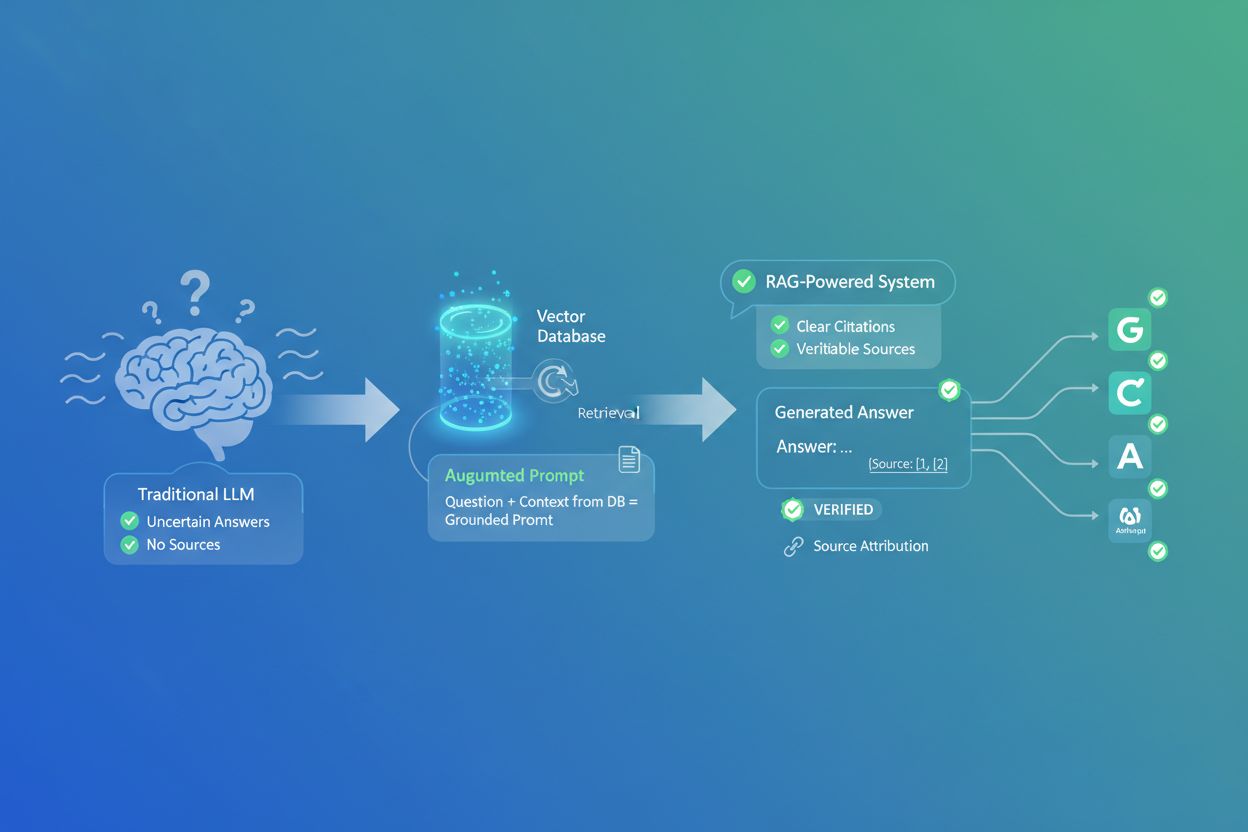
How RAG Changes AI Citations
Discover how Retrieval-Augmented Generation transforms AI citations, enabling accurate source attribution and grounded answers across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and G...

A Large Language Model (LLM) is a deep learning model trained on vast amounts of text data using transformer neural network architecture to understand and generate human-like language. LLMs contain billions of parameters and can perform multiple language tasks including text generation, translation, question answering, and content summarization without task-specific training.
A Large Language Model (LLM) is a deep learning model trained on vast amounts of text data using transformer neural network architecture to understand and generate human-like language. LLMs contain billions of parameters and can perform multiple language tasks including text generation, translation, question answering, and content summarization without task-specific training.
| Aspect | Large Language Models (LLMs) | Traditional Machine Learning | Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) | Fine-Tuned Models |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Data | Billions of tokens from diverse text sources | Structured, task-specific datasets | LLM + external knowledge bases | Domain-specific curated datasets |
| Parameters | Hundreds of billions (GPT-4, Claude 3) | Millions to billions | Same as base LLM | Adjusted from base LLM |
| Task Flexibility | Multiple tasks without retraining | Single task per model | Multiple tasks with context | Specialized domain tasks |
| Training Time | Weeks to months on specialized hardware | Days to weeks | Minimal (uses pre-trained LLM) | Hours to days |
| Real-Time Data Access | Limited to training data cutoff | Can access live data | Yes, through retrieval systems | Limited to training data |
| Hallucination Risk | High (61% concern rate per Telus) | Low (deterministic outputs) | Reduced (grounded in retrieved data) | Moderate (depends on training data) |
| Enterprise Adoption | 76% prefer open-source LLMs | Mature, established | 70% of enterprises using GenAI | Growing for specialized use cases |
| Cost | High inference costs at scale | Lower operational costs | Moderate (LLM + retrieval overhead) | Lower than base LLM inference |
A Large Language Model (LLM) is a sophisticated artificial intelligence system built on deep learning architecture that has been trained on vast amounts of text data to understand and generate human-like language. LLMs represent a fundamental breakthrough in natural language processing, enabling machines to comprehend context, nuance, and semantic meaning across diverse linguistic tasks. These models contain hundreds of billions of parameters—adjustable weights and biases within neural networks—that allow them to capture complex patterns in language and produce coherent, contextually appropriate responses. Unlike traditional machine learning models designed for specific tasks, LLMs demonstrate remarkable versatility, performing multiple language functions including text generation, translation, summarization, question answering, and code development without requiring task-specific retraining. The emergence of LLMs like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini has fundamentally transformed how organizations approach artificial intelligence, moving from narrow, specialized AI systems to general-purpose language understanding and generation capabilities.
The transformer architecture represents the technological foundation enabling modern LLMs to achieve unprecedented scale and capability. Introduced in 2017, transformers revolutionized natural language processing by replacing sequential processing with parallel processing through self-attention mechanisms. Unlike earlier recurrent neural networks (RNNs) that processed text word-by-word sequentially, transformers process entire sequences simultaneously, enabling efficient training on massive datasets using graphics processing units (GPUs). The transformer architecture consists of encoder and decoder components with multiple layers of multi-head attention, allowing the model to simultaneously focus on different parts of the input text and understand relationships between distant words. This parallel processing capability is crucial—AWS research indicates that transformer architecture enables models with hundreds of billions of parameters, making it possible to train on datasets comprising billions of web pages and documents. The self-attention mechanism allows each token (word or subword) to attend to all other tokens in the sequence, enabling the model to capture long-range dependencies and contextual relationships essential for understanding complex language. This architectural innovation directly enabled the explosion in LLM capabilities, as organizations could now train increasingly large models on increasingly diverse datasets, resulting in models that demonstrate emergent abilities in reasoning, creativity, and knowledge synthesis.
Training an LLM involves a sophisticated multi-stage process that begins with massive data collection and preprocessing. Organizations typically source training data from diverse internet sources, including Common Crawl (comprising over 50 billion web pages), Wikipedia (approximately 57 million pages), and specialized domain-specific corpora. The training process uses self-supervised learning, where the model learns to predict the next token in a sequence without explicit human labeling. During training, the model iteratively adjusts billions of parameters to maximize the likelihood of correctly predicting subsequent tokens in training examples. This process requires enormous computational resources—training state-of-the-art LLMs can cost millions of dollars and consume weeks of GPU cluster time. After initial pretraining, organizations often apply instruction tuning, where models are fine-tuned on curated datasets of high-quality examples showing desired behavior. This is followed by reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), where human raters evaluate model outputs and provide feedback that guides further optimization. The quality of training data directly impacts model performance—Databricks research shows that 76% of enterprises using LLMs choose open-source models, often because they can customize training data for their specific domains. Organizations increasingly recognize that data quality, diversity, and relevance are as important as model size, leading to significant investment in data curation and preprocessing infrastructure.
LLMs have enabled transformative applications across virtually every industry, with adoption patterns revealing sector-specific priorities and strategic advantages. In Financial Services, LLMs power fraud detection systems, algorithmic trading analysis, wealth management recommendations, and customer service automation. The sector leads GPU adoption with 88% growth in six months, reflecting aggressive investment in real-time LLM inference for time-sensitive applications. Healthcare & Life Sciences uses LLMs for drug discovery acceleration, clinical research analysis, medical record processing, and patient communication. The industry demonstrates the highest concentration of natural language processing usage at 69% of specialized Python libraries, reflecting LLMs’ critical role in extracting insights from unstructured medical data. Manufacturing & Automotive employs LLMs for supply chain optimization, quality control analysis, customer feedback processing, and predictive maintenance. The sector recorded 148% year-over-year NLP growth, the highest among all industries analyzed. Retail & E-commerce uses LLMs for personalized product recommendations, customer service chatbots, content generation, and market analysis. Public Sector & Education applies LLMs to citizen feedback analysis, document processing, emergency response planning, and educational content generation. This industry-specific adoption demonstrates that LLMs’ value extends far beyond content generation—they’re becoming essential infrastructure for data analysis, decision-making, and operational efficiency across the enterprise.
The trajectory of LLM adoption in enterprise environments reveals a decisive shift from experimentation to production deployment. Databricks’ comprehensive analysis of over 10,000 global organizations, including 300+ Fortune 500 companies, shows that enterprises registered 1,018% more models in 2024 compared to 2023, indicating explosive growth in AI model development. More significantly, organizations put 11 times more AI models into production compared to the previous year, demonstrating that LLMs have moved beyond pilot projects to become core business infrastructure. The efficiency of deployment has improved dramatically—the ratio of experimental-to-production models improved from 16:1 to 5:1, representing a 3x efficiency gain. This improvement indicates that organizations have developed mature operational capabilities, governance frameworks, and deployment pipelines enabling rapid, reliable LLM deployment. Highly regulated industries lead adoption, contrary to expectations that compliance requirements would slow AI implementation. Financial Services demonstrates the strongest commitment with the highest average GPU usage per company and 88% growth in GPU utilization over six months. Healthcare & Life Sciences emerged as a surprise early adopter, with 69% of Python library usage devoted to natural language processing. This pattern suggests that robust governance frameworks actually enable rather than constrain innovation, providing the foundation for responsible, scalable AI deployment. The shift to production deployment is accompanied by increasing sophistication in model selection—77% of organizations prefer smaller models with 13 billion parameters or fewer, prioritizing cost efficiency and latency over raw model size.
A significant trend reshaping enterprise AI strategy is the overwhelming preference for open-source LLMs, with 76% of organizations using LLMs choosing open-source options, often running them alongside proprietary alternatives. This shift reflects fundamental changes in how enterprises approach AI infrastructure and strategy. Open-source models like Meta Llama, Mistral, and others offer several strategic advantages: organizations can customize models for specific use cases, maintain data sovereignty by running models on-premises, avoid vendor lock-in, and reduce inference costs compared to API-based proprietary models. The rapid adoption of new open-source models demonstrates enterprise sophistication—Meta Llama 3 launched on April 18, 2024, and within four weeks accounted for 39% of all open-source LLM usage, showing that organizations actively monitor AI research and quickly integrate improvements. This fluidity contrasts sharply with proprietary models, where organizations face higher switching costs and longer evaluation cycles. The preference for smaller models is particularly pronounced—77% of organizations choose models with 13 billion parameters or fewer, prioritizing the cost-performance tradeoff. This pattern reflects mature enterprise decision-making focused on operational efficiency rather than raw capability. However, proprietary models like GPT-4 and Claude 3 remain important for specialized applications requiring maximum capability, suggesting a hybrid approach where organizations maintain flexibility to choose the right tool for each use case.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as the dominant enterprise pattern for customizing LLMs with proprietary data while addressing fundamental limitations of standalone models. 70% of companies leveraging generative AI are using RAG systems, representing a fundamental shift in how organizations deploy LLMs. RAG works by retrieving relevant documents and data from enterprise knowledge bases to provide context for LLM queries, resulting in responses grounded in organizational data rather than relying solely on training data. This approach directly addresses the hallucination problem—a Telus survey found that 61% of people worry about false information from LLMs, and RAG significantly reduces hallucinations by constraining model outputs to retrieved, verifiable information. The infrastructure supporting RAG has experienced explosive growth—vector databases grew 377% year-over-year, the fastest growth among all LLM-related technologies. Vector databases store numerical representations of documents and data, enabling fast similarity searches essential for RAG. This growth reflects organizations’ recognition that RAG provides a practical path to production LLM applications without the cost and complexity of fine-tuning or pretraining custom models. RAG also enables organizations to maintain data governance, incorporate real-time information, and update knowledge bases without retraining models. The pattern is becoming standard across industries: organizations embed their documents as vectors, store them in specialized databases, then retrieve relevant context when users query the LLM, creating a hybrid system that combines LLM capabilities with organizational knowledge.
Despite remarkable capabilities, LLMs face significant limitations that constrain their reliability and applicability in mission-critical applications. Hallucination—where LLMs generate false, nonsensical, or contradictory information—represents the most visible limitation. Research shows that ChatGPT has a contradiction rate of 14.3%, and hallucinations can have serious real-world consequences. A notable example involved ChatGPT incorrectly summarizing a legal case and falsely accusing a radio host of fraud, resulting in a lawsuit against OpenAI. Hallucinations arise from multiple sources: training data quality issues, model limitations in understanding context, constrained context windows that limit how much text the model can process simultaneously, and difficulty with nuanced language understanding including sarcasm and cultural references. LLMs are constrained by maximum context windows, meaning they can only consider a certain number of tokens simultaneously—this limitation causes misunderstandings in longer conversations or documents. Additionally, LLMs struggle with multi-step reasoning, cannot access real-time information without external integration, and can exhibit bias from training data. These limitations have driven significant investment in mitigation strategies including prompt engineering, fine-tuning, retrieval-augmented generation, and continuous monitoring. Organizations implementing LLMs in production must invest in governance frameworks, quality assurance processes, and human oversight to ensure outputs meet reliability standards. The challenge of hallucination has become a critical focus area—Nexla research identifies multiple hallucination types including factual inaccuracies, nonsensical responses, and contradictions, each requiring different mitigation approaches.
The LLM landscape continues evolving rapidly, with several trends shaping the future of enterprise AI. Multimodal LLMs that process text, images, audio, and video simultaneously are emerging, expanding LLM applications beyond text-only tasks. Agentic AI systems that can perceive environments, make decisions, and take autonomous actions are moving from research to production deployment, with serverless model serving adoption growing 131% in Financial Services and 132% in Healthcare, enabling real-time AI decision-making. The global LLM market reached $7.77 billion in 2025 and is expected to exceed $123 billion by 2034, reflecting sustained enterprise investment. Smaller, more efficient models are gaining adoption as organizations optimize for cost and latency—the preference for 13B parameter models over larger alternatives demonstrates this trend. Specialized domain models fine-tuned for specific industries and use cases are proliferating, as organizations recognize that general-purpose models often underperform compared to domain-optimized alternatives. The gap between AI leaders and laggards is widening—organizations that invested early in data infrastructure, governance frameworks, and LLM capabilities are realizing compound returns as each new model and technique builds on their foundation. Highly regulated industries will continue leading adoption, as their governance-first approach provides a model for responsible AI scaling. The future of LLMs will likely involve increasingly sophisticated integration with enterprise systems, real-time data access through RAG and vector databases, and autonomous decision-making through agentic systems, fundamentally transforming how organizations operate and compete.
The rise of LLMs as primary information sources has created new imperatives for brand management and domain monitoring. Platforms like AmICited track how LLMs reference brands, domains, and URLs in their responses, recognizing that AI systems increasingly mediate how information reaches users. As ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude become primary search and information discovery tools, monitoring LLM outputs becomes critical for understanding brand perception and ensuring accurate representation. Organizations must now consider not just traditional search engine optimization but LLM optimization—ensuring their content is accurately cited and represented when LLMs generate responses. This represents a fundamental shift in digital strategy, as LLMs can synthesize information from multiple sources and present it in novel ways, potentially altering how brands are perceived and positioned. Monitoring LLM mentions reveals how AI systems interpret expertise, niche positioning, and organizational authority. The ability to track and analyze LLM citations enables organizations to identify gaps in representation, correct inaccuracies, and optimize their content strategy for AI-driven discovery. As enterprises increasingly rely on AI systems for information synthesis and decision-making, the importance of LLM monitoring will only grow, making it an essential component of modern digital strategy and brand management.
LLMs differ fundamentally from traditional machine learning models in scale, architecture, and capability. While traditional models are trained on structured data for specific tasks, LLMs are trained on massive unstructured text datasets using transformer architecture with billions of parameters. LLMs can perform multiple tasks without retraining through few-shot or zero-shot learning, whereas traditional models require task-specific training. According to Databricks research, organizations are deploying 11x more AI models in production, with LLMs representing the fastest-growing category due to their versatility and generalization capabilities.
LLMs generate text through a process called autoregressive generation, where the model predicts the next token (word or subword) based on previous tokens in a sequence. Parameters are the weights and biases in the neural network that the model learns during training. A single LLM can contain hundreds of billions of parameters—GPT-3 has 175 billion parameters, while Claude 3 has over 300 billion. These parameters enable the model to capture complex patterns in language and generate contextually appropriate responses. The more parameters a model has, the more nuanced language patterns it can learn, though larger models require more computational resources.
LLMs face several critical limitations including hallucination (generating false or nonsensical information), limited context windows that constrain how much text they can process simultaneously, and difficulty understanding nuanced language like sarcasm or cultural references. A Telus survey found that 61% of people worry about false information from LLMs. Additionally, LLMs can exhibit bias from training data, struggle with reasoning tasks requiring multiple steps, and cannot access real-time information without external data integration. These limitations necessitate careful implementation strategies including retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), which 70% of enterprises now use to customize LLMs with proprietary data.
Enterprises are deploying LLMs across diverse applications including customer service chatbots, content generation, code development, fraud detection, and document analysis. According to Databricks' 2024 State of AI report, 76% of organizations using LLMs choose open-source models like Meta Llama and Mistral, often running them alongside proprietary alternatives. Financial Services leads GPU adoption with 88% growth in six months, while Healthcare & Life Sciences uses NLP (which grew 75% year-over-year) for drug discovery and clinical research. Manufacturing employs LLMs for supply chain optimization and quality control. The shift from experimentation to production is dramatic—organizations improved their experimental-to-production model ratio from 16:1 to 5:1, representing a 3x efficiency gain.
The transformer architecture is a neural network design that uses self-attention mechanisms to process entire sequences of text in parallel, rather than sequentially like earlier recurrent neural networks. This parallel processing enables training on massive datasets using GPUs, dramatically reducing training time. Transformers consist of encoder and decoder components with multi-head attention layers that allow the model to focus on different parts of the input simultaneously. This architecture enables LLMs to understand relationships between distant words and capture long-range dependencies in text. AWS notes that transformer architecture allows models with hundreds of billions of parameters, making it the foundation for all modern LLMs including GPT, Claude, and Llama.
Prompt engineering involves crafting specific instructions and context within prompts to guide LLM outputs without modifying the model itself, making it quick and cost-effective for immediate customization. Fine-tuning involves retraining the model on domain-specific data to adjust its parameters, requiring more computational resources and time but enabling deeper customization for specialized tasks. Organizations choose prompt engineering for rapid prototyping and general applications, while fine-tuning is preferred for domain-specific applications requiring consistent, specialized outputs. According to industry best practices, prompt engineering is ideal for zero-shot and few-shot learning scenarios, while fine-tuning becomes necessary when organizations need reliable performance on proprietary or highly specialized tasks.
LLMs are central to AI monitoring platforms like AmICited that track brand and domain mentions across AI systems including ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude. These platforms use LLMs to analyze how AI systems reference and cite brands, domains, and URLs in their responses. As enterprises increasingly rely on AI systems for information discovery, monitoring LLM outputs becomes critical for brand management, SEO strategy, and understanding how AI systems interpret and present organizational information. The global LLM market reached $7.77 billion in 2025 and is expected to exceed $123 billion by 2034, reflecting growing enterprise investment in LLM-based monitoring and analytics solutions.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Discover how Retrieval-Augmented Generation transforms AI citations, enabling accurate source attribution and grounded answers across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and G...

Understand the difference between AI training data and live search. Learn how knowledge cutoffs, RAG, and real-time retrieval impact AI visibility and content s...
Learn how to implement LLMs.txt on your website to help AI systems understand your content better. Complete step-by-step guide for all platforms including WordP...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.