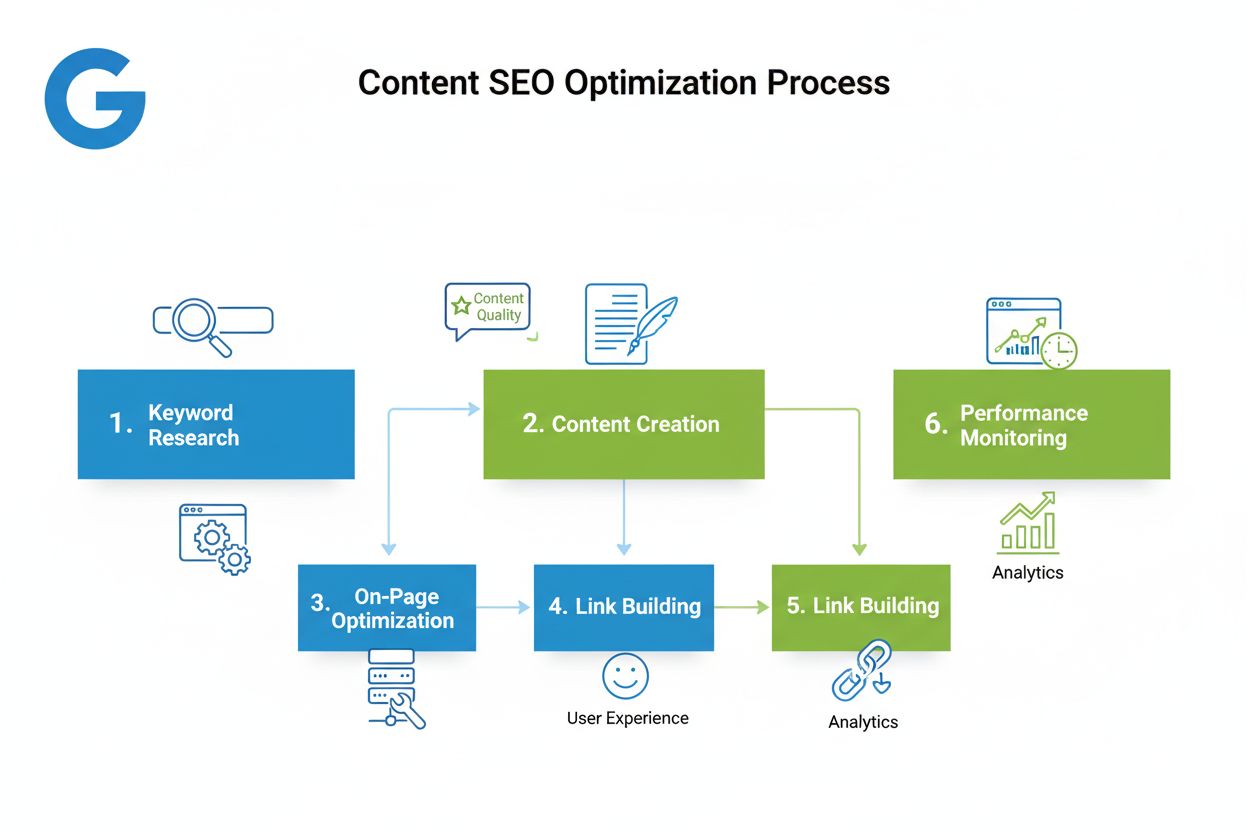
Content SEO
Content SEO is the strategic creation and optimization of high-quality content to improve search engine rankings and organic visibility. Learn how to optimize c...
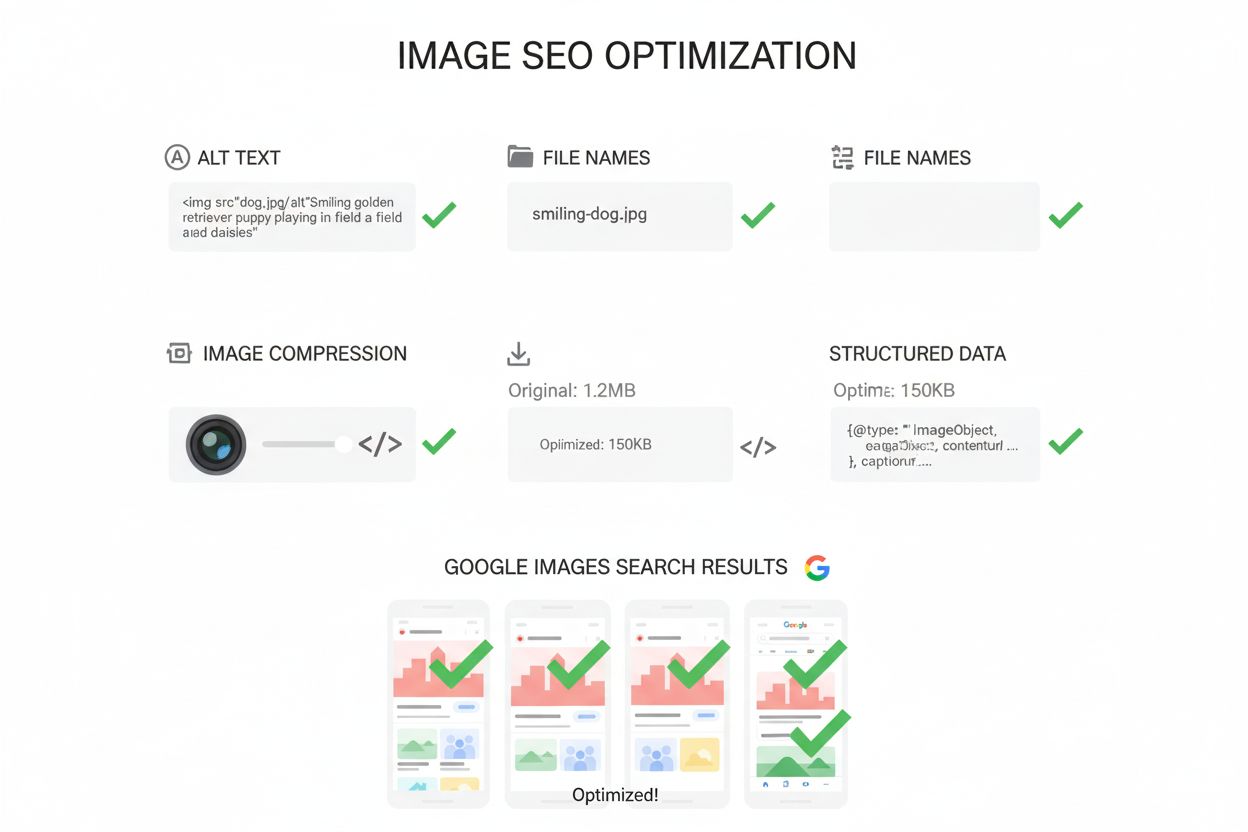
Image SEO is the practice of optimizing images on a website to improve their discoverability in search engines like Google Images and enhance overall page performance. It involves using descriptive file names, alt text, structured data, image compression, and responsive design to help search engines understand and rank visual content appropriately.
Image SEO is the practice of optimizing images on a website to improve their discoverability in search engines like Google Images and enhance overall page performance. It involves using descriptive file names, alt text, structured data, image compression, and responsive design to help search engines understand and rank visual content appropriately.
Image SEO is the practice of optimizing images on a website to improve their discoverability in search engines and enhance overall website performance. It encompasses a comprehensive set of techniques designed to help search engines understand, index, and rank visual content appropriately. Image SEO optimization involves strategic implementation of descriptive file names, alt text, image compression, structured data markup, responsive design, and proper image formatting. The primary goal is to make images easily discoverable through Google Images, visual search platforms like Google Lens, and other image search engines while simultaneously improving page load speed and user experience. Unlike traditional SEO that focuses on text-based content, Image SEO addresses the unique challenges of making visual content searchable and accessible to both search engine algorithms and human users with visual impairments.
The importance of Image SEO has grown exponentially as visual content consumption continues to dominate online behavior. Approximately 10.1% of Google traffic is directed to Google Images, making it a significant traffic source that many websites overlook. Over 35% of users now utilize image search as part of their regular search behavior, representing a substantial audience segment that traditional text-based SEO strategies may miss. The rise of visual search technology, particularly Google Lens, has further elevated the importance of image optimization, with the platform experiencing 65% year-over-year growth and processing over 100 billion visual searches annually. Additionally, nearly 20 billion monthly searches occur through Google Lens alone, with 20% of all Lens searches being shopping-related, indicating significant commercial intent. This shift toward visual discovery has prompted search engines to develop more sophisticated image recognition and ranking algorithms, making Image SEO an essential component of any comprehensive digital marketing strategy.
The technical aspects of Image SEO begin with proper HTML implementation using standard image elements rather than CSS-based images. Search engines can only index images embedded using the <img> tag with a src attribute, making this foundational to discoverability. Responsive images using srcset and sizes attributes ensure that appropriately sized versions load on different devices, improving both performance and user experience. Image file formats play a crucial role in optimization, with JPEG being ideal for photographs, PNG for graphics requiring transparency, WebP for superior compression, and SVG for scalable vector graphics. Image compression is critical for SEO performance, as compressed images reduce file sizes to 100 KB or less without sacrificing quality, directly improving page load times—a confirmed ranking factor. Lazy loading implementation ensures images load only when they enter the user’s viewport, reducing initial page load time and improving Core Web Vitals scores. Additionally, using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) distributes images across geographically dispersed servers, ensuring faster delivery to users worldwide and supporting better SEO performance across global audiences.
Metadata optimization forms the backbone of how search engines understand image content. Descriptive file names are the first signal to search engines about image subject matter; using names like golden-retriever-puppy-playing.jpg instead of IMG00023.JPG provides immediate context. Alt text (alternative text) is perhaps the most critical metadata element, serving dual purposes of accessibility for screen readers and SEO relevance for search engines. Effective alt text should be concise (under 125 characters), descriptive, and include relevant keywords naturally without keyword stuffing. Image captions, while distinct from alt text, provide visible context to users and are among the most-read elements on web pages, offering another opportunity for keyword inclusion and user engagement. Title attributes, though less critical than alt text, can provide additional context when used appropriately. Structured data markup using schema.org vocabulary allows webmasters to explicitly define image properties, creator information, usage rights, and licensing details, enabling search engines to display rich results with prominent badges in Google Images. Research shows that image search CTR is 6.7% higher when images are accompanied by structured metadata and alt descriptions, directly demonstrating the value of comprehensive metadata optimization.
| Optimization Method | Primary Purpose | Impact on SEO | Accessibility Benefit | Implementation Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alt Text | Describe image content for search engines and screen readers | High - directly influences ranking | Critical - enables screen reader interpretation | Low - simple text field |
| File Names | Provide initial context about image subject matter | Medium - light ranking signal | Low - minimal accessibility impact | Low - rename before upload |
| Image Compression | Reduce file size and improve page load speed | High - speed is ranking factor | Low - minimal accessibility impact | Medium - requires tools |
| Structured Data | Enable rich results and enhanced search features | High - increases visibility and CTR | Low - primarily for search engines | High - requires markup knowledge |
| Responsive Images | Deliver appropriate sizes for different devices | High - improves mobile performance | Medium - supports better UX | Medium - requires HTML attributes |
| Image Sitemaps | Help search engines discover images | Medium - improves crawlability | Low - minimal accessibility impact | Low - plugin-based solutions available |
| Lazy Loading | Improve initial page load performance | High - speed is ranking factor | Low - minimal accessibility impact | Low - native browser support |
| Captions | Provide visible context and keyword relevance | Medium - supports topical relevance | Medium - improves content clarity | Low - simple text addition |
Search engines employ sophisticated computer vision algorithms to analyze images beyond their metadata. Google Images uses advanced machine learning to identify objects, text, faces, and visual patterns within images, enabling ranking based on visual similarity and relevance. The ranking process considers multiple factors including keyword relevance (from file names, alt text, and surrounding content), website authority and trustworthiness, image quality and resolution, user engagement signals (clicks, time spent), and contextual relevance (how well the image relates to page content). Google’s computer vision can read embedded text within images, extract visual elements, and understand complex scenes, making image quality and clarity important ranking factors. The surrounding page content significantly influences how images are indexed and ranked; images placed near relevant text and on topically aligned pages receive better ranking signals. Mobile-first indexing means Google prioritizes how images appear and perform on mobile devices, making responsive image implementation essential. Additionally, SafeSearch filtering affects image visibility, with images flagged as explicit potentially excluded from results, making content appropriateness a consideration for visibility.
Image optimization directly impacts overall website performance metrics that search engines use for ranking. Page load speed is significantly influenced by image file sizes and delivery efficiency; unoptimized images are often the largest contributor to slow page loads. Core Web Vitals, Google’s key performance metrics, include Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), which measures when the largest image or text block becomes visible—directly affected by image optimization. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) can be negatively impacted by images without defined dimensions, causing layout instability as images load. First Input Delay (FID) and Interaction to Next Paint (INP) are influenced by overall page performance, which image optimization improves. Mobile performance is particularly critical, as 58.67% of all website traffic originates from mobile devices, and mobile users are especially sensitive to slow-loading images. Implementing responsive images, compression, and lazy loading creates a synergistic effect that improves all performance metrics simultaneously. Websites that prioritize image optimization typically see improvements in bounce rates, time on page, and conversion rates—all positive signals to search engines that contribute to better rankings.
Different platforms and search engines have unique requirements for image optimization. Google Images prioritizes descriptive metadata, structured data, and page relevance, with Google Lens adding visual recognition capabilities that reward high-quality, clear images. Bing Images uses similar optimization principles but may weight certain factors differently, making comprehensive optimization beneficial across platforms. Pinterest functions as both a social platform and visual search engine, requiring optimized pins with descriptive titles and descriptions. E-commerce platforms like Shopify and WooCommerce have specific image optimization requirements for product pages, where all images should have alt text and structured product schema. Social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram use Open Graph meta tags to control how images appear when content is shared, requiring specific image dimensions (typically 1200 x 630 pixels for Facebook). AI-powered search platforms like Perplexity and ChatGPT increasingly incorporate images in responses, making image optimization relevant for AI search visibility. Understanding these platform-specific requirements ensures images are optimized for maximum discoverability across the entire digital ecosystem.
Effective Image SEO requires a systematic approach combining multiple optimization techniques. Start by choosing appropriate image formats based on content type: JPEG for photographs, PNG for graphics with transparency, WebP for modern browsers seeking superior compression. Compress images using tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or ShortPixel to achieve optimal file sizes without quality loss. Implement responsive images using srcset and sizes attributes to serve device-appropriate versions. Write descriptive alt text (under 125 characters) that accurately describes image content and naturally incorporates relevant keywords. Use descriptive file names with hyphens separating keywords, avoiding generic names like image1.jpg. Create informative captions that provide visible context and support topical relevance. Implement structured data markup using schema.org vocabulary to enable rich results. Enable lazy loading to improve initial page load performance. Create image sitemaps to help search engines discover images not easily found through standard crawling. Use Open Graph meta tags to control image appearance on social platforms. Monitor image performance using Google Search Console, PageSpeed Insights, and Google Lighthouse to identify optimization opportunities.
blue-mountain-landscape-photography.jpg)srcset and sizes attributes for device-appropriate deliveryImage SEO continues to evolve as search technology advances and user behavior shifts toward visual discovery. Visual search through Google Lens and similar platforms is growing exponentially, with 100+ billion annual searches indicating this trend will continue accelerating. AI-powered image recognition is becoming increasingly sophisticated, enabling search engines to understand complex scenes, extract text, identify objects, and even recognize emotions or intentions within images. Multimodal AI systems that process both text and images simultaneously are changing how search engines rank and present visual content, making image optimization increasingly important for AI search visibility. E-commerce visual search is expanding, with 20% of Google Lens searches being shopping-related, creating new opportunities for product image optimization. Augmented Reality (AR) integration with image search may soon allow users to visualize products in their environment, requiring new optimization approaches. Video thumbnails and featured snippets increasingly incorporate images, expanding the scope of image optimization beyond traditional image search. Privacy-focused image optimization will become more important as data collection practices evolve. The integration of image SEO with AI monitoring platforms like AmICited represents the future of tracking visual content visibility across AI-powered search systems, ensuring brands maintain visibility as search paradigms shift toward multimodal and visual-first discovery methods.
Image SEO is critical because approximately 10.1% of Google traffic goes to Google Images, and over 35% of users now use image search regularly. Optimized images improve page load speed, which is a key ranking factor, and they enhance user experience by making content more visually appealing and accessible. Additionally, images with proper alt text and structured data have 6.7% higher click-through rates in search results, directly contributing to increased organic traffic and better search engine rankings.
Alt text (alternative text) is essential for both SEO and accessibility, as it describes what an image contains for screen readers and search engines. Title attributes, on the other hand, are optional and primarily display as tooltips when users hover over an image. Google prioritizes alt text for understanding image context and ranking, while title attributes are less critical for SEO. For best practices, always include descriptive alt text but use title attributes sparingly and only when they add meaningful value.
Image compression directly impacts SEO by reducing file sizes, which speeds up page load times—a critical ranking factor for search engines. Compressed images improve user experience, reduce bounce rates, and enhance mobile performance, where 58.67% of all website traffic originates. Tools like TinyPNG and ImageOptim can compress images to 100 KB or less without sacrificing quality. Faster-loading pages signal better technical health to search engines and lead to improved rankings in both regular search results and image search.
Structured data (schema markup) helps search engines better understand and categorize images by providing explicit metadata about image content, creator, usage rights, and context. When properly implemented, structured data enables images to appear in rich results and image packs within Google Images, with prominent badges that increase visibility and click-through rates. Google's Rich Results Test can validate your structured data implementation, ensuring your images are eligible for enhanced search features that drive more targeted traffic.
Google Images uses advanced algorithms, computer vision, and contextual metadata to index and rank billions of images. The ranking process considers factors like keyword relevance, website authority, image quality, alt text, file names, surrounding page content, and user engagement signals. Google's computer vision analyzes visual elements including patterns, colors, and shapes, while also reading text within images. Images from authoritative, trustworthy websites with high-quality visuals and proper optimization typically rank higher in Google Images results.
Visual search through Google Lens has grown 65% year-over-year, with over 100 billion visual searches conducted annually and nearly 20 billion monthly Lens searches. This growth means Image SEO now extends beyond traditional keyword-based image search to include visual recognition and object detection. Optimizing images with clear, high-quality visuals and proper metadata ensures they're discoverable through both text-based and visual search methods, capturing traffic from users who search using photos rather than keywords.
Responsive images should use the srcset and sizes attributes in HTML img tags to deliver appropriately sized images for different screen sizes and resolutions. This approach reduces load times, prevents layout shifts, and signals mobile-friendliness to search engines. The picture element can also be used for more advanced responsive image scenarios. Proper responsive image implementation ensures consistent quality across devices, improves Core Web Vitals scores, and supports Google's mobile-first indexing, all of which contribute to better SEO performance.
AI-generated images are not inherently bad for SEO; their impact depends on relevance, quality, and how they're used. If AI-generated images are high-quality, contextually appropriate, and improve user experience, they can support your SEO efforts. However, using AI images where authenticity and originality matter—such as product photography or testimonial images—may harm credibility and user trust. The key is strategic implementation: use AI images where they add genuine value, maintain proper optimization practices, and ensure they align with your content's purpose and audience expectations.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Content SEO is the strategic creation and optimization of high-quality content to improve search engine rankings and organic visibility. Learn how to optimize c...

Enterprise SEO is the practice of optimizing large, complex websites with thousands of pages for search engines. Learn strategies, challenges, and best practice...

Learn what Video SEO is and how to optimize video content for search engines. Discover best practices for ranking videos on Google, YouTube, and AI Overviews.