Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are Google's three key metrics measuring page loading, interactivity, and visual stability. Learn LCP, INP, CLS thresholds and their impact on S...
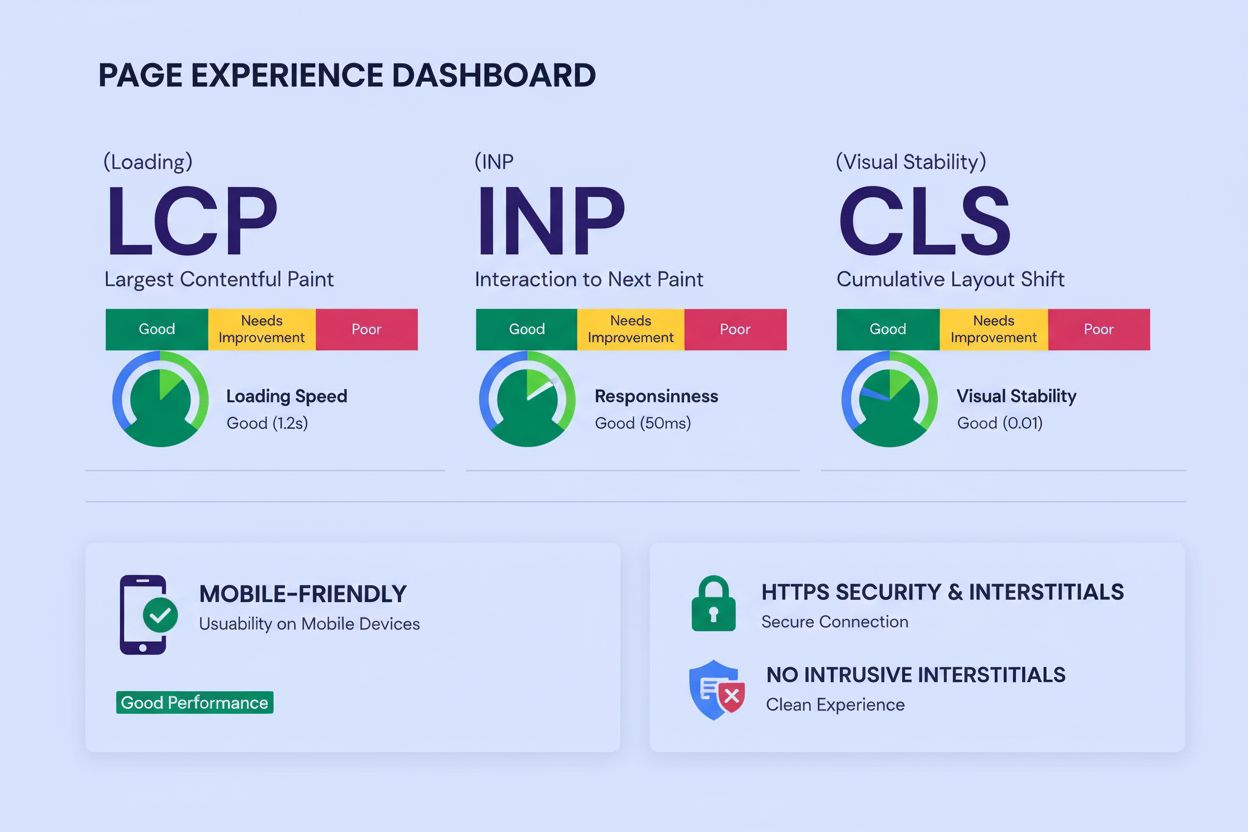
Page Experience is a set of signals that measure how users perceive their interaction with a web page, including Core Web Vitals, mobile usability, HTTPS security, and intrusive interstitials. It is a ranking factor in Google Search that evaluates loading performance, interactivity, visual stability, and overall user satisfaction.
Page Experience is a set of signals that measure how users perceive their interaction with a web page, including Core Web Vitals, mobile usability, HTTPS security, and intrusive interstitials. It is a ranking factor in Google Search that evaluates loading performance, interactivity, visual stability, and overall user satisfaction.
Page Experience is a comprehensive set of signals that measure how users perceive their interaction with a web page, encompassing multiple dimensions of user satisfaction and engagement. Introduced by Google in May 2020, Page Experience has become a critical ranking factor in Google Search, influencing how websites are positioned in search engine results pages (SERPs). The concept extends beyond simple page speed metrics to include loading performance, interactivity, visual stability, mobile usability, security, and the absence of intrusive elements that disrupt user engagement. Google’s core ranking systems evaluate Page Experience on a page-specific basis, meaning each individual page is assessed for its ability to deliver a positive user experience rather than applying site-wide generalizations.
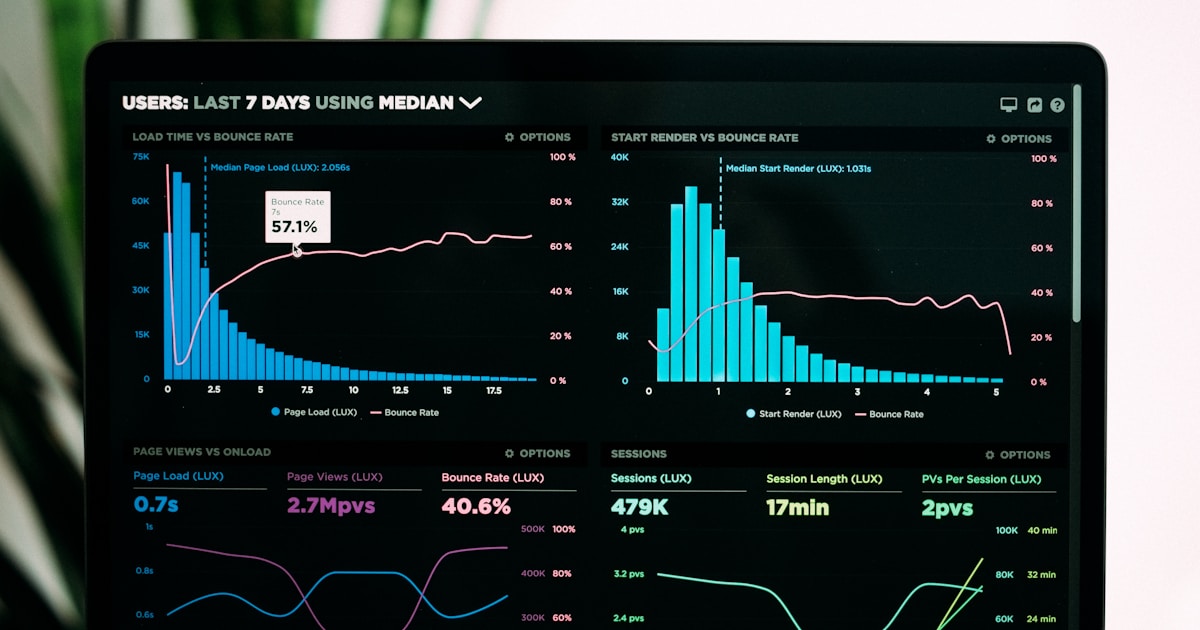
Core Web Vitals represent the three most critical metrics within the Page Experience framework, measuring real-world user experience across loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability. These metrics were specifically designed to quantify aspects of user experience that matter most to visitors and directly impact their satisfaction with a website. The three Core Web Vitals are Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), which measures how long it takes for the largest content element to load and should occur within 2.5 seconds; Interaction to Next Paint (INP), which measures how quickly a page responds to user interactions and should be under 200 milliseconds; and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), which measures unexpected layout shifts and should maintain a score of 0.1 or less. Google evaluates these metrics at the 75th percentile of page views, meaning a page must meet the “Good” threshold for at least 75% of visits to be considered as having good Core Web Vitals performance. Pages that fail to meet these thresholds at the 75th percentile are classified as “Needs Improvement” or “Poor,” which can negatively impact search visibility and user retention.
Mobile usability has become non-negotiable in Page Experience evaluation, particularly given that 64.95% of global website traffic originates from mobile devices. Google’s mobile-first indexing approach means that the mobile version of your website is the primary version evaluated for ranking and indexing purposes. To qualify for a “Good” Page Experience rating, websites must meet specific mobile usability standards, including the absence of incompatible plugins, proper viewport configuration set to “device-width,” content that does not exceed screen width, readable text sizes, and clickable elements that are sufficiently spaced apart to prevent accidental clicks. Mobile users are 5 times more likely to abandon tasks if a website is not optimized for mobile devices, making responsive design a critical investment for both user experience and SEO performance. The relationship between mobile optimization and Page Experience is so significant that 83% of users report that a seamless experience across all devices is very important to them, underscoring the necessity of implementing adaptive and responsive design principles.
HTTPS security is a mandatory component of Page Experience that Google has enforced since September 2016, when the search engine began marking all HTTP websites as “Not Secure” in browser address bars. Websites that do not use HTTPS encryption are considered insecure by Google’s standards, and this security status directly impacts Page Experience evaluation. To achieve a “Good” Page Experience rating, all indexed pages must be served over HTTPS, ensuring that user data is encrypted during transmission and protected from potential interception or attacks. The Page Experience report in Google Search Console displays the ratio of indexed HTTP versus HTTPS URLs on your domain, and having a high proportion of HTTP URLs will trigger warnings and potentially result in ranking penalties. Beyond the SEO implications, HTTPS security builds user trust and confidence, as visitors can verify that their interactions with your website are protected by encryption protocols. Migrating from HTTP to HTTPS is not only an SEO best practice but also a fundamental requirement for maintaining user privacy and complying with modern web security standards.
Intrusive interstitials are pop-ups, ads, dialogs, or other elements that block or interfere with main content and disrupt the user’s ability to access information quickly. Google specifically penalizes websites that use intrusive interstitials as part of Page Experience evaluation, recognizing that such elements create friction and frustration for users. Examples of intrusive interstitials include full-page pop-ups that cover most or all of the page, ads that appear unexpectedly and force users to close them before accessing content, and dialogs that follow users as they scroll or navigate. However, Google recognizes certain exceptions to this rule, including login dialogs on non-publicly indexable pages (such as paywalled content), privacy consent pop-ups that comply with legal requirements, and age verification warnings for age-restricted content. To maintain good Page Experience scores, websites should avoid pop-up banners that cover significant portions of the page, ensure that any pop-ups have easily accessible close buttons, prevent pop-ups from slowing page load times, and avoid creating pop-ups that reappear after users have dismissed them. Non-intrusive interstitials that are designed thoughtfully and do not significantly disrupt user experience can still be valuable tools for lead generation and conversion optimization when implemented correctly.
| Component | Metric Type | Measurement | Good Threshold | Impact on Rankings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) | Loading Performance | Seconds | < 2.5 seconds | High - Direct ranking factor |
| Interaction to Next Paint (INP) | Responsiveness | Milliseconds | < 200 ms | High - Direct ranking factor |
| Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) | Visual Stability | Score (0-1) | < 0.1 | High - Direct ranking factor |
| Mobile Usability | Mobile Optimization | Errors/Issues | Zero errors | Medium - Ranking consideration |
| HTTPS Security | Security | Protocol | HTTPS required | Medium - Ranking consideration |
| Intrusive Interstitials | User Experience | Presence/Type | None/Acceptable only | Medium - Ranking consideration |
| Page Speed | Overall Performance | Seconds | < 3 seconds | High - User retention factor |
| Visual Design | Aesthetics | User perception | Professional/Clean | Low-Medium - Indirect factor |
Research demonstrates the substantial business impact of optimizing Page Experience metrics. According to comprehensive studies, 88% of users are unlikely to return to a website after experiencing poor user experience, and 52% of users who don’t return cite poor aesthetics as the primary reason. In e-commerce contexts, the impact is even more pronounced: 60% of consumers abandon purchases due to poor website user experience, with research indicating that e-commerce companies lose approximately 5 purchases per customer per year to inadequate UX. The financial return on Page Experience optimization is compelling—for every $1 invested in UX, businesses see an average return of $100, representing a 9,900% ROI. Furthermore, a well-designed user interface can increase website conversions by 200%, while comprehensive UX design improvements can increase conversions by 400%. These statistics underscore that Page Experience optimization is not merely an SEO consideration but a fundamental business imperative that directly impacts revenue, customer retention, and brand reputation.
As AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude increasingly generate responses that cite web content, Page Experience becomes relevant to AI citation patterns. Websites with excellent Page Experience metrics are more likely to be indexed and ranked favorably by Google, which increases their visibility in Google AI Overviews. Similarly, well-optimized pages with fast load times, mobile responsiveness, and clear content structure are more likely to be crawled and cited by AI systems that prioritize high-quality, user-friendly sources. For organizations using AmICited to monitor their brand’s appearance in AI-generated responses, maintaining strong Page Experience metrics is foundational—it ensures that your domain remains visible and citable across multiple AI platforms. Pages with poor Page Experience may be deprioritized by search engines and AI systems, reducing the likelihood of citation and visibility in AI responses. This creates a direct connection between Page Experience optimization and AI visibility, making it essential for brands seeking to maintain presence across both traditional search and emerging AI search interfaces.
Optimizing Page Experience requires a multifaceted approach addressing each component systematically. For Core Web Vitals improvement, start by preloading the largest content element on your page, compressing images using tools like TinyPNG, minifying JavaScript to reduce parsing time, and implementing a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to serve content from geographically distributed servers. For mobile optimization, implement responsive design using flexible layouts, relative font sizes, and fluid images; ensure viewport is properly configured; and test across multiple devices to verify seamless functionality. For HTTPS implementation, obtain an SSL certificate from a trusted certificate authority and configure your web server to serve all pages over HTTPS, then update internal links and redirects to use HTTPS URLs. For intrusive interstitial management, audit your website for pop-ups and dialogs, remove or redesign any that block main content, ensure remaining interstitials have clear close buttons, and verify that they do not significantly impact page load times. Use Google Search Console to monitor your Page Experience report, which provides specific data on which pages are failing Core Web Vitals checks and what issues need to be addressed. Additionally, leverage PageSpeed Insights to analyze individual pages and receive actionable recommendations for improvement, and consider using professional website audit tools to identify technical issues that may be impacting Page Experience scores.
Page Experience metrics are not static—they evolve based on user feedback, technological advances, and changing user expectations. The Core Web Vitals lifecycle demonstrates this evolution, with metrics progressing through experimental, pending, and stable phases. For example, First Input Delay (FID) was replaced by Interaction to Next Paint (INP) in March 2024, reflecting a more comprehensive approach to measuring responsiveness that considers all user interactions rather than just the first one. Google has committed to updating Core Web Vitals metrics on an annual cadence at most, providing stability for site owners while allowing for refinement based on real-world performance data. Future iterations of Page Experience may incorporate additional signals related to accessibility, privacy, and emerging user experience concerns. The integration of Page Experience with AI visibility represents an emerging frontier—as AI systems become primary discovery mechanisms alongside traditional search, Page Experience optimization will likely become even more critical for ensuring visibility across multiple platforms. Organizations should view Page Experience not as a one-time optimization project but as an ongoing commitment to user experience excellence, regularly monitoring metrics, implementing improvements, and staying informed about updates to Google’s ranking systems and evaluation criteria.
The three Core Web Vitals are Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), which measures loading performance and should occur within 2.5 seconds; Interaction to Next Paint (INP), which measures responsiveness and should be under 200 milliseconds; and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), which measures visual stability and should be 0.1 or less. These metrics are evaluated at the 75th percentile of page views to determine if a page has good, needs improvement, or poor performance.
Page Experience is a confirmed ranking factor in Google Search, meaning websites with good page experience scores are more likely to rank higher in search results. However, Google prioritizes relevant content first—if a page has poor page experience but highly relevant content, it may still rank well. When multiple pages have similar relevance, good page experience becomes a significant differentiator for ranking position.
Core Web Vitals are a subset of Page Experience metrics. Page Experience encompasses a broader set of signals including Core Web Vitals (LCP, INP, CLS), mobile usability, HTTPS security, and intrusive interstitials. While Core Web Vitals focus specifically on loading, interactivity, and visual stability, Page Experience evaluates the overall user experience across multiple dimensions.
Mobile-friendliness is critical because over 64.95% of global website traffic comes from mobile devices. Google evaluates mobile usability as part of Page Experience, checking for issues like incompatible plugins, improper viewport settings, content wider than the screen, small text, and clickable elements that are too close together. Websites optimized for mobile devices provide better user experience and achieve higher search rankings.
You can measure Page Experience using Google Search Console, which provides a dedicated Page Experience report showing Core Web Vitals, mobile usability, and HTTPS status. PageSpeed Insights is another free tool that analyzes individual pages and provides detailed performance metrics. Both tools evaluate pages separately for mobile and desktop, giving you comprehensive insights into your site's performance across devices.
Intrusive interstitials are pop-ups, ads, or dialogs that block or interfere with main content and disrupt user experience. Google penalizes websites with intrusive interstitials as part of Page Experience evaluation. However, some interstitials are acceptable, including login dialogs on non-publicly indexable pages, privacy consent pop-ups, and age verification warnings. Non-intrusive interstitials that are easy to dismiss and don't slow page load time are generally acceptable.
Studies show that 88% of users are unlikely to return to a website after a bad experience, and 60% of consumers abandon purchases due to poor website user experience. For every $1 invested in UX, businesses see an average return of $100. A well-designed user interface can increase conversions by 200%, while better UX design can increase conversions by 400%, demonstrating the direct financial impact of optimizing Page Experience.
HTTPS security is a mandatory component of Page Experience. Google has deemed all HTTP websites as insecure since 2016, and websites without HTTPS are labeled 'Not Secure' in browsers. To qualify for a 'Good' Page Experience rating, pages must be served over HTTPS. The Page Experience report in Search Console displays the ratio of indexed HTTP versus HTTPS URLs, and having too many HTTP URLs will result in warnings and potential ranking penalties.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Core Web Vitals are Google's three key metrics measuring page loading, interactivity, and visual stability. Learn LCP, INP, CLS thresholds and their impact on S...
Pages Per Session measures average pages viewed per visit. Learn how this engagement metric impacts user behavior, conversion rates, and SEO performance with in...

Page Quality Rating is Google's assessment framework evaluating webpage quality through E-E-A-T, content originality, and user satisfaction. Learn the rating sc...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.