
What Schema Markup Helps with AI Search? Complete Guide for 2025
Discover which schema markup types boost your visibility in AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. Learn JSON-LD implementation strategies for ...
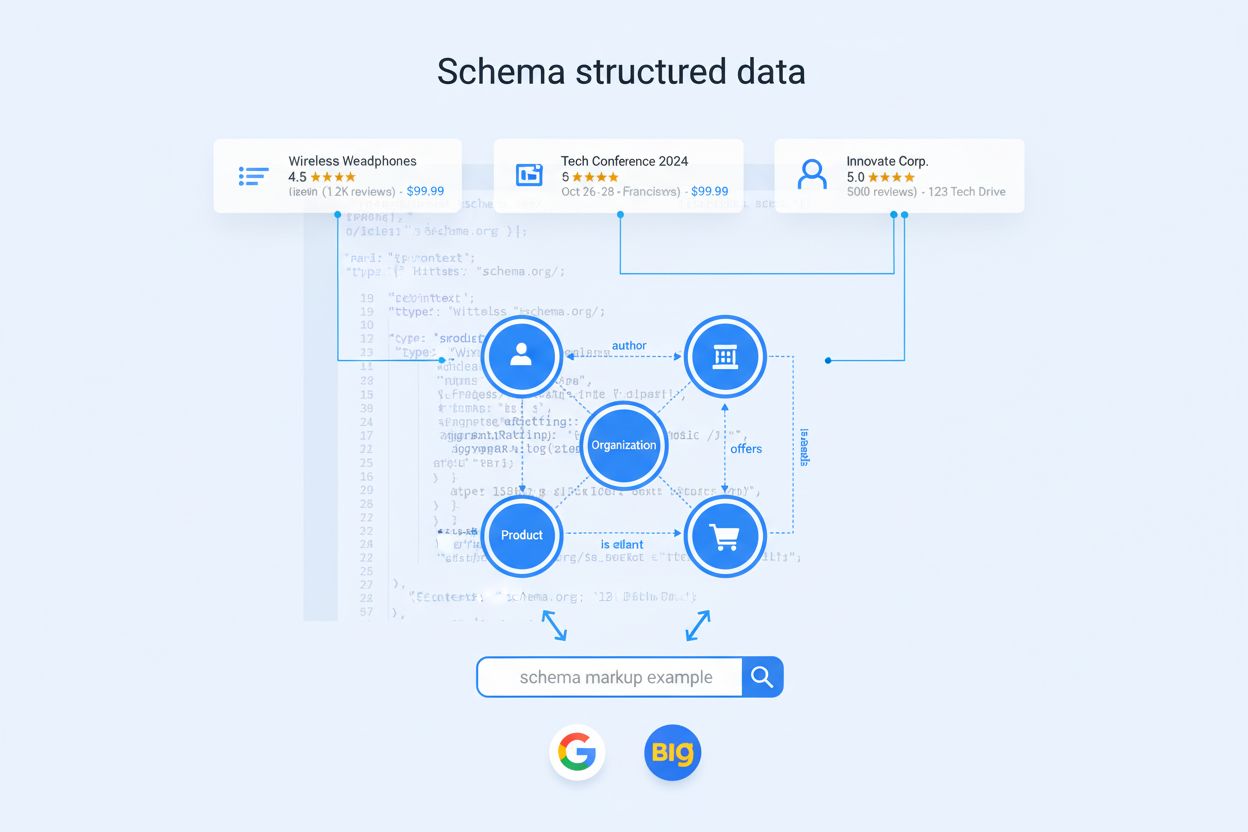
Schema markup is standardized code that helps search engines and AI systems understand the meaning and context of web page content by providing explicit information about entities, their properties, and relationships. Implemented using formats like JSON-LD, Microdata, or RDFa, schema markup enables rich search results and improves content visibility across search engines, AI platforms, and voice assistants.
Schema markup is standardized code that helps search engines and AI systems understand the meaning and context of web page content by providing explicit information about entities, their properties, and relationships. Implemented using formats like JSON-LD, Microdata, or RDFa, schema markup enables rich search results and improves content visibility across search engines, AI platforms, and voice assistants.
Schema markup is standardized code that helps search engines, AI systems, and other machines understand the meaning and context of web page content. It provides explicit information about entities (people, organizations, products, events), their properties, and relationships through a structured format that machines can parse without ambiguity. Developed collaboratively by Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex in 2011, schema.org serves as the vocabulary foundation for schema markup, offering over 800 schema types to describe virtually any type of web content. Unlike traditional HTML, which tells browsers how to display content, schema markup tells search engines and AI systems what the content actually means. This distinction is crucial in modern SEO and AI search optimization, where machines must understand not just the words on a page, but the semantic meaning behind them.
The evolution of schema markup reflects the broader shift in how search engines process information. Before schema markup was standardized, search engines relied entirely on natural language processing (NLP) to interpret page content, which was resource-intensive and prone to errors. In 2011, the major search engines recognized that a standardized vocabulary would improve search quality while reducing computational costs. Schema.org was created as a collaborative effort to establish this universal standard, and it has since become the foundation for structured data implementation across the web. Over 45 million domains currently implement schema markup, representing approximately 12.4% of all registered domains. This widespread adoption demonstrates the growing recognition of schema markup’s importance. The rise of JSON-LD as the dominant format has made implementation easier for developers, further accelerating adoption. Today, schema markup is not just an SEO tactic—it’s essential infrastructure for the semantic web, supporting everything from traditional search to voice assistants to AI-powered language models.
Schema markup operates by embedding structured data directly into web pages using one of three primary formats. JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is the most recommended approach, allowing developers to insert a script block containing structured data without modifying the HTML structure. This format is particularly valuable because it can be dynamically generated and doesn’t interfere with page rendering. Microdata uses HTML attributes like itemscope, itemtype, and itemprop to mark up content inline within the page, while RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes) uses similar attribute-based approaches with slightly different syntax. Regardless of format, schema markup works by defining entities and their properties using key-value pairs. For example, a Product entity might include properties like name, price, availability, and aggregateRating. When search engines crawl a page containing schema markup, they extract this structured data and use it to better understand the page’s content. This understanding enables search engines to display rich results—enhanced search snippets with additional information—and to match pages with more relevant search queries. The semantic relationships defined in schema markup also contribute to knowledge graphs, helping search engines understand how entities relate to each other across the web.
| Aspect | JSON-LD | Microdata | RDFa | Unstructured HTML |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation Method | Script block in <head> or <body> | Inline HTML attributes | Inline HTML attributes | No markup |
| Ease of Implementation | Very easy; no HTML modification | Moderate; requires attribute additions | Moderate; requires attribute additions | N/A |
| Google Recommendation | Highly recommended | Supported | Supported | Not recommended |
| Compatibility with Dynamic Content | Excellent; works with JavaScript | Limited | Limited | N/A |
| Readability for Developers | High; clear JSON structure | Moderate; scattered throughout HTML | Moderate; scattered throughout HTML | N/A |
| Search Engine Support | Full support (Google, Bing, Yandex) | Full support | Full support | Limited understanding |
| Rich Results Eligibility | Yes, when properly implemented | Yes, when properly implemented | Yes, when properly implemented | Unlikely |
| Maintenance Complexity | Low; centralized code | High; distributed throughout page | High; distributed throughout page | N/A |
| Performance Impact | Minimal; no rendering impact | Minimal | Minimal | N/A |
| AI System Compatibility | Excellent; machine-readable format | Good | Good | Poor; requires NLP interpretation |
The implementation of schema markup delivers measurable business results across multiple metrics. Research from Schema App’s 2025 quarterly business reviews shows that pages with review snippets achieve significantly higher click-through rates compared to pages without rich results. Product rich results consistently drive more clicks and engagement, with some enterprises reporting CTR increases of 25-35% after implementing schema markup. For local businesses, schema markup improves visibility in local search results and map listings, directly driving foot traffic and phone inquiries. E-commerce sites benefit from product schema by displaying prices, availability, ratings, and reviews directly in search results, which helps customers make purchasing decisions before clicking through. The Rakuten case study demonstrated that pages with schema markup achieved 2.7x higher organic traffic and 1.5x longer session duration compared to non-marked pages. For job postings, schema markup enables listings to appear in Google’s job search experience, significantly increasing visibility to qualified candidates. The cumulative effect of these improvements is substantial: businesses that properly implement schema markup across their sites typically see improved search visibility, higher qualified traffic, better user engagement, and ultimately improved conversion rates. This makes schema markup a critical component of modern SEO strategy.
The emergence of AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude has elevated the importance of schema markup beyond traditional search. While these AI systems primarily crawl and process HTML content, structured data provides explicit, machine-readable information that reduces ambiguity and improves accuracy. Microsoft’s Bing has officially stated that schema markup helps its LLMs understand content better, and Google’s Gemini uses structured data from Google’s Knowledge Graph—which is enriched by schema markup across the web—to develop its answers. For AmICited’s monitoring platform, which tracks brand and domain mentions across AI search systems, schema markup becomes crucial for ensuring accurate citations. When your content is properly marked up with schema markup, AI systems can more easily identify your brand, understand your content’s context, and cite you accurately in their responses. This is particularly important as AI search grows in market share—currently, Google maintains about 89% of search traffic, but AI-driven search is rapidly expanding. By implementing semantic schema markup, you create a data layer that helps AI systems understand your content’s meaning, relationships, and context, reducing the risk of misrepresentation or hallucinations. This forward-looking approach ensures your brand is properly understood and cited as AI search becomes more prevalent.
Successful schema markup implementation requires a strategic approach that goes beyond simply adding code to pages. The first step is to identify priority pages—typically those already ranking well in search results or those with high conversion value. These pages benefit most from schema markup because they’re already receiving traffic, and rich results can significantly boost CTR. Next, choose the most specific schema type available for your content. For example, use LocalBusiness instead of just Organization for a business with a physical location, or Product instead of Thing for e-commerce items. This specificity helps search engines understand your content more precisely. When implementing schema markup, prioritize complete and accurate data over attempting to include every possible property. Google recommends supplying fewer but complete properties rather than vague or inaccurate data. Use JSON-LD format whenever possible due to its ease of implementation and compatibility with modern web technologies. Always validate your schema markup using Google’s Rich Results Test and Schema.org Validator before deploying to production. For connected schema markup, establish relationships between entities on your pages—for example, linking a Product to its Organization or an Article to its Author. This creates a semantic data layer that helps search engines understand context. Finally, monitor performance using Google Search Console and schema-specific analytics tools to track CTR improvements and rich result eligibility. Regular audits ensure schema markup remains accurate as content changes.
The future of schema markup is intrinsically linked to the evolution of search and AI. As AI search engines become more sophisticated and prevalent, the role of schema markup will expand beyond enabling rich results to serving as a foundational semantic data layer for machine learning systems. Google has already deprecated certain rich result types like FAQ and How-To schema, signaling that search is moving toward more dynamic and contextually relevant content presentation. This evolution suggests that future schema markup implementations will focus less on specific rich result types and more on comprehensive semantic understanding. The development of Content Knowledge Graphs built with schema markup represents the next frontier—these graphs define relationships between entities and enable organizations to create reusable semantic data that serves multiple purposes: traditional search, AI systems, internal knowledge management, and enterprise applications. Research shows that LLMs grounded in knowledge graphs achieve 300% higher accuracy compared to those relying solely on unstructured data, highlighting the strategic value of semantic schema markup. As voice search and conversational AI continue to grow, schema markup will become increasingly important for ensuring accurate information retrieval and presentation. The integration of schema markup with entity optimization and brand monitoring platforms like AmICited will enable organizations to maintain control over how their brands are understood and represented across search and AI systems. Looking ahead, organizations that invest in comprehensive schema markup strategies today will be better positioned to thrive in an increasingly AI-driven search landscape where semantic understanding and data accuracy are paramount.
Schema markup and structured data are closely related but distinct concepts. Structured data refers to organized information in a standardized format that helps machines understand content. Schema markup is the specific implementation of structured data using schema.org vocabulary and formats like JSON-LD, Microdata, or RDFa. In essence, schema markup is the language and code used to create structured data on web pages. All schema markup is structured data, but not all structured data uses schema markup.
Schema markup improves SEO by helping search engines better understand page content, which increases relevancy for specific queries. Pages with schema markup are more likely to appear in rich results—enhanced search snippets showing ratings, prices, availability, and other details—which significantly boost click-through rates. Research shows pages with rich results experience 2.7x higher organic traffic and 1.5x longer session duration compared to non-marked pages. Additionally, schema markup helps search engines display content in more relevant search results, attracting qualified traffic.
The three primary formats for schema markup are JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data), Microdata, and RDFa. JSON-LD is the most recommended and widely adopted format because it's easy to implement, doesn't interfere with HTML structure, and works well with dynamic content. Microdata uses HTML attributes to mark up content inline within the page. RDFa is an HTML5 extension that uses attributes to describe structured data. Google officially recommends JSON-LD for most implementations due to its flexibility and compatibility with modern web technologies.
Schema markup provides AI systems with explicit, machine-readable information about content structure and meaning, reducing the need for complex natural language processing. While AI search engines like ChatGPT and Perplexity primarily crawl HTML content, structured data offers a cost-efficient way for these systems to understand content more accurately and reduce hallucinations. As AI search becomes more prevalent, schema markup serves as a semantic data layer that helps LLMs comprehend entity relationships, context, and content accuracy. This is particularly important for AmICited's monitoring of brand mentions across AI platforms.
Schema.org supports over 800 schema types covering diverse content categories including articles, products, recipes, events, local businesses, job postings, videos, courses, reviews, and organizations. Common types include Article, Product, Recipe, Event, LocalBusiness, Person, Organization, Review, and VideoObject. Each schema type has specific properties that describe relevant information—for example, Product schema includes price, availability, and ratings. The breadth of available schema types means nearly any type of web content can be marked up to help search engines understand it better.
Schema markup does not directly serve as a ranking factor for Google or other search engines. However, it indirectly improves rankings by increasing click-through rates through rich results, improving content relevancy matching, and helping search engines understand content context better. Schema markup enables your pages to appear in more relevant search queries and display as visually enhanced rich results, which attracts more qualified clicks. The improved user engagement signals from higher CTR can positively influence rankings over time, making schema markup a valuable SEO investment.
Schema markup is fundamental to building knowledge graphs by defining entities and their relationships. When you implement schema markup correctly, you create a semantic data layer that helps search engines understand how entities (people, organizations, products) relate to each other. This connected schema markup contributes to Google's Knowledge Graph and helps establish entity authority. For brands, proper schema markup implementation can enhance or create knowledge panels in search results, improve entity recognition across the web, and support AI systems in understanding your brand's context and relationships.
Rich results are enhanced search snippets that display additional information beyond the standard title, URL, and meta description. Examples include star ratings for reviews, product prices and availability, recipe ingredients and cooking time, event dates and locations, and job posting details. Schema markup enables rich results by providing search engines with structured data about this additional information. Google supports over 32 types of rich results, though not all schema markup guarantees rich result display—Google determines eligibility based on content quality, website authority, and compliance with guidelines. Rich results significantly improve CTR and user engagement.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Discover which schema markup types boost your visibility in AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. Learn JSON-LD implementation strategies for ...

Learn how to implement HowTo schema markup for better visibility in AI search engines. Step-by-step guide to adding structured data for ChatGPT, Perplexity, and...

HowTo Schema is structured data markup that helps search engines understand instructional content. Learn how it improves SEO, enables rich results, and increase...