
Title Tag
Learn what title tags are, why they matter for SEO and AI visibility, and how to optimize them for search engines and users. Complete guide to title tag best pr...
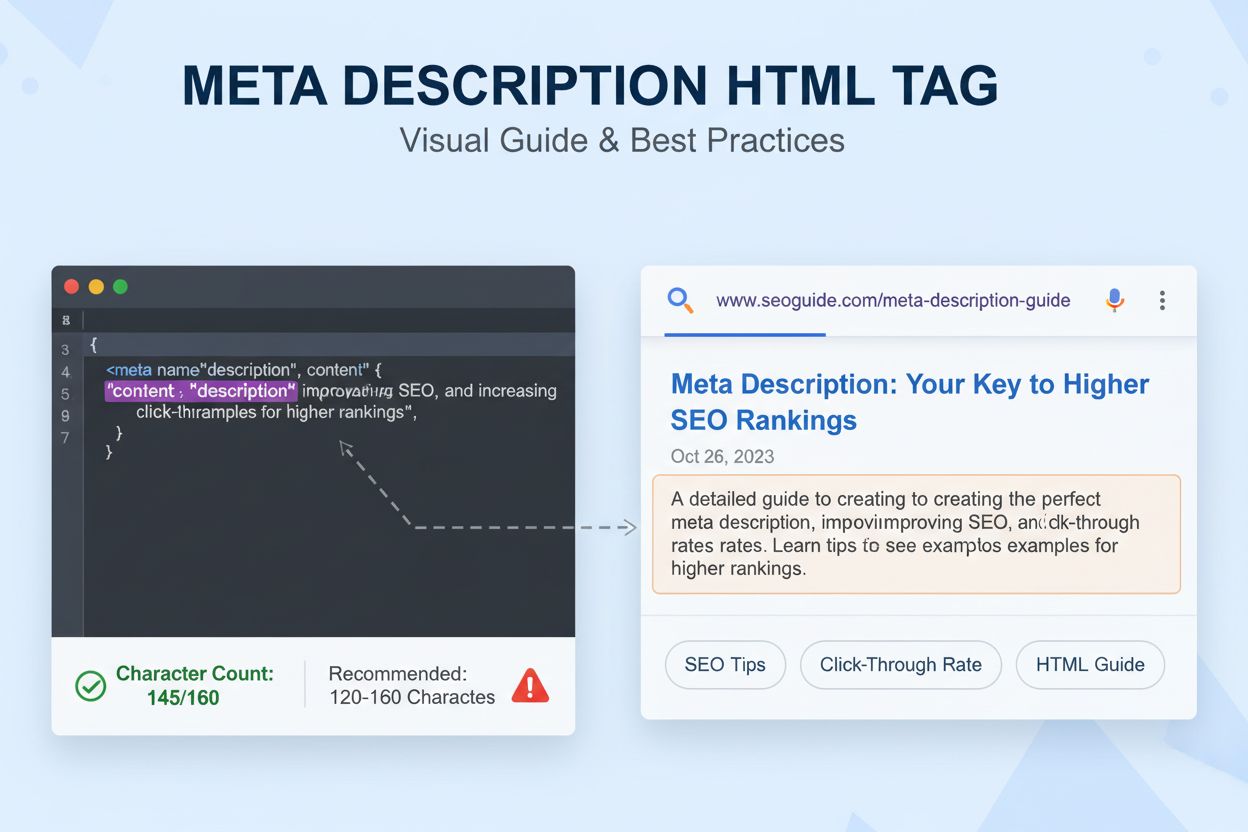
A meta description is an HTML element that summarizes a webpage’s content in 120-160 characters, displayed beneath the page title in search engine results. While not a direct ranking factor, it significantly influences click-through rates and user engagement by providing searchers with a concise preview of what to expect from the page.
A meta description is an HTML element that summarizes a webpage's content in 120-160 characters, displayed beneath the page title in search engine results. While not a direct ranking factor, it significantly influences click-through rates and user engagement by providing searchers with a concise preview of what to expect from the page.
A meta description is an HTML element that provides a concise summary of a webpage’s content, typically displayed beneath the page title and URL in search engine results. Specifically, it is implemented using the <meta name="description" content="..."> tag placed within the <head> section of an HTML document. The meta description serves as a bridge between search engines and users, offering a preview of what visitors can expect to find on the page. While Google and other search engines do not use meta descriptions as a direct ranking factor, they play a crucial role in influencing click-through rates (CTR), which indirectly affects search visibility and user engagement. The optimal length for a meta description is typically 120-160 characters on desktop and 100-120 characters on mobile, ensuring the entire message displays without truncation in search results. Understanding and optimizing meta descriptions is essential for any comprehensive SEO strategy, as they represent one of the first opportunities to convince potential visitors that your page contains the information they’re seeking.
The meta description tag has been a fundamental component of web development and SEO since the early days of search engines in the 1990s. Originally, search engines relied heavily on meta tags to understand page content, as web crawlers had limited ability to interpret page context. Over the past two decades, the importance and implementation of meta descriptions have evolved significantly. In the early 2000s, meta descriptions were often keyword-stuffed and manipulated by SEO practitioners, leading search engines to reduce their reliance on them as ranking signals. However, their value in influencing user behavior remained constant. By 2018, Google expanded the character limit for meta descriptions from approximately 155 characters to 920 pixels (roughly 230 characters), recognizing that longer, more informative descriptions could better serve users. This expansion was later adjusted based on user experience data. Today, meta descriptions are recognized as a critical on-page SEO element that directly impacts user engagement metrics and conversion rates. According to recent data, approximately 72% of websites still use meta descriptions, and studies show that pages with well-optimized descriptions experience 20-30% higher click-through rates compared to pages with generic or missing descriptions. The rise of AI-powered search platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews has further elevated the importance of meta descriptions, as these systems use them to understand content context and generate accurate citations.
The meta description is implemented as a self-closing HTML tag within the document’s <head> section. The standard syntax follows this format: <meta name="description" content="Your description here">. The tag contains two essential attributes: the name attribute, which specifies “description,” and the content attribute, which holds the actual descriptive text. Unlike some other meta tags, the meta description tag does not have a closing tag and must be placed before the closing </head> tag. For content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, Yoast SEO, or Shopify, users typically don’t need to manually edit HTML; instead, they can input the meta description through a dedicated field in the page editor or plugin interface. The character encoding of the meta description should match the page’s overall encoding (typically UTF-8), and special characters should be properly escaped to avoid rendering issues. When implementing meta descriptions programmatically on large websites with thousands of pages, developers often use dynamic variables to automatically generate descriptions based on page data, such as product names, categories, prices, or publication dates. This approach ensures consistency while maintaining uniqueness across pages. The nosnippet meta tag can be used to prevent search engines from displaying any snippet for a particular page, while the max-snippet meta tag allows webmasters to specify the maximum length of snippets displayed in search results.
| Element | Purpose | Character Limit | Display Location | Direct Ranking Impact | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meta Description | Summarizes page content for search results | 120-160 (desktop), 100-120 (mobile) | Below title in SERPs | No (indirect via CTR) | Improve CTR and user engagement |
| Meta Title (Title Tag) | Defines page title for browsers and search engines | 50-60 characters | Browser tab and SERP title | Yes (direct ranking factor) | Primary page identifier |
| H1 Heading | Main heading on the page | No limit | Top of page content | Yes (direct ranking factor) | Content structure and keyword relevance |
| Open Graph Tags | Optimizes social media sharing appearance | Varies by platform | Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter | No (social only) | Control social media previews |
| Schema Markup | Provides structured data about page content | No limit | Not visible to users | Yes (indirect via rich snippets) | Enhanced search result appearance |
| Meta Keywords | Lists page keywords (deprecated) | No limit | Not displayed | No (ignored by Google) | Historical SEO practice (obsolete) |
The meta description’s primary function is to influence whether users click on your search result, making it a critical factor in click-through rate (CTR) optimization. Research from multiple sources demonstrates that well-crafted meta descriptions can increase CTR by 20-30% compared to generic or missing descriptions. When a user searches for a query, they typically scan multiple search results, and the meta description serves as the deciding factor between clicking on your result or a competitor’s. A compelling meta description should address the user’s search intent, clearly communicate the page’s value proposition, and include a subtle call-to-action that encourages clicking. For example, a meta description that says “Learn how to optimize meta descriptions with proven strategies and best practices” is significantly more likely to generate clicks than a generic description like “This page contains information about meta descriptions.” The position in search results also affects CTR; the first result typically receives 39.8% of clicks, while the second receives 18.7%, and the third receives 10.2%. However, a well-optimized meta description can help lower-ranked pages compete more effectively by making their results more visually appealing and relevant-seeming. Mobile users are particularly sensitive to meta description quality, as mobile screens display less text, making every character count. Studies show that mobile CTR can vary by 15-25% based on meta description quality, emphasizing the importance of mobile-specific optimization.
Creating an effective meta description requires balancing multiple considerations: clarity, relevance, keyword inclusion, and persuasiveness. First, keep it concise and specific to the page content; avoid generic descriptions that could apply to multiple pages, as this dilutes their effectiveness and confuses search engines about page uniqueness. Second, include your primary keyword naturally within the first 60 characters, as this increases the likelihood that Google will bold the keyword in search results, making your listing stand out visually. Third, address user intent directly by answering the question or solving the problem that prompted the search; if users search “how to write meta descriptions,” your description should clearly indicate that your page provides actionable guidance. Fourth, incorporate a soft call-to-action using phrases like “Learn more,” “Discover,” “Find out,” or “Get started,” which gently encourages users to click without appearing overly promotional. Fifth, avoid keyword stuffing and misleading claims, as these tactics may increase initial clicks but lead to high bounce rates when users realize the content doesn’t match their expectations, ultimately harming your rankings. Sixth, make it unique for each page to maximize relevance and prevent duplicate content issues. Seventh, prioritize important pages first, such as your homepage, main category pages, and high-traffic landing pages, before optimizing less critical pages. Finally, test and refine regularly by monitoring CTR data in Google Search Console and adjusting descriptions for pages with lower-than-average click-through rates.
Different search platforms and AI systems handle meta descriptions with varying degrees of emphasis. Google Search uses meta descriptions to generate snippets when they closely match the user’s search query, though it rewrites approximately 60-70% of descriptions to improve relevance. Bing and Yahoo display meta descriptions more consistently, making optimization for these platforms slightly more predictable. Mobile search results display shorter meta descriptions (typically 100-120 characters) due to screen size constraints, requiring mobile-specific optimization strategies. Social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter use meta descriptions (or Open Graph tags) when content is shared, with optimal lengths varying by platform. Most critically, AI-powered search platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude increasingly rely on meta descriptions to understand page context and generate accurate citations. These systems use meta descriptions as signals of content relevance and authority, making them essential for AI search visibility. For brands using AI monitoring tools like AmICited, optimized meta descriptions improve the likelihood that your content will be properly cited and attributed in AI-generated responses. Additionally, voice search optimization requires conversational, natural-language meta descriptions that match how users speak rather than how they type, as voice assistants often read meta descriptions aloud to users.
Several common mistakes can undermine the effectiveness of meta descriptions and negatively impact your SEO performance. Keyword stuffing is one of the most prevalent errors, where marketers cram multiple keywords into the description in an attempt to improve rankings; this approach appears spammy, reduces readability, and often results in Google ignoring the description entirely. Duplicate descriptions across multiple pages confuse search engines about page uniqueness and waste the opportunity to differentiate each page’s value proposition. Misleading or vague descriptions may generate initial clicks but lead to high bounce rates when users discover the content doesn’t match their expectations, signaling to search engines that your page isn’t relevant to the search query. Overly long descriptions that exceed 160 characters get truncated in search results, cutting off important information and reducing click-through rates. Ignoring mobile optimization by writing descriptions that are too long for mobile screens means mobile users see incomplete or cut-off descriptions. Not incorporating user intent results in descriptions that don’t address what users are actually searching for, reducing relevance and clicks. Failing to update descriptions as content changes means outdated information appears in search results, confusing users and damaging credibility. Using generic descriptions that could apply to any page on your site wastes the opportunity to differentiate and highlight unique value. Finally, neglecting to include a call-to-action misses the chance to encourage clicks and guide user behavior.
Search engines employ sophisticated algorithms to determine whether to display your meta description or generate their own from page content. Google’s decision-making process considers several factors: whether the meta description matches the user’s search query, whether it accurately represents the page content, and whether it provides more relevant information than text extracted from the page itself. When a user searches for specific keywords, Google analyzes whether those keywords appear in your meta description; if they do, Google is more likely to display your description and bold the matching keywords, making your result stand out. However, if your meta description doesn’t closely match the search query, Google will often generate a new snippet from page content that better aligns with the user’s intent. This behavior is intentional and generally improves user experience, as it ensures search results are as relevant as possible. Dynamic snippet generation means that the same page may display different meta descriptions for different search queries, depending on which description best matches each query. This is why it’s crucial to ensure your page content is well-written and keyword-rich; if your meta description doesn’t match a particular search query, Google will pull relevant text from your content to create a snippet. Additionally, Google sometimes adds supplementary information to snippets, such as publication dates, author names, or review ratings, which can push your meta description down or off the visible area. Understanding this behavior helps you write meta descriptions that are more likely to be displayed and clicked.
Measuring the effectiveness of meta descriptions requires analyzing click-through rate (CTR) data and comparing it against industry benchmarks and your own historical performance. Google Search Console provides detailed CTR metrics, showing the number of impressions (times your page appeared in search results), clicks, and average position for each page. By analyzing this data, you can identify pages with below-average CTR and prioritize them for meta description optimization. A typical benchmark for CTR varies by industry and search position, but pages in position 1 typically receive 39.8% CTR, position 2 receives 18.7%, and position 3 receives 10.2%. If your page is in position 1 but receiving significantly lower CTR than this benchmark, it suggests your meta description may need improvement. A/B testing meta descriptions can provide concrete data on which versions perform better; however, this requires patience, as it may take weeks or months to gather sufficient data for statistical significance. Conversion rate tracking is also important, as a higher CTR doesn’t always translate to more conversions if the traffic isn’t qualified. By tracking both CTR and conversion rates, you can determine whether meta description improvements are driving meaningful business results. Additionally, monitoring competitor meta descriptions can provide insights into what messaging resonates with your target audience and identify opportunities to differentiate your descriptions.
The role and importance of meta descriptions continue to evolve as search technology advances. AI-driven search engines are increasingly rewriting meta descriptions dynamically to match specific user queries, reducing the predictability of what description will be displayed. This trend suggests that future success will depend less on crafting the perfect static description and more on ensuring your page content is comprehensive, well-structured, and aligned with user intent. Semantic search emphasizes meaning and context over exact keyword matching, requiring meta descriptions to convey the overall theme and purpose of content rather than simply listing keywords. Structured data and schema markup are becoming increasingly important for enhancing meta descriptions with rich snippets, such as ratings, prices, and availability information, which can significantly improve click-through rates. Voice search optimization is driving demand for more conversational, natural-language meta descriptions that match how users speak rather than how they type. AI monitoring and citation tracking are emerging as critical concerns for brands, as AI systems increasingly cite and reference web content; optimized meta descriptions improve the likelihood of accurate attribution. Mobile-first indexing continues to emphasize the importance of mobile-optimized descriptions, as Google primarily crawls and indexes the mobile version of websites. Looking ahead, personalization may play a larger role, with search engines potentially displaying different meta descriptions to different users based on their search history, location, and preferences. Additionally, the rise of AI-powered search platforms like ChatGPT and Perplexity suggests that meta descriptions will become increasingly important for AI visibility and citation, making them a critical component of generative engine optimization (GEO) strategies.
As AI-powered search platforms become more prevalent, meta descriptions have taken on new significance for brand visibility and citation tracking. Platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude use meta descriptions to understand page context and determine whether to cite or reference your content in AI-generated responses. A well-optimized meta description that clearly communicates your page’s unique value and expertise increases the likelihood that AI systems will recognize your content as authoritative and cite it appropriately. For brands using AI monitoring tools like AmICited, tracking how your meta descriptions influence AI citations is becoming increasingly important. These tools help you understand where and how your brand appears in AI-generated responses, allowing you to optimize your meta descriptions and overall content strategy to improve AI visibility. Additionally, meta descriptions play a role in entity recognition, as AI systems use them to understand the entities (people, places, organizations, products) discussed on your page, which helps establish topical authority and improve visibility for entity-based searches. As AI search continues to grow, ensuring your meta descriptions are clear, comprehensive, and keyword-rich will be essential for maintaining visibility across both traditional search engines and emerging AI platforms.
No, meta descriptions are not a direct ranking factor according to Google. However, they indirectly influence rankings by improving click-through rates (CTR). When users click on your result more frequently due to a compelling meta description, search engines interpret this as a signal of relevance and quality, potentially improving your position over time. Studies show that well-optimized meta descriptions can increase CTR by 20-30%, which may contribute to better rankings through user engagement signals.
The optimal length is 120-160 characters for desktop and 100-120 characters for mobile devices. Google typically displays meta descriptions within this range before truncating them. However, the actual display depends on pixel width rather than character count. Keeping descriptions concise ensures your key message appears completely in search results across all devices, maximizing the likelihood that users see your full description before deciding whether to click.
No, duplicate meta descriptions across multiple pages should be avoided. Google recommends creating unique descriptions for each page to accurately reflect its specific content. Duplicate descriptions dilute their effectiveness, confuse search engines about page uniqueness, and reduce click-through rates. For large websites with thousands of pages, programmatic generation of descriptions using dynamic variables (product name, category, price) is acceptable, but each description should still be contextually relevant to its page.
If you don't set a meta description, Google will automatically generate one from your page content, typically pulling text from headings, body content, or other on-page elements. While this auto-generated snippet may be relevant, it's often less compelling than a carefully crafted description. For important pages like homepages, category pages, and high-traffic landing pages, setting a custom meta description gives you control over how your page appears in search results and helps maximize click-through rates.
Meta descriptions are increasingly important for AI-powered search platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. These systems use meta descriptions to understand page context and relevance when generating summaries or citations. For brands using AI monitoring tools like AmICited, optimized meta descriptions help ensure your content is properly cited and attributed in AI-generated responses. Clear, descriptive meta tags improve the likelihood that AI systems will reference your content accurately in their outputs.
Yes, including relevant keywords naturally in your meta description is beneficial. When users search for those keywords, Google bolds matching terms in the search results, making your listing stand out visually. However, avoid keyword stuffing, which appears spammy and reduces readability. Instead, write naturally for humans first, incorporating 1-2 primary keywords that genuinely reflect the page's content. This approach improves both user experience and the likelihood that your description will be displayed in search results.
Google rewrites approximately 60-70% of all meta descriptions to better match specific search queries and improve relevance for users. Google prioritizes delivering the most helpful results, so if your meta description doesn't closely align with a user's search query or doesn't adequately describe the page, Google may generate a new one from your page content. This is normal and often improves click-through rates. To minimize rewrites, ensure your meta description accurately reflects page content and includes relevant keywords that match common search queries.
Meta descriptions are used by social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter when content is shared. You can create platform-specific descriptions using Open Graph tags (og:description for Facebook) and Twitter Card tags (twitter:description). If these aren't set, social platforms default to your standard meta description. Keeping descriptions under 120 characters ensures they display properly across all platforms and devices. Optimizing for social sharing increases engagement and extends your content's reach beyond organic search.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn what title tags are, why they matter for SEO and AI visibility, and how to optimize them for search engines and users. Complete guide to title tag best pr...
Learn what an XML Sitemap is, why it matters for SEO and AI search visibility, and how to implement it effectively. Complete guide to XML sitemap structure, bes...

Main Content (MC) is the primary material on a webpage that fulfills its purpose. Learn how MC quality affects SEO rankings, E-E-A-T signals, and AI monitoring ...