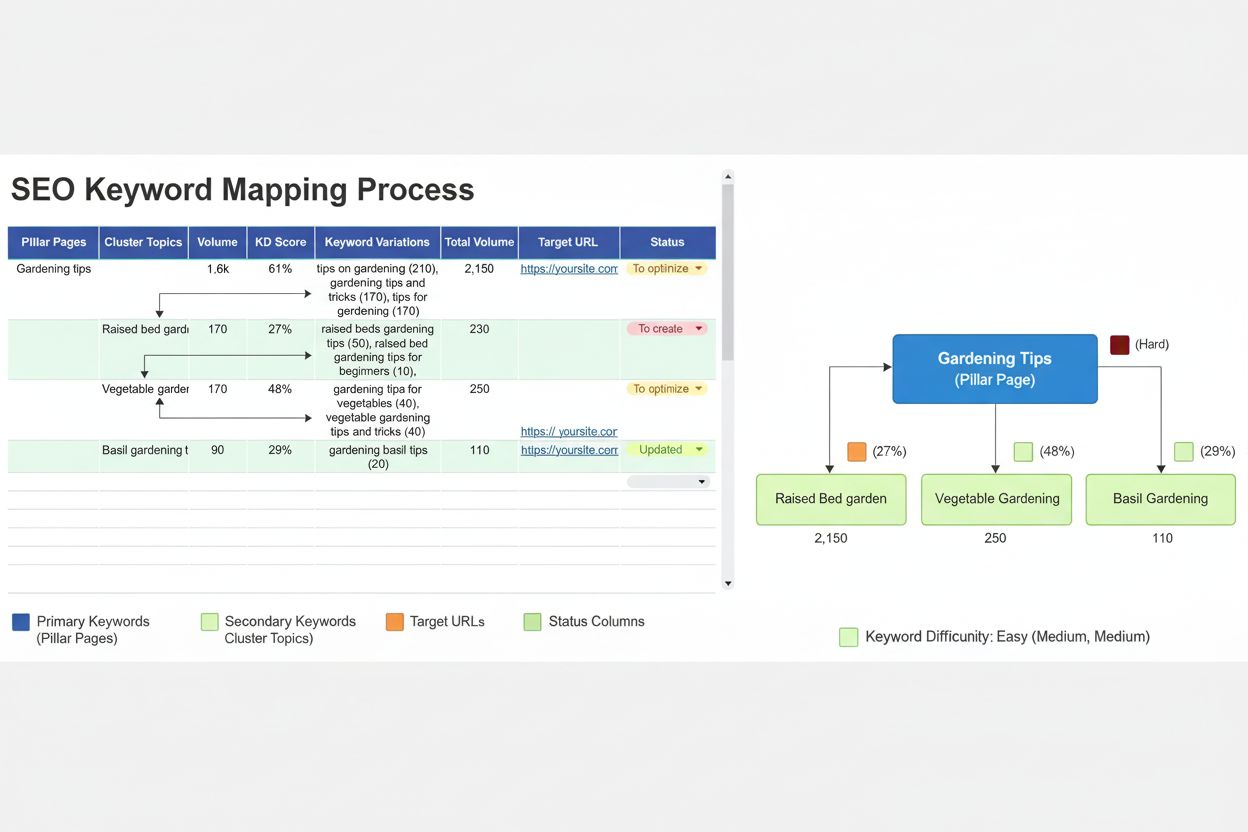
Keyword Mapping
Learn keyword mapping: the process of assigning target keywords to website pages. Discover how to prevent cannibalization, optimize site structure, and improve ...
Keyword clustering is the process of grouping related keywords together based on semantic similarity and search intent, allowing SEO professionals to target multiple related terms on a single webpage. This strategic approach improves content relevance, enhances search engine visibility, and simplifies keyword management by organizing large keyword lists into manageable, topic-focused groups.
Keyword clustering is the process of grouping related keywords together based on semantic similarity and search intent, allowing SEO professionals to target multiple related terms on a single webpage. This strategic approach improves content relevance, enhances search engine visibility, and simplifies keyword management by organizing large keyword lists into manageable, topic-focused groups.
Keyword clustering is the strategic practice of grouping related keywords together based on their semantic similarity, search intent, and relevance to create more effective SEO strategies. Rather than optimizing individual webpages for single keywords, keyword clustering allows SEO professionals to target multiple related search terms on a single page, significantly improving content relevance and search engine visibility. This approach recognizes that users often search for the same concept using different terminology—for example, “running shoes,” “jogging sneakers,” and “athletic footwear” all represent similar user intent and should be targeted together. By organizing keywords into meaningful clusters, businesses can create more comprehensive content that addresses user needs more thoroughly while reducing the time and resources required for content optimization. The practice has become increasingly important in both traditional SEO and AI search engine optimization, where content relevance and topical depth directly influence how AI systems cite and recommend sources.
The concept of keyword clustering emerged as search engines evolved beyond simple keyword matching toward semantic understanding. In 2013, Google’s Hummingbird update marked a pivotal shift in how search algorithms processed queries, moving from individual keyword analysis to phrase-based understanding. This evolution was further accelerated by the 2015 RankBrain update, which introduced machine learning capabilities that could identify thematic relationships between keywords and understand user intent at a deeper level. Prior to these updates, SEO professionals focused on optimizing single keywords per page, often resulting in thin, repetitive content. The introduction of semantic search fundamentally changed this approach, making keyword clustering not just beneficial but essential for competitive SEO. Today, with the rise of generative AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews, keyword clustering has become even more critical—these systems rely on comprehensive, semantically-rich content to generate authoritative responses, and clustered keyword strategies naturally produce the type of content these systems prefer to cite.
Keyword clustering operates on two primary methodological approaches, each with distinct advantages and applications. Semantic clustering uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to analyze the linguistic structure and meaning of keywords, grouping terms that share similar roots, synonyms, or conceptual relationships. This method is often cost-effective and can be implemented using free Python libraries and NLP tools. However, semantic clustering sometimes groups keywords that appear similar in meaning but actually have different search intents according to Google’s algorithm. SERP-based clustering, by contrast, analyzes actual search engine results pages to identify which keywords return similar URLs in their top results. This method aligns more closely with how search engines interpret keyword relationships, making it more reliable for SEO purposes, though it requires access to SERP data and typically involves some cost. Most modern SEO professionals recommend SERP-based clustering for production work, as it reflects real-world search engine behavior rather than theoretical linguistic similarity. The clustering process typically involves setting parameters like “strength” (the minimum number of common URLs required to group keywords) and “method” (soft clustering, which doesn’t require all keywords to share URLs, versus hard clustering, which does), allowing practitioners to fine-tune results based on their specific niche and goals.
| Aspect | Semantic Clustering | SERP-Based Clustering | Manual Clustering | Topical Clustering |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Basis | Linguistic similarity and NLP analysis | Search results similarity and URL matching | Human judgment and intent analysis | Thematic grouping of keyword clusters |
| Cost | Low to free | Moderate to high | Time-intensive labor | Varies by tool |
| Accuracy for SEO | Moderate (may miss intent nuances) | High (aligns with search engines) | High (contextual understanding) | High (comprehensive coverage) |
| Speed | Fast (automated) | Moderate (requires SERP analysis) | Slow (manual review required) | Moderate (cluster-based) |
| Best Use Case | Quick exploration, niche discovery | Production SEO, competitive analysis | Small keyword lists, specific niches | Building topical authority |
| Scalability | Excellent (handles thousands) | Excellent (handles thousands) | Poor (limited to hundreds) | Excellent (organizes clusters) |
| Tools Available | Cluster Army, Simple SEO Tool | Semrush, SE Ranking, Keyword Insights | Excel, Google Sheets | Keyword Insights, Semrush |
| Handles Intent Variation | Inconsistent | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
The practical implementation of keyword clustering follows a structured workflow that begins with comprehensive keyword research. SEO professionals start by compiling an extensive list of keywords relevant to their niche using tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, SE Ranking, or Keyword Insights. This initial list should be as broad as possible, capturing variations in length, specificity, and intent without applying restrictive filters. Once the keyword list is compiled, practitioners upload these keywords into a clustering tool, which analyzes either semantic relationships or SERP similarities depending on the chosen method. The tool then generates clusters, typically named after the keyword with the highest search volume in each group. Each cluster represents a group of keywords that should be targeted together on a single webpage. The clustering process typically takes anywhere from a few minutes to several hours depending on the number of keywords and the complexity of the analysis. After clustering is complete, SEO professionals review the results, validate that keywords within each cluster truly share the same search intent, and may manually adjust clusters to better reflect their specific business goals. This combination of automated clustering with manual validation ensures both efficiency and accuracy, leveraging machine learning while maintaining human expertise and contextual understanding.
Keyword clustering fundamentally transforms how organizations approach content planning and website architecture. Rather than creating individual pages for each keyword, keyword clustering enables the development of comprehensive content pieces that naturally incorporate multiple related keywords while maintaining readability and user value. This approach directly impacts website structure—each keyword cluster typically becomes a single webpage, and related clusters can be grouped into broader topic areas that form the foundation of site navigation and internal linking strategies. According to research from leading SEO platforms, websites implementing keyword clustering strategies see significant improvements in organic traffic; one documented case study showed a 1,250% increase in organic traffic over six months by focusing content creation on keyword clusters rather than individual keywords. The clustering approach also improves internal linking opportunities, as related cluster pages can naturally link to each other, distributing page authority and helping search engines understand content relationships. Furthermore, this structure creates what’s known as topical authority—when a website comprehensively covers a topic through interconnected, cluster-based content, search engines recognize it as an authoritative resource and reward it with higher rankings across all related queries. This is particularly important for AI search engine optimization, where systems like ChatGPT and Perplexity analyze content depth and comprehensiveness when deciding which sources to cite.
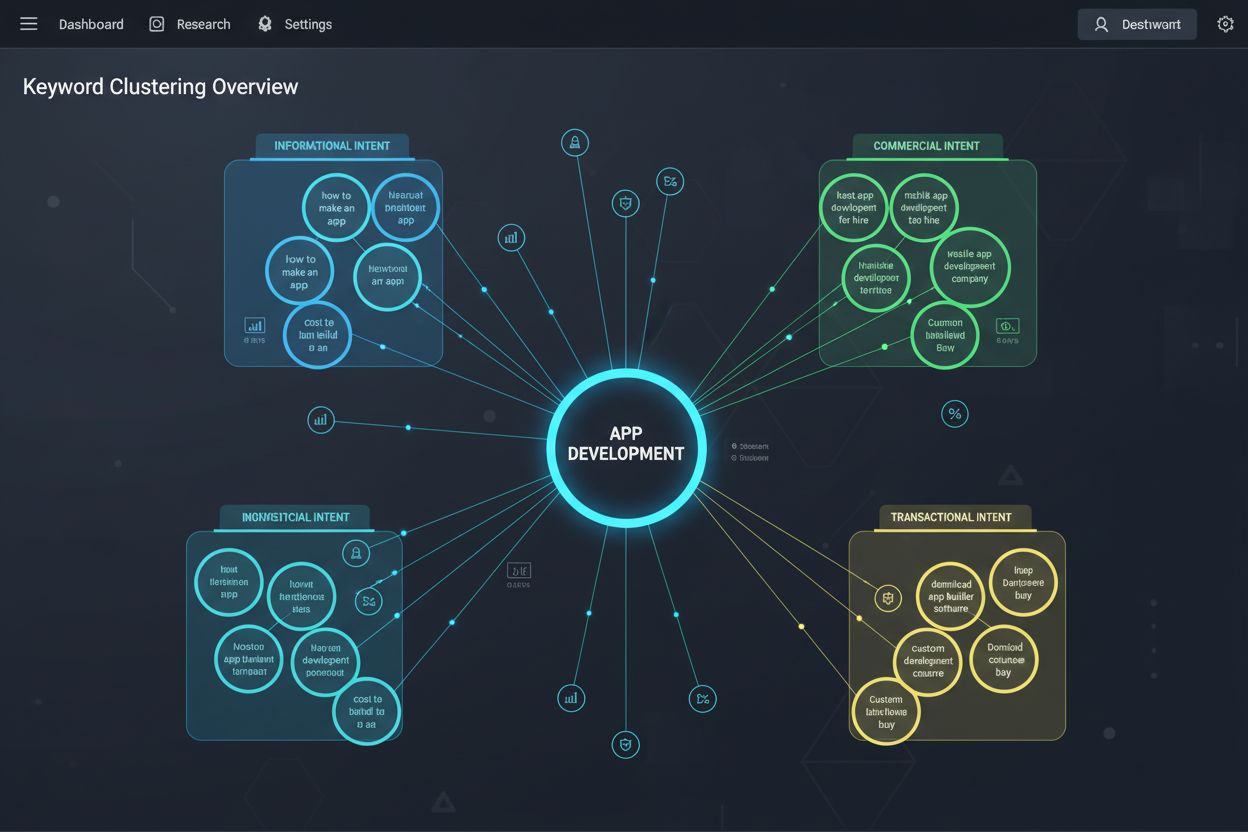
Understanding and aligning with search intent is central to effective keyword clustering. Search intent refers to what a user is trying to accomplish with their search query, and it typically falls into four categories: informational (seeking knowledge), navigational (looking for a specific website), commercial (researching before purchase), and transactional (ready to complete an action like buying). Effective keyword clustering groups keywords that share the same primary search intent, ensuring that the content created for each cluster directly addresses what searchers are looking for. For example, keywords like “best running shoes,” “top-rated athletic footwear,” and “highest-rated jogging sneakers” all share commercial intent and should be clustered together, while “how to choose running shoes” and “running shoe buying guide” share informational intent and might form a separate cluster. This intent-based organization is crucial because it prevents keyword cannibalization—the problematic situation where multiple pages on the same website compete for the same keywords, diluting ranking potential. By ensuring each cluster targets a unique combination of intent and topic, organizations can maximize their ranking potential across their entire keyword portfolio. Additionally, intent-aligned clustering naturally produces content that better satisfies user needs, improving metrics like click-through rate, time on page, and conversion rate, which are increasingly important ranking factors.
Beyond basic keyword organization, keyword clustering has evolved into a sophisticated strategic tool with multiple advanced applications. One emerging use case involves using keyword clustering to identify content fragmentation opportunities—analyzing high-ranking competitor content and breaking it down into more focused, cluster-based articles that target specific aspects of broader topics. This approach allows organizations to create more targeted content that captures long-tail variations while maintaining topical coherence. Another advanced application combines keyword clustering with alternative data sources; for example, extracting questions from Reddit, forums, and user-generated content platforms, then clustering these questions to identify content gaps that competitors aren’t addressing. This approach has proven particularly effective for discovering niche keyword opportunities with lower competition but genuine user demand. Additionally, keyword clustering is increasingly being used in conjunction with AI content generation tools, where clusters are automatically converted into content briefs and outlines that maintain semantic consistency and topical depth. The integration of keyword clustering with AI visibility monitoring represents another frontier—organizations now track not just traditional search rankings but also how their clustered content appears in AI-generated responses, using tools specifically designed to monitor brand and domain mentions across generative AI platforms. This evolution reflects the fundamental shift in search behavior, where AI systems are becoming increasingly important channels for content discovery and citation.
The future of keyword clustering is being shaped by several converging trends in search technology and user behavior. As generative AI search engines continue to mature and capture increasing market share, the importance of keyword clustering will only grow—these systems rely on comprehensive, semantically-rich content to generate authoritative responses, and clustering strategies naturally produce exactly this type of content. We can expect to see more sophisticated clustering algorithms that incorporate additional signals beyond SERP similarity and semantic meaning, such as user engagement metrics, conversion data, and brand authority signals. The integration of Natural Language Processing and machine learning into clustering tools will become more advanced, potentially allowing for dynamic clustering that adapts based on real-time search behavior changes. Additionally, as competition intensifies across niches, keyword clustering will become essential not just for ranking but for establishing and maintaining topical authority—organizations that comprehensively cover topics through well-organized, cluster-based content will increasingly dominate search results and AI citations. The rise of AI monitoring platforms like AmICited reflects this shift, as organizations recognize that tracking visibility across both traditional search and AI systems requires understanding how their clustered content performs in different contexts. Looking forward, keyword clustering will likely become even more integrated with content creation workflows, with AI-assisted tools automatically suggesting cluster-based content structures and optimizations. The practice will also become more sophisticated in handling search intent nuance, as algorithms improve at understanding subtle differences in user intent that may require separate content despite semantic similarity. Ultimately, keyword clustering represents a fundamental shift from keyword-centric to topic-centric SEO, aligning optimization strategies with how modern search systems—both traditional and AI-powered—actually understand and rank content.
Keyword clustering groups individual keywords with similar meanings and search intent that can be targeted on a single page, while topic clustering (also called topical clustering) groups multiple keyword clusters together thematically around a central pillar page. Topic clustering creates a broader content structure with interconnected pages, whereas keyword clustering focuses on organizing keywords for individual page optimization. Both work together to create comprehensive content strategies that establish topical authority.
Keyword clustering helps content appear in AI search systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews by creating comprehensive, semantically-rich content that covers multiple related queries. When you cluster keywords by search intent, your content becomes more thorough and contextually relevant, making it more likely to be cited as an authoritative source by AI systems. This approach aligns with how AI models understand topical relationships and user intent, improving your domain's visibility across generative search platforms.
The two primary methods are semantic clustering (using Natural Language Processing to group keywords by meaning and linguistic similarity) and SERP-based clustering (grouping keywords that return similar search results). Semantic clustering is often cheaper but may miss nuanced differences in search intent, while SERP-based clustering aligns with how search engines actually interpret keywords but requires SERP data analysis. Most SEO professionals recommend SERP-based clustering for better alignment with search engine behavior.
The number of keywords in a cluster varies based on semantic relevance and search intent, but typically ranges from 3 to 20+ keywords per cluster. A well-organized cluster should contain keywords that share the same primary search intent and would naturally fit on a single optimized webpage. Larger clusters may indicate the need for multiple pages targeting different aspects of the topic, while very small clusters might be combined with related groups to create more comprehensive content.
Yes, keyword clustering is one of the most effective strategies for identifying and preventing content cannibalization. By grouping keywords by search intent and SERP similarity, you can ensure each page targets a unique set of keywords, preventing multiple pages from competing for the same rankings. This approach helps you assign the right keywords to the right pages, consolidate overlapping content, and maximize your site's ranking potential across all target queries.
Popular keyword clustering tools include Semrush, SE Ranking, Ahrefs, Keyword Insights, Serpstat, and Clearscope. These tools use SERP-based or semantic algorithms to automatically group keywords, saving significant time compared to manual clustering. Many offer advanced features like search intent detection, ranking data integration, and content optimization recommendations. The best tool depends on your budget, niche complexity, and specific SEO goals.
Keyword clustering is foundational to building topical authority because it helps you systematically cover all aspects of a topic through interconnected content. By organizing keywords into clusters and then grouping clusters into topic areas, you create a comprehensive content framework that demonstrates deep expertise to search engines. This structured approach signals to Google and AI systems that your site is an authoritative resource on specific topics, leading to better rankings and increased visibility.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn keyword mapping: the process of assigning target keywords to website pages. Discover how to prevent cannibalization, optimize site structure, and improve ...

Learn what keyword stuffing is and how AI systems like ChatGPT and Perplexity detect it. Understand AI detection methods and why keyword stuffing fails in moder...

Learn how semantic content clustering for GEO helps your brand appear in AI-generated answers. Discover entity relationships, topical authority, and how to stru...