Event Tracking
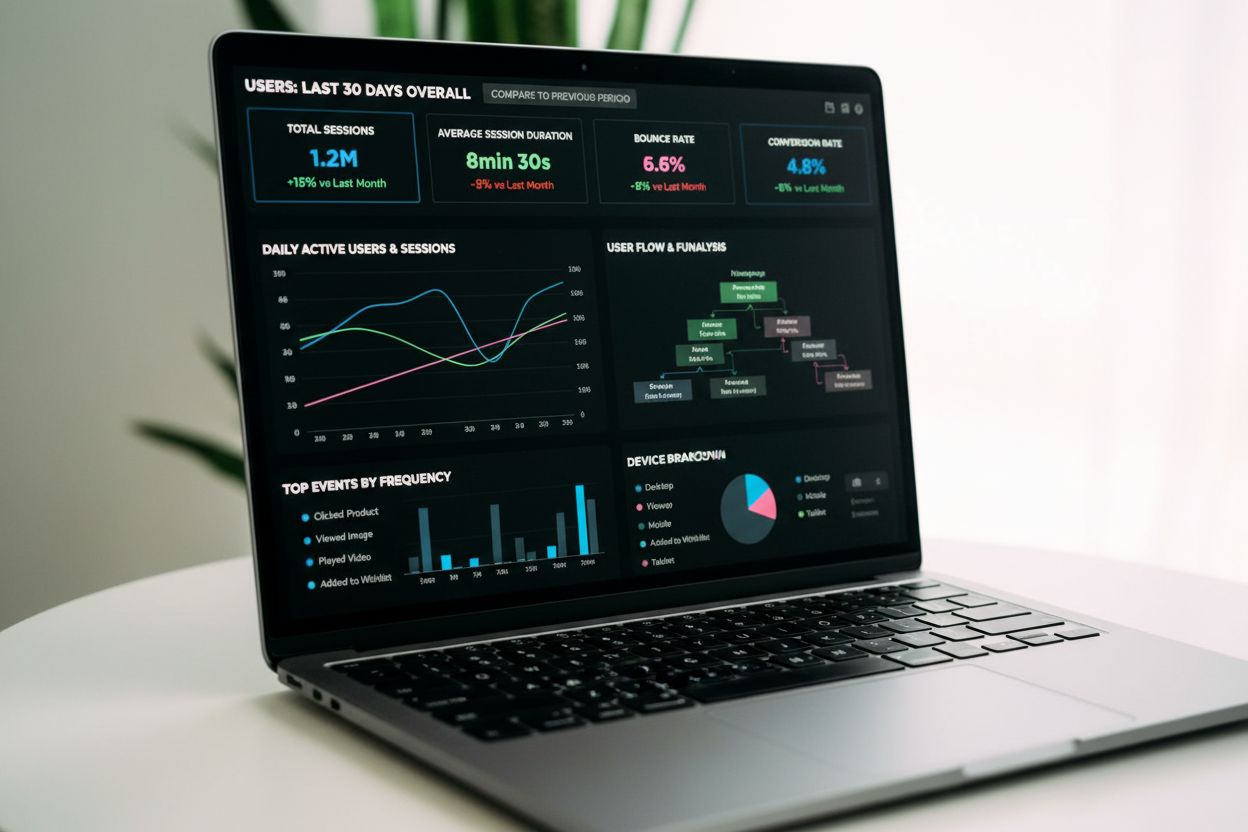
Event tracking captures and records user interactions on digital platforms. Learn how event tracking works, its importance for analytics, and how it drives data...
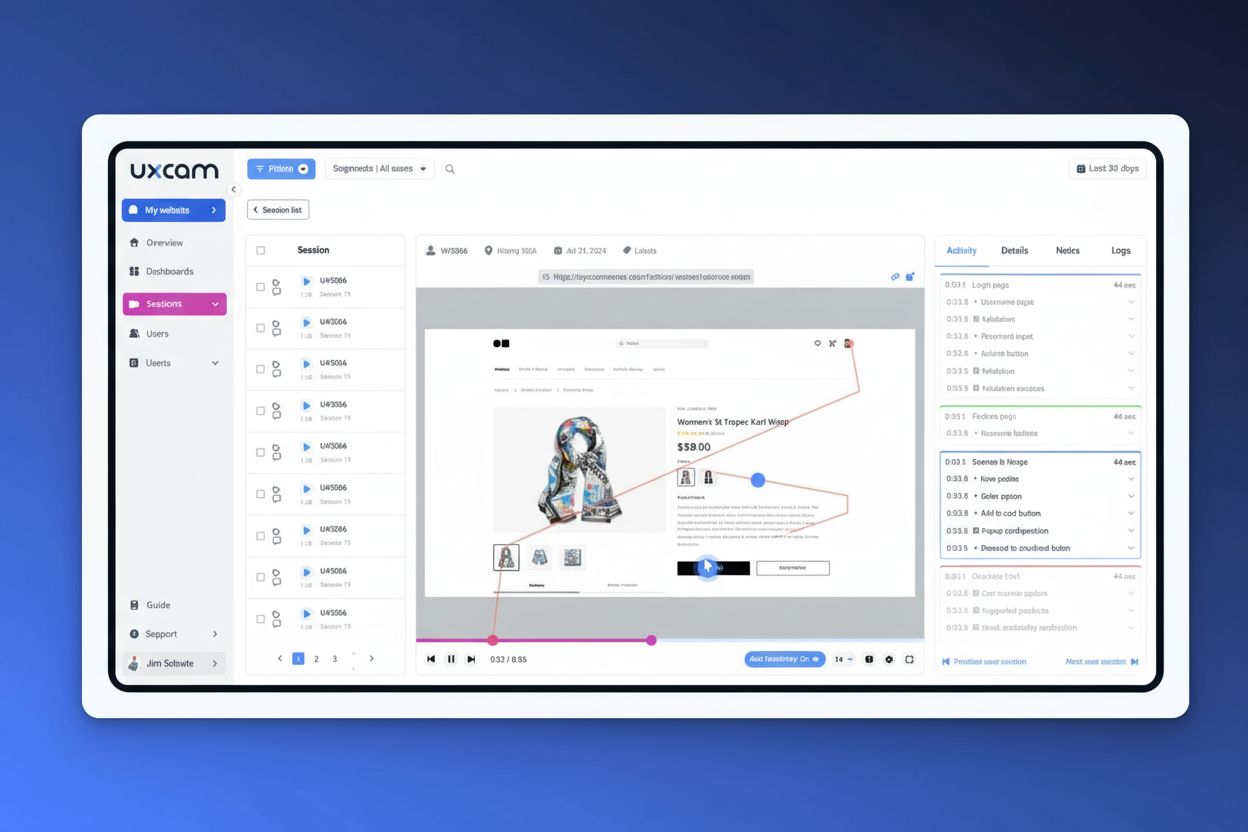
Session recording is a digital video capture of real user interactions with a website or application, tracking every click, scroll, keystroke, and navigation action to create a complete playback of the user’s journey. Also known as session replay, it enables product teams to observe actual user behavior and identify friction points, bugs, and optimization opportunities without relying solely on quantitative analytics data.
Session recording is a digital video capture of real user interactions with a website or application, tracking every click, scroll, keystroke, and navigation action to create a complete playback of the user's journey. Also known as session replay, it enables product teams to observe actual user behavior and identify friction points, bugs, and optimization opportunities without relying solely on quantitative analytics data.
Session recording, also known as session replay, is a digital video reconstruction of real user interactions with a website or mobile application. It captures and replays every user action—including clicks, scrolls, mouse movements, keyboard inputs, page transitions, and form interactions—to create a complete visual record of how an individual user navigates and engages with a digital product. Unlike traditional web analytics that provide aggregate metrics and numbers, session recordings offer qualitative, behavioral insights by showing the actual user experience from the user’s perspective. This technology has become essential for product teams, UX designers, developers, and conversion rate optimization specialists who need to understand not just what users do, but why they do it. The session recording market was valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 3.2 billion by 2032, reflecting the growing recognition of its importance in digital product optimization.
Session recording operates through a lightweight code snippet—typically JavaScript for websites or an SDK (Software Development Kit) for mobile applications—that is installed on your digital property. When a user interacts with your website or app, this code tracks every event in the Document Object Model (DOM), which is the underlying structure that defines what appears on screen. Rather than recording actual video footage like a screen recorder would, session recording tools capture structured data about user interactions: the coordinates of mouse movements, the timestamp and target of each click, the scroll depth and direction, the text entered into form fields, and the sequence of pages visited. This data is then transmitted to secure servers where it is reconstructed into a playable video format that mimics what the user saw and did during their session. The reconstruction happens in real-time or near-real-time, allowing teams to review sessions shortly after they occur. Importantly, session recording is not the same as screen recording—it’s more efficient, privacy-conscious, and provides structured data that can be filtered, searched, and analyzed programmatically.
Session recordings capture a comprehensive range of user interactions that provide deep behavioral insights. Mouse movements and cursor tracking show where users look and how they navigate the interface, revealing hesitation points and areas of confusion. Click tracking records every click, including dead clicks (clicks on non-interactive elements) and rage clicks (multiple rapid clicks on the same element), which are strong indicators of user frustration. Scroll tracking captures how far down pages users scroll, whether they scroll back up to re-read content, and which sections receive attention. Form interactions record which fields users fill out, where they pause or abandon forms, and the sequence of their inputs. Page transitions and navigation paths show the complete journey users take through your site, revealing whether they follow intended flows or take unexpected routes. Performance data including page load times, JavaScript errors, and network issues are also captured. Critically, modern session recording tools automatically mask sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, social security numbers, and other personally identifiable information (PII), displaying asterisks or blank spaces instead of actual values. This privacy-first approach ensures that teams can analyze user behavior without exposing confidential data.
| Aspect | Session Recording | Heatmaps | Web Analytics | Usability Testing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Individual user video playback | Aggregate visual patterns | Quantitative metrics | Controlled observation |
| Scope | Single user journey | Multiple users on one page | Site-wide metrics | Small user group |
| Insight Type | Qualitative (why) | Visual patterns (where) | Quantitative (what) | Direct feedback (why) |
| Time Investment | Medium (watch recordings) | Low (view heatmap) | Low (review dashboards) | High (conduct sessions) |
| Cost | Medium | Low to Medium | Low | High |
| Real-World Context | Yes (actual users) | Yes (actual users) | Yes (actual users) | No (controlled setting) |
| Scalability | High (thousands of sessions) | High (all users) | High (all users) | Low (limited participants) |
| Best For | Debugging, UX friction, conversion analysis | Layout optimization, engagement patterns | Trend identification, KPI tracking | Feature validation, feedback |
Implementing session recording requires minimal technical effort for most organizations. For websites, teams typically add a single JavaScript snippet to their site’s header or use tag management systems like Google Tag Manager to deploy the tracking code without modifying core application code. For mobile applications, developers integrate the session recording SDK into their app’s codebase, which then automatically begins capturing user interactions. The integration process is designed to be non-intrusive and has negligible performance impact when implemented correctly. Most modern session recording platforms support integration with existing analytics stacks, CRM systems, and marketing automation tools, enabling teams to correlate session data with other customer information. Privacy and compliance features are built into the implementation process, allowing organizations to configure which data types to capture, which user segments to exclude, and which page elements to mask. For example, a financial services company might exclude all users from certain geographic regions or mask all numeric input fields to ensure compliance with local regulations. The data captured is encrypted in transit and at rest, with access controls limiting who within an organization can view recordings.
Session recording delivers measurable business value across multiple organizational functions. For product teams, session recordings provide evidence-based insights into how users actually interact with features, validating design decisions or revealing unexpected usage patterns. When a new feature launches, watching 10-15 session recordings of users engaging with it provides confidence that the design works as intended or highlights issues requiring immediate attention. For conversion rate optimization specialists, session recordings are invaluable for identifying barriers in critical user flows like checkout, signup, or lead capture. By analyzing sessions of users who converted versus those who abandoned, teams can pinpoint specific friction points—a confusing form field, an unexpected cost disclosure, a broken button—and test targeted improvements. For customer support and success teams, session recordings help resolve customer issues faster by showing exactly what the customer experienced, reducing back-and-forth communication and enabling faster problem resolution. For developers and QA engineers, session recordings accelerate bug identification and resolution by providing the exact sequence of actions that triggered an error, the browser and device context, and error messages—information that would otherwise require extensive user communication. Research indicates that over 78% of enterprises using session recording report improved user experience metrics, and companies like Happy Trails saved approximately $90,000 in lost sales by using session recordings to identify and fix UX issues within four months.
Session recording operates in a complex regulatory landscape where privacy protection is paramount. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe, CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in the United States, HIPAA in healthcare, and PSD2 in financial services all impose strict requirements on how user data can be collected, stored, and used. Compliant session recording requires several key practices: explicit user consent through clear opt-in mechanisms that explain what data is being recorded and why; transparent privacy policies that detail data collection, retention, and usage practices; automatic data masking of sensitive fields like passwords and payment information; data anonymization where user identities are pseudonymized or separated from behavioral data; and secure storage with encryption and access controls. Organizations must also implement data retention policies that delete recordings after a specified period, typically 30-90 days, unless there is a legitimate business reason to retain them longer. The industry is increasingly moving toward privacy-first approaches, with major platforms like Apple implementing privacy changes and companies recognizing that user trust is a strategic asset. Ethical considerations extend beyond legal compliance—organizations should ask whether recording everything a user does is necessary, whether the insights justify the data collection, and whether users would feel comfortable knowing their sessions are being recorded. Leading organizations now balance powerful analytics capabilities with user respect, implementing sampling strategies to record only relevant sessions rather than indiscriminately capturing all traffic.
While session recording traditionally focuses on website and app user behavior, the rise of AI-powered search and response systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude introduces new considerations for brand monitoring. These AI systems increasingly reference and cite websites in their responses, and understanding how users interact with AI-generated content that mentions your brand is becoming important. AmICited specializes in monitoring where your brand, domain, and URLs appear in AI-generated responses across these platforms. When combined with session recording data, this creates a comprehensive picture: session recordings show how users interact with your website directly, while AI citation monitoring reveals how your brand is being presented and referenced in AI responses that users encounter. For organizations concerned about their digital presence, this dual approach—understanding direct user behavior through session recordings and tracking AI-driven discovery through citation monitoring—provides complete visibility into how users find and engage with your content across both traditional and AI-powered channels.
Session recording technology continues to evolve rapidly, driven by advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning. Modern platforms increasingly incorporate AI-powered analysis that automatically detects frustration signals like rage clicks, identifies common user paths, and surfaces the most important sessions to watch first, dramatically reducing the time analysts spend reviewing data. Predictive analytics capabilities are emerging that can forecast which users are likely to churn or convert based on their session behavior, enabling proactive interventions. Natural language processing is being applied to session data to generate automated summaries and insights, making session recordings more accessible to non-technical stakeholders. The integration of session recording with product analytics platforms is deepening, creating unified systems where teams can seamlessly move from quantitative metrics to qualitative session playback. Privacy-preserving technologies like differential privacy and federated learning are being explored to enable powerful analytics while providing stronger privacy guarantees. As AI systems like ChatGPT and Perplexity become more prevalent in user discovery journeys, session recording tools are beginning to track how users interact with AI-generated content and how they transition between AI responses and direct website visits. The future of session recording likely involves real-time collaboration features where distributed teams can watch and annotate sessions together, advanced segmentation based on behavioral patterns and predictive models, and deeper integration with experimentation platforms to directly test hypotheses derived from session insights. Organizations that master session recording as part of their broader analytics and optimization strategy will have significant competitive advantages in understanding and serving their users effectively.
Session recording captures detailed user interaction data including clicks, scrolls, mouse movements, and form inputs, then reconstructs them as a video playback. Screen recording simply records what appears on a user's screen. Session recording is more privacy-conscious as it can mask sensitive data like passwords, while screen recording captures everything visible. Session recording is also more efficient for analytics purposes as it tracks specific user actions rather than raw video footage.
Session recordings reveal exactly where users abandon forms, hesitate on pages, or experience friction during checkout flows. By watching recordings of users who converted versus those who didn't, teams can identify specific barriers like confusing CTAs, unexpected costs, or broken elements. This qualitative insight combined with quantitative funnel data enables targeted improvements that directly address user pain points and increase conversion rates.
Session recordings can be GDPR compliant when implemented properly with privacy safeguards. Compliant tools automatically mask sensitive data like passwords, credit card numbers, and personal identifiable information (PII). Organizations must obtain user consent, provide transparent privacy policies, and use tools that support data anonymization and configurable restrictions. Many enterprise session recording platforms like UXCam, Hotjar, and FigPii are specifically designed to meet GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA requirements.
Session recordings show the 'why' behind analytics metrics. While analytics reveal that 40% of users abandoned a form, session recordings show exactly which field caused abandonment, whether users encountered errors, or if they were confused by instructions. You can observe rage clicks, hesitant mouse movements, repeated scrolling, and the complete user journey across pages—behavioral context that raw numbers cannot provide.
Modern session recording tools use lightweight JavaScript snippets or SDKs that have minimal performance impact. They track DOM (Document Object Model) events rather than recording actual video, making them efficient. However, recording every session can increase data storage and bandwidth costs. Best practice is to use sampling strategies or filter recordings to capture only relevant sessions, balancing insights with performance and cost considerations.
Heatmaps show aggregate data from many users, visualizing where clicks and scrolls occur across a page to identify popular areas and dead zones. Session recordings show individual user journeys in detail, revealing the sequence of actions and user intent. Heatmaps answer 'what do users collectively do,' while session recordings answer 'why did this specific user behave this way.' Using both together provides comprehensive UX insights.
Yes, session recordings are highly effective for bug detection. They capture JavaScript errors, page load failures, broken links, and unresponsive elements exactly as users experience them. Developers can see the precise sequence of actions leading to errors, the browser and device information, and error messages—enabling faster debugging than relying on user bug reports alone. This is particularly valuable for identifying device-specific or environment-specific issues.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Event tracking captures and records user interactions on digital platforms. Learn how event tracking works, its importance for analytics, and how it drives data...
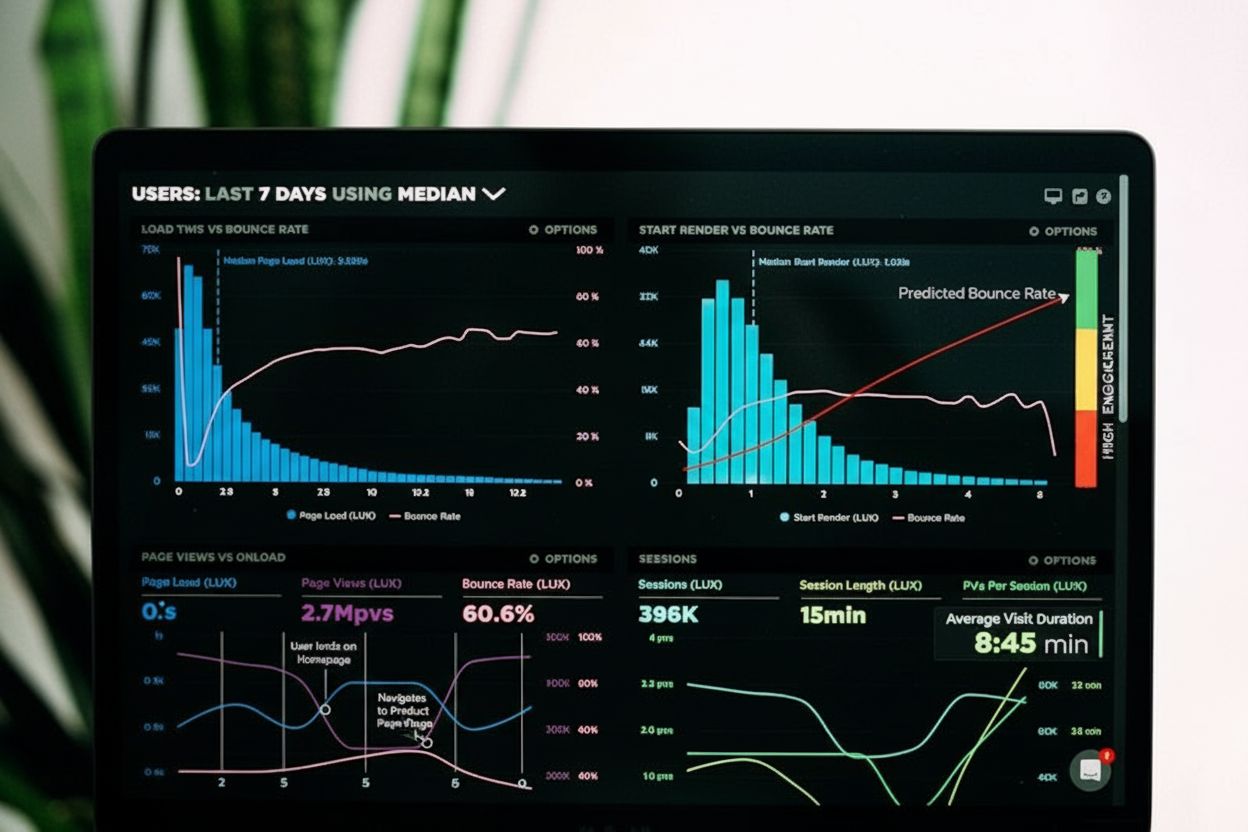
Session duration measures the total time users spend on a website per visit. Learn how to calculate it, why it matters for engagement, and how to improve it wit...
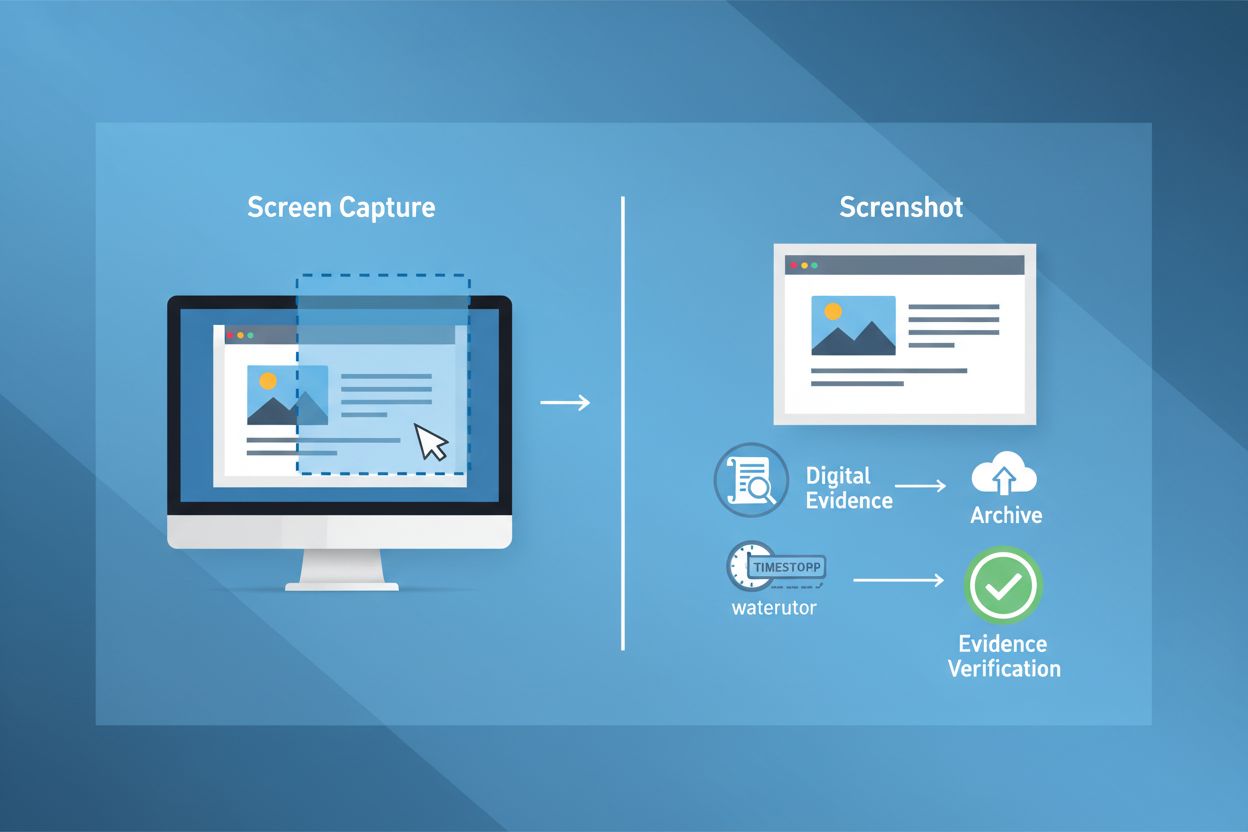
Learn what a screenshot is, how it works, its applications in brand tracking and AI monitoring, and why it matters for digital documentation and legal evidence.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.