, serving as critical navigation aids for users with visual impairments or cognitive disabilities. Screen readers use header tags to create a document outline, allowing users to jump between sections without listening to entire page content. This functionality is essential for users who rely on assistive technology to browse the web efficiently. A properly structured heading hierarchy (H1 to H6 without skipping levels) creates a logical document outline that screen readers can interpret and present to users. Users can typically navigate between headings using keyboard shortcuts, making it possible to quickly scan a page’s structure and jump to relevant sections. Skipping heading levels—for example, using H1 followed by H3—creates confusion for screen reader users, as they may wonder what happened to the H2 level. Beyond screen readers, proper header structure benefits all users by improving content scannability and reducing cognitive load. Users with dyslexia, ADHD, or other cognitive differences benefit from clear visual and structural organization. Mobile users also benefit from header-based navigation, as it allows them to quickly understand page structure on small screens. Implementing proper header tag structure is not just an SEO best practice; it’s an ethical responsibility to ensure your content is accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities or the technology they use to access the web.
The importance of header tags is evolving as AI systems become more sophisticated and prevalent in search and content discovery. As AI-powered search platforms like Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and others expand their market share, the ability of these systems to extract and cite content will depend increasingly on clear content structure. Header tags will likely become even more critical as AI systems develop more advanced understanding of content hierarchy and context. The rise of voice search and conversational AI also elevates header tag importance, as these systems rely on clear content structure to generate natural, contextual responses. Future developments may include more sophisticated AI analysis of heading hierarchies, potentially using header structure as a quality signal for content evaluation. Additionally, as web accessibility standards continue to evolve and enforcement increases, proper header tag implementation will become a legal and ethical requirement rather than just a best practice. The integration of header tags with schema markup and other semantic HTML elements will likely deepen, creating richer signals for search engines and AI systems. Organizations that prioritize proper header tag implementation now will be better positioned to benefit from these evolving technologies and maintain visibility across both traditional search and AI-powered discovery platforms. The convergence of SEO, accessibility, user experience, and AI content extraction means that header tags will remain a foundational element of web content strategy for years to come.
The H1 tag represents the primary heading and should appear only once per page, defining the main topic. H2 tags are subheadings that break content into major sections beneath the H1. While H1 signals the page's central theme to search engines and users, H2s organize supporting topics and improve content scannability. Research shows 93.5% of top-ranking pages use a single H1 tag, making this distinction critical for SEO success.
Header tags provide semantic signals that help search engines understand content hierarchy and topic relevance. Google's John Mueller confirmed that header elements are a 'really strong signal' for interpreting page topics. Additionally, AI systems like those powering Google AI Overviews and Perplexity use header tags to extract and structure answers. Proper header tag usage improves featured snippet chances, enhances user experience through better scannability, and contributes to overall on-page SEO performance.
While HTML5 technically allows multiple H1 tags, best practice recommends using only one H1 per page. Multiple H1s can confuse search engines about your page's primary topic and dilute SEO focus. A single, descriptive H1 that clearly indicates the page's main subject provides the strongest semantic signal. If you need to structure multiple sections, use H2 and H3 tags instead to maintain a logical hierarchy.
Header tags are essential for accessibility because screen readers use them to help visually impaired users navigate pages efficiently. A proper heading hierarchy allows users to jump between sections without listening to entire content. Logical header structure (H1 to H6 without skipping levels) creates a document outline that assistive technologies can interpret, making content accessible to all users and improving overall user experience.
Yes, header tags significantly influence featured snippet acquisition. For paragraph snippets, using a keyword-optimized H2 followed by a concise answer helps Google extract the information. For list snippets, Google pulls from H2-H6 subheadings to create bulleted or numbered lists. Strategic header tag placement with relevant keywords increases visibility in featured snippets, driving additional organic traffic to your site.
The proper hierarchy starts with H1 as the main heading, followed by H2s for major sections, H3s for subsections within H2s, and so on through H6. Never skip heading levels (e.g., jumping from H1 directly to H3). This logical structure helps both users and search engines understand content organization. Each heading level should contain related content to the heading above it, creating a clear outline similar to a book's table of contents.
AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews use header tags to understand page structure and extract relevant information. Header tags help these systems identify key topics, create summaries, and determine content relevance for user queries. Platforms like AmICited monitor how AI systems cite and reference content, and proper header tag implementation ensures your content is correctly interpreted and attributed when AI systems reference your pages.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn the best practices for formatting headers for AI systems. Discover how proper H1, H2, H3 hierarchy improves AI content retrieval, citations, and visibilit...

Learn what title tags are, why they matter for SEO and AI visibility, and how to optimize them for search engines and users. Complete guide to title tag best pr...
Learn how semantic HTML improves AI understanding, LLM comprehension, and content attribution. Discover advanced techniques for optimizing markup for AI systems...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.