
How Retrieval-Augmented Generation Works: Architecture and Process
Learn how RAG combines LLMs with external data sources to generate accurate AI responses. Understand the five-stage process, components, and why it matters for ...
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an AI technique that enhances large language models by connecting them to external knowledge bases and retrieving relevant information in real-time before generating responses. RAG combines information retrieval systems with generative models to produce more accurate, authoritative, and up-to-date answers grounded in specific data sources.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an AI technique that enhances large language models by connecting them to external knowledge bases and retrieving relevant information in real-time before generating responses. RAG combines information retrieval systems with generative models to produce more accurate, authoritative, and up-to-date answers grounded in specific data sources.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an advanced AI technique that enhances the capabilities of large language models by integrating them with external knowledge bases and real-time information retrieval systems. Rather than relying solely on patterns learned during training, RAG systems retrieve relevant information from authoritative data sources before generating responses, creating a hybrid approach that combines the strengths of both retrieval and generative AI. This methodology was formally introduced in a 2020 research paper by Patrick Lewis and colleagues from Meta AI Research, University College London, and New York University, establishing RAG as a foundational architecture for modern generative AI applications. The technique addresses critical limitations of standalone LLMs by providing source-grounded, factually accurate, and current information that users can verify and trace back to original documents.
The conceptual foundations of Retrieval-Augmented Generation trace back to the early 1970s when researchers in information retrieval developed question-answering systems that combined natural language processing with text mining capabilities. These pioneering systems, initially focused on narrow domains like baseball statistics, demonstrated that combining retrieval mechanisms with language understanding could produce more reliable answers than either approach alone. The evolution accelerated through the 1990s with services like Ask Jeeves, which popularized conversational question-answering interfaces, and reached mainstream recognition in 2011 when IBM’s Watson defeated human champions on the television game show Jeopardy!, showcasing advanced question-answering capabilities. However, the modern RAG paradigm emerged from the convergence of three critical technological advances: the development of powerful transformer-based language models like GPT, the emergence of efficient embedding models for semantic understanding, and the maturation of vector databases capable of storing and searching high-dimensional numerical representations at scale. Today, RAG has become the dominant architecture for enterprise AI applications, with the global RAG market estimated at USD 1.85 billion in 2025 and projected to reach USD 67.42 billion by 2034, representing a compound annual growth rate that reflects the technology’s critical importance to organizations worldwide.
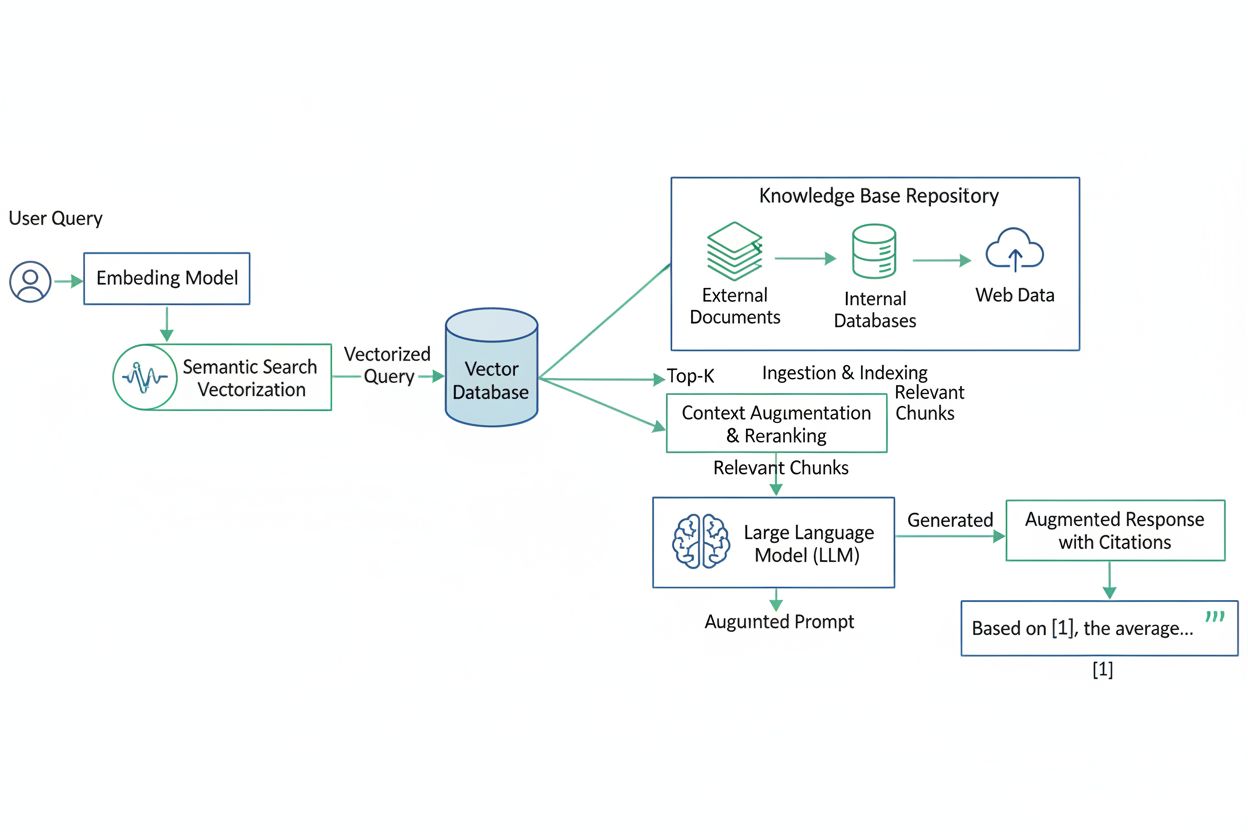
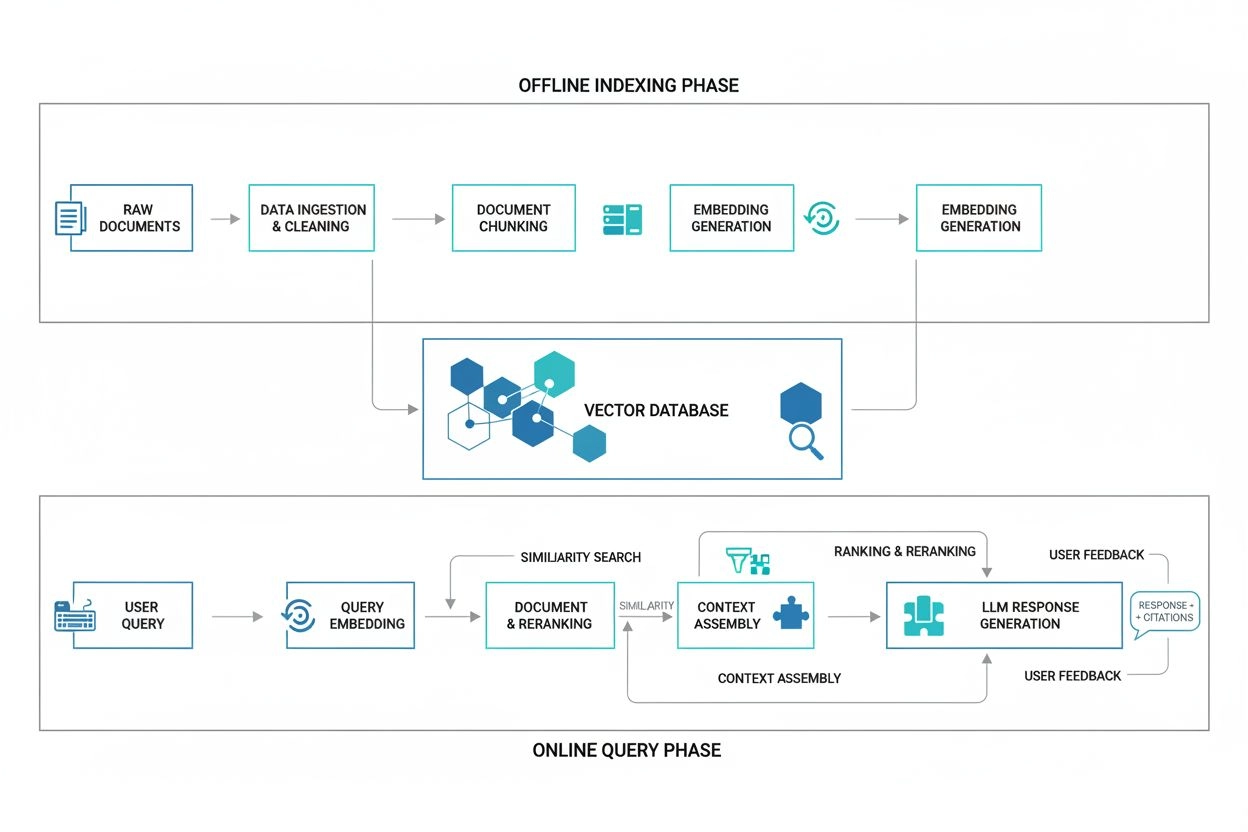
The RAG workflow operates through a sophisticated five-stage process that seamlessly integrates information retrieval with generative AI. When a user submits a query, the system first converts that natural language question into a numerical representation called an embedding or vector, which captures the semantic meaning of the query in multidimensional space. This embedding is then compared against vectors stored in a vector database—a specialized data repository containing numerical representations of documents, articles, policies, and other knowledge base materials. The retrieval component identifies the most semantically similar documents or passages by calculating mathematical distances between vectors, returning the top-ranked results based on relevance scores. These retrieved documents are then passed to an integration layer that combines the original user query with the retrieved context, using prompt engineering techniques to create an augmented prompt that instructs the LLM to consider this additional information. Finally, the generator component—typically a pretrained language model like GPT, Claude, or Llama—synthesizes the user query with the retrieved context to produce a response that is grounded in specific, authoritative sources. The system can optionally include citations or references to the source documents, allowing users to verify claims and access original materials for further investigation.
A comprehensive RAG system architecture comprises four essential components that work in concert to deliver accurate, sourced responses. The knowledge base serves as the external data repository, containing documents, databases, APIs, and information sources that the system can access. This knowledge base can include PDFs, structured databases, web content, internal organizational documents, research papers, and real-time data feeds. The retriever component consists of an embedding model that transforms both user queries and knowledge base documents into vector representations, enabling semantic similarity searches. Modern retrievers employ sophisticated algorithms that understand contextual meaning rather than relying on simple keyword matching, allowing them to identify relevant information even when exact terminology differs. The integration layer orchestrates the entire system, coordinating data flow between components and employing prompt engineering to construct effective prompts that combine user queries with retrieved context. This layer often utilizes orchestration frameworks like LangChain or LlamaIndex to manage complex workflows and ensure reliable system operation. The generator component is the LLM itself, which receives the augmented prompt and produces the final response. Additional optional components include a ranker that re-scores retrieved results based on relevance, and an output handler that formats responses for user consumption, potentially including source citations and confidence scores.
| Aspect | Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) | Fine-Tuning | Semantic Search | Traditional Keyword Search |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Integration | Connects to external sources without modifying model | Embeds knowledge into model parameters | Retrieves semantically similar content | Matches exact keywords or phrases |
| Cost Efficiency | Highly cost-effective; no retraining required | Expensive; requires significant computational resources | Moderate cost; depends on database scale | Low cost but limited accuracy |
| Data Freshness | Real-time access to current information | Static; requires retraining for updates | Real-time if sources are updated | Real-time but limited by keyword matching |
| Implementation Speed | Fast; can be deployed in days or weeks | Slow; requires weeks or months of training | Moderate; depends on infrastructure setup | Very fast; legacy systems available |
| Source Attribution | Excellent; can cite specific sources | Limited; knowledge embedded in parameters | Good; can reference source documents | Excellent; direct document references |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; add new sources easily | Limited; retraining becomes prohibitively expensive | Scalable with proper vector database infrastructure | Scalable but accuracy degrades with scale |
| Hallucination Risk | Significantly reduced through grounding | Moderate; still prone to fabrication | Reduced through semantic matching | High; no factual grounding |
| Use Case Suitability | Domain-specific Q&A, customer support, research | Specialized language patterns, tone adaptation | Content discovery, recommendation systems | Legacy systems, simple lookups |
Successful RAG implementation requires careful attention to several critical factors that directly impact system performance and accuracy. The first consideration is knowledge base preparation, which involves selecting appropriate data sources, converting them into machine-readable formats, and organizing them for efficient retrieval. Organizations must decide which documents, databases, and information sources to include, considering factors like data quality, relevance, security, and compliance requirements. The second critical factor is chunking strategy—the process of dividing documents into appropriately sized segments for embedding and retrieval. Research demonstrates that chunk size significantly affects retrieval accuracy; chunks that are too large become overly general and fail to match specific queries, while chunks that are too small lose semantic coherence and context. Effective chunking strategies include fixed-size chunking (dividing documents into uniform segments), semantic chunking (grouping related content together), and hierarchical chunking (creating multi-level document structures). The third factor is embedding model selection, which determines how effectively the system understands semantic relationships between queries and documents. Modern embedding models like OpenAI’s text-embedding-3, Cohere’s embed-english-v3, and open-source alternatives like BAAI’s BGE models offer varying levels of performance, cost, and customization. The fourth consideration is vector database selection, with popular options including Pinecone, Weaviate, Milvus, and Qdrant, each offering different trade-offs in terms of scalability, latency, and feature richness. Finally, organizations must implement continuous monitoring and optimization, regularly evaluating retrieval accuracy, response quality, and system performance, then adjusting chunking strategies, embedding models, or data sources as needed to maintain effectiveness.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation has become a core technology across major AI platforms, each implementing RAG with distinct architectural approaches. Perplexity AI has built its entire platform around RAG principles, combining real-time web search with LLM generation to provide current, sourced answers with explicit citations to web sources. ChatGPT integrates RAG through its retrieval plugins and knowledge retrieval capabilities, allowing users to upload documents and query them conversationally. Google AI Overviews (formerly Search Generative Experience) employ RAG to combine search results with generative summarization, retrieving relevant web pages before synthesizing them into comprehensive answers. Claude by Anthropic supports RAG through document analysis and retrieval capabilities, enabling users to provide context and source materials for more accurate responses. These platform implementations demonstrate that RAG has become essential infrastructure for modern AI systems, enabling them to provide accurate, current, and verifiable information rather than relying solely on training data. For organizations monitoring their brand presence in AI responses—a critical concern for content creators, publishers, and enterprises—understanding how each platform implements RAG is essential for optimizing content visibility and ensuring proper attribution.
The RAG landscape continues to evolve with sophisticated techniques that enhance retrieval accuracy and response quality. Hybrid RAG combines multiple retrieval strategies, using both semantic search and keyword matching to capture different aspects of relevance. Multi-hop RAG enables systems to perform iterative retrieval, where initial results inform subsequent queries, allowing the system to answer complex questions requiring information synthesis across multiple documents. GraphRAG represents a significant advancement, organizing knowledge as interconnected graphs rather than flat document collections, enabling more sophisticated reasoning and relationship discovery. Reranking mechanisms apply additional machine learning models to re-score retrieved results, improving the quality of information passed to the generator. Query expansion techniques automatically generate related queries to retrieve more comprehensive context. Adaptive RAG systems dynamically adjust retrieval strategies based on query characteristics, using different approaches for factual questions versus reasoning tasks. These advanced patterns address specific limitations of basic RAG implementations and enable organizations to achieve higher accuracy and more sophisticated reasoning capabilities. The emergence of agentic RAG systems represents the frontier of this evolution, where RAG-enhanced models can autonomously decide when to retrieve information, what sources to consult, and how to synthesize complex multi-source answers—moving beyond reactive retrieval toward proactive, reasoning-driven information gathering.
While Retrieval-Augmented Generation offers substantial benefits, organizations implementing RAG systems must navigate several technical and operational challenges. Retrieval quality directly impacts response accuracy; if the retrieval component fails to identify relevant documents, the generator cannot produce accurate answers regardless of its capabilities. This challenge is compounded by the semantic gap problem, where user queries and relevant documents use different terminology or conceptual frameworks, requiring sophisticated embedding models to bridge the gap. Context window limitations present another constraint; LLMs can only process a finite amount of context, so RAG systems must carefully select the most relevant retrieved information to fit within this window. Latency considerations become critical in production environments, as retrieval operations add processing time to response generation. Data quality and currency require ongoing maintenance; outdated or inaccurate information in knowledge bases directly degrades system performance. Hallucination persistence remains a concern even with RAG; while grounding reduces hallucinations, LLMs can still misinterpret or misrepresent retrieved information. Scalability challenges emerge when managing massive knowledge bases with millions of documents, requiring sophisticated indexing and retrieval optimization. Security and privacy concerns arise when RAG systems access sensitive organizational data, necessitating robust access controls and encryption. Organizations must also address evaluation and monitoring challenges, as traditional metrics may not adequately capture RAG system performance, requiring custom evaluation frameworks that assess both retrieval quality and response accuracy.
The trajectory of Retrieval-Augmented Generation points toward increasingly sophisticated and autonomous systems that will reshape how organizations leverage AI. The convergence of RAG with agentic AI represents the most significant emerging trend, where AI systems will autonomously determine when to retrieve information, which sources to consult, and how to synthesize complex multi-source answers. This evolution moves beyond reactive retrieval toward proactive, reasoning-driven information gathering, enabling AI systems to function as genuine research partners rather than simple question-answering tools. Multimodal RAG is expanding beyond text to incorporate images, videos, audio, and structured data, enabling more comprehensive information retrieval and generation. Real-time knowledge graphs are emerging as alternatives to static vector databases, enabling more sophisticated reasoning and relationship discovery. Federated RAG systems will allow organizations to collaborate on shared knowledge bases while maintaining data privacy and security. The integration of RAG with reasoning models will enable systems to perform complex multi-step reasoning while grounding each step in authoritative sources. Personalized RAG systems will adapt retrieval and generation strategies to individual user preferences, expertise levels, and information needs. Market projections indicate that RAG adoption will accelerate dramatically, with vector databases supporting RAG applications growing 377% year-over-year according to recent enterprise adoption studies. By 2030, RAG is expected to become the default architecture for enterprise AI applications, with organizations viewing it not as an optional enhancement but as essential infrastructure for trustworthy, accurate AI systems. The technology’s evolution will be driven by the increasing recognition that AI systems must be grounded in authoritative sources and verifiable facts to earn user trust and deliver business value in mission-critical applications.
RAG anchors large language models in specific, factual knowledge by retrieving verified information from external data sources before generating responses. Instead of relying solely on patterns learned during training, RAG models reference authoritative documents and databases, significantly reducing the likelihood of generating false or fabricated information. This grounding in real data sources makes RAG models substantially more reliable than standard LLMs for accuracy-critical applications.
RAG and fine-tuning are complementary but distinct approaches to improving LLM performance. RAG connects models to external knowledge sources without modifying the model itself, allowing real-time access to current information. Fine-tuning, conversely, retrains the model on domain-specific data, embedding that knowledge into the model's parameters. RAG is typically more cost-effective and faster to implement, while fine-tuning provides deeper domain understanding but requires significant computational resources and becomes outdated as data changes.
Vector databases are fundamental to RAG architecture, storing numerical representations (embeddings) of documents and data. When a user submits a query, the system converts it into a vector embedding and performs semantic similarity searches against the vector database to retrieve the most relevant information. This vector-based approach enables fast, accurate retrieval of contextually similar content at scale, making it far more efficient than traditional keyword-based search methods for RAG applications.
RAG systems continuously retrieve information from external data sources in real-time, ensuring that responses incorporate the latest available information. Unlike traditional LLMs with fixed knowledge cutoff dates, RAG can connect to live data feeds, APIs, news sources, and regularly updated databases. This dynamic retrieval capability allows organizations to maintain current, relevant responses without retraining models, making RAG ideal for applications requiring up-to-date information like financial analysis, medical research, and market intelligence.
A complete RAG system consists of four primary components: the knowledge base (external data repository), the retriever (embedding model that searches for relevant information), the integration layer (coordinates system functioning and augments prompts), and the generator (LLM that creates responses). Additional components may include a ranker to prioritize retrieved results by relevance and an output handler to format responses. These components work together seamlessly to retrieve context-specific information and generate authoritative answers.
Chunking strategy determines how documents are divided into smaller segments for embedding and retrieval. Optimal chunk size is critical because oversized chunks become too general and fail to match specific queries, while undersized chunks lose semantic coherence and context. Effective chunking strategies—including fixed-size chunks, semantic chunking, and hierarchical chunking—directly impact retrieval accuracy, response quality, and system performance. Proper chunking ensures that retrieved information is relevant and contextually appropriate for the LLM to generate accurate responses.
RAG systems can include citations and references to the specific documents or data sources used to generate responses, functioning like footnotes in academic papers. This source attribution allows users to verify information, trace reasoning, and access original materials for deeper understanding. The transparency provided by RAG builds user trust and confidence in AI-generated content, particularly important for enterprise applications where accountability and verifiability are critical requirements for adoption and compliance.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn how RAG combines LLMs with external data sources to generate accurate AI responses. Understand the five-stage process, components, and why it matters for ...

Learn what RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) is in AI search. Discover how RAG improves accuracy, reduces hallucinations, and powers ChatGPT, Perplexity, and...
Learn what RAG pipelines are, how they work, and why they're critical for accurate AI responses. Understand retrieval mechanisms, vector databases, and how AI s...