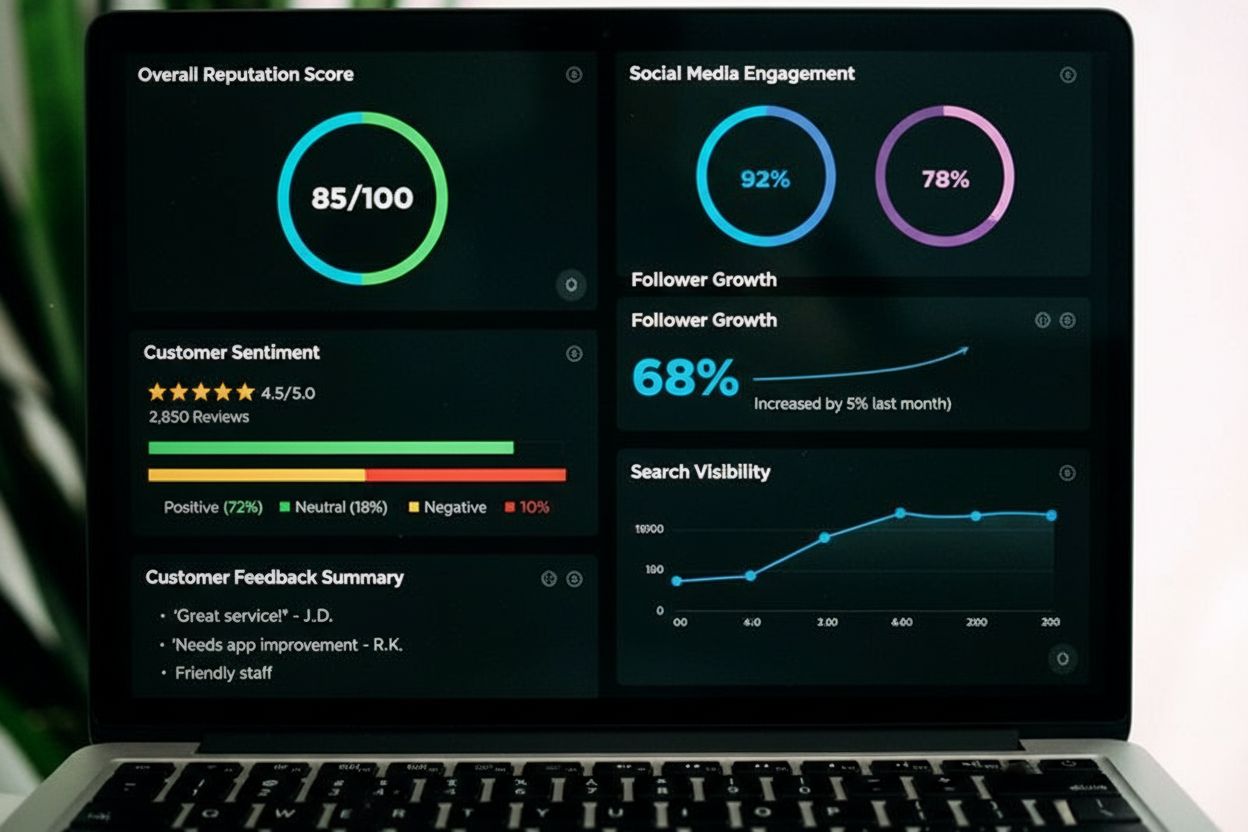
Reputation Score
Learn what a reputation score is, how it's calculated, and why it matters for brand monitoring. Understand the key factors that influence online reputation metr...
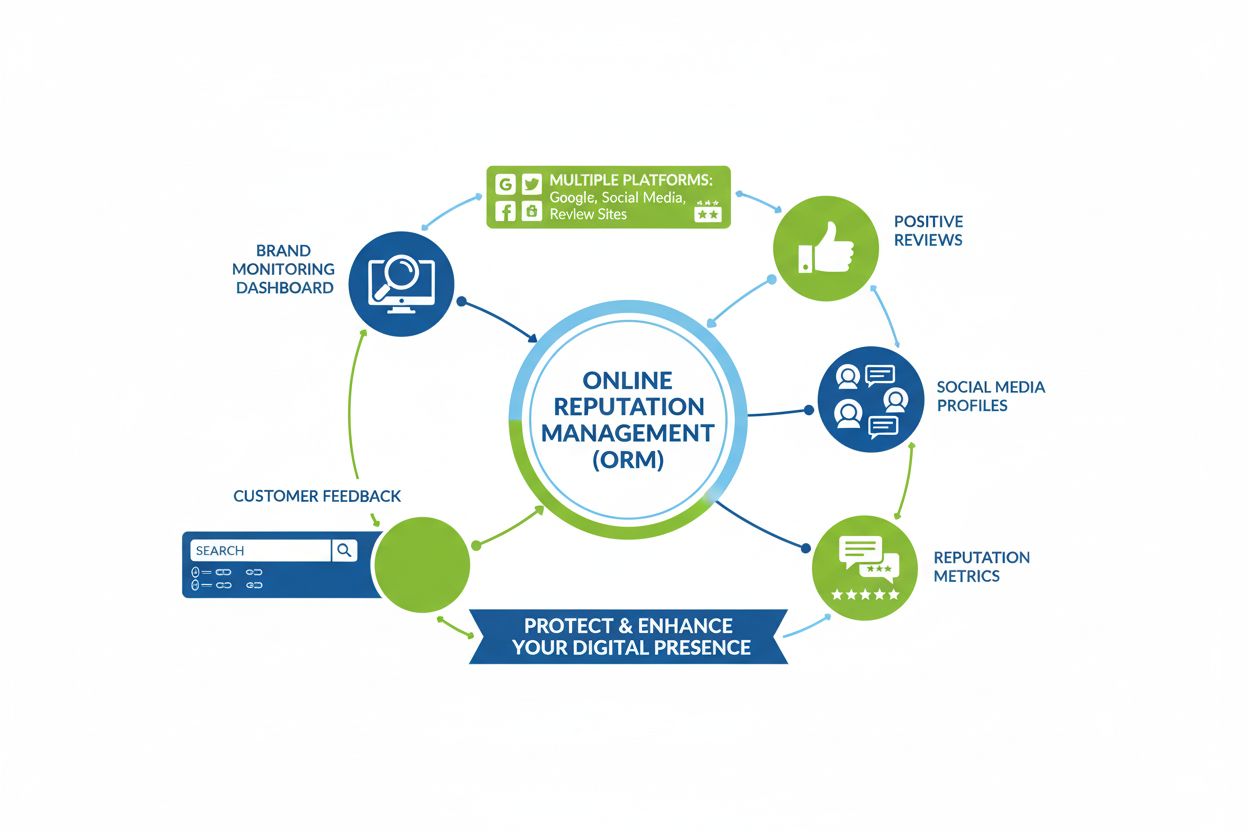
Online Reputation Management (ORM) is the practice of monitoring, influencing, and improving how a brand, individual, or organization is perceived online across search engines, social media, review platforms, and other digital channels. ORM involves managing both owned and earned content to ensure positive search results, address negative feedback, and maintain a favorable digital presence that reflects brand values and builds customer trust.
Online Reputation Management (ORM) is the practice of monitoring, influencing, and improving how a brand, individual, or organization is perceived online across search engines, social media, review platforms, and other digital channels. ORM involves managing both owned and earned content to ensure positive search results, address negative feedback, and maintain a favorable digital presence that reflects brand values and builds customer trust.
Online Reputation Management (ORM) is the strategic practice of monitoring, influencing, and improving how a brand, individual, or organization is perceived across digital channels, including search engines, social media platforms, review sites, forums, and increasingly, AI-powered search systems. ORM encompasses all activities designed to ensure that when people search for a company or individual online, they encounter positive, accurate, and trustworthy information that reflects the brand’s values and builds customer confidence. The primary goal of ORM is to create and maintain a favorable digital presence that attracts customers, retains talent, and protects against reputational damage in an increasingly interconnected online world.
The importance of ORM cannot be overstated in today’s digital landscape. Research shows that 58% of adults in the United States consider a company’s reputation a major factor when deciding whether to purchase a product or service, with an additional 33% citing it as a minor factor. This means that nearly all consumer purchasing decisions are influenced by online perception. Furthermore, 93% of consumers report that online reviews directly impact their buying decisions, and 90% of consumers are more likely to frequent a business if it responds to all reviews, both positive and negative. The stakes are high: businesses with just one negative article ranking online risk losing over 20% of prospective customers, while those with four or more negative articles can experience losses of up to 70%.
ORM is fundamentally different from simply having a website or social media presence. It requires a coordinated, multi-channel approach that addresses the entire digital ecosystem where a brand exists. This includes not only what a company publishes about itself but also what customers, competitors, media outlets, and third-party platforms say about the brand. In the modern era, ORM has expanded beyond traditional search results to include monitoring how brands appear in AI-generated responses from systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude, representing a new frontier in reputation management.
Online Reputation Management emerged as a distinct discipline in the early 2000s as the internet became central to how people research businesses and individuals. Initially, ORM focused primarily on managing search engine results and addressing negative content through search engine optimization (SEO) techniques. However, the landscape has evolved dramatically with the rise of social media platforms, review aggregation sites, and most recently, generative AI systems.
The evolution of ORM can be traced through several key phases. In the early 2000s, ORM was largely reactive—companies would respond to negative reviews or press coverage after the fact. By the 2010s, ORM became more proactive, with businesses actively creating positive content, managing social media, and monitoring brand mentions in real-time. The introduction of platforms like Google My Business, Yelp, and TripAdvisor made review management a central component of ORM strategy. Today, ORM has become increasingly sophisticated, incorporating artificial intelligence, sentiment analysis, and predictive analytics to anticipate reputation risks before they escalate.
A pivotal moment in ORM history was the 2023 Google Core Update, which significantly increased the visibility of user-generated content (UGC) and forum discussions in search results. This update elevated the importance of platforms like Reddit and Quora, where authentic user conversations about brands now rank prominently. Additionally, the 2024 Google partnership with Reddit further cemented the importance of monitoring and managing brand mentions on community platforms. Most recently, the rise of AI search engines and AI Overviews has created an entirely new dimension of ORM, requiring brands to ensure their content is authoritative enough to be cited by AI systems.
The statistics underscore this evolution: 95% of people read online reviews before making a purchase, and 98% of people report reading online reviews about local businesses. Over 80% of consumers are likely to leave a positive review if a business turns a negative experience into a positive one, demonstrating that ORM is not just about damage control but about building genuine customer relationships. The fact that 83% of customers feel more loyal to brands that respond to complaints shows that active engagement is now a core expectation.
Effective ORM operates through a combination of monitoring, content creation, engagement, and optimization strategies. Understanding these components is essential for implementing a successful reputation management program.
Monitoring and Assessment forms the foundation of any ORM strategy. Before taking action, organizations must understand their current online reputation across all relevant platforms. This involves tracking brand mentions on search engines, social media platforms, review sites, forums, and increasingly, AI search systems. Tools like Google Alerts, Mention, Brandwatch, and specialized platforms like Brand Radar enable real-time monitoring of brand mentions. Monitoring also includes sentiment analysis—determining whether mentions are positive, negative, or neutral—and competitive analysis to understand how a brand’s reputation compares to competitors. Over 75% of all online reviews are left on Google, making Google monitoring particularly critical, though a comprehensive approach requires monitoring across multiple platforms.
Content Creation and Promotion is the second pillar of ORM. By creating high-quality, positive content about a brand or individual, organizations can push down negative content in search results and establish authority. This includes blog posts, videos, testimonials, case studies, whitepapers, and social media content. The goal is not to hide negative content but to ensure that positive, authoritative content ranks higher and is more visible to potential customers. Search engine optimization (SEO) plays a crucial role here—optimizing content for relevant keywords ensures that positive material appears prominently in search results. Research shows that 68% of online experiences begin with a search engine, making search visibility paramount.
Review Management has become increasingly important as reviews now dominate consumer decision-making. This involves actively requesting reviews from satisfied customers, responding to all reviews (both positive and negative), and managing review platforms. The data is compelling: 49% of consumers need at least a four-star rating before using a business, and 87% of consumers would not consider a business with an average rating below 3 stars. Interestingly, purchasing likelihood increases for companies with ratings between 4.0 to 4.7 stars but actually decreases for companies approaching a perfect 5-star rating, likely because perfect ratings appear inauthentic. Responding to reviews is critical—90% of consumers are more likely to frequent a business if it responds to all reviews.
Social Media Management represents another critical component. With over 5 billion people on social media and 77% of businesses leveraging social media to reach customers, social platforms are essential for reputation management. This includes creating engaging content, responding to comments and messages promptly, monitoring brand mentions and hashtags, and engaging authentically with followers. Facebook has overtaken Yelp in 2024 as a source for consumer reviews, and 34% of consumers turn to Instagram for reviews, highlighting the importance of active social media presence. The challenge is that social media is real-time and public—negative comments are visible to everyone, making rapid, professional responses essential.
Negative Content Management addresses how to handle damaging information. While some negative content can be removed (particularly if it’s false, defamatory, or violates platform terms), much cannot. The strategy then becomes content displacement—creating and promoting so much positive content that negative material is pushed down in search results. Additionally, responding professionally to negative reviews and feedback can mitigate damage and even build credibility. Research shows that negative news is three times more impactful than positive news, making this component particularly important.
| Aspect | Online Reputation Management (ORM) | Search Engine Optimization (SEO) | Public Relations (PR) | Social Media Marketing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Managing overall digital perception across all platforms | Ranking specific websites/pages in search results | Building public image through media relations | Engagement and community building on social platforms |
| Scope | Entire digital ecosystem (search, social, reviews, forums, AI) | Search engine results pages (SERPs) | Both online and offline public perception | Social media platforms only |
| Goal | Fill first page with positive content; displace negative results | Rank #1 for target keywords | Secure media coverage and manage public narrative | Build audience, drive engagement, foster loyalty |
| Timeframe | Ongoing, long-term reputation building | Ongoing, continuous optimization | Event-driven or ongoing brand building | Real-time engagement and content posting |
| Key Metrics | Brand sentiment, review ratings, search visibility, mention volume | Keyword rankings, organic traffic, click-through rate | Media mentions, brand awareness, sentiment | Followers, engagement rate, reach, conversions |
| Tools Used | Google Alerts, Mention, Brandwatch, ReputationDefender, Brand Radar | SEMrush, Ahrefs, Moz, Google Search Console | Media databases, PR software, press release distribution | Hootsuite, Buffer, Sprout Social, Meta Business Suite |
| Content Type | Diverse (reviews, articles, videos, social posts, testimonials) | Website content, blog posts, technical optimization | Press releases, media pitches, thought leadership | Social media posts, stories, reels, live content |
| Audience | Potential customers, employees, investors, general public | Search engine users looking for specific information | Media, journalists, general public | Existing and potential followers/customers |
| Crisis Response | Rapid monitoring and response to negative mentions | Long-term content strategy to outrank negative results | Immediate media outreach and statement preparation | Real-time community management and transparency |
Implementing an effective ORM program requires understanding the technical mechanisms through which online reputation is built and maintained. Modern ORM relies heavily on data aggregation, sentiment analysis, and real-time alerting systems.
Search Engine Visibility remains the cornerstone of ORM. When someone searches for a brand name, the results that appear on the first page of Google significantly influence perception. Research indicates that 59% of people trust search engines the most when researching a business, making search visibility critical. ORM professionals use tools to track which results appear for branded searches and work to ensure that positive, authoritative content ranks prominently. This involves optimizing website content, building high-quality backlinks, and creating content on authoritative platforms that rank well for branded keywords.
Review Aggregation and Management has become increasingly sophisticated. Platforms now aggregate reviews from multiple sources—Google, Facebook, Yelp, TripAdvisor, industry-specific sites—into centralized dashboards. This allows businesses to monitor all reviews in one place, respond efficiently, and identify trends in customer feedback. The data shows that 65% of people leave reviews if asked to by a business, with email requests, in-person requests, and requests included with invoices yielding the highest response rates. Automated review request systems can significantly increase review volume and improve ratings.
Social Media Listening involves monitoring conversations about a brand across social platforms. This goes beyond simply tracking mentions—it includes analyzing sentiment, identifying influencers, detecting emerging issues, and understanding customer sentiment in real-time. Tools use natural language processing (NLP) to determine whether mentions are positive, negative, or neutral, and to identify key themes in customer feedback. With over 80% of social media users reporting that social media increases accountability for businesses, this real-time visibility is invaluable.
AI-Powered Monitoring represents the newest frontier in ORM. As generative AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews become primary sources of information, brands must monitor how they appear in AI-generated responses. These systems cite and reference online content, making it essential for brands to ensure their content is authoritative, accurate, and well-optimized for AI citation. Tools like Brand Radar specifically track brand mentions across AI search engines, representing a significant evolution in ORM practice.
The business impact of ORM is substantial and measurable. Organizations that invest in reputation management see tangible improvements across multiple metrics.
Customer Acquisition and Conversion are directly influenced by online reputation. Over 90% of people report that positive reviews make them more likely to frequent a business, and 86% feel that online business reviews are as trustworthy as personal recommendations from friends or family. This means that a strong online reputation can function as a powerful marketing tool, essentially providing third-party validation that is often more persuasive than company-created marketing. Conversely, 87% of consumers report that they will reverse a purchase decision after reading negative news or reviews about a business online, demonstrating the significant downside risk of poor reputation management.
Brand Loyalty and Retention are strengthened through active reputation management. 83% of customers feel more loyal to brands that respond to and resolve their complaints, meaning that reputation management is not just about acquiring new customers but about retaining existing ones. By demonstrating responsiveness and commitment to customer satisfaction, brands build emotional connections that increase lifetime customer value. Additionally, approximately 90% of consumers report that they will remain loyal to brands that share their values, highlighting the importance of authentic brand representation online.
Talent Acquisition and Retention are increasingly influenced by online reputation. Nearly 70% of prospective employees report that they would reject a job offer from a company with a bad reputation, even if they were unemployed. This means that reputation management directly impacts a company’s ability to attract and retain top talent. Furthermore, approximately 90% of employers look at the social media presence of prospective employees, and 80% of employers have rejected a candidate based on what they found online, showing that reputation management is a two-way street affecting both employer and employee brands.
Financial Performance is ultimately the most important metric. Presenting your brand consistently across all platforms can increase revenue by up to 23%, and businesses with strong online reputations command premium pricing and customer loyalty. Conversely, businesses with just one negative article ranking online risk losing over 20% of prospective customers, with losses potentially reaching 70% for businesses with four or more negative articles. The financial stakes of reputation management are therefore enormous.
Different platforms require different ORM strategies, and understanding platform-specific dynamics is essential for comprehensive reputation management.
Google and Search Results remain the primary focus of ORM. With over 95% of people going online to learn more about businesses and 68% of online experiences beginning with a search engine, Google visibility is paramount. ORM professionals focus on ensuring that branded searches return positive results, that the company’s official website ranks prominently, and that negative content is displaced by positive material. Google My Business management is critical for local businesses, as it controls how a business appears in local search results and Google Maps.
Review Platforms like Google Reviews, Yelp, Facebook, and TripAdvisor require active management. Almost 75% of all online reviews are left on Google, making Google Reviews management particularly important. However, different platforms have different audiences and dynamics. Facebook has overtaken Yelp in 2024 as a source for consumer reviews, and 34% of consumers turn to Instagram for reviews, indicating that multi-platform review management is necessary.
Social Media Platforms each have unique characteristics. Facebook maintains the top spot with over 3 billion monthly active users, followed by YouTube, Instagram, WhatsApp, and TikTok. Different age groups prefer different platforms—nearly 85% of people between ages 18-29 use at least one social media site, a number that decreases with age. ORM strategies must account for these demographic differences and platform-specific norms.
Forums and Community Platforms have become increasingly important for reputation management. Following the August 2023 Google Core Update, which increased visibility of user-generated content, and the 2024 Google partnership with Reddit, forum discussions now rank prominently in search results. Reddit has roughly 1.22 billion monthly active users, and 21% of consumers report looking to Reddit for reviews—a 6% increase from 2023. Quora has roughly 400 million monthly active users and also ranks prominently in search results. Monitoring and engaging on these platforms is now essential for comprehensive ORM.
AI Search Engines represent the newest frontier. As ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude become primary sources of information, brands must ensure their content is authoritative enough to be cited by these systems. This requires creating high-quality, well-researched content that AI systems will reference. Tools like Brand Radar now track brand mentions across AI search engines, representing a significant evolution in ORM practice.
Successful ORM requires a structured approach combining strategy, execution, and continuous optimization.
The field of Online Reputation Management is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancement and changing consumer behavior. Several trends are shaping the future of ORM.
AI and Generative Search are fundamentally changing how reputation is built and perceived. As AI systems become primary sources of information, the definition of “online reputation” is expanding beyond traditional search results to include how brands appear in AI-generated responses. This requires a shift in ORM strategy—instead of just optimizing for search engines, brands must now ensure their content is authoritative enough for AI systems to cite. This represents a significant evolution from traditional SEO-focused ORM to what some call Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). The implications are substantial: brands that don’t appear in AI responses may become invisible to users who rely on AI for information.
Real-Time Reputation Management is becoming increasingly important as social media and AI systems operate in real-time. The ability to detect and respond to reputation threats within minutes rather than hours is becoming a competitive advantage. This is driving investment in AI-powered monitoring tools that can detect emerging issues and alert teams immediately. Additionally, AI-powered response systems are being developed to help brands respond to reviews and social media comments more efficiently.
Privacy and Data Protection are becoming increasingly important considerations in ORM. As regulations like GDPR and CCPA become more stringent, ORM professionals must balance reputation management with privacy concerns. This includes understanding what content can be removed, how to handle personal data, and how to comply with regulations while managing reputation.
Authenticity and Transparency are increasingly valued by consumers. Over 90% of consumers report that they will remain loyal to brands that share their values, and 83% of customers feel more loyal to brands that respond to complaints. This suggests a shift away from purely promotional ORM toward more authentic, transparent reputation management that acknowledges mistakes and demonstrates genuine commitment to customer satisfaction. Brands that attempt to hide negative feedback or present inauthentic images are increasingly called out on social media and forums.
Integration with Business Intelligence is creating more sophisticated ORM strategies. By integrating reputation data with customer data, sales data, and operational data, organizations can gain deeper insights into how reputation impacts business performance. This allows for more targeted, data-driven ORM strategies that directly tie reputation management to business outcomes.
The future of ORM will likely be characterized by greater sophistication, real-time responsiveness, AI integration, and a focus on authentic, transparent brand representation. Organizations that adapt to these changes and invest in comprehensive reputation management will be better positioned to attract customers, retain talent, and build sustainable competitive advantages in an increasingly digital world.
Online Reputation Management is critical because 93% of consumers say online reviews impact their buying decisions, and 58% of adults consider a company's reputation a major factor when deciding whether to purchase. A positive online reputation increases customer trust, improves search visibility, attracts qualified talent, and can increase revenue by up to 23% through consistent brand presentation. Conversely, negative content can cause businesses to lose up to 70% of prospective customers, making proactive ORM essential for long-term success.
While both ORM and PR aim to portray a company positively, they operate differently. PR is an external-facing strategy that uses media relations, advertising, and strategic communications to build public perception both online and offline. ORM is more internally focused and digital-centric, concentrating on monitoring and managing online mentions, search results, reviews, and social media presence. ORM specifically targets how a brand appears in search engines and online platforms, whereas PR takes a broader approach to overall public perception.
An effective ORM strategy combines four types of media: owned media (company websites, blogs, social content), paid media (sponsored posts, advertising), earned media (PR, influencer partnerships, media coverage), and shared media (community engagement, partnerships). It also includes monitoring customer reviews and responding promptly, creating positive content to rank well in search results, managing social media actively, optimizing for SEO, and using monitoring tools to track brand mentions across platforms. Consistency across all channels is essential for building a cohesive positive reputation.
Responding to negative reviews with empathy and professionalism is crucial—83% of customers feel more loyal to brands that respond to complaints. Best practices include responding quickly, acknowledging the customer's concern, apologizing if appropriate, offering a solution, and taking the conversation offline when necessary. Research shows that turning a negative experience into a positive one through effective response can actually increase customer loyalty. Never delete or ignore negative reviews; instead, use them as opportunities to demonstrate excellent customer service and commitment to improvement.
Online reviews are fundamental to ORM because 95% of people read reviews before making purchases, and 90% of consumers are more likely to frequent a business if it responds to all reviews. Nearly 75% of all online reviews are left on Google, making review management critical. Businesses with ratings between 4.0-4.7 stars see higher purchasing likelihood than those with perfect 5-star ratings. Actively requesting reviews from satisfied customers, monitoring review sites, and responding to feedback helps businesses maintain positive ratings and improve search visibility.
As AI search engines and AI Overviews become more prominent, ORM is evolving to include monitoring brand mentions in AI-generated responses. Tools now track how brands appear in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude responses. This represents a new frontier in ORM, as AI systems cite and reference online content, making it essential for brands to maintain authoritative, high-quality content that AI systems will cite. Monitoring AI mentions helps brands understand how their reputation is being shaped by generative AI systems.
Popular ORM tools include Google Alerts for basic monitoring, Mention and Brandwatch for comprehensive social listening, Sprout Social for social media management, BuzzSumo for content analysis, and specialized platforms like ReputationDefender and Vendasta. Newer tools like Brand Radar track mentions across AI search engines. These platforms offer features like sentiment analysis, real-time alerts, competitor monitoring, review aggregation, and automated response suggestions. Choosing the right tool depends on business size, budget, and specific monitoring needs.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn what a reputation score is, how it's calculated, and why it matters for brand monitoring. Understand the key factors that influence online reputation metr...
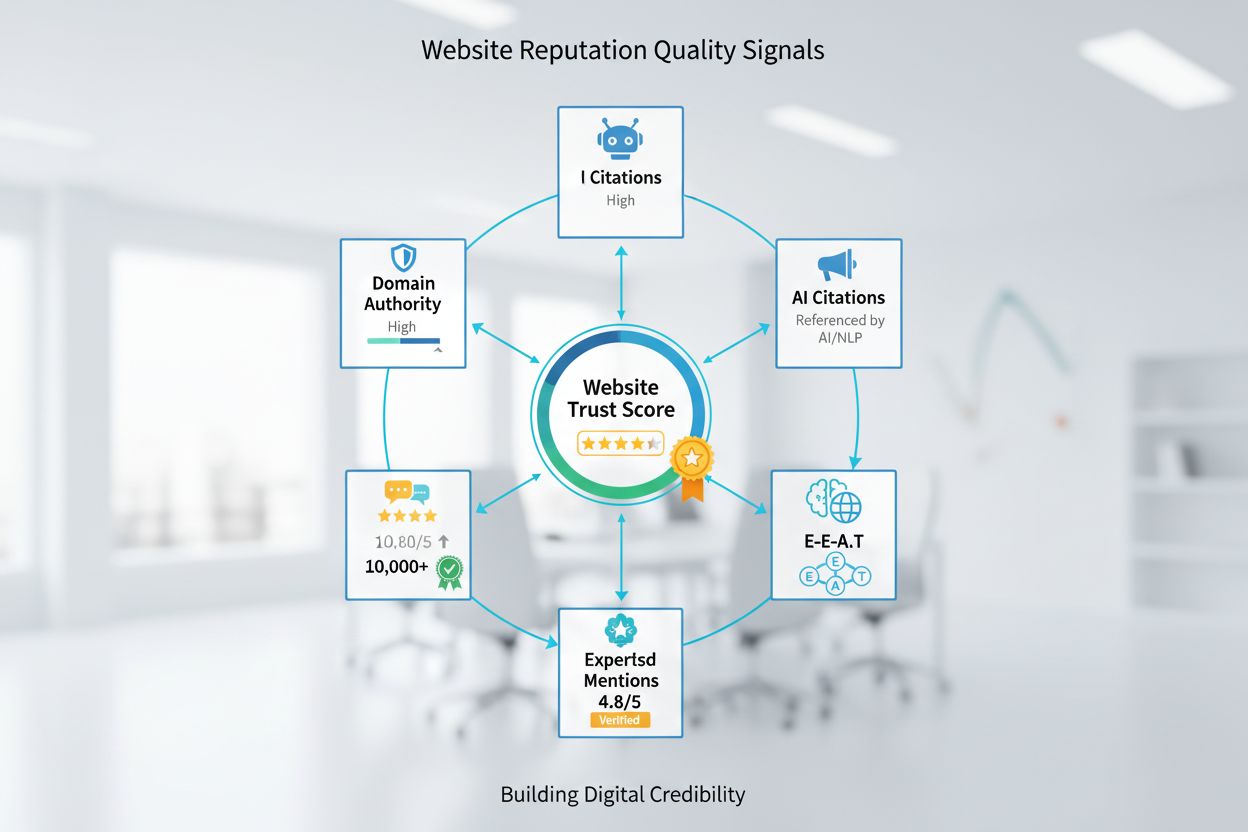
Website reputation is the collective perception of a site's quality and trustworthiness. Learn how domain authority, reviews, E-E-A-T, and AI citations shape on...
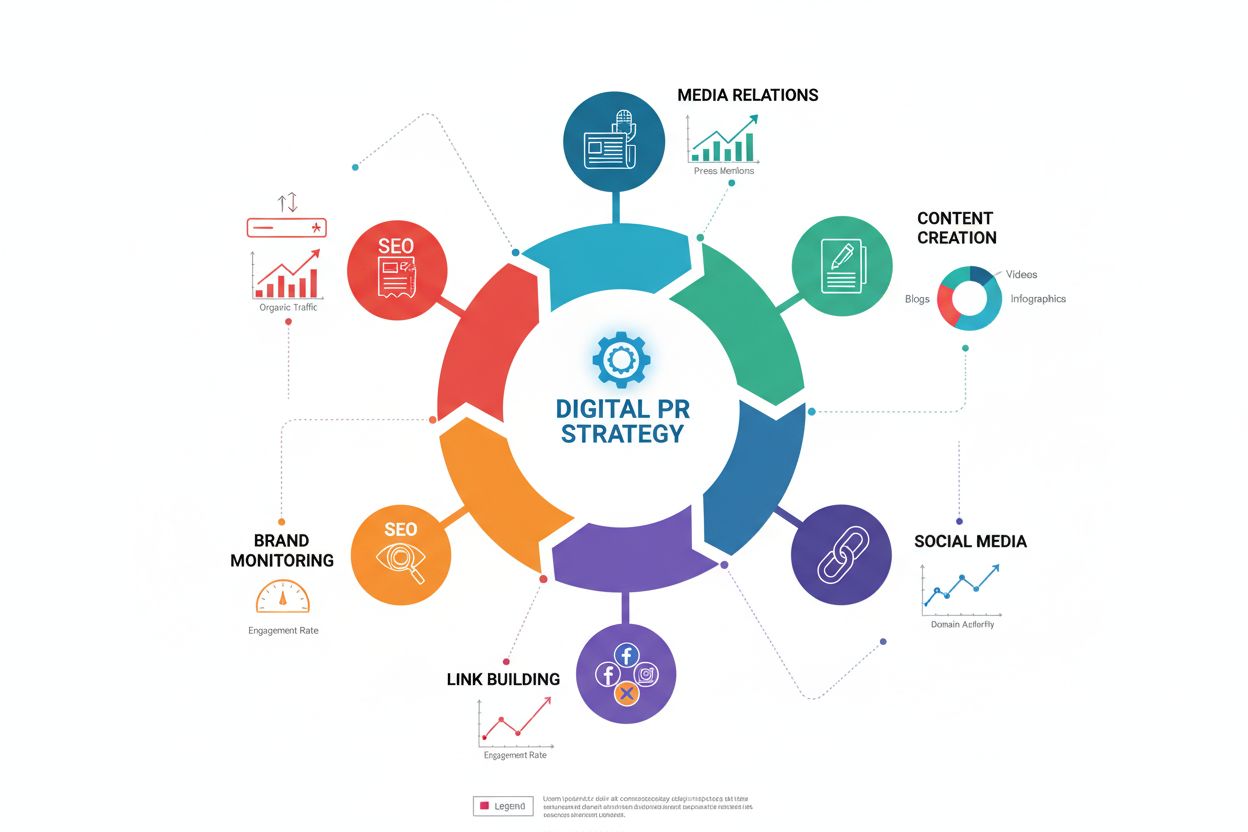
Digital PR is the strategic use of online media and trusted third parties to build brand reputation and visibility. Learn how digital PR strategies drive SEO, b...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.