
What is Semantic Search for AI? How It Works and Why It Matters
Learn how semantic search uses AI to understand user intent and context. Discover how it differs from keyword search and why it's essential for modern AI system...

Semantic query matching is an AI-powered technique that understands user intent and meaning behind search queries, delivering relevant results even when exact keywords don’t match. It uses natural language processing and machine learning to interpret context, synonyms, and relationships between concepts, enabling more accurate and intuitive search experiences across AI systems like GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Semantic query matching is an AI-powered technique that understands user intent and meaning behind search queries, delivering relevant results even when exact keywords don't match. It uses natural language processing and machine learning to interpret context, synonyms, and relationships between concepts, enabling more accurate and intuitive search experiences across AI systems like GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Semantic query matching is a sophisticated search technology that understands the meaning and intent behind user queries rather than simply matching individual keywords. Unlike traditional keyword matching, which looks for exact word matches or simple variations, semantic query matching analyzes the contextual meaning of search terms to deliver more relevant results. For example, a semantic system would recognize that “How do I fix my broken phone screen?” and “My device display is cracked” are essentially the same query, even though they use completely different words, whereas a keyword-based system would treat them as separate searches.
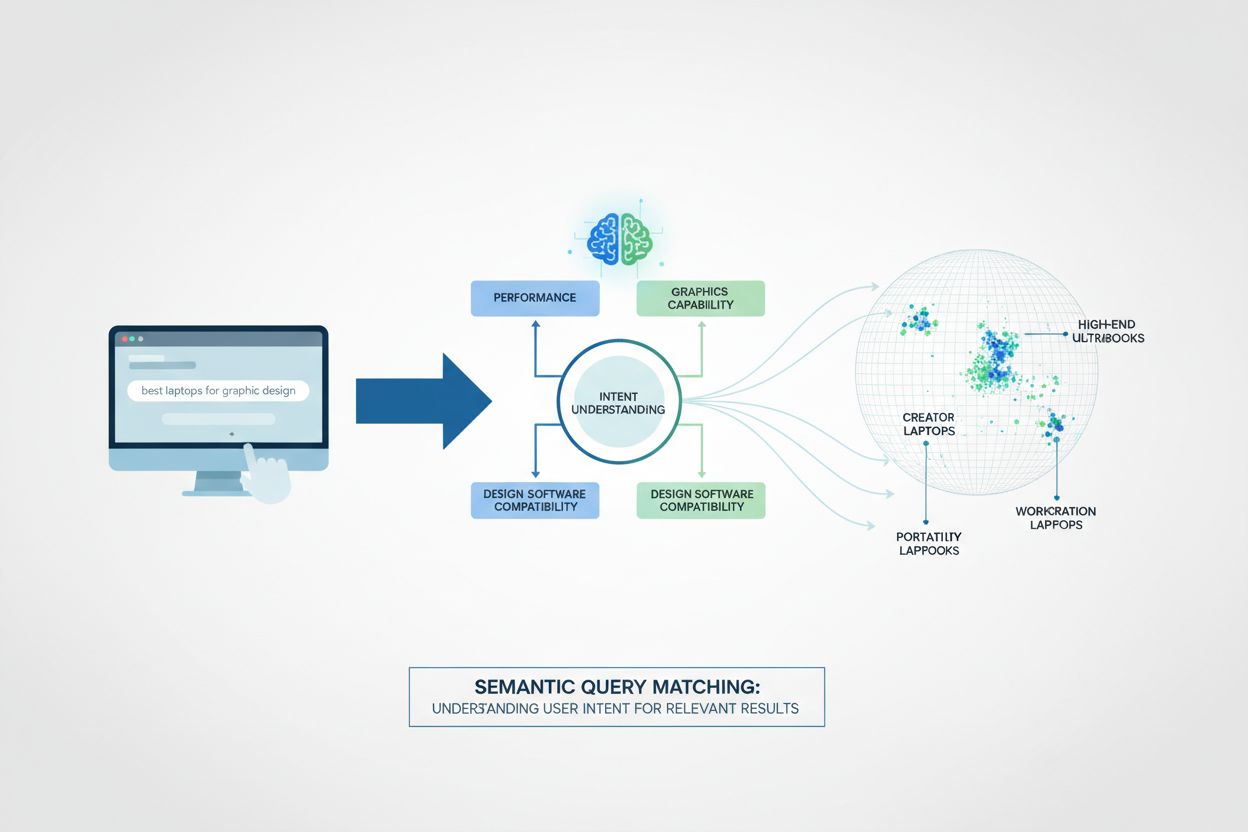
Semantic query matching operates through a multi-layered technical process that transforms both queries and documents into mathematical representations called embeddings. The system first processes natural language through NLP algorithms to extract meaning, then converts this understanding into high-dimensional vectors that capture semantic relationships. A similarity scoring mechanism compares the query vector against document vectors to rank results by relevance rather than keyword frequency. This approach enables the system to understand synonyms, context, and user intent without explicit programming for each variation.
| Aspect | Traditional Keyword Search | Semantic Query Matching |
|---|---|---|
| Matching Method | Exact or partial word matching | Meaning-based similarity scoring |
| Intent Understanding | Limited; relies on keyword presence | Deep contextual analysis of user intent |
| Synonym Handling | Requires manual synonym lists | Automatically recognizes semantic equivalents |
| Context Awareness | Minimal; treats words independently | Comprehensive; analyzes relationships between terms |
| Learning Capability | Static; doesn’t improve from usage | Dynamic; improves through model updates and feedback |
The technological foundation of semantic query matching rests on several interconnected components working in concert:
Semantic query matching has become indispensable across numerous industries and applications. In e-commerce, it helps customers find products using natural language descriptions rather than exact product names—searching “comfortable shoes for running” returns relevant athletic footwear even without those exact keywords. Customer support systems use semantic matching to route inquiries to appropriate departments by understanding the underlying issue rather than keyword triggers. Enterprise search platforms enable employees to find internal documents using conceptual queries. Modern AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews rely heavily on semantic query matching to understand user intent and retrieve relevant training data. Content recommendation engines use semantic matching to suggest articles, videos, and products based on meaning rather than explicit tags.
The advantages of semantic query matching significantly enhance user experience and system effectiveness. Improved relevance means users find what they’re actually looking for on the first try, reducing frustration and search iterations. The technology excels at handling ambiguous or poorly-phrased queries, understanding intent even when users struggle to articulate their needs precisely. Synonym understanding eliminates the need for users to guess exact terminology—whether you search for “automobile,” “car,” or “vehicle,” semantic systems recognize these as equivalent. This capability drives increased engagement as users discover more relevant content, leading to higher satisfaction and conversion rates. The superior user experience created by semantic matching has become a competitive necessity in modern digital products.
Despite its advantages, semantic query matching faces significant technical and practical challenges. Computational complexity remains substantial; processing high-dimensional vectors and calculating similarities across millions of documents requires substantial processing power and infrastructure investment. Data privacy concerns arise because semantic systems must process and analyze user queries in detail, raising questions about data retention and security. Model training demands large, high-quality datasets and significant computational resources, creating barriers for smaller organizations. The technology carries misinterpretation risk—semantic models can confidently return irrelevant results when they misunderstand context or encounter out-of-domain queries. The classic latency versus accuracy tradeoff means that more sophisticated semantic analysis takes longer, potentially degrading real-time search performance.
AmICited.com leverages semantic query matching to revolutionize how brands monitor their presence in AI-generated content and responses. Rather than simply tracking exact brand name mentions, AmICited.com’s platform understands the intent and context of how AI systems reference brands, products, and companies across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other major AI platforms. The semantic approach enables detection of indirect references, comparative mentions, and contextual citations that keyword-based monitoring would miss entirely. This deeper understanding provides brands with comprehensive visibility into how AI systems present their offerings to users—critical intelligence for maintaining brand reputation and market positioning. AmICited.com’s semantic capabilities work seamlessly with complementary tools like FlowHunt.io, which specializes in workflow optimization, creating a comprehensive ecosystem for AI monitoring and brand intelligence. By understanding the semantic meaning behind AI-generated responses, AmICited.com helps brands identify opportunities, address misrepresentations, and optimize their presence in the AI-driven information landscape.
Semantic query matching continues evolving toward more sophisticated and efficient implementations. Multimodal matching represents the frontier, enabling systems to understand queries and match them against images, videos, and audio content using unified semantic frameworks. Researchers are developing more efficient embedding models that maintain semantic understanding while reducing computational requirements, making semantic search accessible to smaller organizations. Improved personalization will allow semantic systems to adapt matching based on individual user preferences, search history, and context. Integration with emerging AI systems will expand semantic matching beyond traditional search into conversational AI, voice assistants, and autonomous systems. Standardization efforts are establishing common frameworks and benchmarks for semantic matching, enabling better interoperability and comparison across platforms. As these technologies mature, semantic query matching will become the default expectation rather than a premium feature.
Semantic matching understands intent and meaning, while keyword search looks for exact word matches. Semantic matching can find relevant results even when exact keywords aren't used, recognizing that different phrases can express the same concept.
Vector embeddings convert text into numerical representations that capture meaning. Similar concepts are positioned close together in vector space, allowing the system to find semantically related content by calculating distances between vectors.
Natural Language Processing (NLP), machine learning models like BERT and GPT, vector embeddings, and knowledge graphs work together to understand query intent and match it with relevant content.
Yes, semantic matching excels at understanding synonyms and semantic variations. It recognizes that 'car,' 'vehicle,' and 'automobile' have similar meanings and can match queries using any of these terms without manual configuration.
It delivers more relevant results faster, reduces the need for users to refine their searches, and enables more natural, conversational query formulation without requiring exact keyword matches.
Key challenges include computational complexity, data privacy concerns, the need for continuous model training, potential for misinterpretation, and balancing accuracy with response speed.
Semantic matching enables systems like AmICited.com to understand the intent behind AI-generated content and track brand mentions even when exact brand names aren't used, providing comprehensive brand visibility monitoring.
While semantic matching is becoming more prevalent, both approaches coexist. Many modern systems use hybrid approaches combining semantic understanding with keyword matching for optimal results.
AmICited.com uses semantic query matching to track your brand mentions across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews—understanding not just what's said, but the intent behind it.

Learn how semantic search uses AI to understand user intent and context. Discover how it differs from keyword search and why it's essential for modern AI system...

Semantic search interprets query meaning and context using NLP and machine learning. Learn how it differs from keyword search, powers AI systems, and improves s...
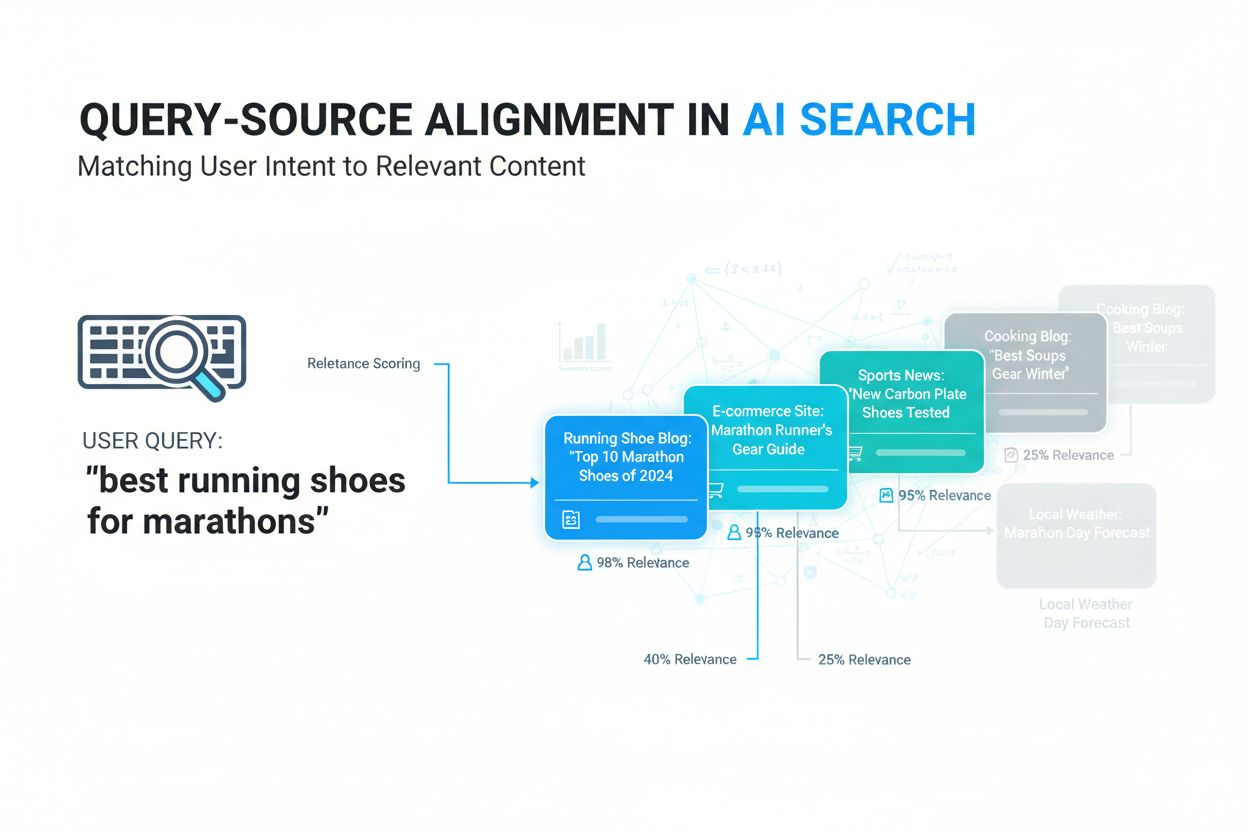
Learn what query-source alignment is, how AI systems match user queries to relevant sources, and why it matters for content visibility in AI search platforms li...