
AI Citation
Learn what AI citations are, how they work across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI, and why they matter for your brand's visibility in generative search engin...

Query-to-citation mapping is the process of analyzing and tracking which specific search queries trigger citations to particular content, brands, or websites in AI-generated answers. It reveals the relationship between user intent, query formulation, and which sources AI models select as authoritative. This enables brands to understand and optimize their visibility across different query types and AI platforms. By mapping queries to citations, organizations can identify patterns in how AI systems cite their content and adjust their content strategy accordingly.
Query-to-citation mapping is the process of analyzing and tracking which specific search queries trigger citations to particular content, brands, or websites in AI-generated answers. It reveals the relationship between user intent, query formulation, and which sources AI models select as authoritative. This enables brands to understand and optimize their visibility across different query types and AI platforms. By mapping queries to citations, organizations can identify patterns in how AI systems cite their content and adjust their content strategy accordingly.
Query-to-citation mapping is the process of analyzing and tracking which specific search queries trigger citations to particular content, brands, or websites in AI-generated answers. Unlike traditional search ranking, which measures how websites appear in blue link results, query-to-citation mapping focuses specifically on when and why AI systems cite your content as a source. This distinction matters because a website might rank well in Google but never be cited by ChatGPT, Gemini, or Perplexity—or conversely, be cited frequently without ranking highly. Understanding this relationship is critical because AI models cite sources differently based on query intent, user location, and platform-specific preferences, making it essential to track which queries actually drive citations to your brand.
Query-to-citation mapping operates through a systematic process of query analysis, citation tracking, and repeated testing across multiple AI platforms. The process begins by categorizing queries along two dimensions: branded versus unbranded (does the query mention your brand?) and objective versus subjective (is it asking for facts or opinions?). Once queries are classified, researchers run them repeatedly through different AI systems—ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews—and record which sources each platform cites in response. This repeated testing reveals a critical phenomenon called citation drift: the tendency of AI systems to rotate between different sources even when answering the same query multiple times. Citation drift occurs because large language models don’t “rank” sources the way traditional search engines do; instead, they dynamically sample from a pool of relevant documents to balance variety, authority, and recency with each response.
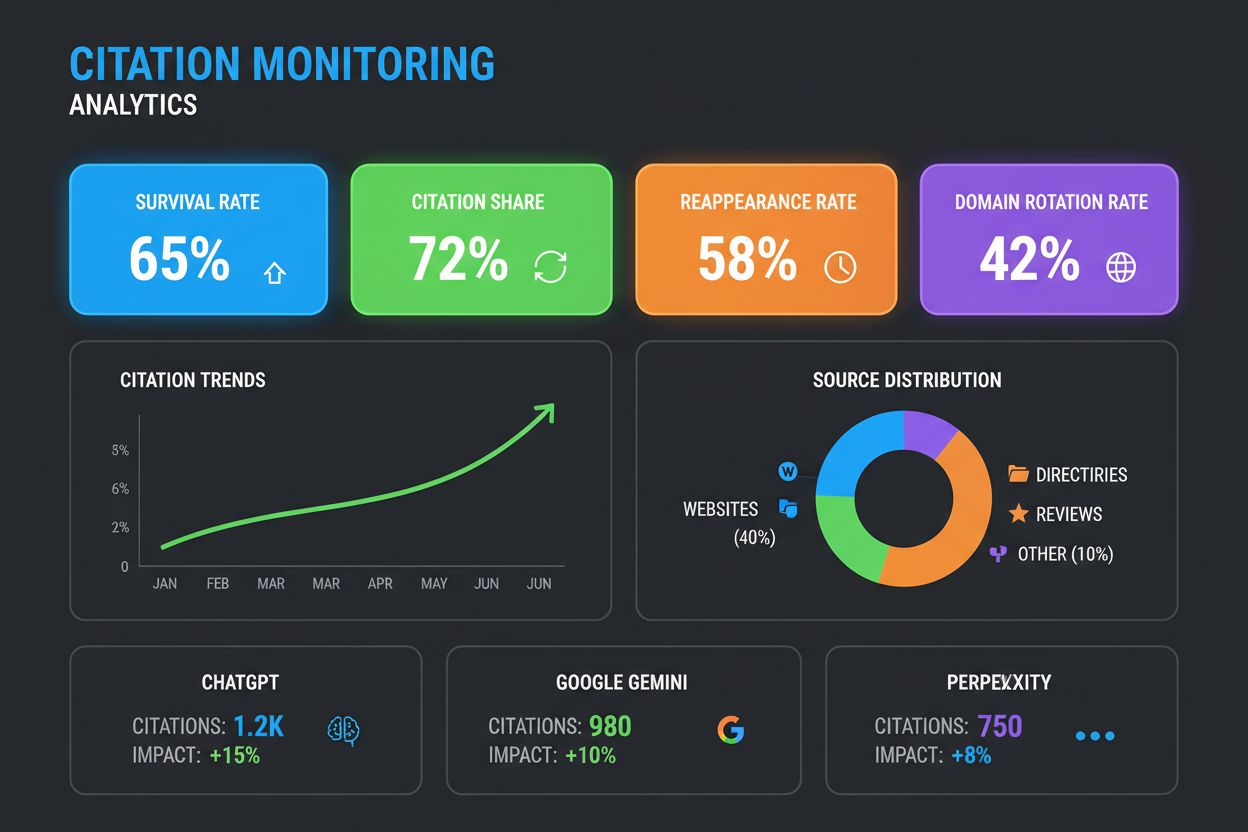
To measure and manage citation drift effectively, brands track several key metrics that reveal whether their visibility is durable or fleeting:
| Metric | What It Measures | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Survival Rate | How long your brand stays visible without interruption | (# of consecutive runs visible) ÷ (total runs) | Cited in 4 consecutive runs out of 10: 40% |
| Reappearance Rate | How often your brand regains visibility after dropping out | (# of times brand resurfaces) ÷ (total dropouts) | Dropped out 5 times, resurfaced 3: 60% |
| Citation Share | How frequently your brand is cited across repeated runs | (# of runs where brand cited) ÷ (total runs) | Cited in 7 out of 10 runs: 70% |
| Domain Rotation Rate | How often the cited URL from your domain changes across runs | (# of runs with different URL cited vs previous run) ÷ (total runs) | URL changes 5 times in 10 runs: 50% |
| Competitor Substitution Rate | How often your brand is replaced by a competitor citation | (# of runs replaced by competitor) ÷ (total runs) | Cited in 6, replaced in 3 of 10: 30% |
The type of query dramatically shapes which sources AI systems cite, making query intent analysis essential for visibility strategy. Queries fall into four distinct categories: branded objective (e.g., “Salesforce pricing”), branded subjective (e.g., “Is Salesforce worth it?”), unbranded objective (e.g., “What is CRM software?”), and unbranded subjective (e.g., “What’s the best CRM software?”). Each category triggers different citation patterns because AI systems adjust their sourcing strategy based on what users are trying to accomplish. For objective queries, AI models prioritize factual accuracy and cite authoritative sources like brand websites, Wikipedia, and official documentation. For subjective queries, they rely more heavily on reviews, expert opinions, and third-party comparisons to provide balanced perspectives. Additionally, B2B and B2C queries show distinct patterns: B2B queries (like “top CRM vendors”) cite industry publications, analyst reports, and company websites at higher rates, while B2C queries (like “best smartphones”) incorporate consumer reviews, tech blogs, and mainstream media more frequently. Understanding these patterns is critical because it reveals that a single brand cannot expect the same citation rate across all query types—instead, brands must optimize different content for different query intents to maximize their overall visibility in AI-generated answers.
Each major AI platform has developed distinct sourcing preferences that significantly impact which brands get cited. ChatGPT heavily favors established, authoritative sources, with Wikipedia accounting for 27% of its citations, followed by major news outlets like Reuters and the Financial Times. This preference for authority means ChatGPT rarely cites user-generated content or vendor blogs, making it essential for brands to build presence in neutral, reference-style materials and major publications. Google Gemini takes a more balanced approach, citing blogs (39%), news (26%), and YouTube (3%) at comparable rates, while incorporating some community content. This diversity makes Gemini more accessible to mid-tier brands that can’t dominate Wikipedia but can create quality blog content. Perplexity AI emphasizes expert sources and specialized review sites, with industry-specific directories like NerdWallet and Consumer Reports appearing frequently alongside blogs and news. For Perplexity, the strategy shifts toward cultivating presence on high-authority niche sites and respected review platforms relevant to your industry. Google AI Overviews cast the widest net, pulling from blogs (46%), news (20%), community content like Reddit (4%), and even LinkedIn articles, making them the most accessible platform for diverse brands. The key insight is that no single optimization strategy works across all platforms—brands must tailor their approach by understanding each platform’s sourcing preferences and building presence in the specific types of sources each one prioritizes.
Understanding which citation sources you can influence is fundamental to query-to-citation mapping strategy. Research analyzing 6.8 million AI citations reveals that brands can be categorized into four control levels: Full Control sources include brand-owned websites and properties (accounting for 40%+ of citations), where you have complete authority over content. Controllable sources include third-party listings and directories like Google Business Profile, Mapquest, and industry-specific platforms (another 40%+ of citations), where you can claim and manage your profile but don’t own the platform. Influenced sources include reviews and social content on platforms like Google Reviews, Yelp, and Facebook (5-10% of citations), where you can’t create content directly but can respond and encourage customer feedback. Uncontrolled sources include news, forums, and other third-party content (5-10% of citations) where you have no direct influence. The most powerful finding from this research is that brands can directly control or influence approximately 86% of all consumer-facing citations, a level of control that’s only visible when analyzing citation patterns at the location and query level rather than at the brand level. This means the path to improving AI visibility is not mysterious or dependent on luck—it’s a matter of strategically managing the sources you can influence while building authority in the sources you can control.
Effective measurement of query-to-citation patterns requires a systematic approach that captures both short-term volatility and long-term trends. The process begins with repeated testing: select a set of high-value queries (informational, commercial, and brand-related) and run them multiple times across different answer engines, recording whether your brand is cited, mentioned, or absent in each run. Research shows that only about 30% of brands maintain back-to-back visibility for a given query in AI search results, highlighting why repeated runs are essential for understanding true visibility patterns. Next, track survival rates by measuring how many consecutive runs your brand remains visible, which helps distinguish pages with durable authority from those that fade quickly. Then monitor fluctuation by tracking when and how often your brand resurfaces after dropping out—high reappearance rates indicate strong topical authority even if you don’t appear in every single run. It’s also critical to classify types of drift: domain rotation (your site swaps between multiple URLs) is positive and signals topical depth, while competitor substitution (a competitor replaces your citation) is negative and requires intervention. For measurement frequency, best practice is to measure across multiple windows rather than relying on a single cadence—daily measurement exposes short-term volatility, weekly shows recurring patterns, and monthly reveals whether visibility is durable or at risk. Finally, interpret the data by comparing your metrics against competitors and industry benchmarks to understand whether your citation patterns are improving, declining, or stagnating over time.
Improving your query-to-citation visibility requires a multi-faceted strategy that addresses content quality, topical authority, and platform presence. The most effective approaches include:
Several platforms now offer specialized tools for tracking and analyzing query-to-citation patterns, making it easier for brands to understand and optimize their AI search visibility. AmICited.com provides AI answers monitoring specifically designed to track how your brand is cited across GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews, giving you real-time visibility into which queries trigger citations to your content. Conductor offers an enterprise-grade AI visibility platform that tracks citations alongside traditional search metrics, helping teams understand how AI search impacts their overall organic strategy. AirOps specializes in measuring and managing citation drift, providing detailed metrics on survival rates, reappearance rates, and citation share to help brands understand the durability of their visibility. Yext Scout takes a location-level approach to citation analysis, revealing how citation patterns vary across geographic markets and helping multi-location brands optimize locally. Rankscale.ai provides comprehensive citation data analysis across multiple AI engines, enabling detailed comparison of how different platforms cite your content. The key to success is not just having access to these tools, but using them consistently to track patterns over time, identify which queries and platforms drive the most valuable citations, and adjust your content strategy based on data-driven insights rather than assumptions about how AI systems work.
Traditional SEO focuses on how websites rank for specific keywords in search results, while query-to-citation mapping tracks which queries trigger AI systems to cite your content as a source. A website might rank well for a keyword but not be cited by AI models, or vice versa. Query-to-citation mapping is specific to AI-generated answers and requires understanding how different AI platforms select and cite sources based on query intent and context.
Best practice is to measure citation drift across multiple time windows rather than relying on a single cadence. Daily measurement exposes short-term volatility, weekly measurement can show recurring patterns, and monthly views reveal whether your visibility is durable or at risk. You should also run back-to-back tests of the same query and compare those snapshots against results from different time frames to capture both immediate swings and longer-term trends.
Yes, citation drift can be positive when it's driven by URL rotation within your own domain. If multiple strong pages from your site rotate in and out of AI citations, it signals topical depth and brand authority. The real risk comes when drift replaces your content with competitor citations, reducing your share of visibility. Positive drift indicates your brand has multiple authoritative pages that AI systems recognize as valuable sources.
The answer depends on your audience and business goals. ChatGPT prioritizes authoritative sources like Wikipedia and news outlets, making it ideal for brand authority building. Google Gemini and AI Overviews offer broad reach with diverse source types. Perplexity emphasizes expert and review sites, valuable for niche industries. Google AI Overviews are critical since they appear in Google Search results. A diversified strategy targeting all major platforms typically yields the best results.
Query intent dramatically shapes citation patterns. Objective queries (factual questions like 'What is X?') tend to cite authoritative sources and brand websites. Subjective queries (opinion-based like 'What's the best X?') rely more on reviews, directories, and expert sites. Branded queries cite more first-party content, while unbranded queries pull from broader sources. B2B queries favor industry publications and directories, while B2C queries include consumer reviews and mainstream media. Understanding these patterns helps you optimize content for the specific query types your audience uses.
The fastest improvements come from optimizing existing content for clarity and query intent alignment. Ensure your content has clear headings that match common queries, place answers early in sections, and use formatting like lists and tables for easy extraction by AI systems. Simultaneously, focus on strengthening authority signals through quality backlinks and third-party mentions. Building topical depth with multiple pages on related topics takes longer but creates more durable visibility. Most brands see measurable improvements within 4-8 weeks of implementing these strategies.
Location context significantly impacts which sources AI systems cite. For location-specific queries (like 'best restaurants near me'), AI models heavily weight first-party websites and local listings. The same brand might have a 70% citation rate in rural markets but only 20% in competitive urban areas where aggregators dominate. Geographic variations make national metrics less helpful for local visibility strategy. Brands with multiple locations should analyze citation patterns at the location level to understand where they're winning and losing visibility.
Branded queries (containing your brand name) typically cite first-party content because users are specifically looking for information about your brand. Unbranded queries (like 'best CRM software') require your brand to compete with many alternatives, and AI systems may prefer third-party reviews or comparisons for objectivity. To improve unbranded query citations, create comprehensive comparison content, build presence on review and directory sites, and establish topical authority through multiple pages addressing different aspects of your category. This signals to AI systems that your brand is a credible source even when not explicitly mentioned in the query.
Track which queries trigger citations to your brand in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI platforms. Get real-time insights into your AI search visibility and optimize your content strategy.

Learn what AI citations are, how they work across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI, and why they matter for your brand's visibility in generative search engin...

Learn proven strategies to improve your brand's citation position in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and other AI answer engines. Discover technical, content, and ...

Learn what citation optimization for AI is and how to optimize your content to be cited by ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google Gemini, and other AI search engines.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.