What is Prompt Engineering for AI Search - Complete Guide
Learn what prompt engineering is, how it works with AI search engines like ChatGPT and Perplexity, and discover essential techniques to optimize your AI search ...
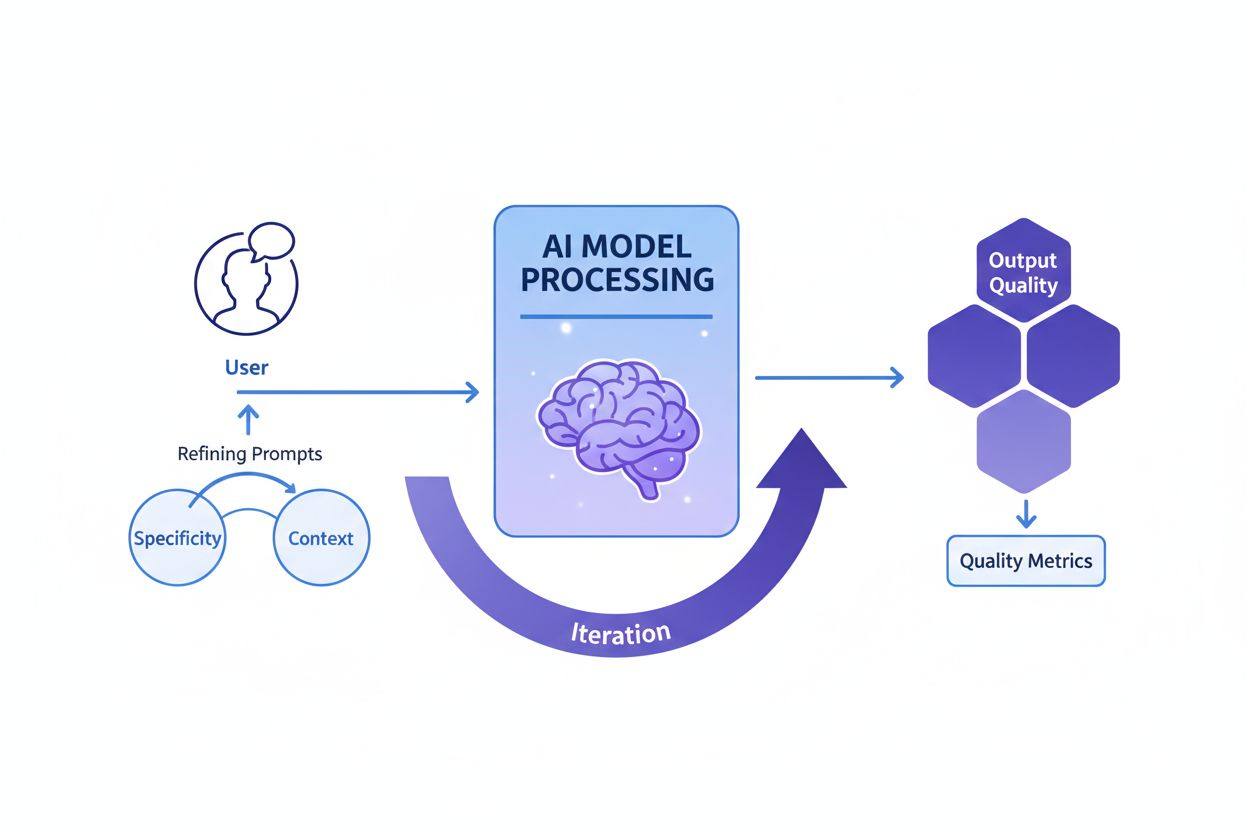
Prompt engineering is the process of crafting, refining, and optimizing natural language instructions to guide generative AI models toward producing desired, accurate, and relevant outputs. It involves iterative experimentation with wording, context, and structure to maximize AI performance without modifying the underlying model.
Prompt engineering is the process of crafting, refining, and optimizing natural language instructions to guide generative AI models toward producing desired, accurate, and relevant outputs. It involves iterative experimentation with wording, context, and structure to maximize AI performance without modifying the underlying model.
Prompt engineering is the systematic process of designing, refining, and optimizing natural language instructions—called prompts—to guide generative AI models toward producing desired, accurate, and contextually relevant outputs. Rather than modifying the underlying AI model itself, prompt engineers work with the model’s existing capabilities by carefully structuring their input to influence how the model processes information and generates responses. This discipline emerged as a critical skill during the 2023-2025 generative AI boom, when organizations realized that access to powerful AI tools like ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and Google AI was insufficient without expertise in effectively communicating with these systems. Prompt engineering bridges the gap between human intent and AI capability, transforming vague business goals into actionable, high-quality AI outputs. The practice is fundamentally iterative, requiring continuous experimentation, testing, and refinement to achieve optimal results for specific use cases.
The concept of prompt engineering emerged organically following the public release of ChatGPT in November 2022, when millions of users began experimenting with how to extract better results from large language models. Early adopters discovered that the quality of AI outputs varied dramatically based on how questions were phrased, what context was provided, and how specific instructions were written. This observation led to the formalization of prompt engineering as a distinct discipline. By 2023, major technology companies including OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, and Anthropic began hiring dedicated prompt engineers, with some positions offering salaries exceeding $300,000. The global prompt engineering market was valued at approximately $222.1 million in 2023 and is projected to reach $2.06 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of significant expansion. This rapid market growth reflects the increasing recognition that prompt engineering is not a temporary trend but a fundamental skill for organizations leveraging AI at scale. The discipline has evolved from simple trial-and-error experimentation to a sophisticated practice incorporating established techniques, evaluation frameworks, and best practices documented by leading AI research institutions and industry practitioners.
Effective prompt engineering rests on several foundational principles that distinguish high-quality prompts from ineffective ones. Specificity is paramount—the more detailed and descriptive a prompt is, the better the AI model can understand the exact requirements and generate aligned outputs. Rather than asking an AI to “write about dogs,” a specific prompt might request “create a 300-word veterinary guide about golden retriever health issues, written for pet owners with an 8th-grade reading level, focusing on preventive care.” Context provision is equally critical; supplying relevant background information, examples, or constraints helps the model narrow its focus and produce more relevant responses. Clarity ensures that instructions are unambiguous and directly communicate the desired task without requiring the model to interpret vague language. Iterative refinement acknowledges that the first prompt rarely produces optimal results; successful prompt engineers continuously test variations, analyze outputs, and adjust their approach based on results. Tone and style alignment involves specifying the desired voice, formality level, and presentation format to ensure outputs match organizational or user expectations. These principles apply across all AI platforms, whether users are crafting prompts for ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, or Google AI Overviews, making them universally valuable for anyone seeking to optimize AI interactions.
The field of prompt engineering has developed numerous sophisticated techniques to address different types of tasks and complexity levels. Zero-shot prompting is the most direct approach, providing the AI with a clear instruction or question without additional examples or context. This method works well for straightforward tasks but may struggle with complex reasoning. Few-shot prompting enhances performance by supplying the model with one or more examples that demonstrate the desired output format or reasoning pattern, effectively teaching the model through demonstration. Chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting breaks down complex problems into intermediate reasoning steps, encouraging the model to show its work and improving accuracy on multi-step problems. Prompt chaining divides a complex task into smaller, sequential subtasks, using the output of one prompt as input for the next, which enhances reliability and consistency for complicated workflows. Tree-of-thought prompting generalizes chain-of-thought by exploring multiple possible reasoning paths simultaneously, allowing the model to evaluate different approaches before selecting the most promising one. Maieutic prompting involves asking the model to explain its reasoning, then asking follow-up questions to expand on specific parts of the explanation, which helps identify and correct inconsistencies. Generated knowledge prompting instructs the model to first generate relevant facts or background information before attempting the main task, conditioning the model on useful context. Self-refine prompting has the model solve a problem, critique its own solution, and then revise based on the critique, repeating until satisfactory results are achieved. Each technique serves specific purposes, and the most effective prompt engineering often combines multiple techniques strategically tailored to the task at hand.
| Technique | Best For | Complexity | Typical Use Case | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-shot Prompting | Simple, direct tasks | Low | Basic questions, straightforward instructions | Good for simple tasks, limited for complex reasoning |
| Few-shot Prompting | Tasks requiring format consistency | Medium | Content generation, classification, formatting | Excellent for demonstrating desired output patterns |
| Chain-of-Thought | Multi-step reasoning problems | Medium-High | Math problems, logical deduction, analysis | Significantly improves accuracy on complex tasks |
| Prompt Chaining | Complex workflows with dependencies | High | Multi-stage content creation, data processing | Excellent for breaking down complex problems |
| Tree-of-Thought | Problems with multiple solution paths | High | Strategic planning, creative problem-solving | Superior for exploring alternative approaches |
| Generated Knowledge | Tasks requiring background context | Medium | Domain-specific questions, technical explanations | Improves relevance and accuracy through context |
| Self-Refine | Quality-critical applications | High | Professional writing, technical documentation | Produces highest quality outputs through iteration |
Understanding how prompts influence AI model behavior requires basic knowledge of how large language models (LLMs) function. These models process text by breaking it into tokens (small units of text), then predicting the most likely next token based on patterns learned during training. The prompt serves as the initial context that shapes all subsequent predictions. When a prompt includes specific instructions, examples, or constraints, it effectively narrows the probability distribution of possible outputs, guiding the model toward responses aligned with the prompt’s intent. Temperature and top-p sampling parameters further influence output variability—lower temperatures produce more deterministic, focused responses, while higher temperatures increase creativity and diversity. The context window (the amount of text the model can consider) limits how much information can be included in a prompt; longer prompts consume more of this window, potentially reducing space for the actual task. Effective prompt engineers understand these technical constraints and design prompts that work within them. For organizations monitoring brand visibility across AI platforms through tools like AmICited, understanding these mechanisms is crucial because the prompts users input determine what information AI systems retrieve and cite. A well-engineered prompt asking an AI to “list the top three companies in cloud computing” will produce different results than “list innovative cloud computing companies founded after 2015,” potentially affecting which brands receive visibility in AI-generated responses.
Implementing effective prompt engineering in organizational settings requires following established best practices that have emerged from both academic research and industry experience. Start simple and iterate is the foundational principle—begin with a basic prompt and gradually add complexity, testing at each stage to understand what changes improve results. Be explicit about requirements by clearly stating the desired output format, length, tone, and any constraints; vague prompts produce vague results. Provide relevant context without overwhelming the model; include background information that helps the model understand the task but avoid unnecessary details that consume context window space. Use clear separators like “###” or “—” to distinguish different sections of a prompt (instructions, context, examples), making it easier for the model to parse the structure. Avoid negations by stating what you want rather than what you don’t want; instead of “don’t be too formal,” specify “use a conversational tone.” Test multiple variations systematically, changing one element at a time to understand what drives better results. Document successful prompts in a centralized repository, creating a library of tested templates that teams can reuse and adapt. Monitor performance metrics including accuracy, relevance, consistency, and user satisfaction to objectively assess whether prompts are achieving their intended goals. Incorporate feedback loops where user feedback directly informs prompt refinement, creating a continuous improvement cycle. Organizations implementing these practices report significant improvements in AI output quality and consistency, reducing the time spent on manual corrections and revisions.
The relationship between prompt engineering and AI visibility monitoring is increasingly important for organizations seeking to understand how their brands, products, and content appear in AI-generated responses. Platforms like AmICited track brand mentions across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude, but the prompts users input into these systems directly determine what information the AI retrieves and cites. Organizations that understand prompt engineering can craft strategic queries to discover how their brand is represented, what competitors are mentioned alongside them, and whether their content is being accurately cited. For example, a company might engineer prompts like “What are the best solutions for enterprise data management?” to see how AI systems position their offerings relative to competitors. By analyzing the prompts that generate favorable or unfavorable brand mentions, organizations can develop content strategies that improve their visibility in AI-generated responses. This represents a new frontier in search engine optimization (SEO) and brand management, where understanding how to communicate with AI systems becomes as important as traditional keyword optimization. Companies investing in prompt engineering expertise gain strategic advantages in the AI-driven information landscape, ensuring their brands receive appropriate visibility and accurate representation.
Measuring whether a prompt is truly effective requires defining clear, objective criteria aligned with specific business goals. Accuracy measures whether outputs are factually correct, particularly important for domains like healthcare, finance, and legal services where errors carry significant consequences. Relevance assesses how closely the output aligns with the user’s original intent, often measured using semantic similarity scores or manual evaluation. Consistency evaluates whether identical prompts produce similar responses across multiple runs, critical for applications requiring reliable, predictable behavior. Completeness determines whether responses cover all required elements or information, measured as the ratio of covered components to total required components. Specificity evaluates the level of fine-grained detail in responses, important for technical documentation and specialized domains. Readability and coherence measure clarity and logical flow, assessed through readability formulas or human evaluation. User satisfaction reflects how satisfied end-users are with outputs, typically gathered through surveys or embedded feedback mechanisms. Organizations implementing comprehensive evaluation frameworks report that prompt effectiveness improves by 40-60% through systematic measurement and refinement. Tools like Portkey, DSPy, and Hugging Face’s Evaluate Library provide automated metrics for assessing these dimensions, while A/B testing platforms enable side-by-side comparison of different prompt versions. The most sophisticated organizations combine multiple evaluation methods, weighting metrics according to their specific priorities to produce an overall prompt quality score.
The prompt engineering job market has experienced explosive growth, reflecting the critical importance of this skill in the AI era. As of 2025, Glassdoor reports an average base salary of approximately $123,274 annually for prompt engineers, with positions ranging from $90,000 at the 25th percentile to over $335,000 for specialized roles at leading AI companies like Anthropic. Indeed lists over 110,000 prompt engineer positions currently open, indicating sustained demand across industries. Big Tech companies including Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and Meta actively recruit prompt engineers with salary ranges spanning $110,000-$250,000. AI-focused companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, Cohere, and Midjourney offer cutting-edge challenges with remote-first cultures and significant equity packages. Enterprise organizations in finance, healthcare, insurance, and other regulated sectors hire prompt engineers for AI integration, often using titles like “AI Solutions Architect.” Consultancies including the Big Four and specialized firms like Booz Allen Hamilton advertise positions up to $212,000 for government and enterprise projects. Freelance opportunities on platforms like Upwork and Toptal command $100-$300 per hour for experienced professionals. The career path typically requires a bachelor’s degree in computer science or related field, though professionals from diverse backgrounds including writing, journalism, and creative fields have successfully transitioned into prompt engineering roles. Most importantly, success in this field depends on demonstrable skills with AI tools, a portfolio showcasing prompt engineering abilities, and continuous learning as the field evolves.
Prompt engineering is poised for significant evolution as AI technology advances and organizational practices mature. Multimodal prompting will increasingly combine text, code, images, and other data types in single prompts, requiring engineers to understand how different modalities interact within AI systems. Adaptive prompts that automatically adjust based on context, user behavior, and real-time feedback will become more sophisticated, moving beyond static templates toward dynamic, responsive systems. Context engineering is emerging as an evolution of prompt engineering, emphasizing the broader context in which prompts operate rather than just the prompt text itself. Ethical and fairness-focused prompting will gain prominence as organizations prioritize responsible AI deployment, with prompts explicitly designed to mitigate bias, ensure transparency, and align with regulatory requirements. Integration with AI agents will blur the line between prompt engineering and broader AI orchestration, as prompts become components of larger autonomous systems. The role of “prompt engineer” may evolve or merge with adjacent roles like “AI strategist,” “context engineer,” or “AI product manager,” reflecting the field’s maturation. Organizations that invest in prompt engineering expertise today will be well-positioned to lead in the AI-driven economy, as the ability to effectively communicate with and guide AI systems becomes increasingly central to competitive advantage. For companies using AmICited to monitor brand visibility in AI responses, prompt engineering knowledge will become essential for optimizing their presence in the AI search landscape and ensuring accurate representation across platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI, and Claude.
Prompt engineering differs fundamentally from traditional programming: instead of writing explicit code that directly controls behavior, prompt engineers guide AI models through natural language instructions. Traditional programming requires precise syntax and logic, while prompt engineering relies on iterative refinement, context provision, and strategic phrasing to steer AI outputs toward desired results. Both require problem-solving skills, but prompt engineering emphasizes communication and experimentation over strict code syntax.
Prompt engineering directly impacts how brands appear in AI-generated responses across platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude. Well-engineered prompts can influence whether and how AI systems cite, mention, or recommend brands. For organizations using tools like AmICited to monitor AI visibility, understanding prompt engineering helps predict and optimize how their brand appears in AI responses, ensuring accurate representation and competitive positioning in the AI search landscape.
Key techniques include chain-of-thought prompting (breaking complex problems into steps), few-shot prompting (providing examples), zero-shot prompting (direct instructions), prompt chaining (splitting tasks into subtasks), and tree-of-thought prompting (exploring multiple reasoning paths). The effectiveness of each technique depends on the task complexity, model capabilities, and desired output type. Most successful implementations combine multiple techniques tailored to specific use cases.
Prompt effectiveness is measured using metrics like accuracy (factual correctness), relevance (alignment with intent), consistency (reproducibility), completeness (coverage of required elements), and user satisfaction. Evaluation methods include manual review, automated assessment using tools like BLEU and ROUGE scores, A/B testing different prompt versions, and collecting direct user feedback. Organizations often combine multiple metrics into a weighted score reflecting their specific priorities.
Prompt engineers need strong communication and writing skills, understanding of how large language models work, familiarity with AI concepts like tokenization and context windows, and creative problem-solving abilities. Technical skills in Python, SQL, or JavaScript are often preferred but not always required. Domain expertise in specific industries (healthcare, finance, legal) commands premium compensation. Most importantly, successful prompt engineers demonstrate continuous learning and experimentation.
Prompt engineering is crucial for AI monitoring because the prompts users input into AI systems determine what information those systems retrieve and cite. By understanding prompt engineering, organizations can craft queries that help them discover how their brand, content, or domain appears in AI responses. AmICited tracks these appearances across multiple AI platforms, making prompt engineering knowledge essential for optimizing brand visibility in AI-generated content.
The prompt engineering job market remains robust with average salaries around $123,274 annually according to Glassdoor, with positions ranging from $90,000 to over $335,000 depending on experience and company. Over 110,000 prompt engineer positions are currently open on job boards. The field is evolving from a specialized role toward broader AI integration responsibilities, with opportunities across tech companies, enterprises, consultancies, and freelance platforms. Remote work is prevalent, making geographic location less restrictive.
Prompt engineering is expected to evolve toward multimodal prompting (combining text, code, and images), adaptive prompts that adjust based on context, and increased focus on AI ethics and fairness. As AI models become more capable, prompt engineering may merge with broader AI strategy and context engineering roles. The field will likely emphasize responsible AI practices, bias mitigation, and ensuring transparency in AI-generated outputs across platforms like those monitored by AmICited.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.
Learn what prompt engineering is, how it works with AI search engines like ChatGPT and Perplexity, and discover essential techniques to optimize your AI search ...
Learn how prompt engineering enhances GEO strategy to get your brand cited by AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Community discussion on whether marketers need prompt engineering skills to optimize for AI search. Understanding how users query AI systems.