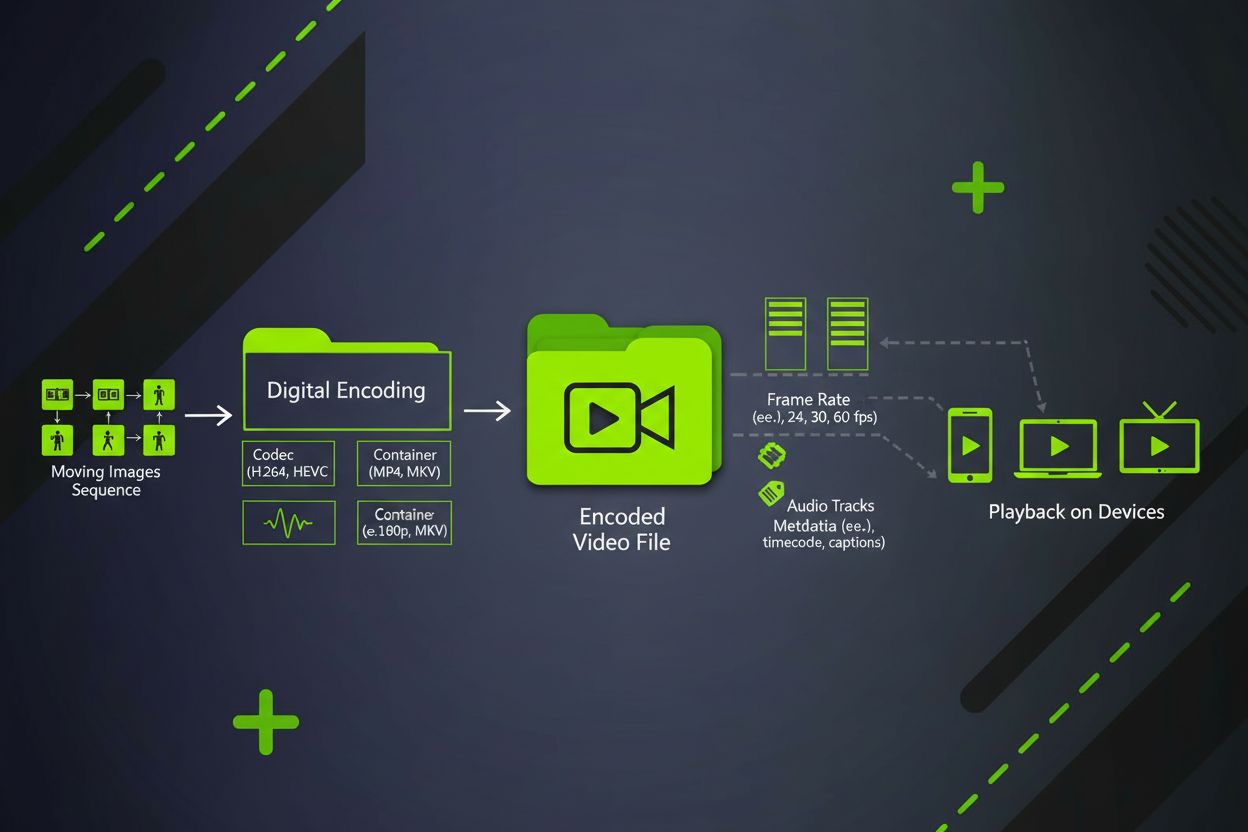
Video Content
Video content is a digital moving image format combining sequential frames, audio, and metadata. Learn about video formats, codecs, specifications, and its role...
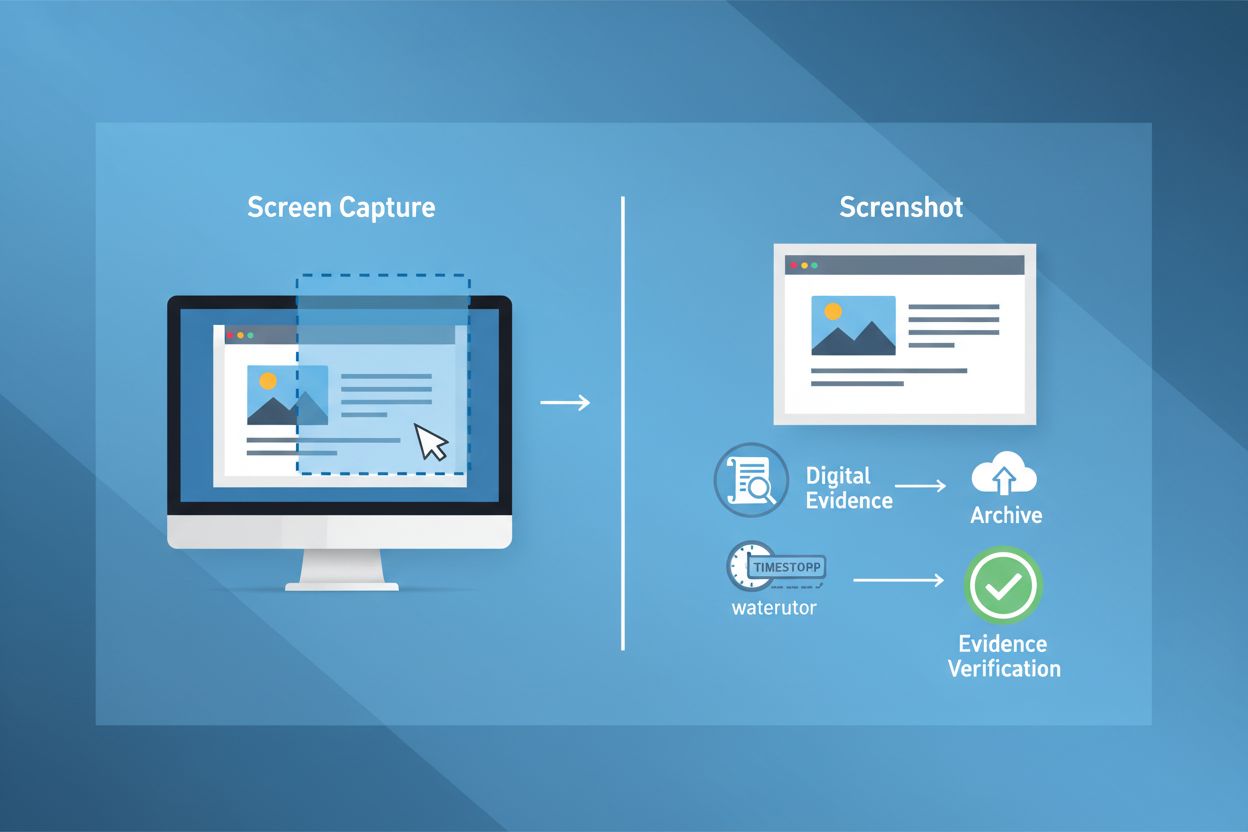
A screenshot is a digital image that captures the contents of a computer, mobile device, or application screen at a specific moment in time. Also known as a screen capture or screengrab, screenshots serve as visual documentation of on-screen content and can be saved, edited, shared, and used as evidence in legal proceedings or brand monitoring.
A screenshot is a digital image that captures the contents of a computer, mobile device, or application screen at a specific moment in time. Also known as a screen capture or screengrab, screenshots serve as visual documentation of on-screen content and can be saved, edited, shared, and used as evidence in legal proceedings or brand monitoring.
A screenshot (also known as a screen capture or screengrab) is a digital image that captures the exact contents displayed on a computer monitor, mobile device, tablet, or application interface at a specific moment in time. According to Merriam-Webster, a screenshot is formally defined as “an image that shows the contents of a computer display.” The term was first documented in 1983 and has become ubiquitous in digital communication, documentation, and evidence gathering. Screenshots serve as static visual snapshots that freeze on-screen content, allowing users to preserve, share, and reference digital information. Unlike video recordings, screenshots capture a single frame without motion or temporal progression, making them ideal for documenting specific states, errors, or moments that require precise visual reference.
The history of screenshots traces back to the early days of personal computing when users needed methods to document and share what appeared on their screens. As digital technology evolved, screenshots became essential tools across virtually every industry and use case. The screenshot software market has experienced significant growth, with the global market valued at USD 250 million in 2023 and projected to reach USD 550 million by 2032, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.1%. This expansion reflects the increasing reliance on digital documentation, remote work collaboration, and the need for visual evidence in legal and compliance contexts.
The rise of cloud-based screenshot tools has transformed how organizations capture and manage digital content. Modern screenshot applications offer far more functionality than the basic built-in capture tools found in Windows and macOS operating systems. These advanced platforms provide automated scheduling, timestamp watermarking, cloud storage integration, and metadata preservation—features essential for professional documentation and legal admissibility. The proliferation of remote work has particularly accelerated screenshot adoption, with teams distributed across locations requiring efficient visual communication and documentation methods.
In the context of AI brand monitoring, screenshots have become indispensable for platforms like AmICited that track brand appearances in AI-generated responses. As artificial intelligence systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude generate increasingly sophisticated responses, organizations need visual proof of how their brands are cited, mentioned, and positioned within these AI outputs. Screenshots provide the definitive evidence of brand visibility in AI responses, creating an auditable record of AI citations and mentions over time.
| Aspect | Built-in OS Tools | Professional Screenshot Software | Automated Cloud-Based Tools | Mobile Screenshot Apps |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capture Speed | Instant (keyboard shortcut) | Instant to scheduled | Automated on schedule | Instant (button press) |
| Annotation Features | Basic (Windows) to moderate (Mac) | Advanced (arrows, text, shapes, callouts) | Advanced with cloud sync | Basic to moderate |
| Cloud Storage | Local storage only | Optional integration | Automatic integration | Platform-dependent |
| Timestamp Watermark | None | Optional | Automatic | None |
| Metadata Preservation | Limited | Comprehensive | Comprehensive | Limited |
| Legal Admissibility | Questionable | High (with documentation) | Very high (automated chain of custody) | Questionable |
| Batch Processing | Not available | Available | Available | Not available |
| Cost | Free (included with OS) | $30-$100+ per year | $50-$500+ per year | Free to $10/month |
| Best Use Case | Quick personal captures | Professional documentation | Legal/compliance monitoring | Mobile documentation |
| Automation Capability | None | Limited | Extensive | None |
When a user initiates a screenshot capture, the operating system or application reads the current state of the frame buffer—the portion of computer memory that stores the visual data currently displayed on screen. This process involves several technical steps that ensure accurate digital representation of on-screen content. The system captures pixel-by-pixel information, including color values, transparency levels, and positioning data for every visual element visible at that moment.
Modern screenshot tools employ sophisticated rendering techniques to ensure complete and accurate capture. Full-page screenshot capabilities extend beyond the visible viewport, capturing content that requires scrolling to view. This is particularly important for web pages, documents, and applications with extensive vertical or horizontal content. The capture process must account for different viewport sizes, browser rendering engines, and device resolutions to ensure consistent quality across platforms. Professional tools offer multiple resolution options and can capture screenshots at different zoom levels or in different browsers simultaneously.
The technical infrastructure supporting automated screenshot capture involves scheduling engines that trigger captures at predetermined intervals—ranging from every 5 minutes to monthly captures depending on organizational needs. These systems must handle concurrent captures of multiple URLs or applications, manage storage allocation efficiently, and maintain data integrity throughout the capture and storage process. Cloud-based systems implement redundant storage across geographically distributed servers to prevent data loss and ensure availability during system failures or disasters.
Screenshots have become fundamental to modern business operations across multiple sectors. In digital marketing, teams use screenshots to monitor competitor websites, track pricing changes, document promotional campaigns, and analyze competitor strategies. According to industry data, over 78% of enterprises use some form of visual monitoring tools for competitive intelligence, with screenshots serving as the primary evidence mechanism. Marketing professionals rely on screenshots to create tutorials, document design feedback, and maintain records of campaign performance across different platforms.
In customer support and technical troubleshooting, screenshots enable support agents to understand customer issues more accurately than verbal descriptions alone. When customers report problems with software, websites, or applications, screenshots provide visual context that accelerates problem resolution. Support teams can annotate screenshots with solutions, creating visual guides that help customers implement fixes independently. This capability has reduced average support resolution times by approximately 30-40% in organizations that systematically use screenshot documentation.
For legal and compliance teams, screenshots serve as critical evidence in intellectual property disputes, trademark infringement cases, and regulatory compliance monitoring. Organizations use automated screenshot systems to maintain continuous records of their digital presence, competitor activities, and regulatory compliance status. The ability to produce timestamped, authenticated screenshots during legal discovery processes significantly strengthens litigation positions. Companies have successfully used screenshot evidence to win cases involving trademark violations, copyright infringement, and false advertising claims.
The emergence of AI-powered search and response systems has created new and critical use cases for screenshots. Platforms like AmICited specifically monitor how brands appear in AI-generated responses across multiple systems including ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude. Screenshots provide the definitive proof of brand visibility in these AI systems, capturing exactly how the AI cited, mentioned, or positioned a brand within its response.
ChatGPT and similar large language models generate responses that may or may not cite specific brands or sources. Screenshots capture these responses with their exact formatting, citations, and positioning, creating an auditable record of how the AI system treated brand mentions. This is particularly important for organizations tracking their share of voice in AI responses or monitoring whether competitors receive preferential treatment in AI citations.
Perplexity AI and Google AI Overviews often display source citations and brand mentions prominently in their responses. Screenshots document the exact placement, prominence, and context of brand mentions within these AI-generated overviews. Organizations can use this visual evidence to verify that their content is being properly cited and that their brand positioning aligns with their SEO and content strategies.
Claude and other enterprise AI systems may be used internally by organizations to monitor how their brands are represented in AI-generated business intelligence reports. Screenshots of these interactions create records that can be used for internal auditing, competitive analysis validation, and strategic decision-making documentation.
Effective screenshot implementation requires establishing clear capture protocols and documentation standards. Organizations should define which content requires screenshots, at what frequency captures should occur, and how long screenshots should be retained. For legal and compliance purposes, daily or hourly captures may be necessary, while marketing monitoring might require weekly or monthly captures depending on the rate of change in monitored content.
Metadata documentation is critical for screenshot validity and usefulness. Each screenshot should include the capture timestamp, the URL or application name, the device and operating system used, the user who initiated the capture, and relevant contextual information about what is being documented. Professional tools automate much of this metadata collection, but organizations must establish protocols for manual documentation when needed.
Storage and access management requires implementing secure systems that protect screenshots from unauthorized access while enabling rapid retrieval when needed. Cloud-based storage solutions provide automatic backup, geographic redundancy, and version control. Organizations should establish access controls that restrict screenshot viewing to authorized personnel and maintain audit logs documenting who accessed which screenshots and when.
Chain of custody documentation is essential for legal admissibility. Organizations must maintain clear records of how screenshots were captured, stored, accessed, and handled throughout their lifecycle. This documentation demonstrates that screenshots have not been altered, manipulated, or compromised, strengthening their evidentiary value in legal proceedings.
The screenshot technology landscape is rapidly evolving in response to emerging business needs and technological capabilities. Artificial intelligence integration is enabling smarter screenshot capture, with AI systems automatically identifying important content changes and prioritizing captures accordingly. Machine learning algorithms can detect when website content has meaningfully changed, triggering captures only when necessary rather than on fixed schedules, improving efficiency and reducing storage requirements.
Mobile screenshot technology is becoming increasingly sophisticated, with advanced tools now capturing full-page screenshots on smartphones and tablets, handling responsive design layouts, and preserving interactive elements. As mobile devices become primary computing platforms for many users, screenshot tools must evolve to capture mobile-specific content accurately, including app interfaces, mobile web pages, and touch-based interactions.
The integration of blockchain technology and digital signatures is enhancing screenshot authentication and legal admissibility. Future screenshot systems may incorporate cryptographic verification that makes tampering immediately detectable and provides mathematical proof of screenshot authenticity. This technological advancement will further strengthen the use of screenshots as legal evidence.
AI-powered screenshot analysis represents another frontier, where artificial intelligence examines screenshot content to extract structured data, identify changes, and generate automated reports. Rather than requiring manual review of thousands of screenshots, AI systems could automatically flag significant changes, extract text content, and generate insights about competitor activities or compliance status.
The screenshot software market is expected to continue growing at 9.1% annually through 2032, driven by increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions, growing demand for compliance monitoring, and the expansion of AI-powered business intelligence tools. Organizations will increasingly rely on automated screenshot systems as part of comprehensive digital monitoring and documentation strategies, particularly as regulatory requirements for digital evidence preservation become more stringent.
A screenshot captures a single static image of what appears on your screen at one moment in time, while a screen recording captures continuous video footage of screen activity over a period of time. Screenshots are ideal for documenting specific states or errors, whereas screen recordings are better for demonstrating processes or capturing dynamic interactions. Both serve different purposes in documentation and evidence gathering.
Yes, screenshots can be legally admissible evidence in court proceedings when properly authenticated and documented. However, they must meet specific criteria including accurate timestamps, metadata preservation, chain of custody documentation, and proof of authenticity. Courts examine whether screenshots accurately represent the original digital content without alterations. Professional automated screenshot tools with timestamp watermarks and digital signatures significantly strengthen the evidentiary value of captured images.
Screenshots are essential for AI brand monitoring platforms like AmICited to capture and document how brands appear in AI-generated responses from systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude. They provide visual proof of brand mentions, citations, and positioning within AI responses, creating an audit trail of brand visibility. Automated screenshot capture enables continuous monitoring and historical comparison of brand appearances across different AI platforms.
Important metadata for legally valid screenshots includes the exact timestamp of capture, the URL or application name, the device and operating system used, the user who captured the screenshot, and any relevant context about what is being documented. Digital signatures, hash values, and chain of custody information strengthen authentication. This metadata helps courts verify the screenshot's authenticity and establishes when and where the content was captured.
Best practices include using cloud-based storage systems for automatic backup and redundancy, implementing consistent naming conventions and folder structures, maintaining detailed metadata tags, establishing regular capture schedules, and restricting access to authorized personnel only. Automated screenshot tools with secure cloud integration ensure screenshots are protected against data loss, tampering, and unauthorized access. Organizations should define clear retention policies based on legal and business requirements.
Built-in screenshot functions like Windows Snipping Tool or Mac's Command+Shift+3 provide basic capture capabilities but lack advanced features. Professional screenshot tools offer automated scheduling, cloud storage integration, annotation capabilities, batch processing, timestamp watermarks, and enhanced metadata preservation. These advanced tools are particularly valuable for legal documentation, compliance monitoring, and continuous brand tracking where reliability and authentication are critical.
The global website screenshot software market was valued at USD 250 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 550 million by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.1% from 2024 to 2032. This growth is driven by increasing demand for digital marketing analytics, competitive analysis, e-commerce monitoring, and the rise of remote work requiring collaborative visual documentation tools.
Screenshots enable organizations to maintain compliance records by automatically capturing and archiving website content, digital communications, and regulatory information at scheduled intervals. This systematic documentation creates an audit trail that demonstrates adherence to regulatory requirements and helps organizations respond quickly to compliance audits or legal discovery requests. Automated capture systems ensure consistent, timestamped records that are difficult to dispute.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Video content is a digital moving image format combining sequential frames, audio, and metadata. Learn about video formats, codecs, specifications, and its role...

Learn what thumbnails are, why they matter for SEO and user engagement, and how to optimize them for better click-through rates across YouTube, web galleries, a...
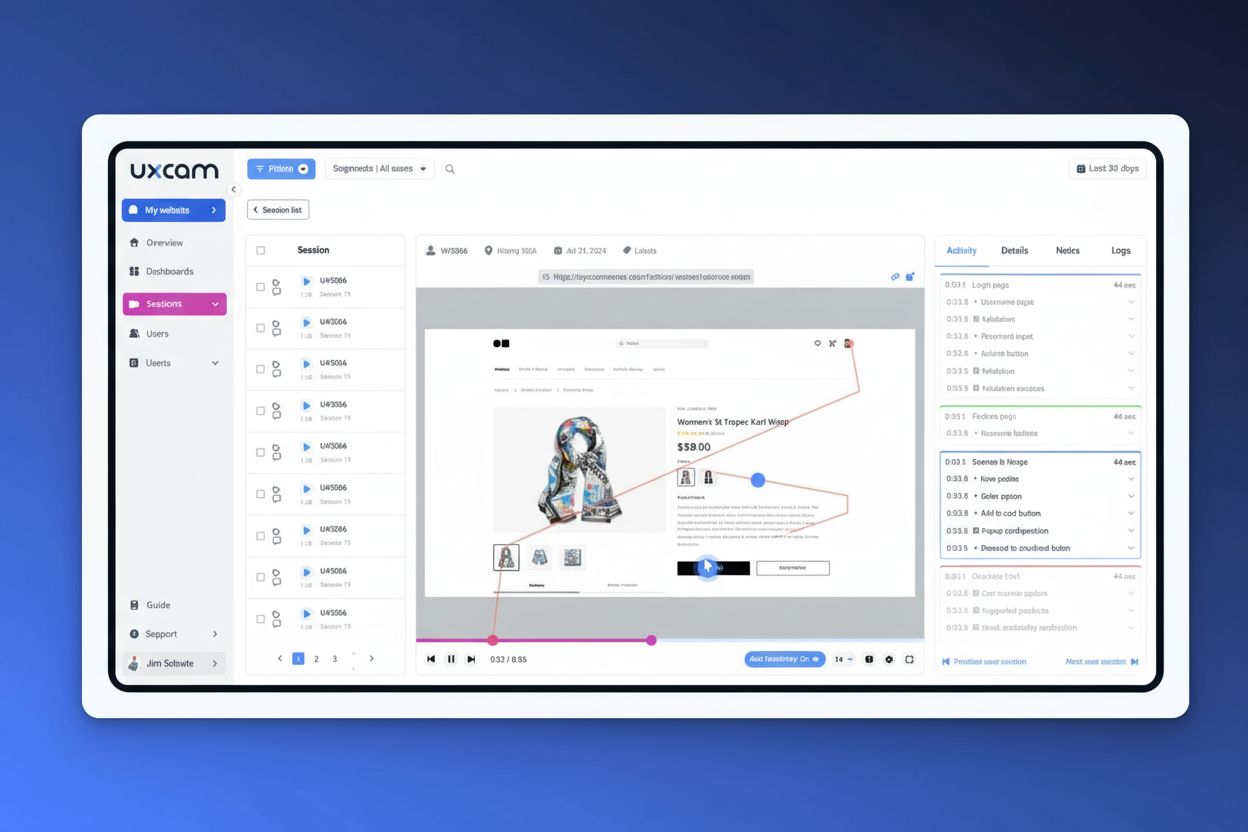
Session recording captures video of user website interactions including clicks, scrolls, and navigation. Learn how session replays work, their benefits for UX o...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.