
Product Schema
Product Schema is structured data markup that helps search engines and AI systems understand product details. Learn how to implement it for better visibility in...

Review Schema is a type of structured data markup that helps search engines interpret and display user reviews, product ratings, and reviewer information directly in search results as rich snippets. It uses schema.org vocabulary to mark up review content, enabling search engines like Google to showcase star ratings, review counts, and reviewer details in enhanced search listings.
Review Schema is a type of structured data markup that helps search engines interpret and display user reviews, product ratings, and reviewer information directly in search results as rich snippets. It uses schema.org vocabulary to mark up review content, enabling search engines like Google to showcase star ratings, review counts, and reviewer details in enhanced search listings.
Review Schema is a standardized structured data markup format that enables search engines to understand, interpret, and display user reviews, product ratings, and reviewer information directly within search results. Built on the schema.org vocabulary, Review Schema uses semantic HTML markup to communicate review content to search engines in a machine-readable format. This markup allows search engines like Google, Bing, and other platforms to extract review data and present it as rich snippets—enhanced search results that include star ratings, review counts, reviewer names, and review summaries. By implementing Review Schema, websites can transform standard search listings into visually compelling, information-rich results that build trust with potential customers and significantly improve click-through rates. The schema serves as a bridge between human-readable review content on web pages and the structured data that search engines require to display reviews prominently in search results.
Review Schema emerged as part of the broader schema.org initiative, a collaborative effort launched in 2011 by Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex to create a standardized vocabulary for structured data markup. As e-commerce and online reviews became increasingly central to consumer decision-making, search engines recognized the need for a standardized way to mark up review content. The schema.org Review type was designed to address this need, providing webmasters with a consistent method to communicate review information to search engines. Over the past decade, Review Schema has evolved significantly, with Google expanding support for review markup across numerous content types including products, recipes, books, movies, local businesses, and services. According to recent data, over 45 million web domains have implemented schema.org structured data as of 2024, representing approximately 12.4% of all registered domains globally. This widespread adoption reflects the growing recognition that structured data is essential for modern SEO strategies. The introduction of JSON-LD as the preferred markup format in 2014 further accelerated adoption, as it eliminated the need to modify existing HTML structure, making implementation significantly easier for developers and content management systems.
Review Schema can be implemented using three primary markup formats: JSON-LD, RDFa, and Microdata. JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) has emerged as the dominant format, accounting for the majority of structured data implementations across the web. JSON-LD embeds schema markup within a script tag in the page’s head or body section, making it non-intrusive and compatible with modern web development practices. A basic Review Schema in JSON-LD format includes properties such as @context (specifying the schema.org vocabulary), @type (identifying it as a Review), author (the reviewer’s name or organization), itemReviewed (the item being reviewed), reviewRating (the numerical rating), and reviewBody (the review text). RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes) embeds structured data directly into HTML attributes, while Microdata uses HTML5 attributes to mark up content. However, JSON-LD’s flexibility and ease of implementation have made it the industry standard, with approximately 80% of structured data implementations using JSON-LD format. The schema supports both individual reviews through the Review type and aggregated ratings through the AggregateRating type, allowing websites to display either single reviewer opinions or collective ratings from multiple users.
| Aspect | Review Schema | AggregateRating | Product Schema | LocalBusiness Schema |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Marks individual reviews from single reviewers | Summarizes multiple reviews into average rating | Comprehensive product information including reviews | Business information with ratings and reviews |
| Required Properties | author, itemReviewed, reviewRating, ratingValue | itemReviewed, ratingValue, ratingCount/reviewCount | name, description, offers, aggregateRating | name, address, telephone, aggregateRating |
| Best For | Single user opinions, critic reviews | Product pages, service listings, business profiles | E-commerce product pages | Local business directories, Google Business |
| Display Format | Individual review snippet with author name | Star rating with review count | Product card with ratings and price | Local pack results with ratings |
| Typical Rating Scale | 1-5 stars (customizable) | 1-5 stars (customizable) | 1-5 stars | 1-5 stars |
| Reviewer Attribution | Required (Person or Organization) | Not required (aggregate only) | Optional (nested reviews) | Optional (nested reviews) |
| Use Case Example | Movie review by critic on review site | Average rating for product across 500 reviews | E-commerce product with nested reviews | Restaurant with customer ratings |
Review Schema directly impacts how search engines display and rank web pages by enabling rich snippets—enhanced search results that include visual elements like star ratings, review counts, and reviewer information. When Google’s crawlers encounter properly implemented Review Schema, they extract the structured data and use it to generate rich results that appear prominently in search engine results pages (SERPs). Research indicates that pages with review schema markup experience significantly higher click-through rates compared to standard search results. The visual distinction created by star ratings and review counts makes listings stand out among competitors, particularly in competitive verticals like e-commerce, hospitality, and local services. Beyond traditional search results, Review Schema also enhances visibility in Google’s Knowledge Panels, which display comprehensive information about entities directly in search results. For local businesses, review schema markup improves visibility in local pack results—the map-based listings that appear for location-based searches. Additionally, Review Schema contributes to the development of knowledge graphs, which search engines use to understand relationships between entities and provide more contextual, relevant information to users. The structured data also supports voice search and AI-driven search features, as these technologies rely on well-organized, machine-readable data to provide accurate answers to user queries.
Implementing Review Schema effectively requires careful attention to several critical factors. First, ensure review content is genuine and user-generated—Google’s guidelines explicitly prohibit self-serving reviews where the reviewed entity controls the review content. This means reviews published on a business’s own website about itself are ineligible for rich snippet display. Second, include all required properties to ensure search engines can properly interpret the markup. For individual reviews, this includes author, itemReviewed, itemReviewed.name, reviewRating, and reviewRating.ratingValue. For aggregate ratings, include itemReviewed, itemReviewed.name, ratingValue, and either ratingCount or reviewCount. Third, use consistent rating scales—the default is 1-5 stars, but if using a different scale, explicitly define bestRating and worstRating properties. Fourth, make review content visible to users—the review text and rating must be immediately apparent on the page; hidden or dynamically loaded reviews may not be eligible for rich snippets. Fifth, validate markup regularly using Google’s Rich Results Test and schema.org’s Schema Markup Validator to identify and fix errors. Sixth, nest reviews appropriately when combining Review Schema with other schema types like Product or LocalBusiness, ensuring proper JSON-LD structure. Finally, monitor implementation at scale using tools like Google Search Console’s Rich Results report to track valid and invalid review structured data items across your site.
Different search engines and platforms handle Review Schema with varying levels of support and display options. Google provides the most comprehensive support for Review Schema, displaying rich snippets across desktop and mobile search results, local pack results, and Knowledge Panels. Google supports review markup for products, recipes, books, movies, courses, events, local businesses, software applications, and numerous other content types. Bing also supports Review Schema and displays review snippets in search results, though with slightly different formatting than Google. Yandex and other regional search engines provide varying levels of support. Beyond traditional search engines, Review Schema is increasingly important for AI-powered search platforms like Perplexity, ChatGPT, and Google’s AI Overviews, which rely on structured data to understand and cite authoritative sources. These AI systems use Review Schema to identify credible review content and incorporate it into their responses. E-commerce platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Shopify have built-in support for Review Schema, automatically generating markup from user reviews. Review aggregation sites like Trustpilot, G2, and Capterra use Review Schema to ensure their review content is properly indexed and displayed across search engines. Local business platforms including Google Business Profile, Apple Maps, and Yelp leverage Review Schema to display ratings and reviews prominently. Understanding these platform-specific implementations helps ensure your Review Schema is optimized for maximum visibility across all relevant search surfaces.
The implementation of Review Schema delivers measurable business benefits across multiple metrics. Click-through rate (CTR) improvement is the most direct impact—pages with review schema markup consistently show higher CTR than identical pages without markup, with some studies indicating improvements of 20-30% or more. This increase occurs because star ratings and review counts make listings more visually appealing and trustworthy, encouraging users to click. Trust and credibility are significantly enhanced when potential customers see real reviews and ratings directly in search results, reducing friction in the decision-making process. Conversion rate optimization benefits from review schema because users who click through from rich snippets have already seen positive reviews, making them more likely to convert. Reduced bounce rates occur because users arriving from review-enhanced listings have clearer expectations about the product or service quality. Competitive advantage emerges in crowded markets where multiple competitors appear on the same SERP—review schema markup helps your listing stand out and capture attention. Local business growth is particularly pronounced for service-based businesses, as review schema in local pack results directly influences which businesses users contact or visit. E-commerce performance improves significantly, as product pages with review schema show higher engagement and conversion rates. Brand reputation management is enhanced through review schema, as positive reviews displayed prominently in search results reinforce brand credibility and counteract negative search results.
Despite the clear benefits of Review Schema, many organizations face significant challenges during implementation. Resource constraints represent the primary obstacle—92% of SEOs surveyed reported lacking sufficient development resources to implement schema markup at scale. This challenge is particularly acute for enterprise websites with hundreds of thousands of pages. The solution involves using no-code or low-code schema deployment tools that allow SEOs to implement markup without developer involvement. Confusion between schema types leads many organizations to implement AggregateRating on pages with single reviews or vice versa. Clear documentation and training on the differences between Review and AggregateRating types can prevent this error. Self-serving review violations occur when organizations mark up testimonials or reviews they control, violating Google’s guidelines. The solution is to only mark up genuine, user-generated reviews from third-party sources. Incomplete or missing properties result in invalid markup that search engines cannot properly interpret. Using schema validation tools during implementation catches these errors before deployment. Inconsistent rating scales create confusion when displayed ratings don’t match schema values. Standardizing on a 1-5 scale and explicitly defining bestRating and worstRating prevents this issue. Maintenance and monitoring challenges emerge when schema markup breaks due to website updates or CMS changes. Implementing automated monitoring through Search Console and site audit tools helps identify and fix issues quickly. Mobile optimization requires ensuring review schema displays correctly on mobile devices, where most searches now occur. Testing across devices and using responsive design principles ensures consistent display.
The landscape of Review Schema is evolving rapidly in response to emerging technologies and changing user behaviors. AI and voice search integration is becoming increasingly important, as AI-powered search engines and voice assistants rely heavily on structured data to understand and cite authoritative sources. Review Schema will become even more critical as these platforms grow in market share. Sentiment analysis and AI-driven review understanding will likely lead to more sophisticated schema properties that capture nuanced review information beyond simple star ratings. Real-time review updates may become more prevalent, with schema markup enabling dynamic display of the most recent and relevant reviews in search results. Personalized review display could emerge, with search engines showing reviews most relevant to individual users based on their preferences and search history. Video review integration is expanding, with schema markup increasingly supporting video content alongside text reviews. Multi-language review support will improve as schema.org expands its vocabulary to better support international review content. Blockchain-based review verification may eventually be integrated with Review Schema to provide cryptographic proof of review authenticity. Integration with e-commerce platforms will deepen, with platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, and BigCommerce providing increasingly sophisticated built-in Review Schema support. Regulatory compliance will likely influence Review Schema evolution, as governments worldwide implement stricter rules about review authenticity and disclosure. Organizations that stay ahead of these trends by implementing robust Review Schema strategies will maintain competitive advantages in search visibility and user trust.
In the context of AI-powered search and content monitoring, Review Schema has taken on new strategic importance. As platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude increasingly cite sources in their responses, properly implemented Review Schema helps ensure your content is recognized as authoritative and trustworthy. These AI systems use structured data to identify credible sources and understand content context, making Review Schema a critical signal for inclusion in AI-generated responses. AmICited’s monitoring platform tracks how your brand, domain, and URLs appear across these AI search engines, and Review Schema implementation directly impacts your visibility in these emerging search channels. When your reviews are properly marked up with Review Schema, AI systems can more easily identify and cite your review content, increasing your brand’s presence in AI-generated summaries and responses. This is particularly important for e-commerce sites, review aggregators, and service providers whose review content is frequently referenced by AI systems. As AI search continues to grow—with some projections suggesting AI will handle 25% of all searches by 2026—ensuring your Review Schema is properly implemented becomes essential for maintaining visibility across all search channels. Organizations that combine traditional SEO optimization with AI search visibility monitoring through tools like AmICited gain significant competitive advantages in capturing traffic from both conventional and AI-powered search engines.
Review Schema represents a fundamental component of modern SEO strategy, enabling search engines to understand and display review content in rich, visually compelling formats that drive higher click-through rates and user engagement. By implementing Review Schema correctly—using JSON-LD format, including all required properties, ensuring genuine user-generated reviews, and validating markup regularly—organizations can significantly enhance their search visibility and build trust with potential customers. The distinction between Review Schema for individual reviews and AggregateRating for collective ratings is critical for proper implementation. As search evolves to include AI-powered platforms and voice search, Review Schema becomes even more important for ensuring your content is recognized as authoritative and trustworthy. Organizations facing resource constraints can leverage modern schema deployment tools to implement Review Schema at scale without requiring extensive developer involvement. Monitoring Review Schema performance through Google Search Console and regular validation ensures continued effectiveness and helps identify implementation issues quickly. Looking forward, Review Schema will continue to evolve to support emerging technologies and user behaviors, making it essential for organizations to stay informed about best practices and platform-specific requirements. By prioritizing Review Schema implementation and monitoring, organizations position themselves to capture maximum visibility across traditional search engines, AI-powered search platforms, and emerging search channels.
Review Schema marks up individual reviews from a single reviewer, including properties like author, reviewRating, and reviewBody. AggregateRating, conversely, summarizes multiple reviews into an average rating, displaying the overall rating value and total review count. Use Review Schema for single reviews and AggregateRating when displaying collective ratings from multiple reviewers on products, services, or businesses.
Review Schema enables rich snippets in search results, displaying star ratings and review counts directly on the SERP. This visual enhancement makes listings more eye-catching and trustworthy, leading to higher click-through rates. Studies show that pages with review schema markup experience improved visibility and user engagement compared to standard search results, making it a valuable SEO signal.
For individual Review Schema, required properties include author (Person or Organization), itemReviewed (the item being reviewed), itemReviewed.name, reviewRating, and reviewRating.ratingValue. For AggregateRating, required properties are itemReviewed, itemReviewed.name, ratingValue, and either ratingCount or reviewCount. Recommended properties include datePublished, bestRating, and worstRating for enhanced context.
Review Schema supports multiple content types including products, recipes, books, movies, courses, events, local businesses, software applications, and more. However, Google has specific guidelines about eligible content types and prohibits self-serving reviews where the reviewed entity controls the review content. Always ensure reviews come from genuine users and follow Google's quality guidelines.
JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is a structured data format that embeds schema markup in a script tag without disrupting HTML structure. It's the most widely adopted format for Review Schema because it's easy to implement, compatible with modern web technologies, and doesn't require changes to existing HTML elements, making it ideal for enterprise-scale deployment.
Use Google's Rich Results Test tool to validate Review Schema markup and preview how it appears in search results. Additionally, use schema.org's Schema Markup Validator to check for syntax errors. Google Search Console's Rich Results report also shows valid and invalid review structured data items detected on your site, helping identify implementation issues.
Common mistakes include confusing Review with AggregateRating, including self-serving reviews that violate Google policies, applying schema to ineligible pages without actual reviews, missing required properties, using incorrect rating scales, and improper nesting in JSON-LD format. Always follow Google's structured data guidelines and ensure reviews are genuine, user-generated content.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Product Schema is structured data markup that helps search engines and AI systems understand product details. Learn how to implement it for better visibility in...
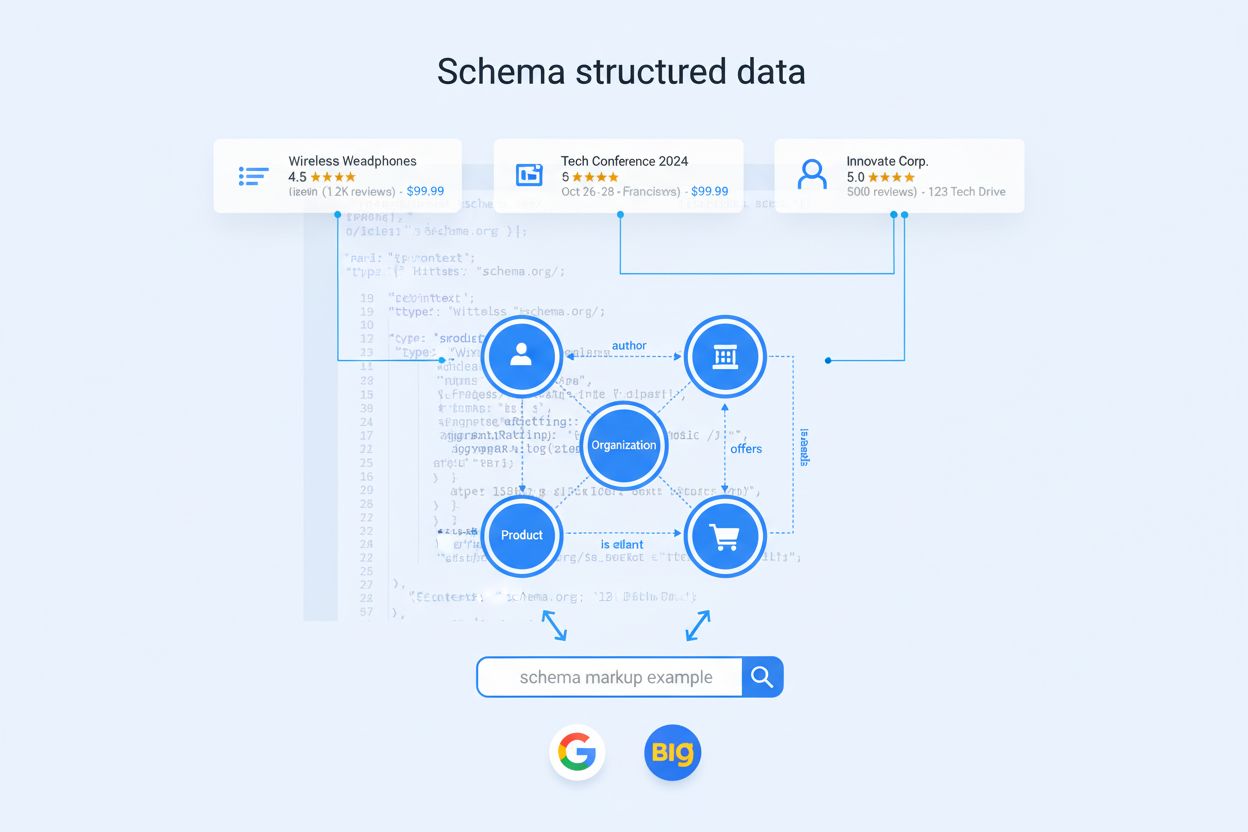
Schema markup is standardized code that helps search engines understand content. Learn how structured data improves SEO, enables rich results, and supports AI s...

HowTo Schema is structured data markup that helps search engines understand instructional content. Learn how it improves SEO, enables rich results, and increase...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.