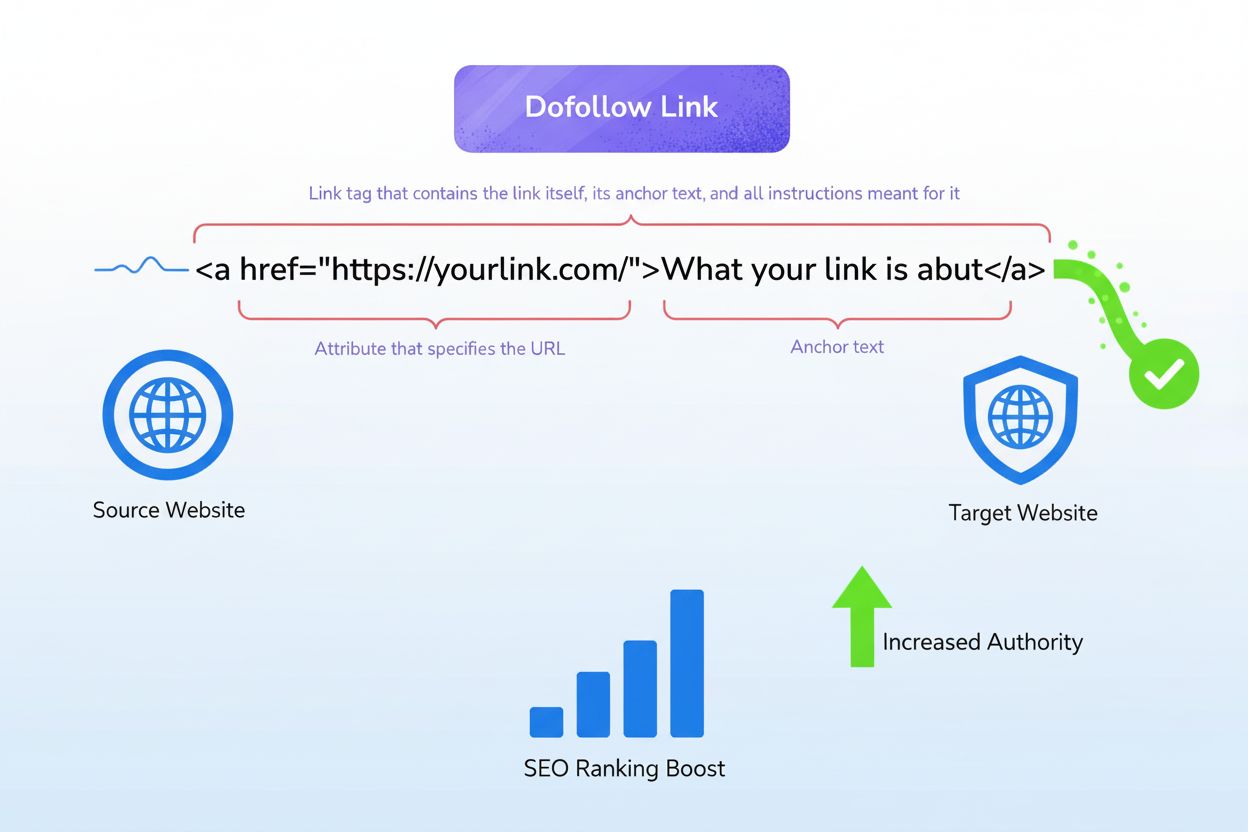
DoFollow Link
Learn what dofollow links are, how they pass ranking value and authority through link juice, and why they're critical for SEO success and AI search visibility.
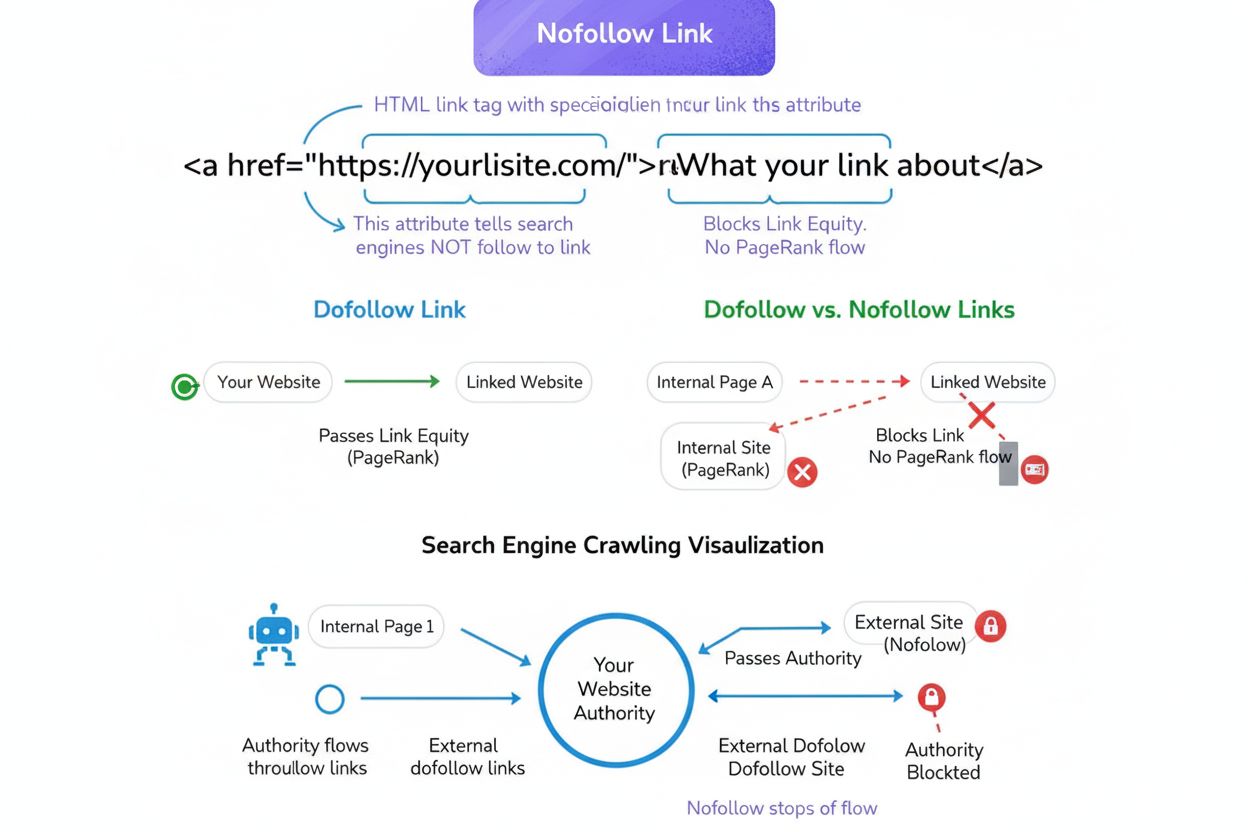
A nofollow link is a hyperlink with the rel=“nofollow” HTML attribute that instructs search engines not to pass ranking authority or PageRank to the linked page. While nofollow links do not directly contribute to search rankings, they remain valuable for driving referral traffic, building natural link profiles, and maintaining SEO compliance with Google’s guidelines.
A nofollow link is a hyperlink with the rel="nofollow" HTML attribute that instructs search engines not to pass ranking authority or PageRank to the linked page. While nofollow links do not directly contribute to search rankings, they remain valuable for driving referral traffic, building natural link profiles, and maintaining SEO compliance with Google's guidelines.
A nofollow link is a hyperlink that includes the rel="nofollow" HTML attribute, which serves as a signal to search engines that the linking website does not endorse or vouch for the destination page. This attribute instructs search engines not to pass PageRank, link equity, or ranking authority through the link to the target page. While nofollow links do not directly contribute to improving search engine rankings, they remain an essential component of a healthy, natural backlink profile and continue to provide indirect SEO benefits through referral traffic and brand visibility. The nofollow attribute was originally created by Google in 2005 in partnership with MSN Search and Yahoo to combat comment spam and manipulative linking practices. Today, it represents one of the most fundamental concepts in search engine optimization and link building strategy, with widespread adoption across major platforms and content management systems.
The nofollow attribute emerged in 2005 as a direct response to the explosive growth of blog comment spam, where malicious actors would leave links to their own websites in blog comments to artificially inflate their search rankings. Before the introduction of nofollow, these spam links passed full PageRank and authority, creating a significant problem for website owners and search engine quality. Matt Cutts from Google and Jason Shellen from Blogger collaborated to develop the rel=“nofollow” microformat as a solution, allowing webmasters to indicate that certain links should not be followed or credited by search engines. This innovation fundamentally changed how the web approached link management and trust signals. For nearly 15 years, Google treated nofollow as a strict directive—links marked with this attribute were completely ignored during crawling and indexing. However, in March 2020, Google announced a significant algorithmic shift, reclassifying nofollow from a command to a “hint,” meaning search engines could now choose to crawl and consider nofollow links in their ranking calculations if they deemed them relevant or high-quality. This evolution reflects Google’s growing sophistication in understanding link context and quality beyond simple attribute values.
At the technical level, a nofollow link is implemented through a simple HTML attribute within the anchor tag. A standard dofollow link appears as <a href="https://example.com">Link Text</a>, while a nofollow link includes the rel attribute: <a href="https://example.com" rel="nofollow">Link Text</a>. When a search engine crawler encounters a nofollow link, it receives a signal that the linking website is not endorsing the destination page and does not intend to pass authority through that link. Modern search engines like Google, Bing, DuckDuckGo, and Yahoo all recognize and respect the nofollow attribute, though they may treat it with varying degrees of strictness. Google’s 2020 update introduced additional specificity through two complementary attributes: rel="sponsored" for paid or sponsored links, and rel="ugc" for user-generated content like comments and forum posts. These attributes allow website owners to provide more granular information about the nature of their links while maintaining backward compatibility with the original nofollow standard. Multiple attributes can be combined in a single link—for example, rel="nofollow sponsored" indicates a paid link that should not pass authority. This technical flexibility enables websites to maintain compliance with search engine guidelines while accurately describing their link ecosystem.
| Attribute | Purpose | Passes Authority | Best Use Cases | Search Engine Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dofollow (default) | Regular link without restrictions | Yes, passes full PageRank | Editorial links, citations, trusted sources | Crawled, indexed, counted as ranking signal |
| NoFollow | Indicates non-endorsement | No, blocks PageRank transfer | Comments, untrusted sources, general disclaimers | Treated as hint; may be crawled and considered |
| rel=“sponsored” | Identifies paid/sponsored links | No, blocks PageRank transfer | Ads, affiliate links, paid partnerships | Crawled but not counted as editorial endorsement |
| rel=“ugc” | Marks user-generated content | No, blocks PageRank transfer | Blog comments, forum posts, user reviews | Crawled but distinguished from editorial links |
| Internal Links | Links within same domain | Yes (if dofollow) | Navigation, site structure, content hierarchy | Essential for crawlability and indexing |
The relationship between nofollow links and search rankings has been a subject of considerable debate within the SEO community, but recent evidence provides clearer insights. Google’s official position states that nofollow links do not pass PageRank and therefore do not directly improve search rankings. However, the 2020 reclassification of nofollow as a “hint” rather than a command introduced nuance—Google reserves the right to follow and evaluate nofollow links if they appear relevant or high-quality. Multiple case studies have demonstrated that nofollow links can correlate with ranking improvements, though this correlation may be indirect, resulting from increased brand visibility and referral traffic rather than direct authority transfer. Notably, 78.8% of SEO professionals believe nofollow links impact rankings, suggesting widespread recognition of their value beyond the official Google narrative. The emergence of AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude has introduced a new dimension to this discussion. Recent research from 2024 indicates that nofollow links correlate nearly as strongly with AI visibility as dofollow links, with some AI models showing even stronger correlation with nofollow citations than traditional search engines. This suggests that large language models may evaluate link authority and relevance differently than Google’s PageRank algorithm, potentially valuing the contextual relevance of a link over its formal authority status. For brands seeking visibility in AI-generated responses, this finding underscores the importance of maintaining a diverse, natural backlink profile that includes both dofollow and nofollow links from authoritative sources.
Nofollow links serve several critical functions in modern web management and SEO strategy. First, they provide a mechanism for compliance with search engine guidelines—Google explicitly requires the use of nofollow or sponsored attributes for paid links, affiliate links, and sponsored content. Failure to properly mark paid links can result in manual penalties or algorithmic demotions. Second, nofollow links protect your website’s authority by preventing the transfer of PageRank to sources you do not endorse or control. This is particularly important when linking to low-quality websites, competitors, or sources with questionable credibility. Third, user-generated content like blog comments and forum posts should automatically include nofollow attributes to prevent spam and maintain editorial integrity. Most modern content management systems, including WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla, automatically apply nofollow to comment links by default. Fourth, nofollow links contribute to a natural and diverse backlink profile. Websites with exclusively dofollow backlinks may appear suspicious to search engines, as this pattern suggests artificial link building or paid link schemes rather than organic, earned links. A healthy backlink profile typically includes a mix of both dofollow and nofollow links from varied sources, which signals to search engines that your content has earned genuine recognition across the web. Finally, nofollow links can drive high-quality referral traffic from authoritative sources—a link from a major publication like Forbes or The New York Times will send valuable visitors to your site even if marked as nofollow, and these visitors may become customers, subscribers, or sources of future dofollow links.
Implementing nofollow links effectively requires understanding both when to use them and how to manage them across your website. For external links on your website, the general principle is to use dofollow links for trusted, high-quality sources that you genuinely endorse and want to support. Reserve nofollow for links to low-quality websites, competitors, or sources you cannot verify. When linking to paid or sponsored content, use rel="sponsored" as the preferred attribute, though rel="nofollow" remains acceptable. For user-generated content, ensure that all comment links, forum posts, and user-submitted content automatically receive the rel="ugc" attribute or nofollow designation. Most CMS platforms handle this automatically, but verify your settings to ensure compliance. For internal links, avoid using nofollow on important pages you want to rank—internal nofollow links can damage your site’s crawlability and prevent search engines from properly discovering and indexing your content hierarchy. The only exceptions are non-essential pages like login pages, registration pages, or internal search results, which you may want to exclude from crawling. To implement nofollow links, you can either manually edit the HTML code or use CMS plugins like Yoast SEO, Rank Math, or All in One SEO for WordPress, which provide user-friendly interfaces for managing link attributes. Regularly audit your backlink profile using tools like SE Ranking’s Backlink Checker, Ahrefs, or Semrush to understand the ratio of dofollow to nofollow links and identify any suspicious or low-quality sources linking to your site. According to industry data, YouTube maintains approximately 23% nofollow links in its backlink profile, demonstrating that even the most authoritative websites maintain a significant proportion of nofollow links as part of their natural link ecosystem.
The rise of AI search engines and large language models has introduced new considerations for nofollow link strategy. Traditional SEO focused on optimizing for Google’s PageRank algorithm, which explicitly ignores nofollow links. However, AI models like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google Gemini, and Claude appear to evaluate links differently, potentially considering factors beyond formal authority transfer. A 2024 study analyzing AI search visibility found that nofollow links correlate nearly as strongly with AI visibility as dofollow links, with some platforms showing even stronger correlation with nofollow citations. This suggests that LLMs may prioritize the contextual relevance and topical authority of a link over its formal PageRank value. Additionally, the study revealed that ChatGPT and Gemini show particularly strong correlation with nofollow links, while Google AI Overviews and Perplexity treat dofollow and nofollow links more similarly. This divergence indicates that different AI platforms may have distinct algorithms for evaluating link authority and relevance. For brands seeking visibility in AI-generated responses, this finding has significant implications: maintaining a diverse, high-quality backlink profile that includes both dofollow and nofollow links from topically relevant sources may be more important than ever. Tools like AmICited enable brands to monitor their visibility across AI search platforms and understand how different types of links influence their presence in AI-generated content, providing actionable insights for optimizing link strategy in the AI era.
Several persistent myths about nofollow links continue to mislead website owners and SEO professionals. The first misconception is that nofollow links are completely worthless—in reality, they provide significant indirect benefits through referral traffic, brand visibility, and profile diversity. The second myth is that nofollow links can harm your website—Google has consistently stated that nofollow links cannot damage your site unless they originate from spammy link exchanges or manipulative schemes. A third misconception is that all external links should be nofollowed—this approach is counterproductive, as it prevents you from supporting and endorsing high-quality sources, which is a natural part of web publishing. The fourth myth is that nofollow links are outdated—in fact, they remain essential for SEO compliance and are increasingly relevant for AI search visibility. A fifth misconception is that you should nofollow all internal links—this practice severely damages your site’s crawlability and should be avoided except for non-essential pages. Finally, some believe that nofollow links have no impact on rankings whatsoever—while they don’t pass direct PageRank, recent evidence suggests they can correlate with ranking improvements through indirect mechanisms and may have stronger impact on AI search visibility than traditional rankings.
The landscape of nofollow links and link-based ranking signals continues to evolve as search engines and AI models become more sophisticated. Google’s 2020 reclassification of nofollow as a hint rather than a command represents a fundamental shift toward more nuanced evaluation of link context and quality. As machine learning and natural language processing advance, search engines and AI models may increasingly evaluate links based on contextual relevance, topical authority, and semantic relationships rather than simple attribute values. The emergence of AI search engines introduces additional complexity, as these platforms may develop entirely different approaches to evaluating link authority and relevance. The growing importance of brand mentions and unlinked citations in AI-generated responses suggests that the future of link-based SEO may extend beyond traditional hyperlinks to include broader recognition and citation patterns. Additionally, the rise of zero-click search and AI Overviews means that visibility in AI-generated responses may become as important as traditional search rankings, requiring brands to optimize for both traditional and AI search visibility simultaneously. The nofollow attribute will likely remain relevant, but its strategic importance may shift from a ranking factor to a compliance and trust signal. Website owners should expect continued evolution in how search engines and AI models treat different link types, making it essential to maintain a diverse, natural backlink profile and monitor visibility across multiple search and AI platforms. Tools that track AI search visibility and provide insights into how different link types influence presence in AI-generated responses will become increasingly valuable for competitive advantage in the evolving search landscape.
Nofollow links do not directly pass PageRank or link equity to improve search rankings, as Google treats the nofollow attribute as a hint rather than a strict directive since 2020. However, they can indirectly benefit SEO by driving referral traffic, increasing brand visibility, and contributing to a natural and diverse backlink profile that appears organic to search engines. Recent studies suggest that nofollow links may have more impact on AI search visibility than traditional Google rankings.
Dofollow links (regular links without the rel="nofollow" attribute) pass authority and PageRank to the linked page, directly contributing to search rankings. Nofollow links include the rel="nofollow" attribute and explicitly signal to search engines not to pass ranking authority. From a user perspective, both types function identically—they can be clicked and visited—but the technical difference in the HTML code determines how search engines treat them.
Use nofollow links for untrusted external sources, user-generated content like comments and forum posts, paid or sponsored links, and pages you don't want to endorse. Google requires the rel="sponsored" attribute for paid links and rel="ugc" for user-generated content, though rel="nofollow" remains acceptable as a catch-all. Avoid nofollowing internal links to important pages, as this prevents search engines from properly crawling and indexing your site structure.
Nofollow links cannot harm your website unless they originate from spammy sources or are part of manipulative link schemes. Google has consistently stated since 2013 that nofollow links do not negatively impact rankings. In fact, having a natural mix of both dofollow and nofollow links in your backlink profile appears more organic and helps avoid penalties for unnatural link patterns.
You can check a link's attribute by right-clicking on it, selecting 'Inspect,' and looking for the rel="nofollow" attribute in the HTML code. Browser extensions like NoFollow or SEOquake highlight nofollow links in red. For comprehensive backlink analysis, use SEO tools like SE Ranking's Backlink Checker or Ahrefs, which display the dofollow/nofollow status of all inbound links to your domain.
Recent research indicates that nofollow links may have greater impact on AI search visibility than on traditional Google rankings. A 2024 study found that nofollow links correlate nearly as strongly with AI visibility as dofollow links, with ChatGPT and Gemini showing particularly strong correlation with nofollow citations. This suggests that AI language models may evaluate link authority differently than traditional search algorithms.
According to 2024 link building statistics, approximately 78.8% of SEO professionals believe nofollow links impact rankings, indicating widespread recognition of their value. Major platforms like Wikipedia, Reddit, Medium, YouTube, and Quora use nofollow attributes on all outbound links by default, demonstrating that nofollow links are a standard and expected part of the web's link ecosystem.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn what dofollow links are, how they pass ranking value and authority through link juice, and why they're critical for SEO success and AI search visibility.

Unlinked brand mentions are online references to your brand without backlinks. Learn how they impact SEO, AI visibility, and why converting them to links matter...
Link equity is the SEO authority transferred through hyperlinks between pages. Learn how link equity flows, what factors determine its value, and how to maximiz...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.