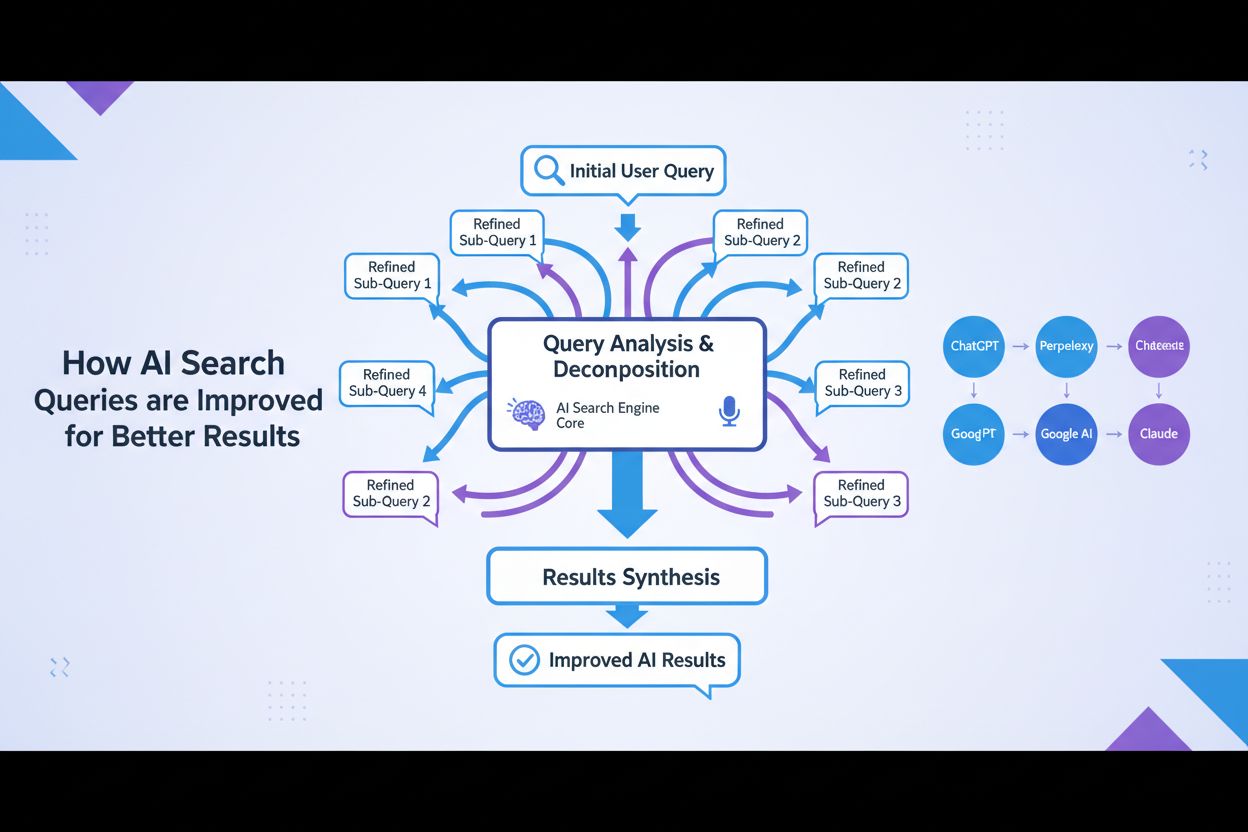
Query Refinement
Query refinement is the iterative process of optimizing search queries for better results in AI search engines. Learn how it works across ChatGPT, Perplexity, G...
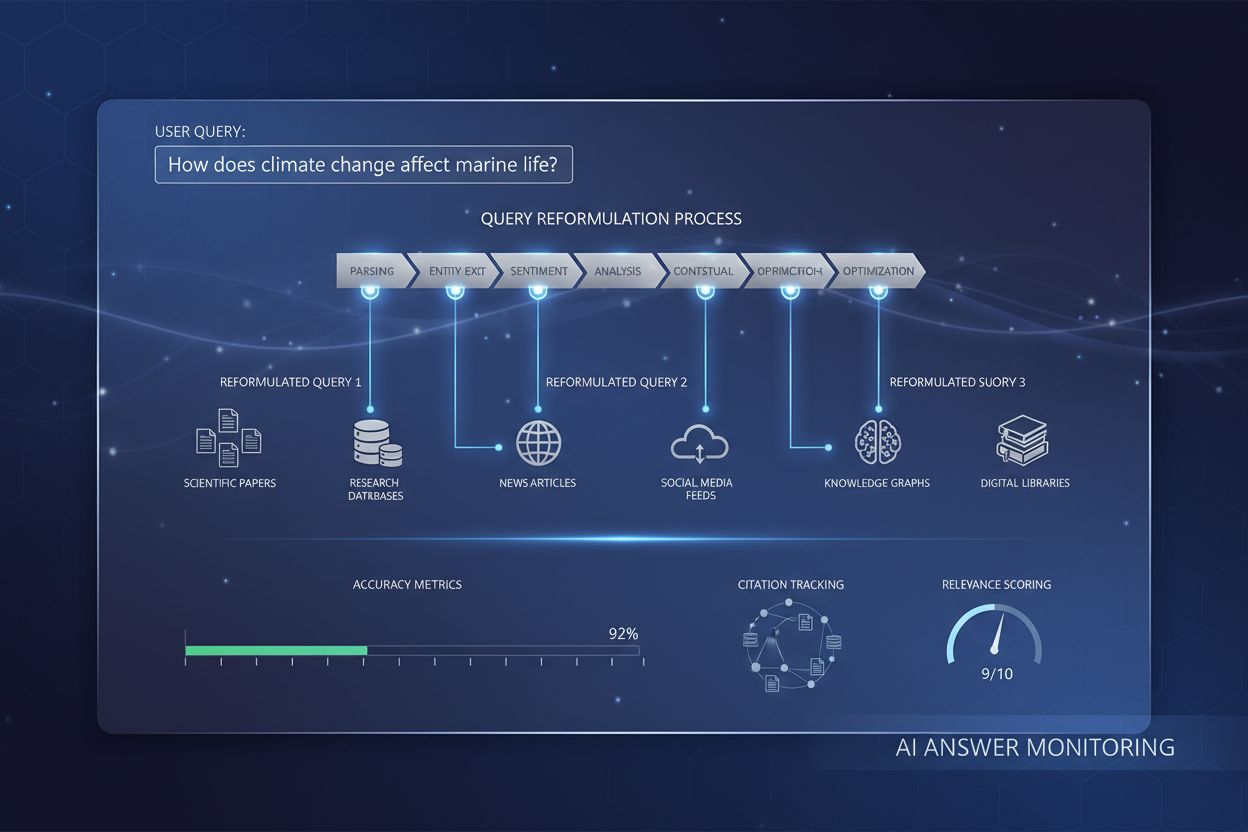
Query reformulation is the process by which AI systems interpret, restructure, and enhance user queries to improve information retrieval accuracy and relevance. It transforms simple or ambiguous user inputs into more detailed, contextually enriched versions that align with the AI system’s understanding, enabling more precise and comprehensive responses.
Query reformulation is the process by which AI systems interpret, restructure, and enhance user queries to improve information retrieval accuracy and relevance. It transforms simple or ambiguous user inputs into more detailed, contextually enriched versions that align with the AI system's understanding, enabling more precise and comprehensive responses.
Query reformulation is the process of transforming, expanding, or rewriting a user’s original search query to better align with the underlying information retrieval system’s capabilities and the user’s actual intent. In the context of artificial intelligence and natural language processing (NLP), query reformulation bridges the critical gap between how users naturally express their information needs and how AI systems interpret and process those requests. This technique is essential in modern AI systems because users often phrase queries imprecisely, use domain-specific terminology inconsistently, or fail to include contextual information that would improve retrieval accuracy. Query reformulation operates at the intersection of information retrieval, semantic understanding, and machine learning, enabling systems to generate more relevant results by reinterpreting queries through multiple lenses—whether through synonym expansion, contextual enrichment, or structural reorganization. By reformulating queries intelligently, AI systems can dramatically improve answer quality, reduce ambiguity, and ensure that retrieved information more accurately matches user intent.
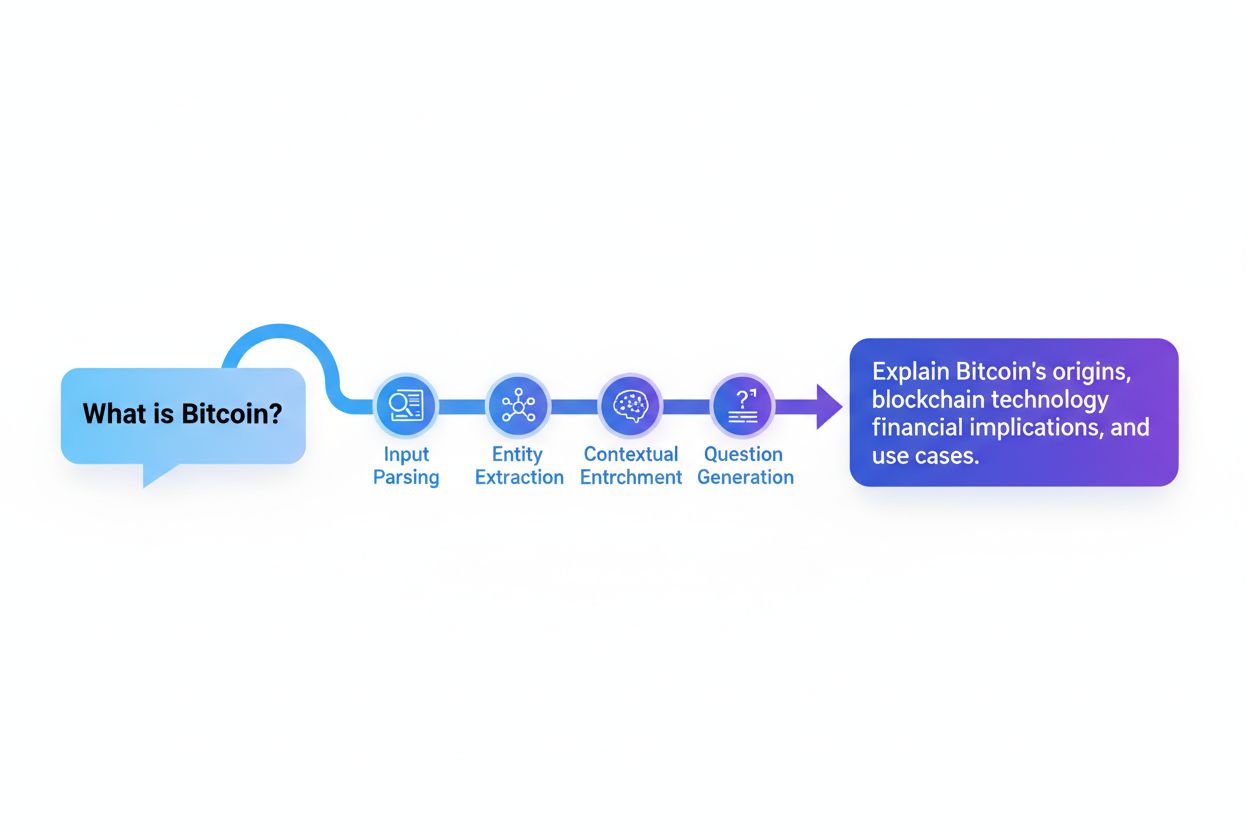
Query reformulation systems typically operate through five interconnected components that work together to transform raw user input into optimized search queries. Input parsing breaks down the original query into its constituent parts, identifying keywords, phrases, and structural elements. Entity extraction identifies named entities (people, places, organizations, products) and domain-specific concepts that carry semantic weight. Sentiment analysis preserves the emotional tone or evaluative stance of the original query, ensuring reformulated versions maintain the user’s original perspective. Contextual analysis incorporates session history, user profile information, and domain knowledge to enrich the query with implicit meaning. Question generation converts declarative statements or fragments into well-formed questions that retrieval systems can process more effectively.
| Component | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Input Parsing | Tokenizes and segments query into meaningful units | “best Python libraries” → [“best”, “Python”, “libraries”] |
| Entity Extraction | Identifies named entities and domain concepts | “Apple’s latest iPhone” → Entity: Apple (company), iPhone (product) |
| Sentiment Analysis | Preserves evaluative tone and user perspective | “terrible customer service” → Maintains negative sentiment in reformulation |
| Contextual Analysis | Incorporates session history and domain knowledge | Previous query about “machine learning” informs current “neural networks” query |
| Question Generation | Converts fragments into structured questions | “Python debugging” → “How do I debug Python code?” |
The query reformulation process follows a systematic six-step methodology designed to progressively enhance query quality and relevance:
Input Parsing and Normalization
Entity and Concept Extraction
Sentiment and Intent Preservation
Contextual Enrichment
Query Expansion and Synonym Generation
Optimization and Evaluation
Query reformulation employs diverse techniques ranging from traditional lexical approaches to cutting-edge neural methods. Synonym-based expansion leverages established resources like WordNet, word embeddings such as Word2Vec and GloVe, and contextual models like BERT to identify semantically similar terms. Query relaxation progressively loosens query constraints to increase recall when initial results are insufficient—for instance, removing rare terms or broadening date ranges. User feedback and session context integration allows systems to learn from user interactions, refining reformulations based on which results users actually find relevant. Transformer-based rewriters like T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer) and GPT models generate entirely new query formulations by learning patterns from large training datasets of query pairs. Hybrid approaches combine multiple techniques—for example, using rule-based synonym expansion for high-confidence terms while applying neural models for ambiguous phrases. Real-world implementations often employ ensemble methods that generate multiple reformulations and rank them using learned relevance models. For instance, e-commerce platforms might combine domain-specific synonym dictionaries with BERT embeddings to handle both standardized product terminology and colloquial user language, while medical search systems might use specialized ontologies alongside transformer models to ensure clinical accuracy.
Query reformulation delivers substantial improvements across multiple dimensions of AI system performance and user experience:
Improved Retrieval Accuracy: Reformulated queries more precisely capture user intent, resulting in higher-quality retrieved documents and more relevant AI-generated answers. By expanding queries with synonyms and related concepts, systems retrieve documents that might use different terminology than the original query, dramatically increasing the likelihood of finding truly relevant information.
Enhanced Recall and Coverage: Query expansion increases the number of relevant documents retrieved by exploring semantic variations and related concepts. This is particularly valuable in specialized domains where terminology varies significantly, ensuring users don’t miss relevant information due to vocabulary differences.
Reduced Ambiguity and Clarification: Reformulation processes disambiguate vague or ambiguous queries by incorporating context and generating multiple interpretations. This allows systems to handle queries like “apple” (fruit vs. company) by generating context-specific reformulations that retrieve appropriate results.
Better User Experience and Satisfaction: Users receive more relevant results faster, reducing the need for query refinement iterations. Fewer failed searches and more accurate first-result hits translate directly to improved user satisfaction and reduced cognitive load.
Scalability and Efficiency: Reformulation enables systems to handle diverse user populations with varying vocabulary, expertise levels, and linguistic backgrounds. A single reformulation engine can serve users across different domains and languages, improving system scalability without proportional increases in infrastructure.
Continuous Improvement and Learning: Query reformulation systems can be trained on user interaction data, continuously improving their reformulation strategies based on which reformulations lead to successful outcomes. This creates a virtuous cycle where system performance improves over time as more user data accumulates.
Domain Adaptation and Specialization: Reformulation techniques can be fine-tuned for specific domains (medical, legal, technical) by training on domain-specific query pairs and incorporating domain ontologies. This enables specialized systems to handle domain terminology with greater precision than generic approaches.
Robustness to Query Variations: Systems become resilient to typos, grammatical errors, and colloquial language by reformulating queries into standardized forms. This robustness is particularly valuable for voice-based interfaces and mobile search where input quality varies significantly.
Query reformulation plays a critical role in the accuracy and reliability of AI-generated answers, making it essential for AI answer monitoring platforms like AmICited.com. When AI systems reformulate queries before generating answers, the quality of those reformulations directly impacts whether the AI retrieves appropriate source material and generates accurate, well-cited responses. Poorly reformulated queries can lead AI systems to retrieve irrelevant documents, causing the AI to generate answers that lack proper grounding or cite inappropriate sources. In the context of AI monitoring and citation tracking, understanding how queries are reformulated is crucial for verifying that AI systems are actually answering the user’s intended question rather than a distorted interpretation of it. AmICited.com tracks how AI systems reformulate queries to ensure that the sources cited in AI-generated answers are genuinely relevant to the original user question, not merely relevant to a misinterpreted reformulation. This monitoring capability is particularly important because query reformulation happens invisibly to end users—they see only the final answer and citations, unaware of how the underlying query was transformed. By analyzing query reformulation patterns, AI monitoring platforms can identify when AI systems are generating answers based on reformulated queries that diverge significantly from user intent, flagging potential accuracy issues before they reach users. Furthermore, understanding reformulation helps platforms assess whether AI systems are appropriately handling ambiguous queries by generating multiple reformulations and synthesizing information across them, or whether they’re making unwarranted assumptions about user intent.
Query reformulation has become indispensable across numerous AI-driven applications and industries. In healthcare and medical research, query reformulation handles the complexity of medical terminology where patients might search for “heart attack” while clinical literature uses “myocardial infarction”—reformulation bridges this vocabulary gap to retrieve clinically accurate information. Legal document analysis systems use query reformulation to handle the precise, archaic language of legal documents while accommodating modern search terminology, ensuring lawyers can find relevant precedents regardless of how they phrase their queries. Technical support systems reformulate user queries to match knowledge base articles, converting colloquial descriptions of problems (“my computer is slow”) into technical terms (“system performance degradation”) to retrieve appropriate troubleshooting guides. E-commerce search optimization employs query reformulation to handle product searches where users might search for “running shoes” while the catalog uses “athletic footwear” or specific brand names, ensuring customers find desired products despite terminology differences. Conversational AI and chatbots use query reformulation to maintain context across multi-turn conversations, reformulating follow-up questions to include implicit context from previous exchanges. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems rely heavily on query reformulation to ensure that retrieved context documents are genuinely relevant to the user’s question, directly impacting the quality of generated responses. For example, a RAG system answering “How do I optimize database queries?” might reformulate this into multiple variants like “database query performance tuning,” “SQL optimization techniques,” and “query execution plans” to retrieve comprehensive context before generating a detailed answer.
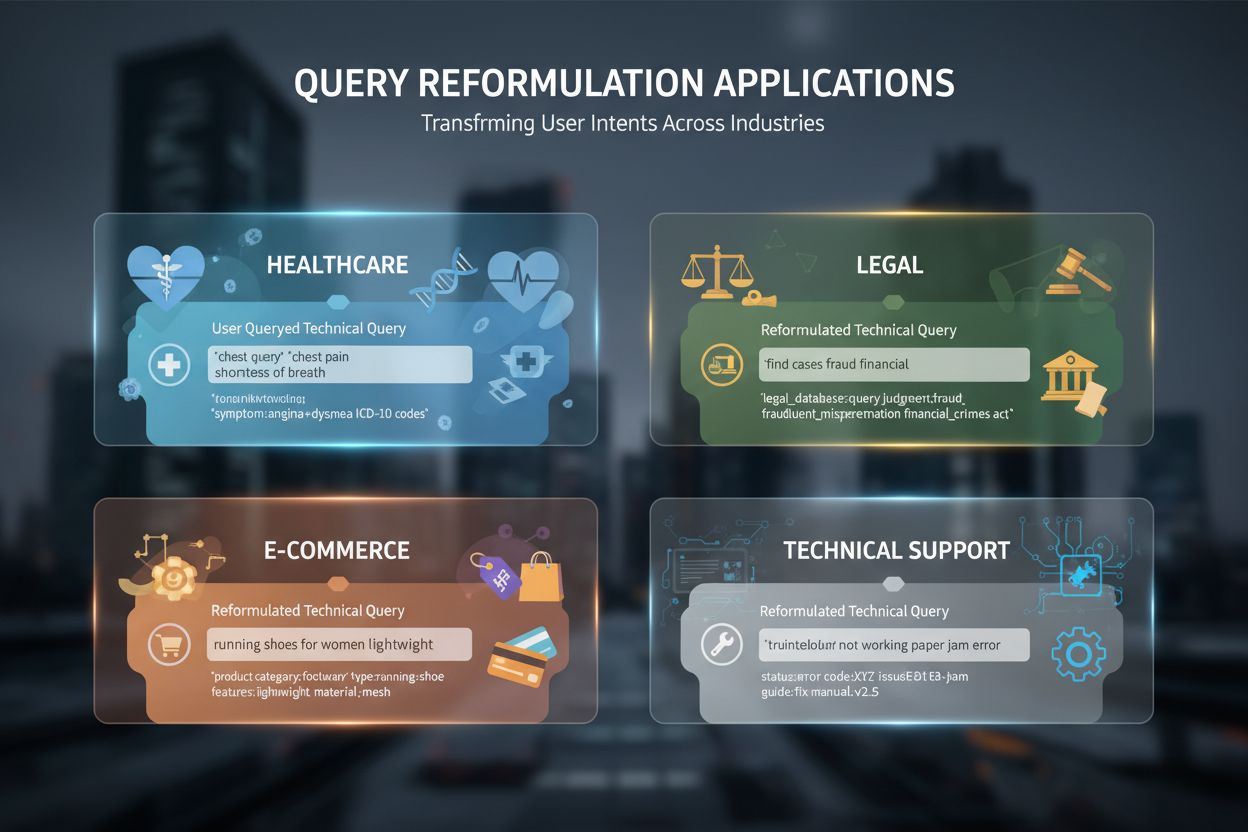
Despite its benefits, query reformulation presents several significant challenges that practitioners must carefully navigate. Computational complexity increases substantially when generating multiple query reformulations and ranking them by relevance—each reformulation requires processing, and systems must balance the quality gains against latency requirements, particularly in real-time applications. Training data quality directly determines reformulation effectiveness; systems trained on poor-quality query pairs or biased datasets will perpetuate those biases in their reformulations, potentially amplifying existing problems rather than solving them. Risk of over-reformulation occurs when systems generate so many query variants that they lose focus on the original intent, retrieving increasingly tangential results that confuse rather than clarify. Domain-specific adaptation requires significant effort—reformulation models trained on general web queries often perform poorly on specialized domains like medicine or law without substantial retraining and domain-specific tuning. Precision versus recall balance presents a fundamental tradeoff: aggressive query expansion increases recall but may decrease precision by retrieving irrelevant results, while conservative reformulation maintains precision but misses relevant documents. Potential bias introduction can occur when reformulation systems encode societal biases present in training data, potentially amplifying discrimination in search results or AI-generated answers—for instance, reformulating “nurse” queries might disproportionately retrieve female-associated results if training data reflects historical gender biases.
Query reformulation continues to evolve rapidly as AI capabilities advance and new techniques emerge. Advances in LLM-based reformulation are enabling more sophisticated, context-aware query transformations as large language models become more capable of understanding nuanced user intent and generating natural, semantically rich reformulations. Multimodal AI integration will extend query reformulation beyond text to handle images, audio, and video queries, reformulating visual search queries into text descriptions that retrieval systems can process. Personalization and learning will enable query reformulation systems to adapt to individual users’ preferences, vocabulary, and search patterns, generating increasingly personalized reformulations that reflect each user’s unique communication style. Real-time adaptive reformulation will allow systems to reformulate queries dynamically based on intermediate retrieval results, creating feedback loops where initial reformulations inform subsequent refinements. Knowledge graph integration will enable reformulation systems to leverage structured knowledge about entities and relationships, generating more semantically precise reformulations grounded in explicit knowledge representations. Emerging standards for query reformulation evaluation and benchmarking will facilitate comparison across systems and drive industry-wide improvements in reformulation quality and consistency.
Query reformulation is the broader process of transforming a query to improve retrieval, while query expansion is a specific technique within reformulation that adds synonyms and related terms. Query expansion focuses on widening the search scope, whereas reformulation encompasses multiple techniques including parsing, entity extraction, sentiment analysis, and contextual enrichment to fundamentally improve query quality.
Query reformulation helps AI systems better understand user intent by clarifying ambiguous terms, adding context, and generating multiple interpretations of the original query. This leads to retrieval of more relevant source documents, which in turn enables the AI to generate more accurate, well-grounded answers with proper citations.
Yes, query reformulation can serve as a security layer by standardizing and sanitizing user inputs before they reach the main AI system. A specialized reformulation agent can detect and neutralize potentially harmful inputs, filter suspicious patterns, and transform queries into safe, standardized formats that reduce vulnerability to prompt injection attacks.
In Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems, query reformulation is critical for ensuring that retrieved context documents are genuinely relevant to the user's question. By reformulating queries into multiple variants, RAG systems can retrieve more comprehensive and diverse context, directly improving the quality and accuracy of generated responses.
Implementation typically involves selecting appropriate techniques for your use case: use synonym-based expansion with BERT or Word2Vec for semantic similarity, apply transformer models like T5 or GPT for neural reformulation, incorporate domain-specific ontologies for specialized fields, and implement feedback loops to continuously improve reformulations based on user interactions and retrieval success metrics.
Computational costs vary by technique: simple synonym expansion is lightweight, while transformer-based reformulation requires significant GPU resources. However, using smaller specialized models for reformulation and larger models only for final answer generation can optimize costs. Many systems employ caching and batch processing to amortize computational expenses across multiple queries.
Query reformulation directly impacts citation accuracy because the reformulated query determines which documents are retrieved and cited. If reformulation diverges significantly from the original user intent, the AI may cite sources relevant to the reformulated query rather than the original question. AI monitoring platforms like AmICited track these transformations to ensure citations are genuinely relevant to what users actually asked.
Yes, query reformulation can amplify existing biases if training data reflects societal prejudices. For example, reformulating certain queries might disproportionately retrieve results associated with particular demographics. Mitigating this requires careful dataset curation, bias detection mechanisms, diverse training examples, and continuous monitoring of reformulation outputs for fairness and representativeness.
Query reformulation affects how AI systems understand and cite your content. AmICited tracks these transformations to ensure your brand gets proper attribution in AI-generated answers.

Query refinement is the iterative process of optimizing search queries for better results in AI search engines. Learn how it works across ChatGPT, Perplexity, G...
Learn how query expansion optimization improves AI search results by bridging vocabulary gaps. Discover techniques, challenges, and why it matters for AI monito...
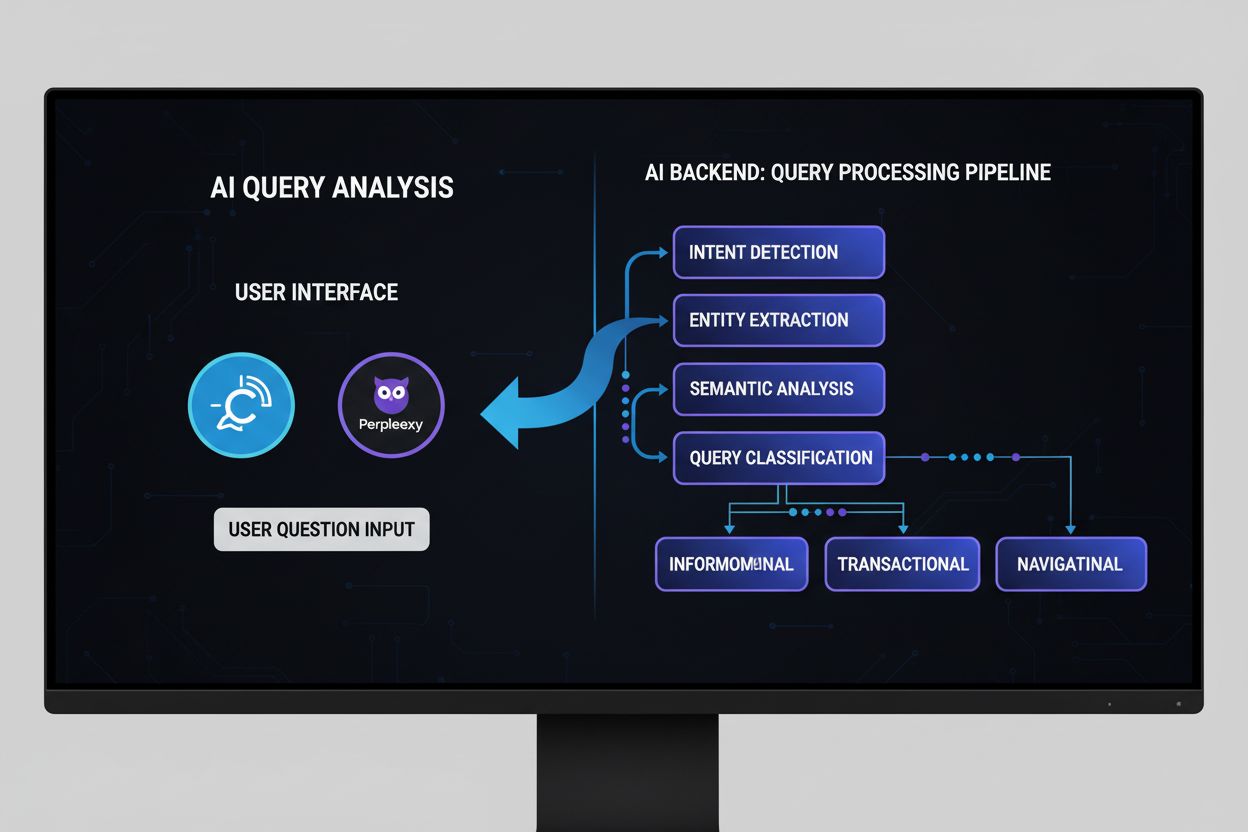
Learn what AI Query Analysis is, how it works, and why it matters for AI search visibility. Understand query intent classification, semantic analysis, and monit...