
Opinion Content
Learn what opinion content is, explore different types including editorials, op-eds, and commentary pieces, and understand how perspective-driven content impact...

News content refers to information about current events and timely occurrences that are factual, important to society, and distributed through various media channels. It encompasses breaking news, investigative reporting, and coverage of events that affect public understanding and civic engagement.
News content refers to information about current events and timely occurrences that are factual, important to society, and distributed through various media channels. It encompasses breaking news, investigative reporting, and coverage of events that affect public understanding and civic engagement.
News content is factual, timely information about current events that is distributed through various media channels and holds significance for public understanding and civic engagement. According to the Pew Research Center’s comprehensive 2025 study, news content is defined by three core attributes: it must be factual (85% of Americans identify this as essential), up-to-date (78% emphasize timeliness), and important to society (72% consider societal importance critical). News content encompasses breaking news, investigative reporting, feature stories, and analysis that inform audiences about events, trends, and developments affecting their communities, nations, and the world. The definition of news content has evolved significantly in the digital age, shifting from a journalist-controlled gatekeeping model to a more audience-driven interpretation where individuals determine what constitutes news based on their personal interests, values, and information needs.
The concept of news content has undergone dramatic transformation over the past two decades. Historically, news content was primarily defined and controlled by professional journalists and media institutions who determined what was newsworthy based on established editorial standards. The traditional definition emphasized hard news—stories about politics, economics, crime, and conflict—as more inherently newsworthy than soft news covering entertainment, lifestyle, or human interest topics. However, the digital revolution fundamentally altered this landscape. The rise of social media platforms, citizen journalism, and algorithmic content distribution has democratized news content creation and consumption. Pew Research’s 2025 analysis reveals that the power to define news has largely shifted from media gatekeepers to the general public, with audiences now determining what qualifies as news based on personal relevance, platform algorithms, and social sharing patterns. This shift reflects broader changes in media consumption habits, with 53% of U.S. adults now getting news from social media at least sometimes, compared to declining reliance on traditional broadcast and print sources.
News content is distinguished by several fundamental characteristics that differentiate it from other information types. Timeliness remains paramount—news content must address recent events or developments currently unfolding. According to journalism scholars at Purdue University, timeliness is of utmost importance in today’s 24-hour news cycle, with recent events or events in development most likely to lead news coverage. Factuality is equally essential; news content must be verifiable and based on evidence rather than opinion or speculation. The Reuters Institute’s 2025 Digital News Report confirms that 85% of Americans identify factuality as a major factor in determining whether information qualifies as news. Relevance and importance are also critical—news content should address topics that affect audiences either personally or collectively. Pew Research found that 72% of Americans consider whether information is important to society a major factor in identifying news. Additionally, credibility of sources matters significantly; news content sourced from recognized, trusted outlets is more likely to be perceived as legitimate news than content from unknown or unverified sources. The attribution and evidence supporting news content—including cited sources, expert opinions, and documented facts—further distinguish legitimate news from misinformation or opinion-based commentary.
| Characteristic | News Content | Opinion/Commentary | Entertainment | Misinformation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Inform about current events | Express viewpoints on issues | Entertain and engage audiences | Mislead or deceive audiences |
| Factual Basis | Verified facts and evidence | Personal interpretation of facts | Fictional or entertainment-focused | False or unverified claims |
| Timeliness | Recent or ongoing events | May reference current events | Not time-dependent | Often presented as urgent/current |
| Source Attribution | Named sources and citations | Author’s perspective stated | Not applicable | Sources often absent or false |
| Journalistic Standards | Follows ethics codes | May lack editorial oversight | No journalistic standards | Deliberately violates standards |
| Audience Expectation | Objective reporting | Acknowledged bias/perspective | Entertainment value | Perceived as factual |
| AI Platform Citation | Frequently cited in responses | Cited with opinion labels | Rarely cited in news contexts | Actively filtered by AI systems |
| Verification Process | Fact-checked and verified | Not typically fact-checked | Not applicable | Flagged as false by fact-checkers |
News content operates through sophisticated distribution mechanisms that have evolved dramatically with technological advancement. Traditionally, news content was distributed through broadcast media (television and radio), print publications (newspapers and magazines), and wire services that syndicated stories to multiple outlets. The digital era introduced web-based news sites, email newsletters, social media platforms, and news aggregators as primary distribution channels. Today, news content reaches audiences through multiple simultaneous channels—a phenomenon known as omnichannel distribution. According to Deloitte’s 2025 Digital Media Trends analysis, consumers now access news content across an average of six hours of daily media consumption, distributed across streaming services, social platforms, podcasts, and traditional media. The algorithmic curation of news content on platforms like Facebook, TikTok, and YouTube means that individual users receive personalized news feeds based on their engagement history, interests, and social connections. This algorithmic distribution has profound implications for how news content reaches audiences and which stories gain prominence. Real-time news alerts and push notifications have also transformed news content delivery, enabling immediate notification of breaking news to mobile device users. The integration of AI-powered content recommendation systems means that news content is increasingly filtered, ranked, and presented based on machine learning algorithms rather than editorial judgment alone.
The emergence of AI-powered answer engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude has created a new dimension for news content distribution and monitoring. These platforms source information from across the internet, including news content, to generate responses to user queries. Research from Profound reveals that news content citation patterns vary significantly across AI platforms. ChatGPT prioritizes Wikipedia (7.8% of total citations) and established media sources, reflecting a preference for authoritative knowledge bases. Perplexity relies heavily on Reddit (6.6% of citations) and community-driven platforms, emphasizing peer-to-peer information sharing. Google AI Overviews balances professional content with social platforms, citing Reddit at 2.2% while maintaining broader source diversity. These citation patterns have direct implications for brand visibility in AI responses. When news content about a brand or organization is cited by AI systems, it influences how that brand is perceived by users seeking information through these platforms. This has created a new category of AI visibility monitoring, where organizations track how their news mentions appear across different AI systems. Platforms like AmICited specialize in monitoring brand appearances in news content as cited by AI response engines, providing insights into how organizations are represented in AI-generated responses. This monitoring is critical because over 78% of enterprises now recognize the importance of tracking their presence in AI-driven information systems, according to industry research on AI monitoring adoption.
Journalists and media organizations evaluate news content using established newsworthiness frameworks that determine which stories receive coverage and prominence. The Galtung and Ruge model (1973) identifies nine key newsworthiness criteria: timeliness, relevance, simplification, predictability, unexpectedness, continuity, composition, elite people, and negativity. The Shoemaker et al. framework (1987) emphasizes timeliness, proximity, importance/impact, interest, conflict/controversy, sensationalism, prominence, and novelty. Pew Research’s 2025 study found that hard news topics—including politics (66% of Americans say election updates are “definitely news”), international conflicts (62% for war coverage), and local crime—are most consistently identified as news content. Soft news topics, including celebrity coverage (only 3% consider celebrity information “definitely news”) and lifestyle content, are less likely to be classified as news. The study also revealed that news content perception varies by source; information from established news organizations like newspapers and verified news outlets on social media is more likely to be perceived as news than content from individual social media users or YouTube creators. Breaking news—urgent, developing stories that warrant immediate coverage—represents a special category of news content characterized by its time-sensitive nature and evolving information. The inverted pyramid structure commonly used in news writing places the most important information about news content in the opening paragraphs, allowing readers to quickly grasp the essential facts.
The rise of social media platforms as primary news content distribution channels has fundamentally altered how news reaches audiences and which stories gain prominence. According to Pew Research, approximately 53% of U.S. adults get news from social media at least sometimes, with younger generations showing even higher reliance on these platforms. Deloitte’s 2025 analysis reveals that 56% of Gen Z and 43% of millennials find social media content more relevant than traditional news, spending 54% more time on social platforms and user-generated content than the average consumer. This shift has created a fragmented news landscape where algorithmic curation determines which news content reaches which audiences. Algorithmic amplification means that news content with high engagement—measured through likes, shares, and comments—receives greater visibility, potentially prioritizing sensational or emotionally provocative stories over substantive reporting. The filter bubble effect means that users increasingly see news content aligned with their existing beliefs and interests, potentially limiting exposure to diverse perspectives. Misinformation and disinformation spread more rapidly through social media than through traditional news channels, with false news content sometimes reaching audiences faster than corrections. The Reuters Institute’s 2025 Digital News Report found that traditional news media is struggling to connect with much of the public, with declining engagement, low trust, and stagnating digital subscriptions—trends directly attributable to the shift toward social media-based news content consumption. However, social platforms have also democratized news content creation, enabling citizen journalism and allowing individuals to document and share news content from their communities in real-time.
Research reveals complex emotional responses to news content consumption that influence how audiences engage with and perceive news. Pew Research’s 2025 study found that Americans experience predominantly negative emotions when consuming news content: 42% say news makes them feel angry, 38% report feeling sad, 27% experience fear, and 25% feel confused. However, 46% also report feeling informed, indicating that audiences recognize the value of news content despite negative emotional responses. The phenomenon of news avoidance—where individuals deliberately limit their exposure to news content—has increased significantly, with the Reuters Institute reporting that news avoidance is particularly high in Eastern European countries (Bulgaria at 63%, Croatia at 61%). This avoidance stems from multiple factors: news fatigue from constant coverage of negative events, distrust in news sources, perception that news content is biased or sensationalized, and feeling overwhelmed by information volume. Conversely, some audiences experience news addiction, compulsively consuming news content despite negative emotional impacts. The concept of doomscrolling—continuously scrolling through social media feeds consuming negative news content—reflects this paradoxical relationship with news. Pew Research found that 55% of Americans believe it’s at least somewhat important that their news sources share their political views, indicating that political identity significantly influences which news content audiences consume and how they perceive its credibility. This creates a tension between audiences’ stated preference for objective, unbiased news content and their actual behavior of seeking news aligned with their political perspectives.
The definition and distribution of news content continues to evolve rapidly in response to technological innovation and changing audience behaviors. Artificial intelligence is increasingly influencing how news content is created, curated, and distributed. AI-powered tools now assist journalists in research, fact-checking, and story identification, while also enabling automated news content generation for routine stories like financial reports and sports summaries. The rise of AI answer engines has created new pathways for news content distribution, with these systems synthesizing information from multiple news sources to generate comprehensive responses to user queries. Personalization algorithms will likely become increasingly sophisticated, potentially creating highly individualized news content experiences tailored to each user’s interests, reading level, and preferences. However, this raises concerns about filter bubbles and echo chambers that limit exposure to diverse news content perspectives. Blockchain technology and decentralized platforms may enable new models of news content distribution that reduce reliance on centralized social media platforms. Subscription models and paywalls are becoming more prevalent as news organizations seek sustainable revenue models, potentially creating a two-tiered news landscape where premium news content is available only to paying subscribers. The credibility crisis facing news content—with trust in traditional media declining according to the Reuters Institute—will likely drive innovation in verification technologies, fact-checking automation, and source transparency. Additionally, the integration of video content, interactive elements, and multimedia storytelling will continue to reshape how news content is presented and consumed. The localization of news content may increase as audiences seek information relevant to their specific communities, potentially reversing decades of consolidation in the news industry.
Understanding news content and its distribution across media channels and AI systems has become strategically critical for organizations seeking to maintain brand visibility and reputation. Media monitoring has evolved from tracking traditional news mentions to encompassing AI visibility monitoring, where organizations track how their brand appears in news content cited by AI response engines. The citation patterns of different AI platforms mean that organizations must develop platform-specific strategies for news content visibility. For example, organizations seeking visibility in ChatGPT responses should focus on authoritative, well-documented news content, while those targeting Perplexity users might prioritize community engagement and peer-reviewed information. Crisis communication strategies must now account for how news content about organizational incidents spreads across social media and AI systems simultaneously. Thought leadership and expert positioning increasingly depend on having organizational representatives quoted in news content that reaches both human audiences and AI systems. The news cycle has accelerated dramatically, with breaking news content now spreading globally within minutes, requiring organizations to respond rapidly to emerging news stories. Proactive media relations and strategic news content placement remain essential for shaping how organizations are represented in news coverage. Additionally, organizations must understand that news content about competitors appearing in AI responses can influence customer perceptions and purchasing decisions, making competitive news monitoring increasingly important. The integration of news content monitoring with broader AI monitoring strategies enables organizations to understand their complete visibility landscape across both traditional and emerging information channels.
News content is distinguished by its focus on factual, timely information about current events that hold societal importance. According to Pew Research Center's 2025 study, 85% of Americans identify factuality as a major factor in determining whether something qualifies as news, while 78% emphasize timeliness. News must be verifiable, recent, and relevant to audiences, differentiating it from opinion pieces, entertainment, or historical information that lacks immediate relevance.
AI platforms employ distinct citation patterns when sourcing news content. Research from Profound reveals that ChatGPT prioritizes Wikipedia (7.8% of citations) and established media sources, while Perplexity relies heavily on Reddit (6.6% of citations) and community-driven platforms. Google AI Overviews balances professional content with social platforms, citing Reddit at 2.2%. These differences reflect each platform's philosophy: ChatGPT favors authoritative knowledge bases, Perplexity emphasizes peer-to-peer information, and Google AI seeks balanced coverage across multiple source types.
Timeliness is fundamental to news content because it distinguishes current events from historical information. Journalism scholars at Purdue University identify timeliness as one of the core newsworthiness criteria, noting that recent events or events in development are most likely to lead news coverage in today's 24-hour news cycle. The Reuters Institute's 2025 Digital News Report confirms that 78% of U.S. adults consider whether information is up-to-date a major factor in identifying news, making recency essential to the definition.
Traditional media outlets like newspapers and broadcast networks apply editorial gatekeeping to news content, emphasizing verification and journalistic standards. Social platforms, however, distribute news content algorithmically, often mixing professional journalism with user-generated content and commentary. Deloitte's 2025 Digital Media Trends report shows that 56% of Gen Z and 43% of millennials find social media content more relevant than traditional news, reflecting a fundamental shift in how news content is curated and consumed across different platforms.
News content serves as a critical indicator of brand visibility and reputation in AI systems. Platforms like AmICited track how brands appear in news mentions across AI response engines including ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. When news content about a brand is cited by these AI systems, it directly influences how the brand is perceived by users seeking information. This makes monitoring news content distribution across AI platforms essential for brand management and understanding AI-driven visibility.
Journalists use established newsworthiness criteria to evaluate potential stories. The Galtung and Ruge model (1973) and Shoemaker et al. framework (1987) identify factors including timeliness, relevance, impact, prominence of people involved, conflict or controversy, and unexpectedness. Pew Research's 2025 study found that journalists and editors agree the power to define news has shifted from media gatekeepers to the general public in the digital age, though professional standards around factuality and verification remain central to news content evaluation.
According to Pew Research Center's 2025 findings, approximately 77% of U.S. adults say they follow the news at least some of the time, with 44% intentionally seeking out news extremely often or often. However, the Reuters Institute's 2025 Digital News Report reveals concerning trends: traditional news media is struggling to connect with much of the public, with declining engagement, low trust, and stagnating digital subscriptions. This indicates that while news consumption remains widespread, the sources and methods of accessing news content are rapidly evolving.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn what opinion content is, explore different types including editorials, op-eds, and commentary pieces, and understand how perspective-driven content impact...
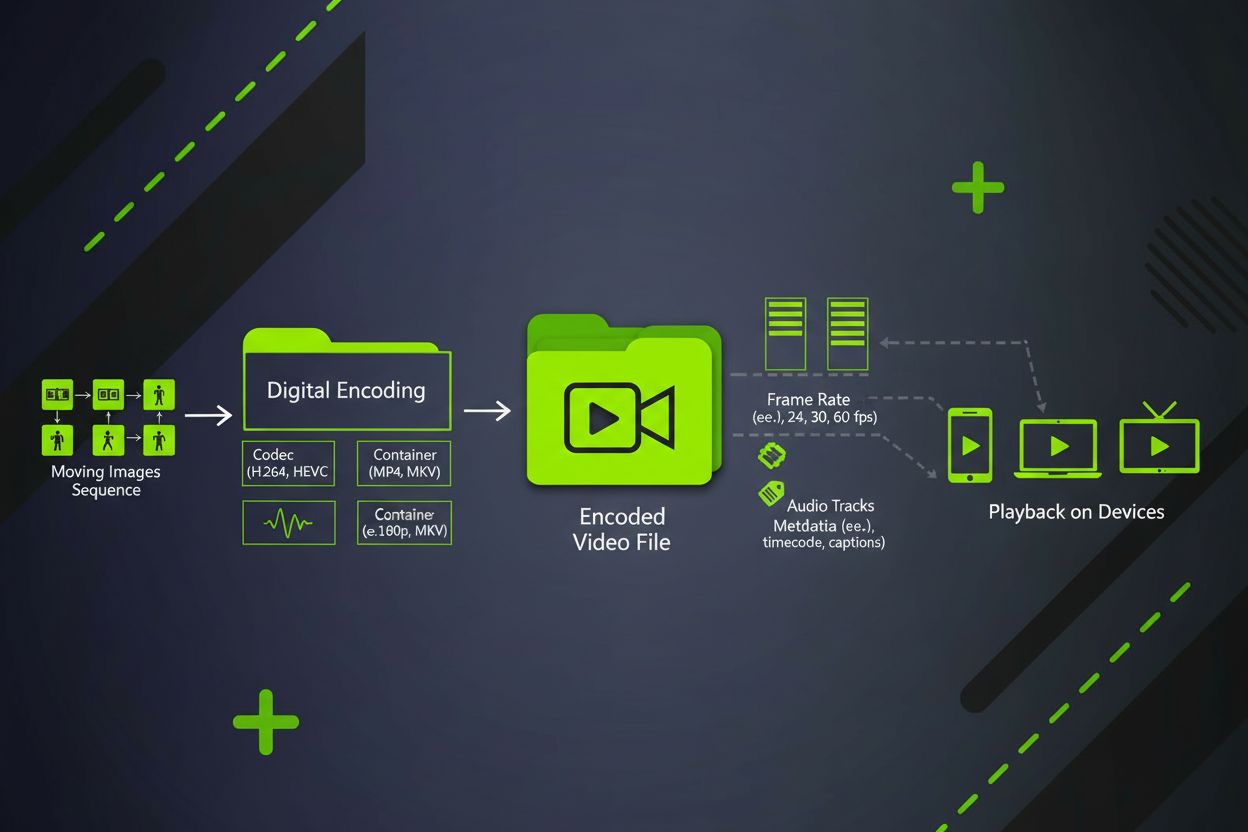
Video content is a digital moving image format combining sequential frames, audio, and metadata. Learn about video formats, codecs, specifications, and its role...
Learn what statistical content is, why it matters for AI citations, and how data-driven content builds authority. Discover how 74% of B2B buyers trust research-...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.