
Link Building
Link building is the process of acquiring backlinks from external websites. Learn strategies, best practices, and how quality links improve SEO rankings and bra...
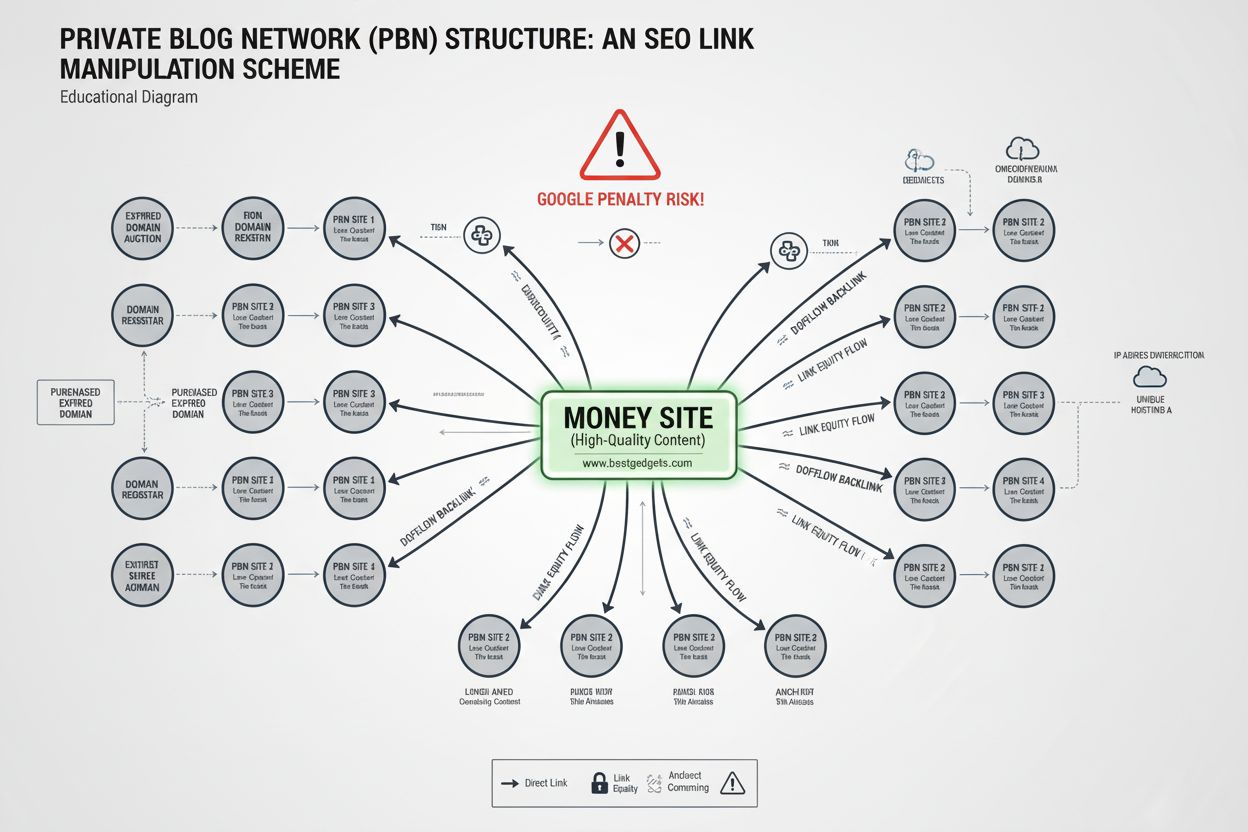
A Private Blog Network (PBN) is a network of websites owned and controlled by a single entity, created primarily to build backlinks to a central ‘money site’ in order to manipulate search engine rankings. PBNs violate Google’s Webmaster Quality Guidelines and are considered black hat SEO tactics that carry significant risks including manual penalties, deindexation, and algorithmic demotion.
A Private Blog Network (PBN) is a network of websites owned and controlled by a single entity, created primarily to build backlinks to a central 'money site' in order to manipulate search engine rankings. PBNs violate Google's Webmaster Quality Guidelines and are considered black hat SEO tactics that carry significant risks including manual penalties, deindexation, and algorithmic demotion.
A Private Blog Network (PBN) is a network of websites owned and controlled by a single person or entity, created and maintained primarily to build backlinks to a central website—commonly referred to as the “money site”—in order to artificially manipulate that website’s authority and search engine rankings. Unlike legitimate website networks that serve genuine user purposes and are transparent about their ownership connections, PBNs exist solely to exploit search engine algorithms by funneling link equity from multiple domains to a single target. These networks typically consist of websites built on expired or auctioned domains that already possess established authority and backlink profiles, which are then repurposed with low-quality or generic content designed to pass link value rather than provide genuine value to readers. Google explicitly categorizes PBNs as violations of its Webmaster Quality Guidelines, classifying them as black hat SEO tactics that constitute link spam and manipulative link schemes. The fundamental purpose of a PBN distinguishes it from legitimate multi-site operations: while a company like Ford may own multiple dealership websites that link to each other to serve customers, a PBN’s sole objective is ranking manipulation with no regard for user experience or content quality.
The concept of Private Blog Networks emerged in the mid-2000s as SEO practitioners sought ways to accelerate ranking improvements by controlling their own link-building destiny. Early PBNs were relatively simple operations—often just collections of basic WordPress blogs hosted on cheap shared servers, with minimal content and obvious linking patterns. However, as Google’s detection capabilities improved and the search engine began issuing manual actions against PBN operators in 2014, the sophistication of PBN tactics evolved dramatically. Modern PBNs have become increasingly complex, incorporating professional website designs, high-quality niche-specific content, diverse hosting infrastructure across multiple providers, and sophisticated footprint elimination techniques. This evolution reflects an ongoing arms race between PBN operators attempting to avoid detection and Google’s increasingly advanced algorithmic systems designed to identify and penalize link manipulation schemes. According to industry observations, Google’s SpamBrain AI system, launched in 2018, has fundamentally changed the landscape by enabling the search engine to identify spam sites and networks with unprecedented accuracy. The December 2022 link spam update represented a major escalation in Google’s efforts, with the company deploying enhanced detection functionality that could identify closely related sites and model their relationships through sophisticated link graph analysis. Today, PBNs represent a diminishing but persistent segment of the SEO landscape, with many practitioners recognizing that the increasing costs, complexity, and risks associated with maintaining undetectable networks often outweigh the temporary ranking benefits they provide.
PBNs operate on a fundamental principle: link equity transfer through controlled networks. The basic mechanics involve purchasing or registering multiple domains, developing websites on those domains, and strategically linking from those sites back to a central money site to artificially boost its perceived authority in the eyes of search engines. The process typically begins with domain acquisition, where operators identify and purchase expired domains that already possess established authority metrics, relevant backlink profiles, and historical ranking performance. These aged domains are valuable because they retain the link equity and topical authority they accumulated under previous ownership, allowing new operators to leverage that existing authority for their purposes. Once acquired, these domains are rebuilt with new content—often generic, AI-generated, or lightly modified from other sources—designed to appear legitimate enough to avoid immediate detection while serving the primary function of hosting links to the money site. The linking structure within a PBN is carefully orchestrated to create natural-appearing link patterns while maximizing the flow of link equity to the target site. Links may be placed in blog posts, sidebar widgets, footer areas, or other strategic locations, often using keyword-rich anchor text selected to help the money site rank for specific search terms. The network sites may also link to each other in various patterns to create the appearance of a legitimate ecosystem of related websites, further obscuring the true purpose of the network. Link velocity—the rate at which new backlinks are acquired—is carefully managed to avoid triggering algorithmic red flags that would indicate unnatural link acquisition patterns. Successful PBN operators understand that a sudden spike in backlinks followed by silence appears suspicious to Google’s algorithms, so they implement gradual, steady linking strategies that attempt to mimic organic link growth patterns.
| Aspect | Private Blog Networks (PBN) | White Hat Link Building | Gray Hat Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Manipulate rankings through controlled link equity transfer | Earn genuine links through valuable content and relationships | Balance between risk and reward with questionable tactics |
| Link Quality | Low to medium; often from low-traffic, low-engagement sites | High; from authoritative, relevant, topically aligned sources | Medium; from established sites but with artificial placement |
| Detection Risk | Very high; Google actively targets PBN footprints | Minimal; aligns with Google guidelines | Moderate to high; depends on specific tactics employed |
| Time to Results | Fast (4-8 weeks) but temporary | Slow (3-6 months+) but sustainable | Medium (2-4 months) with variable sustainability |
| Cost | $100-500 per domain + monthly maintenance | Higher upfront content costs but lower ongoing expenses | Variable; depends on specific tactics |
| Sustainability | Low; penalties and deindexation common | High; builds long-term authority and trust | Low to medium; vulnerable to algorithm updates |
| E-E-A-T Signals | Fails to signal expertise, authority, or trustworthiness | Strong E-E-A-T signals through genuine expertise and citations | Weak E-E-A-T signals; appears manipulative |
| User Value | None; content exists only for search engines | High; content serves genuine user needs and questions | Low to medium; content may have some value but is primarily link-focused |
| Google Penalties | Manual actions, algorithmic demotion, deindexation | No penalties; follows guidelines | Possible penalties if detected; varies by tactic |
| Recovery Difficulty | Extremely difficult; may require site rebuild | Not applicable; no penalties to recover from | Difficult; requires removing problematic links and content |
The technical infrastructure of a modern PBN is far more sophisticated than early iterations, reflecting the ongoing evolution of detection avoidance strategies. Successful PBN operators employ diverse hosting solutions across multiple providers and different geographic locations, ensuring that network sites don’t share IP addresses or hosting patterns that would immediately signal their connection to each other. This diversification extends to DNS configurations, with each site using different nameservers and DNS providers to avoid creating obvious technical footprints. The content management systems used across the network are deliberately varied, with some sites running on WordPress, others on Blogger, Weebly, or custom platforms, preventing the kind of template uniformity that would suggest automated network construction. Each site maintains distinct analytics accounts and tracking codes, avoiding the reuse of Google Analytics IDs, Google AdSense accounts, or other tracking mechanisms that Google can easily correlate across multiple domains. The site architecture and design of each network property is customized to match its specific niche and purpose, with different color schemes, layouts, navigation structures, and branding elements that create the appearance of independent websites rather than a coordinated network. Content publishing patterns are deliberately varied across the network, with different sites maintaining different posting frequencies, content types, and update schedules to avoid the kind of synchronized publishing that would indicate automated or coordinated management. Advanced PBN operators also implement strategic 301 redirects from expired domains to intermediate pages before linking to the money site, attempting to obscure the direct connection between the PBN network and the target website. This layering of redirects and intermediary pages is designed to make the link path less obvious to both algorithmic analysis and manual review.
Google employs multiple sophisticated detection methods to identify and penalize Private Blog Networks, combining algorithmic analysis with manual review processes. The search engine’s SpamBrain AI system represents a major advancement in automated spam detection, using machine learning to identify spam sites and networks by analyzing patterns across billions of websites. SpamBrain examines link graph relationships, modeling how websites connect to each other and identifying clusters of sites that appear to be artificially linked for ranking manipulation purposes. The system can detect shared IP addresses and hosting patterns, recognizing when multiple domains are hosted on the same server or within the same IP range, particularly when those sites link exclusively or primarily to each other. Tracking code reuse is another critical detection signal; when multiple domains use the same Google Analytics ID, Google AdSense account, or other tracking codes, it creates a clear technical fingerprint linking those sites together. WHOIS and RDAP data analysis allows Google to identify domains registered by the same person or entity, especially when combined with other red flags like shared hosting or similar content patterns. The search engine monitors link velocity patterns, recognizing when a website suddenly acquires a large number of backlinks in a short timeframe—a pattern inconsistent with organic link growth. Anchor text distribution analysis identifies unnatural patterns where a website receives an unusually high percentage of links using the same keyword-rich anchor text, suggesting coordinated link placement rather than natural editorial linking. Content quality assessment flags sites with thin, scraped, AI-generated without human oversight, or duplicate content that provides little value to users. Manual review by Google’s Search Quality Raters involves human evaluation of suspected spam sites using the company’s detailed Search Quality Rater Guidelines, which provide specific criteria for identifying PBN characteristics and link manipulation schemes. According to Google’s own statements, the company’s automated systems detect approximately 40 billion spam pages every single day, demonstrating the scale and sophistication of modern spam detection capabilities.
The risks associated with Private Blog Network usage have escalated significantly as Google’s detection capabilities have improved, making the potential consequences far more severe than any temporary ranking benefits. Algorithmic demotion represents the most common outcome, where Google’s spam detection systems identify a website as participating in link manipulation and reduce its visibility in search results, often dramatically. This demotion can occur without any notification to the website owner, making it difficult to identify the cause of ranking losses until significant damage has already occurred. Manual actions issued by Google’s review team represent a more severe penalty, where human reviewers determine that a website violates Google’s guidelines and take direct action to reduce its rankings or remove it from search results entirely. Website owners receive notification of manual actions through Google Search Console, but recovery requires identifying and fixing all violations, then submitting a reconsideration request that may take weeks or months to process. Deindexation—complete removal from Google’s index—represents the most severe consequence, effectively erasing a website from Google search results entirely. Recovery from deindexation is extremely difficult and may require rebuilding the entire website from scratch. Wasted investment is another significant risk; the time, money, and resources spent building and maintaining a PBN are completely lost if Google detects and penalizes the network. Reputational damage occurs when PBN usage becomes public knowledge, potentially damaging relationships with customers, business partners, and the broader industry community. Inability to signal E-E-A-T means that PBN links fail to contribute to the Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trustworthiness signals that Google increasingly prioritizes, particularly for YMYL (Your Money, Your Life) content. Long-term instability results from the fact that any ranking improvements achieved through PBNs are inherently temporary and vulnerable to algorithm updates, meaning websites must continuously invest in maintaining and expanding their networks just to maintain current rankings.
Identifying potential PBN activity requires understanding the specific footprints and patterns that distinguish coordinated link manipulation from legitimate website networks. Shared IP addresses represent one of the most obvious red flags; when multiple domains are hosted on the same IP address or within the same IP range, particularly when they link exclusively to each other, it suggests coordinated network activity. Common hosting providers across multiple domains, especially when combined with other indicators, suggest that sites may be part of the same network. Identical or near-identical WHOIS registration data across multiple domains—such as the same registrant name, email address, or phone number—indicates common ownership and control. Reused tracking codes such as Google Analytics IDs, Google AdSense publisher IDs, or other analytics and advertising platform identifiers create a clear technical connection between sites. Uniform website design and templates across multiple domains, including identical color schemes, layouts, navigation structures, or WordPress themes, suggest automated or coordinated site construction. Minimal user engagement and traffic on network sites, indicated by low click-through rates in search results, minimal time on site, and low scroll depth, suggests that sites exist primarily for search engines rather than users. Low-quality or generic content that provides little value, appears scraped or AI-generated without human oversight, or uses excessive keyword stuffing indicates sites designed for ranking manipulation rather than user service. Unnatural anchor text patterns where a high percentage of backlinks use the same keyword-rich anchor text suggest coordinated link placement. Suspicious link patterns where sites link exclusively to each other or to unrelated high-authority websites in ways that lack contextual relevance. Rapid domain acquisition where someone purchases multiple domains in a short timeframe, particularly expired domains with established authority, may indicate PBN construction.
Google’s explicit prohibition of PBNs is grounded in the search engine’s fundamental mission to provide users with relevant, high-quality search results. The company’s Webmaster Quality Guidelines clearly state that “any links intended to manipulate rankings in Google Search results may be considered link spam,” and PBNs are the quintessential example of such manipulation. This prohibition reflects Google’s broader commitment to E-E-A-T principles—ensuring that websites demonstrating genuine Expertise, Experience, Authority, and Trustworthiness rank higher than those attempting to game the system. The ethical implications of PBN usage extend beyond search engine guidelines; they involve deception of users who may click on search results expecting to find authoritative, valuable content but instead encounter low-quality PBN sites designed solely for link placement. Market distortion occurs when PBN operators gain unfair ranking advantages over legitimate competitors who invest in creating genuinely valuable content and earning links through ethical means. Resource waste results from the fact that PBN operators invest significant time and money in activities that provide no real value to users or the broader internet ecosystem. The reputational risk to SEO professionals and agencies is substantial; association with PBN tactics can permanently damage professional credibility and client relationships. Legal considerations may arise in certain jurisdictions where deceptive practices violate consumer protection laws or where PBN operators engage in trademark infringement or other illegal activities. Industry leaders and reputable SEO organizations have increasingly distanced themselves from PBN tactics, recognizing that sustainable, ethical SEO practices provide better long-term value than short-term manipulation schemes.
The future of Private Blog Networks appears increasingly bleak as Google’s detection capabilities continue to advance and the costs and complexity of maintaining undetectable networks escalate. AI and machine learning advancements will enable Google to identify spam patterns with even greater accuracy, making it increasingly difficult for PBN operators to avoid detection. The company’s SpamBrain system will likely become more sophisticated, potentially incorporating new signals and patterns that current PBN operators haven’t yet anticipated. Link graph analysis will become more granular and effective, allowing Google to identify even subtle connections between seemingly unrelated websites. The rise of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and AI search platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews introduces new considerations for link building strategy; these platforms may have different ranking factors and detection mechanisms than traditional Google Search, potentially making PBN tactics even less effective. Increased transparency requirements may emerge, with search engines demanding more disclosure about website ownership and connections, making it harder to hide PBN networks. The shift toward E-E-A-T signals means that search engines will increasingly prioritize direct evidence of expertise, authority, and trustworthiness over link-based signals, reducing the relative importance of backlinks and making PBN links even less valuable. Integration of brand monitoring tools like AmICited that track brand mentions across AI platforms will make it easier for businesses to identify suspicious linking patterns and PBN activity targeting their brands. Industry trends suggest that legitimate link building methods will continue to become more sophisticated and effective, making the risk-reward calculation for PBN usage increasingly unfavorable. The most successful SEO practitioners are already shifting toward diversified, sustainable strategies that combine content marketing, digital PR, technical SEO, and genuine relationship building rather than relying on manipulative link schemes. As search engines become smarter and more sophisticated, the fundamental principle that quality content and genuine authority provide the most sustainable path to search visibility will become increasingly undeniable.
The key difference lies in intent and transparency. A legitimate website network is transparent about ownership connections and serves users with genuine value across multiple properties. A PBN, by contrast, is intentionally hidden, exists solely to manipulate search rankings, and provides little to no real value to users. Legitimate networks like Ford's dealership sites serve a user-focused purpose, while PBNs are designed purely for link equity manipulation. Google's guidelines explicitly state that the primary objective determines whether a network is legitimate or a PBN.
Google uses multiple detection methods including shared IP addresses, identical hosting providers, repetitive WHOIS data, tracking code reuse, minimal user engagement, and manual quality reviews. The search engine's AI-powered SpamBrain system identifies spam sites and networks by analyzing link graphs and modeling relationships between websites. Google also monitors link velocity patterns, template similarities, and unnatural anchor text distribution. Additionally, Google processes billions of disavow files from SEOs, which helps train its detection systems to recognize PBN footprints more effectively.
The primary risks include algorithmic demotion where Google's spam detection systems push spammy content down in search results, manual actions that can severely reduce ranking ability, complete deindexation removing your site from Google's index, and wasted investment since PBN links are increasingly ignored by search engines. Additionally, PBNs fail to signal E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust), damage brand reputation if discovered, and provide only temporary ranking boosts before detection. Recovery from PBN penalties can take months or years and may never fully restore original rankings.
Yes, some practitioners combine PBN links with legitimate white hat techniques like guest posting, digital PR, and content marketing to create a more diverse link profile. However, this approach still carries the risks associated with PBN usage and violates Google's guidelines. A better strategy is to focus entirely on white hat methods including high-quality content creation, genuine outreach, broken link building, and resource link building. These legitimate techniques take longer but provide sustainable, long-term results without the risk of penalties or deindexation.
Building a PBN requires significant investment including domain acquisition costs ($100-500 per domain), premium hosting services with distributed locations, professional content creation, technical infrastructure, and ongoing maintenance. Monthly costs vary based on network size but typically range from hundreds to thousands of dollars. Individual PBN links from existing networks cost $50-300 each, with premium domains commanding $500+. Many practitioners allocate 20-30% of their budget for unexpected challenges, making PBNs a substantial financial commitment with uncertain returns.
Google recommends doing nothing in most cases, as the search engine is effective at ignoring low-quality backlinks. However, if you've received a manual action for unnatural links or notice a clear pattern of toxic backlinks affecting your rankings, you can request link removal from the PBN owner (though this is usually difficult) or use Google Search Console's disavow tool. Only disavow links if you have clear evidence they're harming your site, as disavowing can itself impact rankings. Document all actions taken and monitor your search visibility closely after any interventions.
Google's PBN detection has become significantly more sophisticated since the company issued widespread manual actions against PBNs in 2014. The search engine now uses advanced algorithmic systems including SpamBrain (launched in 2018), enhanced link graph modeling, and machine learning to identify spam networks. Google processes approximately 40 billion spam pages daily, making detection increasingly effective. The company also benefits from years of disavow file data that helps train its systems to recognize PBN patterns. Modern PBNs must employ increasingly complex techniques to avoid detection, making them more expensive and resource-intensive to maintain.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Link building is the process of acquiring backlinks from external websites. Learn strategies, best practices, and how quality links improve SEO rankings and bra...

Learn what a link farm is, how it manipulates search rankings, why Google penalizes them, and how to detect and avoid these black-hat SEO schemes that damage we...

Paid traffic definition: visitors from paid ads on Google, Facebook, display networks. Learn CPC costs, conversion rates, ROI, and how paid traffic differs from...