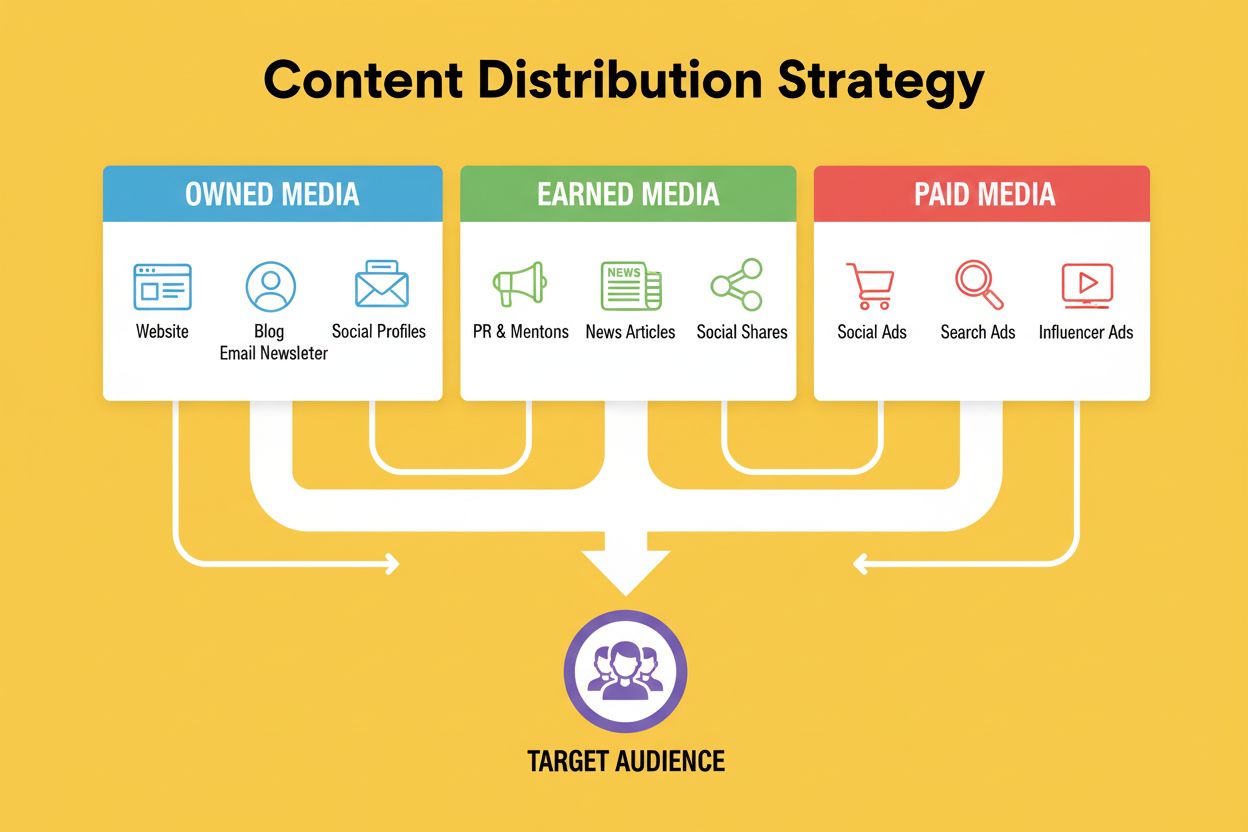
Content Distribution
Learn what content distribution is, explore owned, earned, and paid channels, and discover strategies to amplify your content across platforms including AI sear...

Omnichannel content is the strategic delivery of consistent, unified messaging and brand experiences across all customer touchpoints—including websites, mobile apps, email, social media, SMS, and physical stores—using a centralized content repository. It ensures customers receive the same core message and brand voice regardless of which channel they interact with, creating seamless and personalized experiences throughout their journey.
Omnichannel content is the strategic delivery of consistent, unified messaging and brand experiences across all customer touchpoints—including websites, mobile apps, email, social media, SMS, and physical stores—using a centralized content repository. It ensures customers receive the same core message and brand voice regardless of which channel they interact with, creating seamless and personalized experiences throughout their journey.
Omnichannel content is the strategic approach of delivering consistent, unified messaging and brand experiences across all customer touchpoints—including websites, mobile applications, email campaigns, social media platforms, SMS messaging, and physical retail locations. Unlike traditional multichannel approaches where each channel operates independently, omnichannel content leverages a centralized content repository to ensure customers receive the same core message, brand voice, and contextually relevant information regardless of which channel they interact with. This approach treats the entire customer journey as a seamless experience, where data, messaging, and personalization flow intelligently across all platforms. The fundamental principle is that customers should experience a unified brand identity that feels intentional and connected, whether they’re browsing on a smartphone, reading an email, visiting a physical store, or engaging on social media.
The concept of omnichannel content emerged from the evolution of retail and marketing strategies over the past two decades. Initially, businesses operated through isolated channels—a website here, a physical store there, email marketing in another silo. As consumer behavior shifted dramatically with the rise of mobile devices and social media, companies realized that customers no longer thought in terms of channels; they thought in terms of their relationship with the brand. According to research from CapitalOne, 73% of retail consumers are omnichannel shoppers, meaning they expect seamless transitions between channels. This fundamental shift in consumer expectations forced businesses to rethink their content strategies entirely. The rise of headless CMS platforms and API-first architectures made it technically feasible to manage content centrally and distribute it dynamically to any channel. Today, omnichannel content is no longer a competitive advantage—it’s a baseline expectation. Data from Worldmetrics shows that omnichannel retailers maintain an average retention rate of 89%, compared to just 33% for companies with weak omnichannel strategies. This dramatic difference underscores why forward-thinking organizations are investing heavily in unified content management systems and cross-channel orchestration capabilities.
The technical foundation of omnichannel content relies on several interconnected components working in harmony. At the core is a centralized content repository—often called the “single source of truth”—where all content is created, stored, and managed. This repository is typically powered by a headless CMS (Content Management System), which separates content management from presentation logic. Unlike traditional monolithic CMS platforms that tightly couple content with design, a headless CMS allows content to be delivered to any channel through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). When a marketer creates a product description in the centralized repository, that same content can be automatically formatted and delivered to the website, mobile app, email template, social media post, and in-store kiosk—each rendering it appropriately for that specific channel. Metadata and taxonomy play crucial roles in this architecture, allowing content to be tagged with attributes like audience segment, customer journey stage, locale, and content type. This rich metadata enables intelligent content reuse and personalization. For example, a single product description might be tagged as “beginner-friendly,” “summer collection,” and “mobile-optimized,” allowing the system to automatically select and adapt it for different customer segments and channels. API integrations connect the centralized repository to various marketing automation platforms, customer data platforms, analytics tools, and channel-specific systems, creating a fully orchestrated ecosystem where content flows seamlessly and data informs every decision.
| Aspect | Single-Channel Content | Multichannel Content | Omnichannel Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Channel Integration | One isolated channel | Multiple independent channels | All channels unified and synchronized |
| Data Approach | Siloed customer data | Fragmented data across channels | Unified customer view across all touchpoints |
| Messaging Strategy | One-size-fits-all | Same message repeated across channels | Personalized, contextually relevant per channel |
| Customer Experience | Limited, channel-specific | Disjointed, inconsistent | Seamless, consistent, interconnected |
| Content Management | Single repository | Multiple repositories per channel | Centralized repository with API distribution |
| Personalization | Minimal or none | Basic segmentation | Advanced, real-time, behavior-driven |
| Customer Retention Rate | ~40-50% | ~33% | ~89% |
| Implementation Complexity | Low | Medium | High (requires robust infrastructure) |
| Time-to-Market | Fast for single channel | Slow (content duplication) | Fast (content reuse across channels) |
| Technology Required | Basic CMS | Multiple platforms | Headless CMS + APIs + CDP + Marketing Automation |
| ROI Potential | Moderate | Good | Excellent (287% sales increase potential) |
| Scalability | Limited | Moderate | Highly scalable to new channels |
The business case for omnichannel content is compelling and well-documented. Research demonstrates that omnichannel campaigns generate 494% higher order rates compared to single-channel campaigns, a staggering difference that reflects the power of coordinated, consistent messaging. Customers who engage with brands across multiple touchpoints are 30% more valuable than single-channel customers, and they spend 3-4 times more on average. Beyond immediate sales metrics, omnichannel strategies boost incremental store visits by 80%, according to Google’s Consumer Insights, showing that consistent messaging drives offline engagement as well. The retention benefits are equally impressive: companies with strong omnichannel engagement strategies retain 89% of customers, compared to just 33% for weak strategies—a 170% difference. This retention advantage translates directly to revenue, as repeat customers contribute approximately 40% of total revenue despite representing a smaller portion of the customer base. Additionally, omnichannel personalization increases customer satisfaction by 20%, creating a virtuous cycle where satisfied customers become loyal advocates. For organizations managing content at scale, omnichannel approaches reduce production costs by eliminating content duplication and accelerating time-to-market for campaigns and product launches. When a new product launches, teams don’t need to create separate content for each channel; they create once and distribute everywhere, dramatically reducing time-to-market and associated costs.
Omnichannel content reaches its full potential when combined with sophisticated personalization capabilities powered by customer data. A single customer view—a unified profile containing all relevant customer information including purchase history, browsing behavior, preferences, location, and interaction history—enables truly personalized content delivery. When a customer visits a website after abandoning a shopping cart, the system knows this context and can deliver a personalized message referencing the abandoned items. When that same customer receives an email the next day, it references their specific abandoned products and offers a personalized incentive. When they visit the physical store, staff can access their digital history and provide informed, personalized service. This level of contextual relevance is only possible with omnichannel architecture that unifies data and orchestrates messaging. Behavioral targeting uses real-time customer actions to inform content delivery—if a customer is browsing winter coats on the website, they might receive an SMS with a winter collection offer. Localization ensures content is tailored to geographic location, cultural preferences, and language. Contextual relevance means delivering content that aligns with the customer’s current situation or needs. For example, a customer browsing on mobile at 9 PM might receive different messaging than one browsing on desktop at 2 PM. This sophisticated personalization is what transforms omnichannel content from a nice-to-have into a revenue-driving necessity.
Different channels have unique characteristics that require thoughtful content adaptation within an omnichannel framework. Email marketing benefits from longer-form content, detailed product information, and personalized recommendations based on purchase history. Social media demands shorter, more visual, and more conversational content that encourages engagement and sharing. Mobile apps require concise, action-oriented content optimized for small screens and touch interaction. SMS messaging necessitates ultra-concise, time-sensitive content that drives immediate action. In-store experiences can leverage digital touchpoints like interactive kiosks to bridge online and offline, displaying personalized recommendations and inventory information. Website content should be comprehensive, SEO-optimized, and designed for discovery and detailed product exploration. The beauty of omnichannel content is that a single product description, blog post, or promotional message can be intelligently adapted for each channel without requiring separate creation. A headless CMS enables this by storing content in a channel-agnostic format and allowing each channel’s interface to request and format content according to its specific requirements. For instance, a product’s full description might be 500 words on the website, 150 words in email, 50 words on social media, and 25 words in SMS—all derived from the same source content through intelligent adaptation rules.
Implementing omnichannel content at scale presents significant challenges that organizations must navigate strategically. Fragmented customer data remains one of the most persistent obstacles—many organizations have customer information scattered across legacy systems, email platforms, CRM systems, and analytics tools that don’t communicate with each other. Solving this requires investing in a customer data platform (CDP) or unified data warehouse that can ingest, unify, and activate customer data across all systems. Content consistency at scale becomes increasingly difficult as organizations grow and add new channels, team members, and content types. This is addressed through robust content governance frameworks that include version control, approval workflows, style guides, and automated consistency checks. Technology integration complexity arises when trying to connect legacy monolithic CMS platforms with modern marketing tools—this is why headless CMS adoption is accelerating, as these platforms are designed for seamless API-based integration. Team alignment and organizational silos often prove more challenging than technology issues; breaking down silos between marketing, sales, product, and customer service requires clear governance, shared KPIs, and collaborative tools. Measuring success across channels with varying metrics and attribution models requires implementing unified marketing measurement frameworks that combine person-level insights with aggregate historical trends. Lack of omnichannel expertise within organizations is addressed through training programs, hiring specialists, and partnering with experienced agencies or consultants.
The omnichannel content landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by advances in artificial intelligence, changing consumer expectations, and the emergence of new channels and technologies. AI-powered content generation is becoming increasingly sophisticated, enabling marketers to create variations of content for different channels and segments at scale. Predictive personalization uses machine learning to anticipate customer needs and deliver proactive, relevant content before customers even realize they need it. Voice and conversational interfaces are creating new channels for content delivery—smart speakers, chatbots, and voice assistants require content to be structured and optimized for conversational interaction. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are emerging as new channels where omnichannel content strategies must extend, requiring immersive content experiences that maintain brand consistency. Real-time decisioning powered by AI enables content to be dynamically optimized in milliseconds based on real-time customer context, device, location, and behavior. Privacy-first personalization is becoming critical as third-party cookies disappear and regulations like GDPR and CCPA restrict data usage—organizations must deliver personalization using first-party data and privacy-compliant methods. The integration of omnichannel content with AI monitoring platforms like AmICited represents a new frontier, where brands can track how their consistent messaging appears across AI-generated responses in systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude. As AI systems become primary discovery mechanisms for consumers, ensuring that omnichannel content is properly indexed, cited, and represented in AI responses will become as important as traditional search engine optimization. Organizations that master omnichannel content while simultaneously optimizing for AI visibility will gain significant competitive advantages in the emerging AI-driven commerce landscape.
In an increasingly fragmented digital landscape where customers interact with brands across dozens of touchpoints, omnichannel content has evolved from a competitive differentiator to a fundamental business requirement. The data is unambiguous: organizations implementing omnichannel strategies achieve dramatically higher retention rates (89% vs. 33%), generate significantly more revenue per customer, and build stronger brand loyalty. The technical infrastructure to support omnichannel content—including headless CMS platforms, APIs, customer data platforms, and marketing automation systems—has matured to the point where implementation is feasible for organizations of all sizes. The challenge is no longer technological but organizational, requiring cross-functional alignment, clear governance, and commitment to customer-centric thinking. As AI systems become increasingly important discovery mechanisms and as platforms like AmICited enable brands to monitor their presence in AI-generated responses, the importance of consistent, high-quality omnichannel content will only increase. Brands that invest in unified content strategies, maintain consistency across channels, and optimize for both human and AI audiences will thrive in the next era of digital commerce and customer engagement.
Omnichannel content treats all channels as an integrated ecosystem where messaging, data, and customer experiences are unified and synchronized. Multichannel content, by contrast, delivers content across multiple independent channels that often operate in silos without integration. With omnichannel, customers experience consistent brand voice and context as they move between channels, while multichannel may result in disjointed or repetitive messaging. Omnichannel is customer-centric, whereas multichannel is channel-centric.
Omnichannel content strategies deliver significant business benefits including increased customer retention (89% retention rate vs. 33% for weak strategies), higher conversion rates (494% higher order rates than single-channel campaigns), and improved customer lifetime value. Customers engaging across multiple touchpoints spend 3-4 times more than single-channel customers. Additionally, businesses reduce content duplication, accelerate time-to-market, and build stronger brand loyalty through consistent messaging and personalized experiences.
AI is essential for omnichannel content success, enabling real-time analysis of vast customer data across channels, automating content personalization, and orchestrating campaigns that adapt to individual customer behaviors. AI-powered systems consolidate fragmented data into a single customer view, predict customer preferences, optimize content delivery timing, and provide actionable insights for continuous strategy refinement. Without AI, manually managing consistent, personalized experiences across multiple channels at scale would be virtually impossible for modern enterprises.
Brands ensure consistency by implementing a centralized content repository (single source of truth), establishing clear brand guidelines and style standards, using version control and approval workflows, and leveraging headless CMS platforms with API-first architecture. Regular content audits, automated synchronization tools, and cross-departmental collaboration frameworks help maintain consistency. Metadata tagging and content categorization systems make it easier to manage and reuse content components across channels while maintaining brand integrity.
Omnichannel content is fundamentally aligned with customer journey mapping, as it requires understanding how customers interact across touchpoints at each stage (awareness, consideration, decision, post-purchase). By mapping the customer journey, brands identify optimal channels and content types for each stage, ensuring messaging is contextually relevant and timely. This alignment enables personalized content delivery that guides customers seamlessly through their journey, improving engagement and conversion rates at every touchpoint.
Omnichannel content consistency is critical for brand monitoring in AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. When brands maintain unified messaging across channels, AI systems can more reliably cite and reference brand information, improving brand visibility in AI-generated responses. Inconsistent content across channels creates confusion in AI training data and reduces citation accuracy. Platforms like AmICited track how brand content appears across AI responses, making omnichannel consistency essential for maintaining brand authority and trustworthiness in AI-driven search results.
Key challenges include managing fragmented customer data across siloed systems, ensuring content consistency at scale, integrating legacy systems with modern platforms, and measuring success across diverse channels with varying metrics. Organizations often struggle with team alignment, lack of omnichannel expertise, and the complexity of personalizing content for different segments and channels simultaneously. Additionally, connecting online and offline data, maintaining real-time inventory visibility, and attributing conversions to specific touchpoints remain significant obstacles that require robust technology infrastructure and cross-functional collaboration.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn what content distribution is, explore owned, earned, and paid channels, and discover strategies to amplify your content across platforms including AI sear...
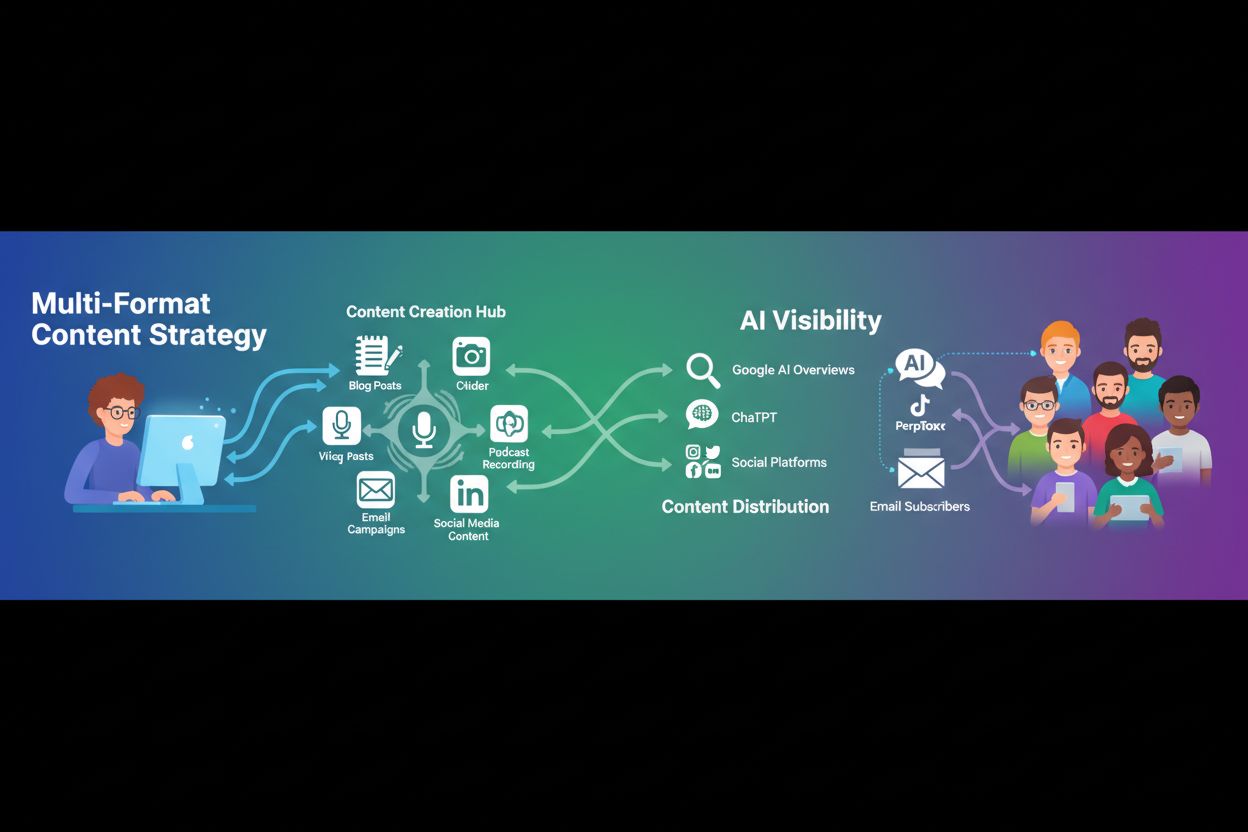
Learn what multi-format content strategy is and how to create content in multiple formats (text, video, audio) for comprehensive AI visibility. Discover how to ...
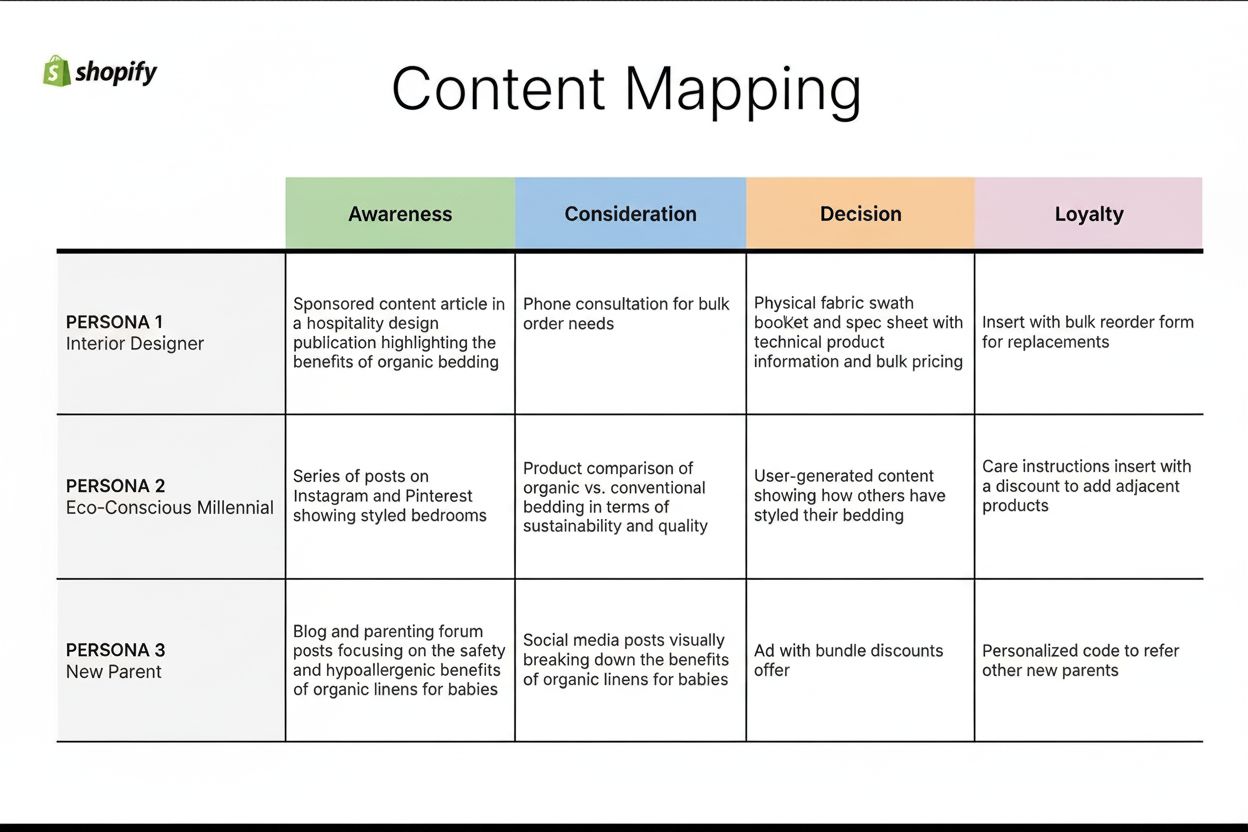
Learn what content mapping is and how aligning content with buyer journey stages drives engagement, conversions, and customer loyalty. Comprehensive guide for B...