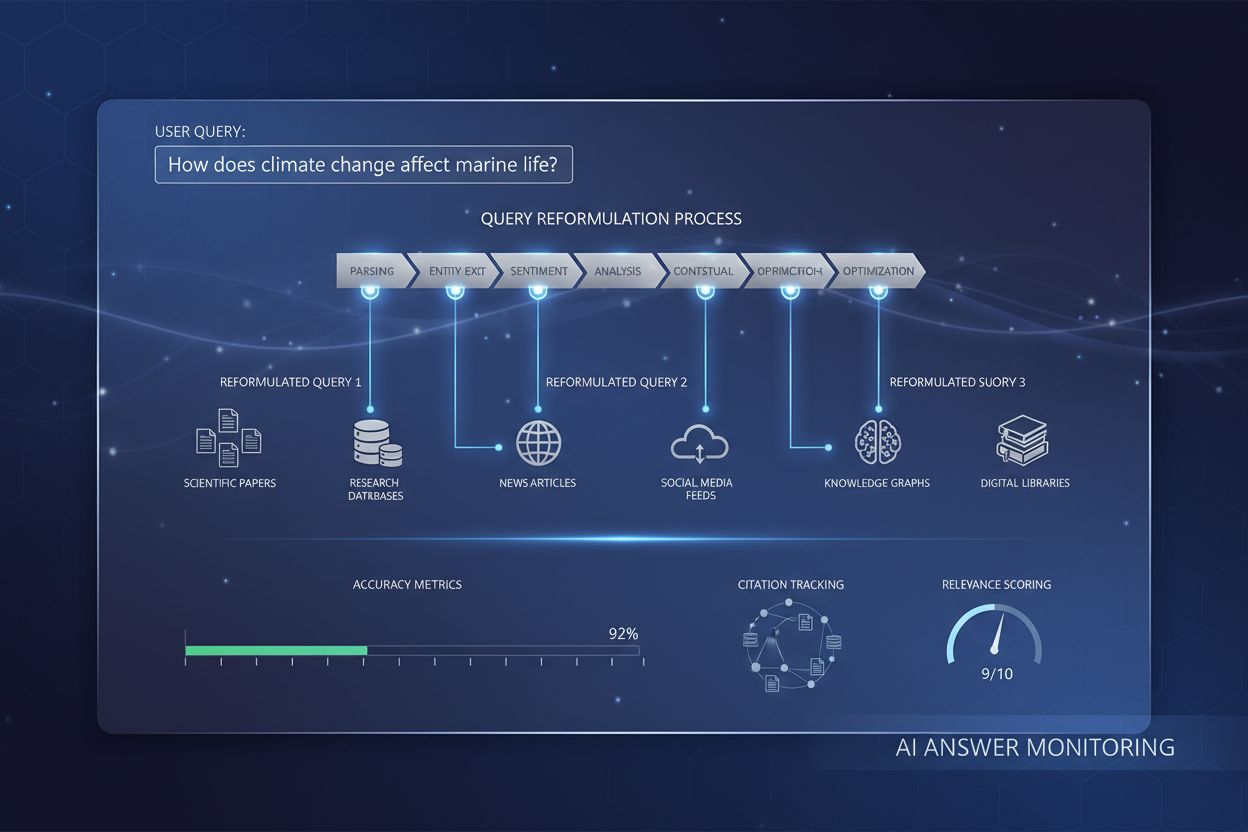
Query Reformulation
Learn how query reformulation helps AI systems interpret and enhance user queries for better information retrieval. Understand the techniques, benefits, and imp...
Query refinement is the process of improving and optimizing search queries through iterative adjustments, clarifications, and expansions to generate more accurate, relevant, and comprehensive results from AI search engines and information retrieval systems. It involves breaking down complex user queries into sub-queries, adding contextual details, and leveraging feedback loops to progressively enhance search performance and result quality.
Query refinement is the process of improving and optimizing search queries through iterative adjustments, clarifications, and expansions to generate more accurate, relevant, and comprehensive results from AI search engines and information retrieval systems. It involves breaking down complex user queries into sub-queries, adding contextual details, and leveraging feedback loops to progressively enhance search performance and result quality.
Query refinement is the iterative process of improving and optimizing search queries through systematic adjustments, clarifications, and expansions to generate more accurate, relevant, and comprehensive results from information retrieval systems and AI search engines. Rather than treating a user’s initial search as final, query refinement recognizes that users often need to modify, expand, or clarify their queries to find exactly what they’re looking for. This process involves analyzing how users modify their searches, suggesting improved query formulations, and leveraging feedback loops to progressively enhance search performance. In the context of modern AI search platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude, query refinement has become a fundamental mechanism for delivering comprehensive, multi-sourced answers that address complex user questions. The technique transforms search from a single, static interaction into a dynamic, multi-step conversation where each refinement brings users closer to their desired information.
Query refinement is not a new concept in information retrieval, but its application has evolved dramatically with the rise of artificial intelligence and large language models. Historically, search engines relied primarily on keyword matching, where a user’s query was compared directly against indexed documents. If you searched for “running shoes,” the engine would return documents containing those exact words, regardless of context or user intent. This approach was rigid and often produced irrelevant results because it ignored the nuance of human language and the complexity of user needs.
The evolution toward query refinement began with the introduction of query suggestion systems in the early 2000s, where search engines started analyzing user behavior patterns to suggest related or refined queries. Google’s “Did you mean?” feature and autocomplete suggestions were early implementations of this concept. However, these systems were relatively simple, based primarily on historical query logs and frequency analysis. They lacked the semantic understanding necessary to truly comprehend user intent or the relationships between different query formulations.
The introduction of natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning fundamentally transformed query refinement. Modern systems can now understand that “best waterproof running shoes” and “top-rated rain-resistant athletic footwear” are essentially the same query, despite using completely different terminology. This semantic understanding enables systems to recognize query variations, identify implicit user needs, and suggest refinements that genuinely improve search results. According to research from the Kopp Online Marketing SEO Research Suite, query refinement methodologies have become increasingly sophisticated, with systems now capable of generating synthetic queries (artificially created queries that simulate real user searches) to enhance training data and improve retrieval accuracy.
The emergence of generative AI and large language models has accelerated this evolution further. Modern AI search engines don’t just refine queries; they decompose them into multiple sub-queries, execute them in parallel across diverse data sources, and synthesize the results into comprehensive answers. This represents a fundamental shift from query refinement as a user-facing suggestion feature to query refinement as a core architectural component of AI search systems.
Query refinement operates through several interconnected technical mechanisms that work together to improve search quality. The first mechanism is query analysis and intent detection, where the system processes the user’s initial query to identify the underlying intent, complexity level, and type of response needed. Advanced NLP models analyze factors such as query length, terminology specificity, and contextual signals to determine whether simple keyword matching will suffice or whether more sophisticated refinement is necessary. For example, a simple factual query like “capital of Germany” might not trigger extensive refinement, while a complex query like “best practices for optimizing content for AI search engines” would activate comprehensive refinement processes.
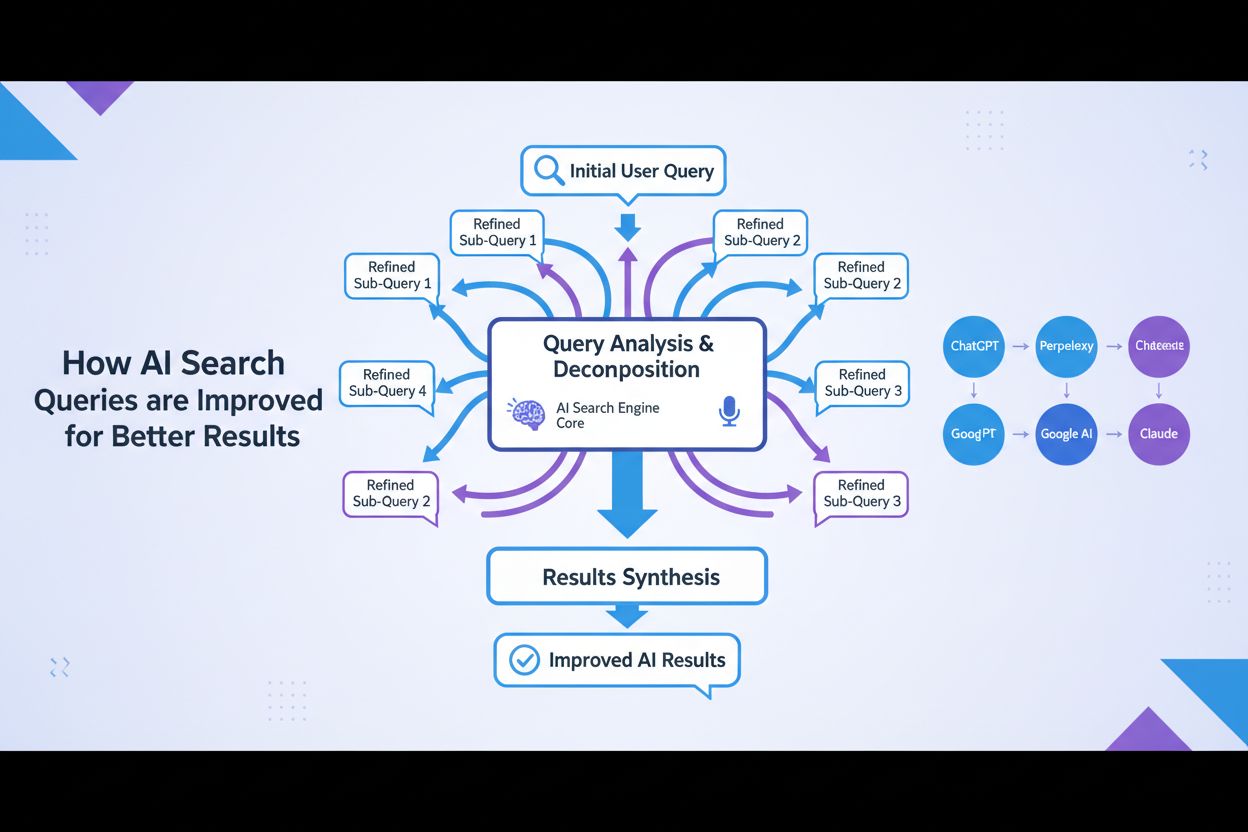
The second mechanism is query decomposition and fan-out, a technique where complex queries are broken down into multiple constituent sub-queries. This process, known as query fan-out, is particularly important in AI search systems. When a user asks “What are the best waterproof running shoes for someone with flat feet who runs on trails?”, the system decomposes this into multiple sub-queries: one exploring product listings, another investigating expert reviews, another analyzing user experiences, and another examining technical specifications. These sub-queries are then executed simultaneously across different data sources, including the live web, knowledge graphs, and specialized databases. This parallel execution dramatically expands the information pool available for synthesis, enabling the AI to provide more comprehensive and nuanced answers.
The third mechanism is query augmentation, which involves generating additional queries to enhance search performance. According to research from the Kopp Online Marketing SEO Research Suite, query augmentation uses several methods: historical data analysis (examining previous query refinements in user search histories), n-gram substitution (modifying queries by replacing contiguous sequences of terms), entity association (identifying entities from search results and combining them with original query terms), and sibling query identification (finding related queries that share common parent queries). These augmentation techniques ensure that the system explores multiple angles and perspectives on the user’s information need.
The fourth mechanism is feedback loops and continuous improvement, where user interactions with search results inform the refinement process. When users click on certain results, spend time on particular pages, or reformulate their queries, this data feeds back into the system to improve future refinements. Reinforcement learning techniques can be applied to optimize generative models, improving the quality of query variants over time based on satisfactory responses. This creates a virtuous cycle where each user interaction makes the system smarter and more effective at refining queries.
| Aspect | Google AI Overviews | ChatGPT | Perplexity | Claude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Refinement Method | Query fan-out with thematic search | Conversational multi-turn refinement | Interactive query suggestions with follow-ups | Contextual clarification through dialogue |
| Sub-Query Generation | Automatic decomposition based on intent | User-guided through conversation | Suggested refinements displayed as pills | Implicit through context understanding |
| Data Sources | Live web, knowledge graphs, shopping graphs | Training data + web search (with plugins) | Real-time web search across multiple sources | Training data with web search capability |
| Citation Mechanism | Direct source attribution in overview | Link references in responses | Source cards with detailed attribution | Inline citations with source links |
| User Control | Limited (system-driven refinement) | High (user directs conversation) | Medium (suggested refinements + custom input) | High (user can request specific refinements) |
| Refinement Visibility | Implicit (user sees synthesized answer) | Explicit (user sees conversation history) | Explicit (refinement suggestions visible) | Implicit (refinement through dialogue) |
| Speed of Refinement | Immediate (parallel processing) | Sequential (turn-by-turn) | Immediate (real-time search) | Sequential (conversation-based) |
| Personalization Level | High (based on search history & location) | Medium (based on conversation context) | Medium (based on session data) | Medium (based on conversation context) |
The process of query refinement in contemporary AI search engines follows a sophisticated, multi-stage workflow that differs significantly from traditional search. When a user submits a query to a system like Google AI Mode or ChatGPT, the system doesn’t immediately search for results. Instead, it first analyzes the query using advanced natural language processing to understand what the user is really asking. This analysis considers factors such as the user’s search history, location, device type, and the complexity of the query itself. The system determines whether the query is straightforward (requiring simple keyword matching) or complex (requiring decomposition and multi-source synthesis).
For complex queries, the system activates the query fan-out process. This involves breaking the original query into multiple related sub-queries that explore different facets of the user’s information need. For instance, if a user asks “How should I optimize my website for AI search engines?”, the system might generate sub-queries such as: “What are the key ranking factors for AI search engines?”, “How do AI systems evaluate content quality?”, “What is E-E-A-T and why does it matter for AI?”, “How do I structure content for AI citation?”, and “What are the best practices for AI-friendly content formatting?”. Each of these sub-queries is executed in parallel across different data sources, retrieving diverse information that addresses different aspects of the original question.
The system then evaluates the retrieved information using quality signals such as domain authority, content freshness, topical relevance, and citation patterns. Information from multiple sources is combined and synthesized into a coherent, comprehensive response that directly addresses the original query. Throughout this process, the system identifies the most authoritative and relevant sources, which are then presented as citations or references in the final answer. This is why understanding query refinement is critical for AmICited users—the sources that appear in AI-generated answers are determined largely by how well they align with the refined sub-queries that the AI system generates.
The relationship between query refinement and search visibility in AI Overviews is direct and measurable. Research shows that over 88% of searches that trigger AI Overviews have informational intent, meaning users are seeking to learn about something rather than make a purchase or navigate to a specific site. These informational queries are precisely the ones most likely to undergo extensive refinement, as they often require synthesis from multiple sources to provide a complete answer. When your content aligns with the refined sub-queries that an AI system generates, your website has a significantly higher chance of being cited as a source.
The data is compelling: being featured as an AI Overview source increases click-through rates from 0.6% to 1.08%, nearly doubling the traffic compared to appearing only in traditional search results below the overview. This makes query refinement understanding essential for modern SEO strategy. Rather than optimizing for a single keyword, content creators must now think about how their content addresses the various refined queries that an AI system might generate. For example, if you’re writing about “sustainable fashion,” you should anticipate that an AI system might refine this into sub-queries about “environmental impact of fast fashion,” “ethical manufacturing practices,” “sustainable materials,” “fair trade certifications,” and “cost-effective sustainable brands.” Your content should comprehensively address these refined angles to maximize citation potential.
Additionally, research indicates that approximately 70% of users read only the first third of AI Overviews, meaning that being cited early in the response is significantly more valuable than appearing later. This suggests that content creators should structure their information with the most critical, summary-level answers at the top, in a clear and citable format. The goal is to become the source that the AI system “must” cite to provide a credible, comprehensive answer to the refined queries it generates.
Effective query refinement requires understanding and implementing several key techniques. The first technique is contextual detail addition, where users or systems add specific context to make queries more precise. Instead of searching for “running shoes,” a refined query might be “best waterproof running shoes for women with high arches under $150.” This additional context helps AI systems understand the specific constraints and preferences that matter to the user, enabling more targeted information retrieval. For content creators, this means anticipating these contextual refinements and creating content that addresses specific use cases, demographics, and constraints.
The second technique is constraint specification, where users define boundaries or limitations for their search. This might include price ranges, geographic locations, time frames, or quality standards. AI systems recognize these constraints and refine their search accordingly. For example, a query about “best project management software for remote teams with fewer than 50 employees” includes multiple constraints that should guide content creation. Your content should explicitly address these constraint scenarios to improve citation likelihood.
The third technique is follow-up questioning, where users ask clarifying questions to refine their understanding. In conversational AI systems like ChatGPT, users might ask “Can you explain that more simply?” or “How does that apply to small businesses?” These follow-up questions trigger query refinement, where the system adjusts its approach based on the user’s feedback. This is why conversational depth and the ability to address multiple angles on a topic are increasingly important for content visibility.
The fourth technique is query decomposition, where complex questions are broken into simpler component questions. This is particularly important for AI systems, which use this technique to ensure comprehensive coverage of a topic. If a user asks “What are the best practices for optimizing e-commerce websites for AI search engines?”, an AI system might decompose this into: “What are AI search engines?”, “How do AI systems rank e-commerce content?”, “What technical optimizations matter?”, “How should product descriptions be structured?”, and “What role does user-generated content play?”. Content that addresses these component questions comprehensively will be more likely to be cited across multiple refined queries.
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), also known as Large Language Model Optimization (LLMO), is fundamentally about understanding and optimizing for query refinement processes. Traditional SEO focused on ranking for specific keywords; GEO focuses on becoming a cited source across the refined queries that AI systems generate. This represents a paradigm shift in how content creators should approach search optimization.
In the GEO context, query refinement is not something that happens to your content—it’s something you must anticipate and prepare for. When you create content, you should think about all the ways an AI system might refine or decompose your topic into sub-queries. For example, if you’re writing about “sustainable fashion,” you should create content that addresses: the environmental impact of conventional fashion, sustainable materials and their properties, ethical manufacturing and labor practices, certifications and standards, cost considerations, brand recommendations, and how to transition to sustainable fashion. By comprehensively addressing these refined angles, you increase the likelihood that your content will be cited across multiple AI-generated answers.
Research from Elementor’s 2026 AI SEO Statistics shows that AI search traffic increased 527% year-over-year, with some sites now reporting over 1% of total sessions coming from platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Copilot. This explosive growth underscores the importance of understanding query refinement. The traffic from AI platforms is also significantly more valuable—AI referral visitors are worth 4.4x more than traditional organic search visitors, with 27% lower bounce rates and 38% longer session durations for retail sites. This means that optimizing for query refinement isn’t just about visibility; it’s about driving high-quality, conversion-ready traffic.
The future of query refinement is moving toward increasingly sophisticated, personalized, and autonomous systems. Synthetic query generation is becoming more advanced, with AI systems capable of generating diverse, contextually appropriate queries that simulate real user search patterns. These synthetic queries are crucial for training AI systems to handle novel or rarely-used queries by leveraging learned patterns and contextual information. As AI systems become more capable, they will generate increasingly nuanced and specific sub-queries, requiring content creators to think even more deeply about the various angles and perspectives on their topics.
Another emerging trend is stateful query refinement, where AI systems maintain context across multiple turns of conversation, allowing for more sophisticated refinement based on the user’s evolving needs and preferences. Rather than treating each query as independent, these systems understand how queries relate to previous interactions, enabling more personalized and contextually appropriate refinements. This has implications for content strategy—your content should be structured to support multi-turn conversations where users progressively refine their understanding.
The integration of reinforcement learning into query refinement systems is also significant. These systems can learn from user feedback to continuously improve the quality of query refinements over time. If users consistently click on certain sources or spend more time on particular pages, the system learns to prioritize those sources in future refinements. This creates a competitive advantage for content creators who consistently provide high-quality, authoritative information—they become the “go-to” sources that AI systems learn to cite.
Additionally, the rise of AI agents and autonomous search systems suggests that query refinement will become even more sophisticated. Rather than users manually refining queries, AI agents will autonomously generate and execute refined queries on behalf of users, exploring information spaces comprehensively to answer complex questions. This means that content creators must ensure their content is discoverable not just by human searchers, but by autonomous AI agents that are systematically exploring and refining queries across the web.
The competitive landscape is also evolving. As more platforms implement query refinement capabilities, the ability to appear in refined queries becomes a key differentiator. AmICited users who understand and monitor their presence across refined queries in different AI platforms will have a significant advantage over competitors who focus solely on traditional search rankings. The future belongs to content creators and brands that recognize query refinement as a fundamental aspect of search visibility and optimize accordingly.
Query refinement focuses on enhancing the relevance and accuracy of search results by adjusting or suggesting queries based on user context and historical data, aiming to provide more precise information. Query expansion, by contrast, involves generating additional queries to enhance search engine performance by addressing issues like poorly phrased initial queries or irrelevant results. While refinement improves an existing query, expansion creates multiple related queries to broaden the search scope. Both techniques work together in modern AI search systems to improve information retrieval quality.
AI search engines use query refinement through a process called query fan-out, where a single user query is decomposed into multiple sub-queries that are executed simultaneously across various data sources. For example, a complex question about 'best waterproof running shoes for flat feet' might be broken down into sub-queries exploring product listings, expert reviews, user experiences, and technical specifications. This parallel retrieval of information from different sources significantly expands the information pool available for answer synthesis, enabling the AI to provide more comprehensive and accurate responses.
Natural language processing is fundamental to query refinement as it enables AI systems to interpret meaning beyond simple keyword matching. NLP uses patterns and contextual relationships between words to decipher how humans speak, making searches more intuitive and accurate. For instance, NLP allows a system to understand that 'open coffee shops' means businesses that are currently operating and located nearby, not just documents containing those exact words. This contextual understanding is what allows modern AI systems to refine queries intelligently and provide results that match user intent rather than just literal keyword matches.
Query refinement improves search visibility in AI Overviews by helping content creators understand how users modify their searches to find better results. By targeting both initial and refined queries with comprehensive content that anticipates user needs and follow-up questions, websites can increase their chances of being cited as sources. Research shows that being featured as an AI Overview source increases click-through rates from 0.6% to 1.08%, making query refinement understanding essential for modern SEO strategy and AI citation visibility.
Synthetic queries are artificially generated queries created by large language models that simulate real user search queries. They are crucial for query refinement because they expand labeled training data, improve recall, and enable generative retrieval to scale to large datasets by filling data gaps. Synthetic queries are generated through mining structured data, analyzing document titles and anchor texts, and using structured rule sets. They help AI systems understand and refine queries by providing diverse examples of how users might phrase similar information needs, ultimately improving the system's ability to refine and expand user queries effectively.
Businesses can optimize for query refinement by analyzing Google Search Console data to identify related keywords and query variations that users search for sequentially. They should create comprehensive content that addresses both initial broad queries and refined, specific variations. Using tools like seoClarity or similar platforms, businesses can mine query refinements and autosuggest data to find relevant query variations for keyword research. Additionally, monitoring ranks by query refinement and tracking how different faceted pages perform helps drive decisions around content strategy and technical implementation.
Query refinement is deeply connected to user intent because it reveals how users' information needs evolve throughout their search journey. By analyzing query refinement patterns, businesses can understand what users are really looking for at each stage of their decision-making process. For example, a user might start with broad intent ('running shoes') and progressively refine to more specific intent ('best waterproof running shoes for flat feet'). Understanding these refinement patterns allows content creators to develop targeted content for each stage of the user journey, ultimately improving both search visibility and conversion rates.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn how query reformulation helps AI systems interpret and enhance user queries for better information retrieval. Understand the techniques, benefits, and imp...
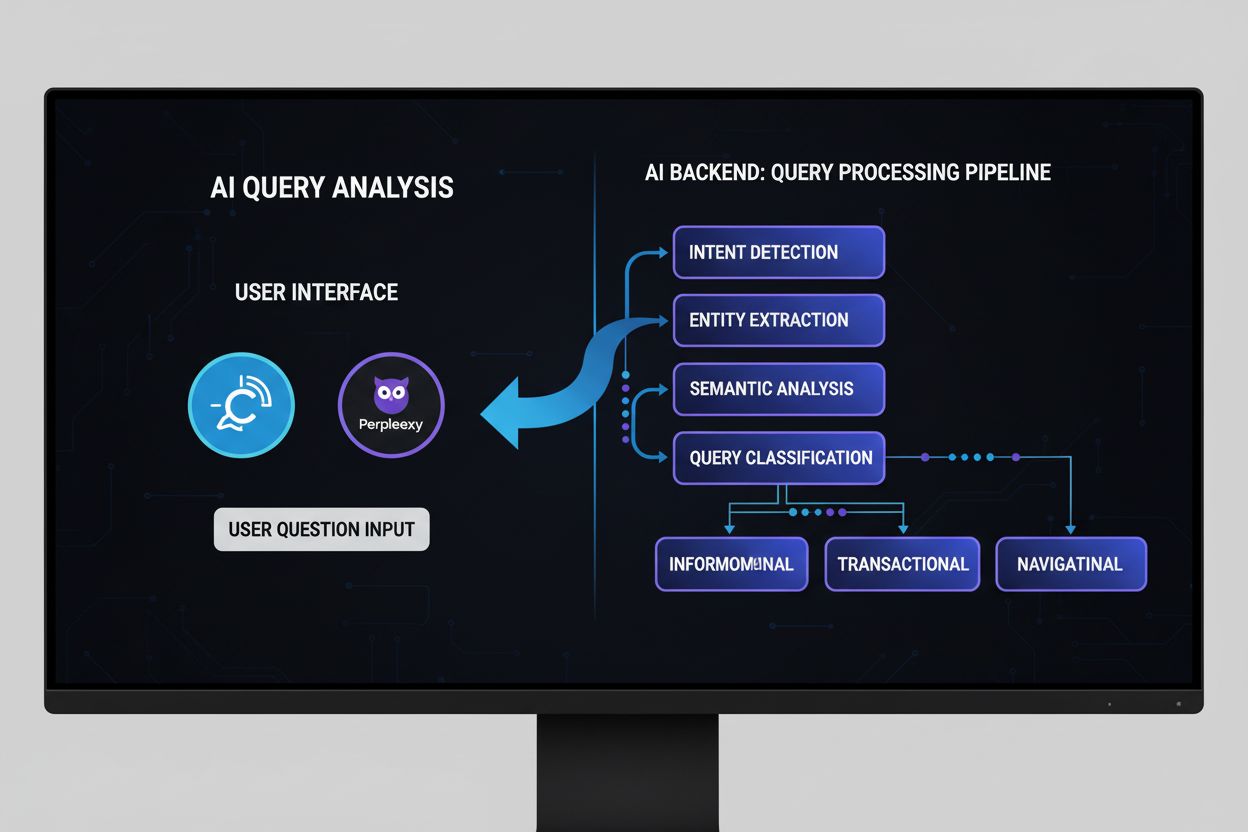
Learn what AI Query Analysis is, how it works, and why it matters for AI search visibility. Understand query intent classification, semantic analysis, and monit...
Learn how query expansion optimization improves AI search results by bridging vocabulary gaps. Discover techniques, challenges, and why it matters for AI monito...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.