GPTBot vs OAI-SearchBot: Understanding OpenAI's Different Crawlers
Learn the key differences between GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot crawlers. Understand their purposes, crawl behaviors, and how to manage them for optimal content visi...
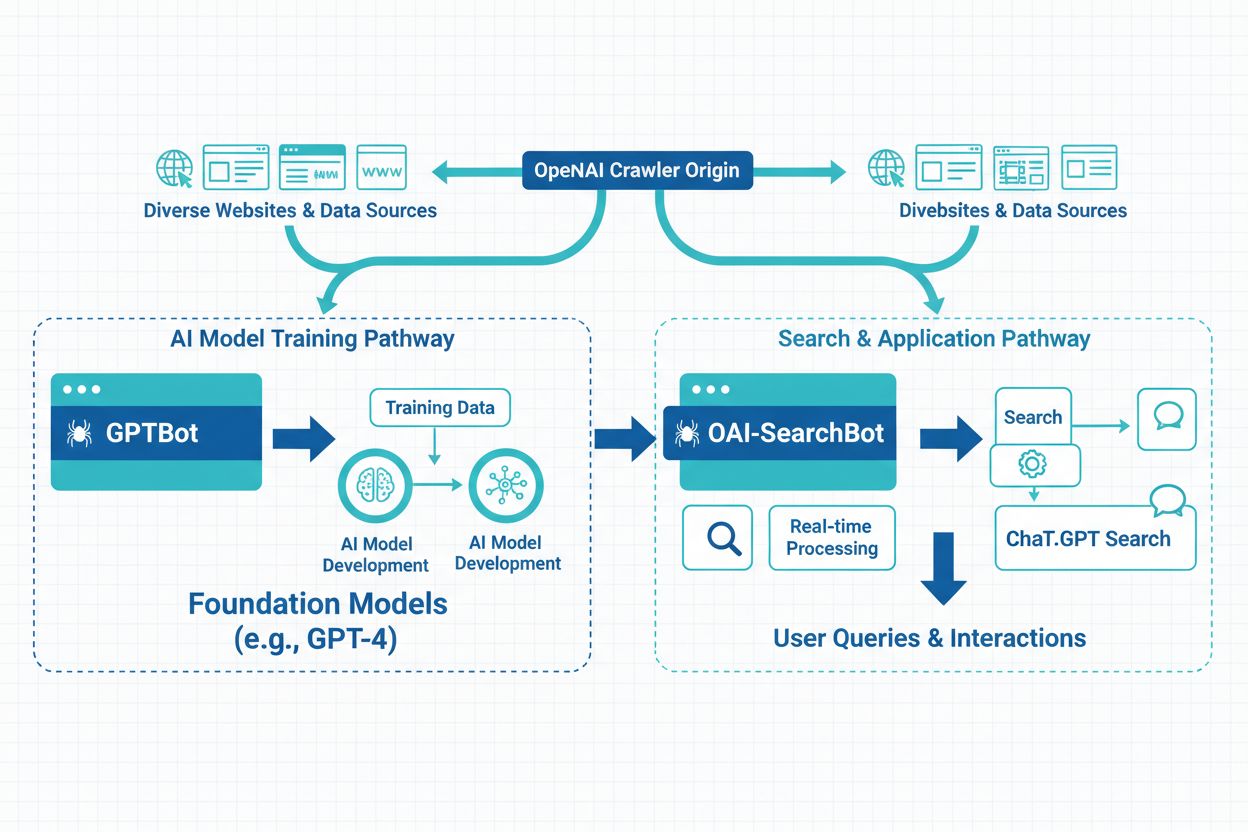
OAI-SearchBot is OpenAI’s dedicated web crawler designed specifically for SearchGPT and ChatGPT’s web browsing capabilities. It indexes publicly accessible website content to power AI-driven search results and real-time information retrieval, operating separately from GPTBot which is used for AI model training.
OAI-SearchBot is OpenAI's dedicated web crawler designed specifically for SearchGPT and ChatGPT's web browsing capabilities. It indexes publicly accessible website content to power AI-driven search results and real-time information retrieval, operating separately from GPTBot which is used for AI model training.

OAI-SearchBot is OpenAI’s dedicated web crawler designed specifically to index publicly accessible content for SearchGPT and ChatGPT search features. Unlike traditional search engine crawlers that gather data for general web indexing, OAI-SearchBot operates with a singular purpose: to provide real-time, relevant search results within OpenAI’s AI-powered search interfaces. It’s crucial to understand that OAI-SearchBot is completely separate from GPTBot, which is OpenAI’s training crawler used to gather data for model training. While both are OpenAI products, they serve distinct functions and operate independently. OAI-SearchBot focuses exclusively on delivering current, accurate information to users performing searches through ChatGPT and SearchGPT, making it an essential component of OpenAI’s search infrastructure.
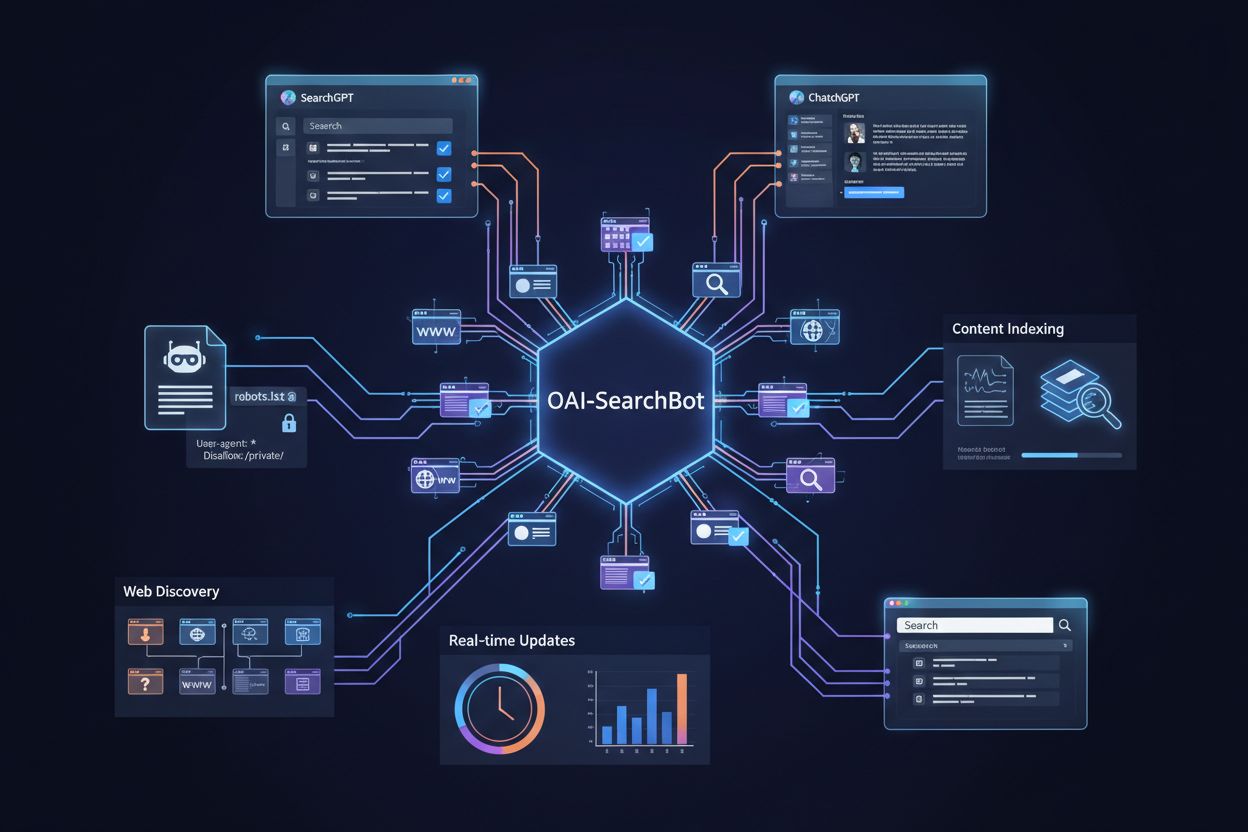
OAI-SearchBot operates through a sophisticated crawling mechanism that systematically discovers and indexes web content to power AI-driven search results. The bot identifies websites through various methods, including following links from already-indexed pages, processing XML sitemaps, and discovering new domains through web references. However, OAI-SearchBot’s crawling frequency is notably sporadic and infrequent compared to traditional search engine crawlers like Googlebot or Bingbot, which continuously revisit pages to maintain fresh indexes. This difference reflects OAI-SearchBot’s specific purpose: rather than maintaining a comprehensive, constantly-updated index of the entire web, it focuses on retrieving relevant, current information when users perform searches. The bot respects standard web protocols and authentication barriers, meaning it won’t attempt to access password-protected content or private pages.
| Feature | OAI-SearchBot | Traditional Crawlers | GPTBot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Real-time search indexing | General web indexing | Training data collection |
| Crawl Frequency | Sporadic/infrequent | Continuous/frequent | Periodic |
| Content Usage | Search results | Search engine index | Model training |
| Respects robots.txt | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Accesses Private Content | No | No | No |
| User Agent | OAI-SearchBot/1.3 | Varies (Googlebot, Bingbot) | GPTBot/1.0 |
While both OAI-SearchBot and GPTBot are OpenAI products, they serve fundamentally different purposes and should not be confused. OAI-SearchBot is designed exclusively for search functionality, crawling the web to provide current, relevant results when users search within ChatGPT or SearchGPT. In contrast, GPTBot is OpenAI’s training crawler, used to gather data for training and improving AI models. The distinction extends to their technical identifiers: OAI-SearchBot uses the user agent string “OAI-SearchBot/1.3,” while GPTBot identifies itself as “GPTBot/1.0.” Additionally, these bots may operate from different IP ranges and have different crawling patterns—OAI-SearchBot visits pages more sporadically based on search demand, while GPTBot follows a more systematic training data collection schedule. Understanding this difference is critical for website owners who want to manage their content’s visibility in AI search results versus AI training datasets.
Identifying OAI-SearchBot in your server logs is straightforward once you know what to look for. The bot identifies itself through a specific user agent string that appears in HTTP request headers whenever it visits your website. This user agent string contains version information and a link to OpenAI’s searchbot documentation, making it easily distinguishable from other crawlers. Website owners can monitor their server logs to track OAI-SearchBot visits and analyze crawling patterns. The bot typically operates from OpenAI’s IP address ranges, which can be cross-referenced with OpenAI’s published documentation for verification purposes. By understanding these technical identifiers, you can accurately distinguish OAI-SearchBot traffic from other bots and search engine crawlers in your analytics.
Mozilla/5.0 AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko); compatible; OAI-SearchBot/1.3; +https://openai.com/searchbot
Website owners have multiple methods to manage and control OAI-SearchBot access to their content. The most straightforward approach is through robots.txt configuration, a standard file placed in your website’s root directory that provides crawling instructions to all bots. You can use specific directives to allow or disallow OAI-SearchBot from accessing particular sections of your site. For websites that prefer not to appear in AI search results, blocking the bot entirely is a simple process. Beyond robots.txt, several additional control methods are available:
Here are practical examples of robots.txt configurations:
# Block OAI-SearchBot entirely
User-agent: OAI-SearchBot
Disallow: /
# Allow OAI-SearchBot only for specific directories
User-agent: OAI-SearchBot
Allow: /public/
Disallow: /private/
# Block OAI-SearchBot from specific file types
User-agent: OAI-SearchBot
Disallow: /*.pdf$
Disallow: /*.zip$

Allowing OAI-SearchBot to crawl your website can significantly enhance your content visibility in AI-powered search results, opening a new channel for organic traffic. As AI search becomes increasingly prevalent, appearing in SearchGPT and ChatGPT search results represents a valuable opportunity for websites to reach users who rely on these platforms. When OAI-SearchBot indexes your content, it makes your information available to be cited and referenced in AI search responses, potentially driving qualified traffic to your site. The bot respects source attribution, meaning when your content appears in search results, it typically includes proper credit and links back to your website. This creates a beneficial cycle: users discover your content through AI search, visit your site, and you gain both traffic and authority. Blocking OAI-SearchBot means missing out on this emerging traffic channel, particularly important for content creators, publishers, and businesses that want to maintain visibility across all search platforms.
Tracking OAI-SearchBot visits to your website provides valuable insights into how AI search engines interact with your content. Several analytics tools and monitoring services can help you identify and analyze OAI-SearchBot activity in real-time. Specialized services like Dark Visitors and xSeek offer dedicated bot monitoring capabilities, allowing you to see exactly when OAI-SearchBot crawls your site and which pages it accesses. Your standard web analytics platform, such as Google Analytics, can also be configured to identify OAI-SearchBot traffic by filtering for the specific user agent string. By analyzing crawl patterns, you can understand which content OAI-SearchBot prioritizes and optimize accordingly. Monitoring also helps you verify that your robots.txt directives are working as intended and that the bot respects your access controls. Regular monitoring enables you to make data-driven decisions about your content strategy and AI search visibility.
To maximize your content’s visibility and indexing by OAI-SearchBot, implement several optimization strategies that improve crawlability and content quality. Start with semantic HTML markup and proper heading structure (H1, H2, H3 tags) that clearly organize your content hierarchy, making it easier for the bot to understand your page’s structure and main topics. Ensure your content is easily accessible without requiring JavaScript rendering or complex interactions that might prevent the bot from reading your material. Implement schema markup and metadata tags that provide context about your content, helping OAI-SearchBot understand the nature and relevance of your information. Maintain factual accuracy and cite credible sources within your content, as AI search systems prioritize reliable, well-sourced information. Create and maintain an updated XML sitemap that lists all your important pages, helping OAI-SearchBot discover content more efficiently. Finally, ensure clear source attribution within your content—when you reference external sources, provide proper citations and links, which reinforces your credibility and helps the bot understand your content’s context and reliability.
OAI-SearchBot is designed exclusively for search functionality in ChatGPT and SearchGPT, indexing content to provide real-time search results. GPTBot, in contrast, is OpenAI's training crawler used to gather data for training and improving AI models. They serve different purposes, use different user agent strings, and operate independently.
Generally, no. Blocking OAI-SearchBot means missing out on visibility in AI-powered search results, which represents an emerging traffic channel. Allowing the bot to crawl your content can drive qualified traffic from users who discover your information through SearchGPT and ChatGPT search features.
You can block OAI-SearchBot by adding specific directives to your robots.txt file. Use 'User-agent: OAI-SearchBot' followed by 'Disallow: /' to block all access, or customize the disallowed paths to block only specific sections of your website.
Blocking OAI-SearchBot will reduce your visibility in AI-powered search engines. As AI search becomes increasingly prevalent, preventing indexing could significantly reduce your visibility in AI search results and organic traffic from users who prefer AI-powered search interfaces.
You can set up analytics tools like Dark Visitors or xSeek to monitor OAI-SearchBot visits in real-time. Alternatively, configure your standard web analytics platform to filter for the specific OAI-SearchBot user agent string in your server logs.
No. OAI-SearchBot only indexes publicly accessible content, similar to traditional search engines. It respects authentication barriers and doesn't attempt to access password-protected content or private pages behind login walls.
The user agent string for OAI-SearchBot is: 'Mozilla/5.0 AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko); compatible; OAI-SearchBot/1.3; +https://openai.com/searchbot'. This string appears in HTTP request headers and helps identify the bot in server logs.
OAI-SearchBot has a sporadic and infrequent crawl frequency compared to traditional search engine crawlers. Rather than maintaining a constantly-updated index, it focuses on retrieving relevant, current information when users perform searches, so crawl frequency varies based on search demand and content relevance.
Track how OAI-SearchBot and other AI crawlers index and cite your content across SearchGPT, ChatGPT, and other AI platforms. Get real-time insights into your AI search visibility.

Learn the key differences between GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot crawlers. Understand their purposes, crawl behaviors, and how to manage them for optimal content visi...
Learn what GPTBot is, how it works, and whether you should block it from your website. Understand the impact on SEO, server load, and brand visibility in AI sea...

Learn what GPTBot is, how it works, and whether you should allow or block OpenAI's web crawler. Understand the impact on your brand visibility in AI search engi...