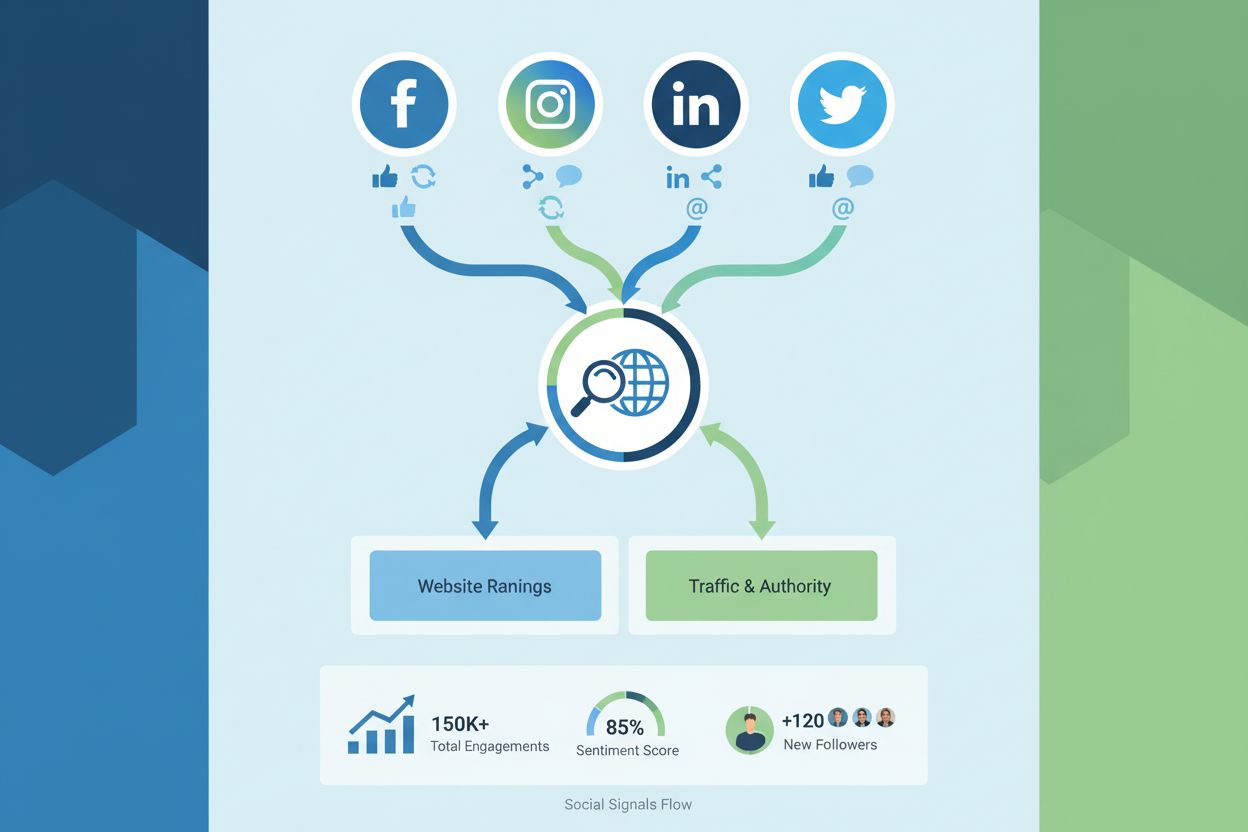
Social Signals
Learn what social signals are, how they affect SEO rankings, and why monitoring brand mentions across AI platforms matters for your digital strategy.

Social signals are engagement metrics such as likes, shares, comments, and other interactions that content receives on social media platforms. While not a direct Google ranking factor, social signals indirectly influence SEO by driving traffic, building brand awareness, and potentially generating backlinks that improve search visibility.
Social signals are engagement metrics such as likes, shares, comments, and other interactions that content receives on social media platforms. While not a direct Google ranking factor, social signals indirectly influence SEO by driving traffic, building brand awareness, and potentially generating backlinks that improve search visibility.
Social signals are engagement metrics and interactions that content receives on social media platforms, including likes, shares, comments, retweets, pins, saves, and other forms of user engagement. These signals represent how audiences interact with and respond to content across platforms like Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Twitter (now X), Pinterest, and TikTok. While Google has consistently stated that social signals are not a direct ranking factor in their search algorithm, they play a significant indirect role in search engine optimization by influencing traffic patterns, brand visibility, and the potential generation of backlinks. Social signals serve as indicators of content quality and audience resonance, helping both social platforms and search engines understand which content provides value to users. In the context of AI monitoring and brand tracking, social signals have become increasingly important as they contribute to overall brand authority and online presence that AI systems consider when generating responses and citations.
The concept of social signals emerged in the early 2000s as social media platforms gained prominence and search engines began exploring how social engagement might relate to content quality. In 2010, Google engineer Matt Cutts confirmed that Google uses Facebook and Twitter links in ranking, though he emphasized that the quality of engagement mattered more than quantity. However, by 2014, Google’s position shifted, with Cutts stating that Google treats social media posts like any other web pages but does not use them as direct ranking signals. This distinction became crucial: while social signals don’t directly influence rankings, they create conditions that indirectly support SEO success. Over the past decade, research has consistently shown a strong correlation between high social engagement and better search rankings, though experts debate whether this represents causation or simply reflects that quality content naturally attracts both social shares and search visibility. The rise of AI search tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews has added a new dimension to social signals, as these platforms increasingly consider social proof and brand mentions when generating responses and recommendations.
Different social media platforms measure and prioritize social signals in distinct ways, each contributing uniquely to overall brand visibility and engagement metrics. Facebook tracks likes, shares, comments, and reactions as primary engagement signals, with shares being particularly valuable as they extend content reach beyond immediate followers. Instagram emphasizes likes, saves, shares, and comments, with the platform’s algorithm giving special weight to saves as an indicator of content value. LinkedIn focuses on professional engagement including shares, comments, and reactions, with the platform prioritizing meaningful discussion over simple likes. Twitter (X) measures retweets, replies, likes, and quote tweets, with retweets being especially significant due to Google’s partnership that displays tweets in search results. Pinterest operates differently, tracking pins, repins, and saves as primary signals, though these correlate less directly with search rankings than other platforms. TikTok measures views, likes, shares, and comments, with the platform’s algorithm heavily weighting watch time and completion rate. Understanding these platform-specific metrics is essential for developing a comprehensive social media strategy that maximizes engagement across channels while supporting broader SEO objectives.
| Factor | Direct Ranking Impact | Indirect SEO Value | Measurement Method | Platform Dependency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social Signals | No (confirmed by Google) | High (traffic, brand awareness, backlinks) | Likes, shares, comments, engagement rate | Platform-specific |
| Backlinks | Yes (primary factor) | Very High (authority, trust, relevance) | Link count, domain authority, anchor text | Cross-domain |
| Content Quality | Yes (primary factor) | Very High (user satisfaction, E-E-A-T) | Dwell time, bounce rate, user feedback | On-page metrics |
| Page Speed | Yes (confirmed factor) | High (user experience, crawlability) | Core Web Vitals, load time | Technical metrics |
| Mobile Optimization | Yes (confirmed factor) | High (user experience, accessibility) | Mobile-friendly test, responsive design | Device-based |
| Brand Signals | Indirect (via user behavior) | Very High (trust, recognition, direct traffic) | Branded searches, direct traffic, mentions | Cross-channel |
| User Engagement | Indirect (via RankBrain) | High (content relevance, satisfaction) | Time on page, scroll depth, click-through rate | Behavioral metrics |
While Google explicitly denies using social signals as a direct ranking factor, extensive research demonstrates a strong correlation between social engagement and search visibility. A comprehensive study analyzing 23 million shares across 300,000 pieces of content found that pages ranking in the top positions consistently received significantly more social engagement than lower-ranking pages. This relationship, however, operates through indirect mechanisms rather than direct algorithmic weighting. When content receives high social engagement, it generates increased traffic to the website, which Google interprets as a quality signal through metrics like dwell time, bounce rate, and click-through rate. Additionally, viral social content often attracts natural backlinks from other websites, journalists, and industry publications, which are confirmed direct ranking factors. Social signals also contribute to brand authority and brand recognition, leading to increased branded searches—a powerful signal that Google uses to assess brand strength and relevance. Furthermore, content that performs well on social media often reflects genuine user interest and satisfaction, suggesting that the correlation between social signals and rankings may reflect a shared underlying factor: content quality that appeals to both social audiences and search engine algorithms.
Different social platforms present unique opportunities and challenges for leveraging social signals to support SEO objectives. Facebook remains the largest social platform by user base, with approximately 3 billion monthly active users, making it a critical channel for reaching broad audiences and generating engagement. However, Facebook’s algorithm increasingly prioritizes content from friends and family over brand content, requiring strategic use of paid promotion and community engagement to maximize reach. LinkedIn has emerged as particularly valuable for B2B brands and professional content, with research showing strong correlation between LinkedIn shares and first-page rankings for business-related keywords. Twitter (X) gained SEO significance following Google’s partnership to display tweets in search results, making it essential for real-time content distribution and industry conversations. Instagram and TikTok present challenges for direct SEO impact due to their link restrictions, but they excel at building brand awareness and driving traffic through bio links and profile optimization. Pinterest operates as a visual search engine with its own ranking algorithm, making it particularly valuable for e-commerce and lifestyle brands seeking to drive qualified traffic. Understanding these platform-specific dynamics allows marketers to allocate resources strategically and maximize both social engagement and SEO benefits.
Research reveals a nuanced relationship between content length, social signals, and search rankings that challenges the assumption that longer content always performs better. Analysis of content across different length categories shows that micro-content (1-50 words) demonstrates the strongest correlation between social signals and first-page rankings, with first-position content receiving dramatically higher engagement than all other positions combined. This pattern suggests that short, shareable content—such as social media posts, quotes, and quick tips—naturally attracts social engagement and ranks well when it addresses specific user queries. In contrast, long-form content (1001-5000 words) shows weaker direct correlation between social signals and rankings, indicating that longer articles rely more heavily on other ranking factors like backlinks, topical authority, and E-E-A-T signals. This distinction has important implications for content strategy: brands should create short, highly shareable content optimized for social platforms while simultaneously developing comprehensive long-form content that establishes authority and attracts links. The relationship also varies by platform, with Facebook and Google+ showing stronger correlation for micro-content, while Pinterest demonstrates more linear correlation for longer content. Understanding these patterns enables marketers to tailor content formats to platform-specific audiences and maximize both social engagement and search visibility.
Effective measurement of social signals requires understanding both quantitative metrics and qualitative indicators of engagement quality. Engagement rate, calculated as total engagements (likes, shares, comments) divided by total impressions or followers, provides a normalized metric for comparing performance across different content pieces and platforms. Share rate specifically measures how often content is shared relative to views, serving as a particularly strong indicator of content value since sharing requires active user effort. Comment rate and comment sentiment reveal not just engagement volume but also audience perception and discussion quality, with meaningful comments indicating deeper engagement than simple likes. Reach and impressions measure content visibility, while click-through rate from social platforms to website indicates how effectively social content drives traffic. Tools like Hootsuite, Sprout Social, and AmICited provide comprehensive monitoring of these metrics across platforms, enabling brands to track performance in real-time and identify trends. For AI monitoring purposes, tracking social signals becomes even more critical, as platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews increasingly consider social proof and brand mentions when generating responses. Advanced analytics should also track share velocity (how quickly content accumulates shares), influencer engagement (shares from high-follower accounts), and cross-platform amplification (how content performs across multiple channels).
The emergence of AI search tools and generative AI platforms has fundamentally changed how social signals contribute to brand visibility and online presence. Platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude increasingly reference and cite sources based on multiple factors, including social proof, brand authority, and online mentions. Research indicates that approximately 46% of Gen Z users now use social media instead of Google for searching, making social signals increasingly important for brand discovery and visibility. AmICited and similar AI monitoring platforms track how brands appear in AI-generated responses, revealing that social signals contribute to this visibility through multiple pathways: strong social presence builds brand authority that AI systems recognize, viral social content attracts media coverage and backlinks that AI systems cite, and active social engagement demonstrates brand legitimacy and relevance. The integration of social signals into AI evaluation represents a shift from traditional SEO metrics, where social engagement now serves as a proxy for brand trustworthiness and content quality. Brands that maintain strong social presence across multiple platforms benefit from increased visibility not just in traditional search results but also in AI-generated responses, making social signal optimization a critical component of modern digital strategy. This evolution underscores why monitoring social signals through specialized tools has become essential for understanding overall brand visibility in both traditional and AI-powered search environments.
Maximizing social signals requires a strategic approach that balances content quality, platform optimization, and audience engagement. The foundation begins with content quality and relevance, as research consistently shows that high-quality, valuable content naturally attracts more social engagement than mediocre content. Content should address specific audience needs, provide actionable insights, and present information in formats that encourage sharing—such as infographics, videos, and data-driven articles. Timing and frequency matter significantly, with studies showing that accounts posting 7+ times per week on Instagram grow audiences faster than those posting less frequently, though quality should never be sacrificed for quantity. Platform optimization involves tailoring content format and messaging to each platform’s unique audience and algorithm, recognizing that content performing well on LinkedIn may not resonate on TikTok. Engagement reciprocity is critical: brands must actively respond to comments, engage with audience content, and participate in conversations rather than simply broadcasting messages. Visual optimization through high-quality images, videos, and design elements significantly increases engagement rates, as visual content typically receives 40% more engagement than text-only posts. Hashtag strategy should balance popular hashtags for reach with niche hashtags for targeted audience connection. Influencer partnerships and user-generated content amplify reach and credibility, with content from influencers and customers often receiving higher engagement than brand-created content. Finally, consistency in posting schedule, brand voice, and visual identity builds audience familiarity and trust, leading to sustained engagement over time.
The role of social signals in SEO and brand visibility continues to evolve as search engines and AI platforms refine their algorithms and evaluation criteria. Google’s increasing focus on E-E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) suggests that social signals will become more important as indicators of brand authority and credibility, particularly for YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) content. The rise of zero-click searches and AI-generated answers means that traditional ranking positions matter less, while brand visibility in AI responses becomes increasingly critical—a domain where social signals play a growing role. Bing has explicitly stated that social signals carry approximately 8% weight in their ranking algorithm, suggesting that other search engines may follow suit in formally incorporating social metrics. The emergence of social commerce and shoppable posts on platforms like Instagram and TikTok creates new opportunities for brands to drive both engagement and conversions directly from social platforms. Privacy regulations like GDPR and evolving cookie policies will likely make social signals more valuable as alternative indicators of user behavior and content quality. The integration of blockchain technology and decentralized social platforms may create new forms of social signals that are more transparent and resistant to manipulation. As AI systems become more sophisticated in evaluating source credibility and brand authority, maintaining strong social presence across multiple platforms will become increasingly essential for visibility in both traditional search results and AI-generated responses. Brands that invest in authentic social engagement and community building now will be best positioned to benefit from these evolving dynamics.
Google has officially stated that social signals are not a direct ranking factor in their algorithm. However, they serve as indirect signals that can influence rankings through increased traffic, brand awareness, and the potential generation of backlinks. Research shows a strong correlation between social engagement and higher search rankings, though correlation does not necessarily mean causation.
According to research analyzing 23 million shares, Facebook and Google+ show the strongest linear correlation with search rankings, particularly for micro-content (1-50 words). LinkedIn shows moderate correlation with first-position rankings, while Pinterest demonstrates minimal correlation with search visibility. Twitter's integration with Google Search results also makes it increasingly important for SEO visibility.
Social signals impact rankings indirectly through multiple pathways: increased social shares drive more traffic to your website, which signals quality to search engines; viral content attracts natural backlinks from other websites; strong social presence builds brand authority and recognition; and social engagement can lead to more branded searches, which Google interprets as a popularity signal.
Social signals include likes, shares, comments, retweets, pins, saves, and any form of user interaction with content on social platforms. Different platforms measure these differently: Facebook tracks likes, shares, and comments; Twitter counts retweets and replies; LinkedIn measures shares and professional engagement; Instagram tracks likes, saves, and shares; and Pinterest counts pins and repins.
You can monitor social signals using tools like Hootsuite, Sprout Social, and specialized platforms like AmICited that track brand mentions across social media and AI platforms. These tools provide real-time notifications of engagement metrics, help you analyze which content performs best, and show how social signals correlate with your search visibility and brand mentions in AI responses.
No, fake social signals can actually harm your SEO efforts. Search engines and social platforms have become sophisticated at detecting artificial engagement from bots and fake accounts. Using fake signals violates platform terms of service, can result in account suspension, and provides no genuine SEO benefit since Google values authentic user engagement and behavior signals.
Research shows that content length significantly affects how social signals correlate with rankings. Micro-content (1-50 words) shows strong correlation between social signals and first-page rankings, while longer content (1001-5000 words) shows weaker direct correlation. This suggests that social signals matter more for short-form content, while longer content relies more on other ranking factors like backlinks and topical authority.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn what social signals are, how they affect SEO rankings, and why monitoring brand mentions across AI platforms matters for your digital strategy.
Engagement signals are measurable indicators of user interaction with digital content. Learn how clicks, time spent, shares, and conversions impact SEO, AI moni...

Social traffic is website visitors from social media platforms. Learn how to measure, track, and optimize social referrals for better ROI and brand visibility.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.