Open Graph Image
Learn what Open Graph Images are, their technical specifications, platform requirements, and how they boost social media engagement and click-through rates acro...
The Open Graph Protocol is a Facebook-developed specification that enables web pages to become rich objects in social graphs by embedding standardized meta tags in HTML. These tags control how content appears when shared on social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and other networks.
The Open Graph Protocol is a Facebook-developed specification that enables web pages to become rich objects in social graphs by embedding standardized meta tags in HTML. These tags control how content appears when shared on social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and other networks.
The Open Graph Protocol is a standardized specification developed by Facebook that enables web pages to become rich objects within social graphs by embedding structured metadata in HTML. Specifically, Open Graph uses meta tags placed in a webpage’s <head> section to provide social media platforms with standardized information about content, including titles, descriptions, images, and URLs. When a user shares a link on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, or other social networks, these platforms use Open Graph meta tags to extract and display a rich preview of the content rather than relying on auto-generated summaries. The protocol was inspired by existing technologies including Dublin Core, RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes), Microformats, and link-rel canonical standards, creating a unified approach to social content representation.
The Open Graph Protocol was originally created by Facebook in 2010 as a solution to the fragmentation problem in social media metadata standards. Before its introduction, different social platforms used proprietary methods to extract and display shared content, resulting in inconsistent and often poor-quality previews. Facebook recognized that developers needed a single, unified standard to implement rather than managing multiple competing specifications. The protocol was designed with developer simplicity as a core principle, making it easy for webmasters to add just a few lines of code to gain control over social sharing appearance. According to the 2024 Web Almanac by HTTP Archive, Open Graph adoption has reached 64% of all web pages, making it one of the most widely implemented structured data standards globally. This widespread adoption reflects the protocol’s effectiveness and the critical importance of social media sharing in modern digital marketing strategies.
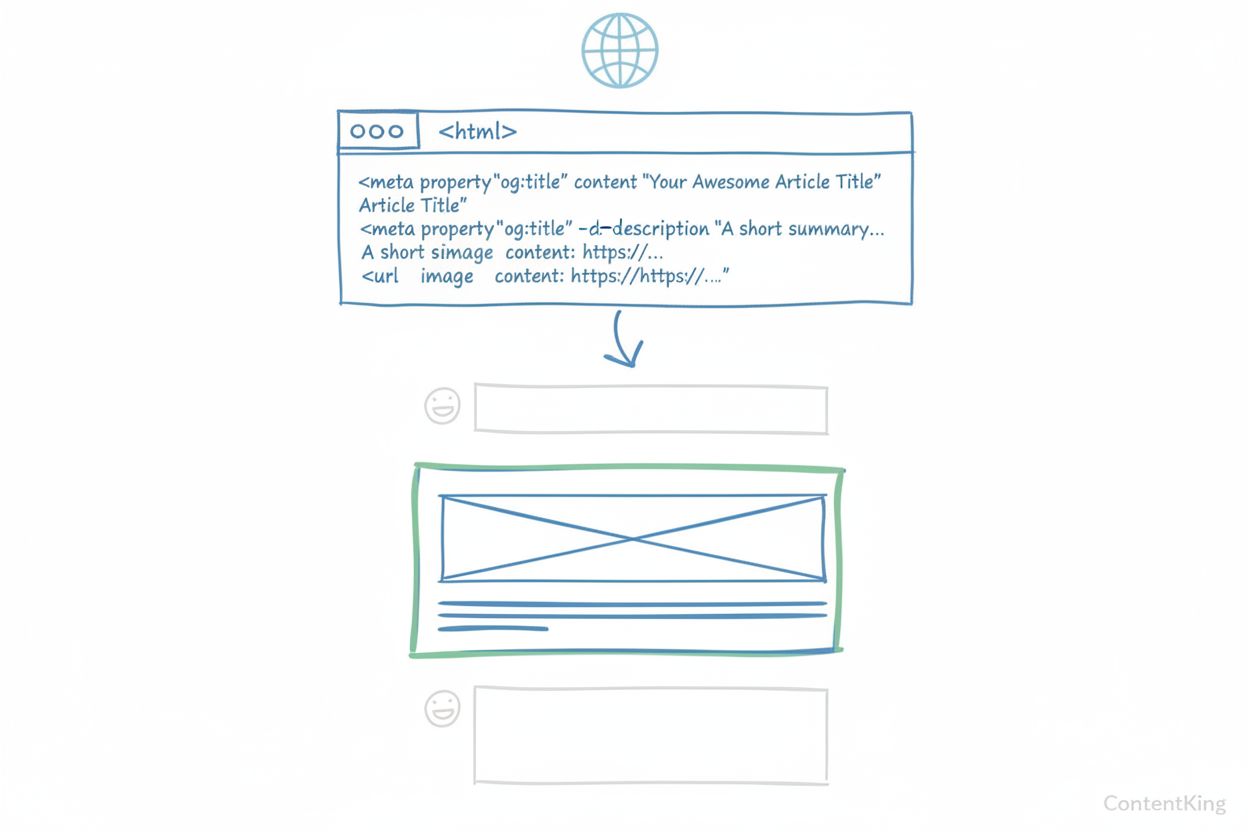
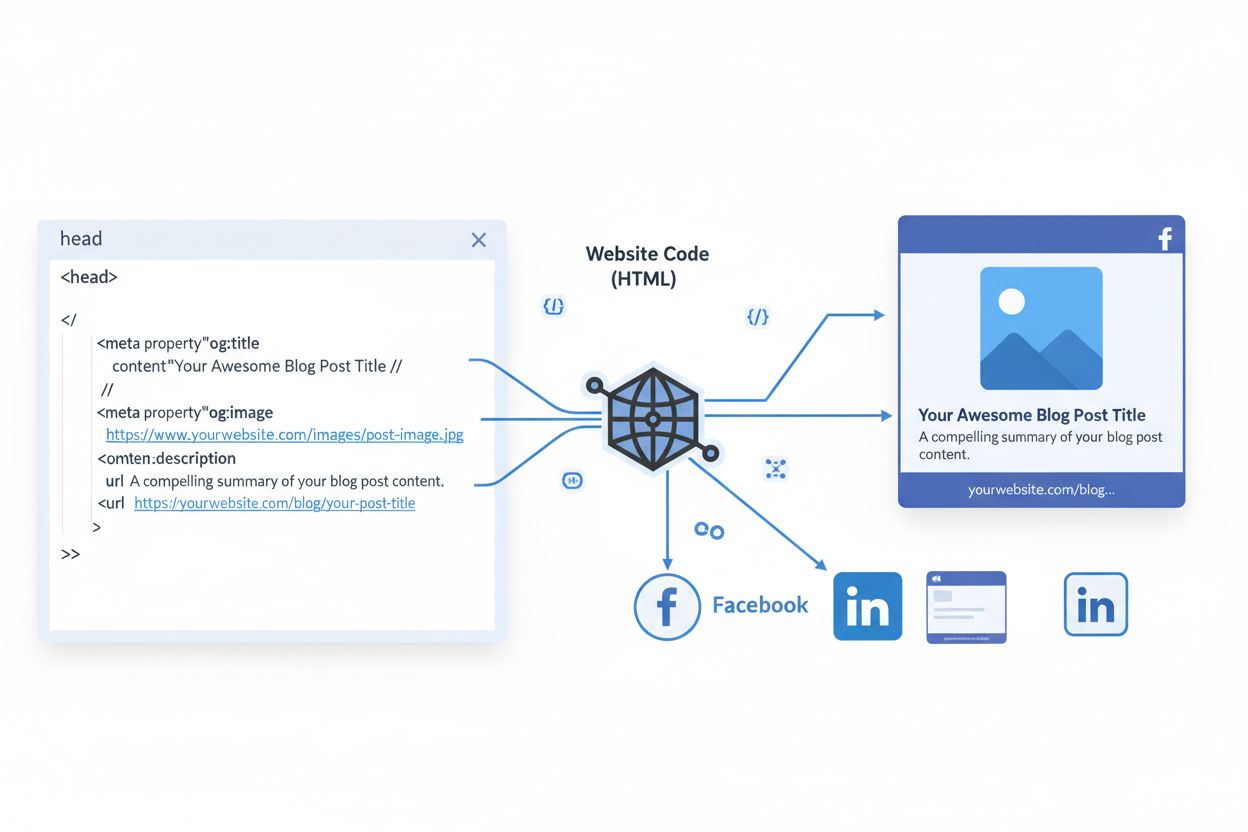
Every webpage implementing the Open Graph Protocol must include four essential meta tags to function properly. The og:title tag specifies the title that appears in social previews and should be concise, accurate, and compelling to encourage clicks. The og:type tag defines the content category (such as “article,” “website,” “video.movie,” or “product”), which helps social platforms understand how to display and categorize the content. The og:image tag provides the URL of a thumbnail image that represents the content, with Facebook recommending dimensions of 1200x630 pixels for optimal clarity across all devices. The og:url tag specifies the canonical URL of the page, ensuring that all social shares consolidate data (such as likes and comments) across duplicate URLs. Beyond these required tags, Facebook and other platforms support numerous optional tags including og:description (a 2-4 sentence summary), og:locale (language specification), og:site_name (overall website name), og:video (video file URL), and og:audio (audio file URL). According to 2024 HTTP Archive data, the most frequently used Open Graph tags are og:title (used by 61% of mobile pages) and og:url (58%), demonstrating that most implementations focus on these foundational elements.
| Aspect | Open Graph Protocol | Twitter Cards | Schema.org Markup | RDFa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Creator | Google, Microsoft, Yahoo | W3C Community | ||
| Primary Use | Social media previews | Twitter-specific sharing | Search engine understanding | Semantic web data |
| Meta Tag Format | <meta property="og:*"> | <meta name="twitter:*"> | JSON-LD or microdata | RDF attributes in HTML |
| Adoption Rate | 64% of web pages | 54.3% of structured data sites | 51.5% of structured data sites | 66% of web pages |
| Supported Platforms | Facebook, LinkedIn, Pinterest, WhatsApp | Twitter/X only | Google, Bing, search engines | Multiple semantic platforms |
| Image Optimization | 1200x630px recommended | 1200x675px for large image | Flexible dimensions | Flexible dimensions |
| Direct SEO Impact | Indirect (via engagement) | Indirect (via engagement) | Direct (search rankings) | Indirect (semantic understanding) |
| Ease of Implementation | Very simple (4 required tags) | Moderate (multiple card types) | Complex (extensive properties) | Complex (RDF syntax) |
Implementing the Open Graph Protocol requires adding properly formatted meta tags to the HTML <head> section of your webpage. Each tag follows the structure <meta property="og:property_name" content="value" />, where the property attribute defines the metadata type and the content attribute contains the actual information. For example, a basic implementation includes tags like <meta property="og:title" content="Article Title" />, <meta property="og:type" content="article" />, <meta property="og:image" content="https://example.com/image.jpg" />, and <meta property="og:url" content="https://example.com/page" />. The protocol also supports structured properties that allow additional metadata to be attached to primary tags, such as og:image:width, og:image:height, og:image:type, and og:image:alt for enhanced image specifications. For video and audio content, similar structured properties exist, including og:video:secure_url, og:video:type, og:video:width, and og:video:height. The protocol supports arrays of values, allowing multiple images or videos to be specified for a single page by repeating the same meta tag multiple times. Content Management Systems like WordPress, Shopify, Wix, and Squarespace have simplified implementation through plugins and built-in settings, eliminating the need for manual code editing in most cases.
While the Open Graph Protocol was created by Facebook, its adoption extends far beyond the platform. LinkedIn uses Open Graph tags to generate professional content previews, Pinterest relies on them for rich pin creation, and WhatsApp uses them for link previews in messages. Twitter initially developed its own Twitter Cards specification but now supports Open Graph tags as a fallback when Twitter Card tags are absent, making Open Graph a universal standard. Google does not directly use Open Graph tags for search rankings but recognizes them as valid structured data. However, Google AI Overviews and other AI-powered search features may utilize Open Graph metadata when extracting and displaying content summaries. Perplexity, ChatGPT, and other AI search engines increasingly rely on standardized metadata like Open Graph tags to understand page context and generate accurate citations. For e-commerce platforms, Open Graph tags work in conjunction with Schema.org product markup to provide comprehensive product information across social networks and search engines. The og:locale tag is particularly important for international websites, allowing specification of content language and regional variations, which helps social platforms display content to appropriate audiences.
The implementation of Open Graph Protocol has demonstrable effects on social media engagement and click-through rates. Research shows that pages with optimized Open Graph tags experience significantly higher social sharing rates compared to pages without them. When a user shares content with a compelling og:image, descriptive og:title, and engaging og:description, the resulting social preview is far more likely to attract clicks from other users scrolling through their feeds. Facebook search results, which display previously shared content, rely entirely on Open Graph tags to populate titles and images, making proper implementation essential for discoverability within the platform. For e-commerce businesses, optimized Open Graph tags on product pages can increase social traffic by 30-50%, as attractive product images and clear descriptions encourage sharing and purchasing. Content marketers benefit from Open Graph optimization because it extends the reach of content beyond organic search, leveraging social networks as distribution channels. Brand visibility is enhanced when Open Graph tags accurately represent content, as they prevent social platforms from displaying generic or incorrect information that could damage brand perception. The protocol also supports multilingual content through the og:locale and og:locale:alternate tags, enabling international businesses to present localized content appropriately across different regions.
The Open Graph Protocol continues to evolve as social media platforms and AI systems become more sophisticated in their content understanding capabilities. Recent developments include expanded support for video and audio content, payment links, and product-specific metadata that integrate with e-commerce platforms. The protocol’s role in AI monitoring and brand tracking has become increasingly important as AI search engines like Perplexity, ChatGPT, and Google AI Overviews rely on standardized metadata to extract and cite content accurately. AmICited and similar AI monitoring platforms track how brands and URLs appear in AI-generated responses, making Open Graph implementation critical for ensuring accurate representation in these emerging search channels. The future of Open Graph likely involves deeper integration with Schema.org markup, creating a more unified structured data ecosystem that serves both traditional search engines and AI systems. As social commerce grows, Open Graph tags will become increasingly important for e-commerce businesses seeking to drive sales through social channels. The protocol’s simplicity and widespread adoption position it as a foundational standard that will remain relevant even as new metadata standards emerge. Organizations that invest in proper Open Graph implementation today will benefit from improved social sharing performance, better AI citation accuracy, and enhanced brand visibility across both current and future social platforms.
The Open Graph Protocol plays a crucial role in how AI systems and content monitoring platforms understand and represent web content. When AI search engines crawl and index web pages, they extract Open Graph metadata to understand page context, which directly influences how content appears in AI-generated responses and summaries. AmICited monitors how your brand, domain, and specific URLs appear across AI platforms like Perplexity, ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, and Claude, and proper Open Graph implementation ensures that your content is accurately represented in these citations. The standardized nature of Open Graph tags makes them easily parseable by web crawlers and AI systems, reducing ambiguity and improving the accuracy of content extraction. For organizations concerned with brand monitoring and AI visibility, ensuring that Open Graph tags are properly implemented and regularly updated is essential for maintaining accurate representation across AI-powered search results. The protocol’s metadata provides AI systems with structured information that helps them understand content type, publication date, authorship, and other contextual factors that influence how content is cited and ranked in AI responses. As AI systems become more prevalent in information discovery, the importance of Open Graph implementation will only increase, making it a critical component of modern digital marketing and brand management strategies.
The four essential Open Graph tags that every page should include are og:title (the page title), og:type (content type like article or website), og:image (thumbnail URL), and og:url (canonical URL). These tags provide social platforms with the minimum information needed to create a rich preview when content is shared. Without these tags, social networks will attempt to auto-generate previews, which often results in poor formatting or incorrect information.
While Open Graph Protocol is a universal standard created by Facebook for all social platforms, Twitter Cards are Twitter-specific meta tags that provide more granular control over how content appears on Twitter. Twitter Cards include additional properties like twitter:card type (summary, summary_large_image, app, player) and twitter:creator. However, Twitter can fall back to Open Graph tags if Twitter Card tags are not present, making Open Graph a foundational standard.
The og:image tag is critical because images occupy the most visual real estate in social media feeds and are the first element users notice. Facebook recommends images with dimensions of 1200x630 pixels for optimal display across devices. A compelling, well-optimized image can significantly increase click-through rates and social engagement compared to pages without custom Open Graph images.
Open Graph tags are crucial for AI monitoring platforms like AmICited because they standardize how content metadata is extracted and displayed across social networks. When AI systems and web crawlers parse shared content, they rely on these structured meta tags to understand page context, which directly affects how your brand appears in AI-generated summaries, social media previews, and search results across platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Open Graph tags do not directly impact Google search rankings, as Google primarily uses Schema markup for structured data. However, they indirectly improve SEO by increasing social media click-through rates and engagement, which drives more traffic to your website. Better social sharing performance can lead to increased brand visibility, more backlinks, and higher overall domain authority over time.
Without Open Graph tags, social platforms will attempt to auto-generate previews by extracting content from your page's HTML. This often results in incorrect titles, missing images, truncated descriptions, or generic fallback content. The lack of control over social previews typically leads to lower click-through rates, reduced social engagement, and diminished brand presentation when your content is shared across social networks.
You can test Open Graph tags using Facebook's Sharing Debugger (developers.facebook.com/tools/debug/sharing/), Twitter Card Validator, or LinkedIn Post Inspector. These tools crawl your page and display exactly how your content will appear when shared. If tags aren't displaying correctly, you can use the 'Scrape Again' button to refresh the cache, or use Facebook's Batch Invalidator to clear cached data.
While Open Graph tags are technically optional, they should be implemented on all pages that are likely to be shared socially, particularly blog posts, articles, product pages, and homepages. For internal pages or administrative sections unlikely to be shared, basic fallback tags are acceptable. Best practice is to implement at least the four required tags (og:title, og:type, og:image, og:url) site-wide for consistency.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn what Open Graph Images are, their technical specifications, platform requirements, and how they boost social media engagement and click-through rates acro...

Discover what knowledge graphs are, how they work, and why they're essential for modern data management, AI applications, and business intelligence.

Twitter Card is a meta tag specification enabling rich media previews on Twitter/X. Learn how this sharing format works, card types, implementation, and its imp...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.